『 学习笔记 』网络最大流
2018/9/3 14:55 Update
今天做了一道题 Luogu P1231
发现自己的 Dinic 写的很慢,居然超时 7 个点,于是决定加一些优化。
然后就在题解中看到了一种这样的写法
inline int Dinic(int u, int cap) { if(u == t || !cap) return cap; int delta, ret = 0; for(int i=head[u]; i; i=ed[i].nxt) { if(ed[i].w > 0 && Depth[ed[i].v] == Depth[u] + 1) { delta = Dinic(ed[i].v, min(ed[i].w, cap-ret)); if(delta > 0) { ed[i].w -= delta; ed[i^1].w += delta; ret += delta; } } } return ret; }
所以来更新一下这篇文章。这样写确实跑的很快。
1231 这道题直接过了。
然后又去试了试网络最大流的模板 Luogu P3376.
已经是无话可说。
两张图为证:
这是改之前的评测结果

这是改之后的评测结果

下面放上完整的模板,底下的那个就留着给大家观赏好了
#include <iostream> #include <cstring> #include <cstdio> #include <queue> #define INF 2147483647 using namespace std; const int maxnode = 1e4+3, maxedge = 2e5+3; inline int read() { int x = 0, f = 1; char c = getchar(); while (c < '0' || c > '9') {if(c == '-') f = -1; c = getchar();} while (c <= '9' && c >= '0') {x = x*10 + c-'0'; c = getchar();} return x * f; } int n, m, s, t, head[maxnode], cnt=1, Depth[maxnode], Ans; struct Edge { int nxt, v, w; }ed[maxedge]; inline void addedge(int u, int v, int w) { ed[++cnt].nxt = head[u]; ed[cnt].v = v, ed[cnt].w = w; head[u] = cnt; } inline bool BFS() { memset(Depth, 0, sizeof(Depth)); queue <int> Q; Depth[s] = 1, Q.push(s); while (!Q.empty()) { int u = Q.front(); Q.pop(); for(int i=head[u]; i; i=ed[i].nxt) { if(ed[i].w > 0 && Depth[ed[i].v] == 0) { Q.push(ed[i].v); Depth[ed[i].v] = Depth[u] + 1; if(ed[i].v == t) return true; } } } return false; } inline int Dinic(int u, int cap) { if(u == t || !cap) return cap; int delta, ret = 0; for(int i=head[u]; i; i=ed[i].nxt) { if(ed[i].w > 0 && Depth[ed[i].v] == Depth[u] + 1) { delta = Dinic(ed[i].v, min(ed[i].w, cap-ret)); if(delta > 0) { ed[i].w -= delta; ed[i^1].w += delta; ret += delta; } } } return ret; } int main() { n = read(), m = read(), s = read(), t = read(); static int x, y, z; for(register int i=1; i<=m; i++) { x = read(), y = read(), z = read(); addedge(x, y, z), addedge(y, x, 0); } while (BFS()) Ans += Dinic(s, INF); printf("%d\n", Ans); }
以下为原文内容
我知道学这种东西有个图辅助理解更好,所以我尽量把图画好。flag
简介 & 一些定义
网络流,顾名思义是个流。是个怎么样子的流?
