javascript中实现AOP
前言
在一个express项目中,构建了基于MVC架构的服务。而希望能够在 controller 层调用 model 层中的 services 层,以及 services 层调用 dao 层,能够自动将数据进行一些打包并过滤操作。
问题
比如页面添加了一个任务,数据有 任务id,任务名称 等等。controller 层将数据传给了 services层。
通常 services 层接收到数据后,会对数据进行判断,比如 任务id不能为空,名称不能为空。
// 添加一个任务,需要对任务数据进行判断 function add (data) { if(!data.id && !data.name && !data.time && !data.status){ // ... } // ... } // 根据任务id 修改任务内容,同样需要对不能为空的数据进行判断 function update (data) { if(!data.id && !data.name && !data.time){ // ... } // ... }
上面代码模拟 services 层对任务的添加和修改,这里就希望在 services 层处理之前就能够对数据进行筛选判断了,不必在手动判断。
可以看出,添加和修改对数据的判断都是不一样的,如果在 services 层之前进行AOP处理,那么同样需要写这两份判断代码,还不如老老实实在services 层内进行判断。
解决方案
为了能够AOP处理时能够统一处理数据,需要找到不同处理间的相同点。
这里都是对 任务 的处理,所以可以将 任务 单独定义一个对象类型(javaBean),然后将数据封装到 任务 对象类型中。但这并没有解决问题,这里只是将数据封装而已。
那可以在数据封装时进行判断即可。如果是简单的判断,那么也并没有解决问题,还是手动的写了不同的判断代码。
所以就需要定义一套能够自定义规则的判断,数据封装时根据规则进行通用判断即可。
这样就能够对数据进行自动封装了,并且还筛选了数据。
实现
-
实现AOP
首先要实现一个能够自定义处理的AOP。
目录如下:
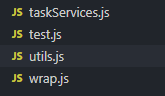
分别为:
taskServices:代表services层task的处理模块;
test:代表controller层的action;
wrap:AOP的实现代码
utils.js:工具方法文件
wrap.js
/** * wrap.js * @param {*} ins 传入需要包装的实例 */ function Wrap (ins) { this.ins = ins // 遍历实例下的所有属性,将函数保存一份 for(let attr in ins) { if (typeof ins[attr] === 'function') { this[attr] = ins[attr] } } } Wrap.prototype = { constructor: Wrap, /** * * @param {string} method 需要包装的方法 * @param {function} handle 回调处理 */ before: function (method, handle) { let self = this // 重新定义实例下的方法 this.ins[method] = function () { // 执行处理函数,并将参数一并传递 handle(arguments) // 执行保存的函数,就是被包装方法的原功能 self[method].apply(this, arguments) }
return self
} } module.exports = Wrap
上面是一个较简单的一个AOP(有待优化),本质就是装饰者模式。将需要包装的方法重新定义,重新定义时插入需要自定义处理的功能。最后执行。
而执行为了能够正确执行,除了执行时要改变this指向外,还需要在包装前对原方法进行保存一份。
taskServices.js
const Wrap = require('./wrap')
function TaskServices() {}
TaskServices.prototype = {
constructor: TaskServices,
add: function(){
console.log('add')
},
update: function(){
console.log('update')
}
}
const ins = new TaskServices()
new Wrap(ins)
.before('add', function(){
console.log('add before')
})
.before('update', function(){
console.log('update before')
})
module.exports = ins
taskServices 定义了两个方法,add 和 update,是处理 task的方法,需要对这两个进行拦截。引入 wrap.js,传入taskServices实例,用 wrap 的before方法 将add 和 update 进行拦截,拦截处理为打印 ‘.... before’。
test.js
const taskServices = require('./taskServices')
taskServices.add()
taskServices.update()
test.js 相当于controller层中的某个action,可以看到,调用了task的add 和 update,打印出了:
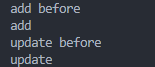
这跟预期的一致,这样一个简单的AOP就实现了。接下来要进行数据封装。
-
数据封装
新建一个 task.js 文件,此文件代表 task 对象。
task.js
1 function Task ({id = undefined, name = undefined, time = undefined, status = undefined}) { 2 3 // 任务ID 4 this.id = id 5 // 任务名称 6 this.name = name 7 // 任务时间 8 this.time = time 9 // 任务状态 10 this.status = status 11 12 13 } 14 Task.prototype = { 15 constructor: Task, 16 17 } 18 19 module.exports = Task
task 有 id、name、time、status 属性,并且以对象解析进行传参,所以能够直接传一个对象即可,会自动解析需要的字段。并且默认值为 undefined 。这样一个简单的数据封装就实现了。如:
1 new task({ 2 id: 1, 3 name: '任务一', 4 time: new Date(), 5 status: false, 6 a: 1, 7 b: 2 8 })
即时传入了无关的字段,也会自动过滤,因为只会解析定义好的字段。
这里会产生一个问题,就是如何将封装好的数据传给 Services。
只需修改 wrap.js 即可。
修改前:
1 this.ins[method] = function () { 2 3 // 执行处理函数,并将参数一并传递 4 handle(arguments) 5 6 7 // 执行保存的函数,就是被包装方法的原功能 8 self[method].apply(this, arguments) 9 }
修改后:
1 this.ins[method] = function () { 2 3 // 执行处理函数,并将参数一并传递 4 let r = handle(arguments) 5 6 7 // 执行保存的函数,就是被包装方法的原功能 8 if (r) { 9 self[method].apply(this, r) 10 } else { 11 self[method].apply(this, arguments) 12 } 13 14 }
上面,封装好的数据是从 回调处理函数返回的,所以判断 handle 是否有返回值,有就用返回值作为 原函数的参数。
-