下面我们通过一个形象的比喻(fAke)来了解一下。有一种高端大气上档次的操作叫扯淡
就像是有很多管道,既然是管道那肯定有容量,这些管道链接着水厂和用水户。水厂通过管道将水流进用水户家中,不过水厂滞销(好像并不会出现,这只是一个假设),为了不浪费水,老板决定免费送水。而老板只有一个用水户??!!所以他需要在不撑爆管道的情况下最大化流到用水户家里的水。
呵呵,我都被自己的比喻吓到了,不过说的应该很形象的吧
在上面这个比喻中水厂只能流出水,我们称其为源点,而用水户只能流入水,我们称其为汇点,其他的点既能流入也能流出,我们称其为(对不起,该字体无法显示我也不知道叫啥)。
管道的容量就叫容量,必须保证流过的水的量不能超过容量。但有的时候流过水的量会小于管道的容量,这个管道就会剩余一些容量,我们将这些剩余的容量成为残量。
将这个问题的一个合法解称之为流。一条边上水流过的量称为这条边的流量。
0x01
这个问题如何来解决,我们自然而然的就能想到一种错误的方法。如下:
源点我们用 $S$ 来表示,汇点用 $T$ 表示。
每次任意选择一条 $S\rightarrow T$ 的路径。将这条路径上所有边的容量都减去容量最小值。我们称这样的操作为增广。
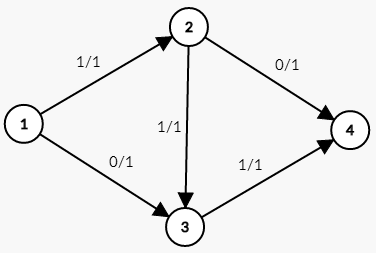
结合图片来理解一下 $0/1$ 代表容量是 $1$ ,水流过的量是 $0$ 。下图中我们选择的是 $1\rightarrow 2\rightarrow 3 \rightarrow 4$ 这条路径。
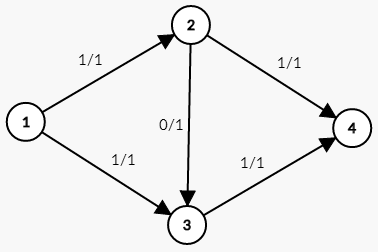
这条路径的流量为 $1$ 。刚刚已经说过这是个错误的解法,这张图的最大流并不是 $1$ 。而是 $2$ ,走 $1\rightarrow 2\rightarrow 4$ 和 $1\rightarrow 3\rightarrow 4$ 这两条路径。如第二张图所示。
问题就出在 $2\rightarrow 3$ 这条边上。从第三张图可以看出来。
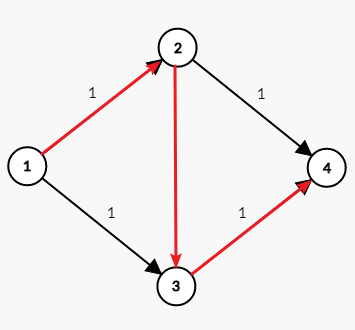
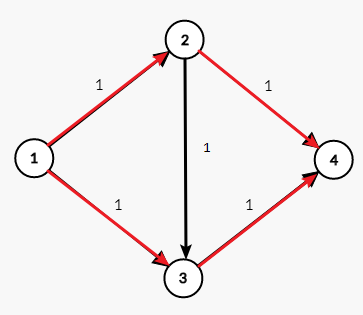
如何解决这个问题,我们需要引入一种很骚气的操作叫做反悔。在走了 $2\rightarrow 3$ 这条边之后我们发现这条路不对,我们反悔再折回去走 $3\rightarrow 2$ 像下面第一张图,那就会有人说了。我们建的不是有向图吗。为啥还能跑回去啊?