筛选数据
上面提到了,希望能够在处理数据之前进行数据筛选。
筛选数据需要:数据源和筛选规则。这里数据源就是封装好的 task.js,而筛选规则则自己定义。
这里将筛选数据的功能函数写在 utils.js 中。
首先规则是这样的:
1 { 2 id: { 3 required: true 4 }, 5 6 name: { 7 required: true, 8 maxlength: 6 9 } 10 }
一个对象,对象的字段是 task 对象的属性,值为规则对象,规则对象每个字段都对应相应规则,如,required 为true 的话就是不能为空,maxlength 就是最大长度。
所以筛选功能函数如下:
utils.js
1 module.exports = { 2 filteData: function (source, rule) { 3 let ruleKeys = Object.keys(rule) // 获取设定了规则的字段 4 ruleKeys.forEach(ele => { 5 6 if (rule[ele]['required']) { // 判断规则中是否有 required ,有就判断源数据是否符合相应规则,required 就是不能为空,判断源数据是否有值即可。 7 if (!source[ele]) { 8 9 throw new Error('不能为空') // 直接抛出异常,方便在统一异常处理中处理 10 } 11 } 12 13 if (rule[ele]['maxlength']) { 14 if (source[ele].length > rule[ele]['maxlength']) { 15 throw new Error(`长度超过${rule[ele]['maxlength']}`) 16 } 17 } 18 19 }) 20 21 } 22 }
完整实现
将 AOP、封装、筛选组合一起就能实现完整功能。
有以下文件结构:
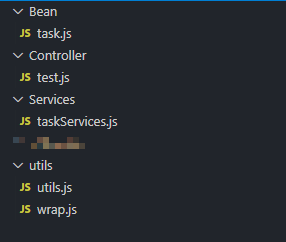
controller 中的 test 接收数据并传给 taskServices。
这其中,在 taskServices 处理数据之前进行数据封装筛选。
Controller/test.js
1 const taskServices = require('../Services/taskServices') 2 3 function test () { 4 taskServices.add({ 5 id: 1, 6 name: '任务一任务一任务一', 7 time: new Date(), 8 status: false, 9 a: 1, 10 b: 2 11 }) 12 } 13 14 test()
Services/taskServices.js
1 const Wrap = require('../utils/wrap') 2 const task = require('../Bean/task') 3 const utils = require('../utils/utils') 4 5 function TaskServices() {} 6 TaskServices.prototype = { 7 constructor: TaskServices, 8 9 add: async function(data){ 10 11 console.log(data) 12 13 }, 14 15 update: function(data){ 16 17 } 18 19 } 20 21 22 const ins = new TaskServices() 23 24 25 new Wrap(ins) 26 .before('add', function(args){ 27 28 utils.filteData(new task([...args][0]), { 29 id: { 30 required: true 31 }, 32 33 name: { 34 required: true, 35 maxlength: 6 36 } 37 }) 38 39 return { 40 0: new task([...args][0]) 41 } 42 43 }) 44 45 module.exports = ins
utils/wrap.js
1 /** 2 * 3 * @param {*} ins 传入需要包装的实例 4 */ 5 function Wrap (ins) { 6 this.ins = ins 7 8 // 遍历实例下的所有属性,将函数保存一份 9 10 for(let attr in ins) { 11 12 if (typeof ins[attr] === 'function') { 13 this[attr] = ins[attr] 14 } 15 } 16 } 17 Wrap.prototype = { 18 constructor: Wrap, 19 20 21 /** 22 * 23 * @param {string} method 需要包装的方法 24 * @param {function} handle 回调处理 25 */ 26 before: function (method, handle) { 27 let self = this 28 29 // 重新定义实例下的方法 30 this.ins[method] = async function () { 31 32 // 执行处理函数,并将参数一并传递 33 let r = await handle(arguments) 34 35 // console.log(arguments) 36 // 执行保存的函数,就是被包装方法的原功能 37 if (r) { 38 await self[method].apply(this, r) 39 } else { 40 await self[method].apply(this, arguments) 41 } 42 43 } 44 45 46 47 return self 48 49 } 50 } 51 52 module.exports = Wrap
utils/utils.js
1 module.exports = { 2 filteData: function (source, rule) { 3 let ruleKeys = Object.keys(rule) 4 ruleKeys.forEach(ele => { 5 6 if (rule[ele]['required']) { 7 if (!source[ele]) { 8 console.log() 9 throw new Error('不能为空') 10 } 11 } 12 13 if (rule[ele]['maxlength']) { 14 if (source[ele].length > rule[ele]['maxlength']) { 15 throw new Error(`长度超过${rule[ele]['maxlength']}`) 16 } 17 } 18 19 }) 20 21 } 22 }
Bean/task.js
1 function Task ({id = undefined, name = undefined, time = undefined, status = undefined}) { 2 3 // 任务ID 4 this.id = id 5 // 任务名称 6 this.name = name 7 // 任务时间 8 this.time = time 9 // 任务状态 10 this.status = status 11 12 13 } 14 Task.prototype = { 15 constructor: Task, 16 17 } 18 19 module.exports = Task
总结
在Controller中传数据给Services,或者从Services中传数据给DAO。在接收数据之前进行一些数据操作,比如判断一些字段是否符合要求。而这核心使用AOP即可实现。
而在接收数据进行数据封装,封装是为了避免一些无用的字段。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号