其实我们在建有向图的时候同时建立反边。反边具有一个性质,反边流量的相反数等于正边的流量。这一点怎么理解?其实就是反悔的时候把流过去的水又流了回来。
再往下一直找别的路径就找到了这个图的最大流了。

上面就是通常所说的EK算法(全称自己百度吧)。这种算法的时间复杂度并不是很优。
下面看一下EK算法的代码
inline void EK() { int cap = INF; for(int i=t; i!=s; i=ed[pre[i]].u) //这个pre数组是记录路径的一个前缀数组 cap = min(cap, ed[pre[i]].w); //找出这条路径上的最小的容量 for(int i=t; i!=s; i=ed[pre[i]].u) { ed[pre[i]].w -= cap; //正向边的容量减 ed[pre[i]^1].w += cap; //反向边的容量加 } max_flow += cap; //记录最大流 }
0x02
下面看一种针对EK算法的极限数据,如下图。
不难看出这个图的最大流是 $2000$ 。
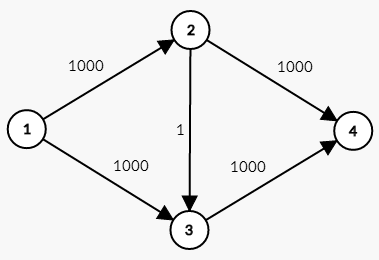
假设第一次增广是我们选择了 $1\rightarrow 2\rightarrow 3\rightarrow 4$ 这条路径。第一次增广完之后就变成了这个样子
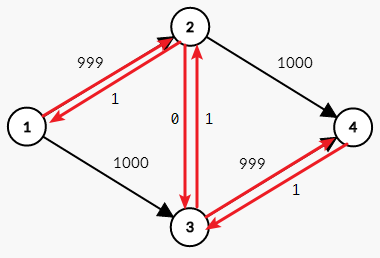
不出意外下一次增广选择了 $1\rightarrow 3\rightarrow 2\rightarrow 4$这条路。
重复这一过程,需要很多次才能将 $2000$ 算出来。为了减少这种无聊的操作。我们引入了分层图的概念
在BFS寻找路径的时候记录节点的深度, $Depth(v)=Depth(u)+1$,这样就将图分为了一层一层的
这就是Dinic算法
先看下代码,还有BFS的代码
inline bool BFS() { memset(Depth, 0, sizeof(Depth)); queue <int> Q; Depth[s] = 1, Q.push(s); //源点的深度初始化为1 while (!Q.empty()) { int u = Q.front(); Q.pop(); for(int i=head[u]; i; i=ed[i].nxt) { if(ed[i].w > 0 && Depth[ed[i].v] == 0) { Q.push(ed[i].v); //记录节点深度 Depth[ed[i].v] = Depth[u] + 1; if(ed[i].v == t) return true; //还能找到可增广路径 } } } return false; //没有找的可增广路径 }
inline int Dinic(int u, int cap) { if(u == t) return cap; //流到了汇点 int delta; for(int i=head[u]; i; i=ed[i].nxt) { if(ed[i].w != 0 && Depth[ed[i].v] == Depth[u] + 1) { delta = Dinic(ed[i].v, min(cap, ed[i].w)); if(delta > 0) { //增广成功 ed[i].w -= delta; //正边减 ed[i^1].w += delta; //负边加 return delta; //向上传递 } } } return 0; //没有增广成功 }
完整代码
#include <iostream> #include <cstring> #include <cstdio> #include <queue> #define INF 2147483647 using namespace std; const int maxnode = 1e4+3, maxedge = 2e5+3; inline int read() { int x = 0, f = 1; char c = getchar(); while (c < '0' || c > '9') {if(c == '-') f = -1; c = getchar();} while (c <= '9' && c >= '0') {x = x*10 + c-'0'; c = getchar();} return x * f; } int n, m, s, t, head[maxnode], cnt=1, Depth[maxnode], Ans; struct Edge { int nxt, v, w; }ed[maxedge]; inline void addedge(int u, int v, int w) { ed[++cnt].nxt = head[u]; ed[cnt].v = v, ed[cnt].w = w; head[u] = cnt; } inline bool BFS() { memset(Depth, 0, sizeof(Depth)); queue <int> Q; Depth[s] = 1, Q.push(s); while (!Q.empty()) { int u = Q.front(); Q.pop(); for(int i=head[u]; i; i=ed[i].nxt) { if(ed[i].w > 0 && Depth[ed[i].v] == 0) { Q.push(ed[i].v); Depth[ed[i].v] = Depth[u] + 1; if(ed[i].v == t) return true; } } } return false; } inline int Dinic(int u, int cap) { if(u == t) return cap; int delta; for(int i=head[u]; i; i=ed[i].nxt) { if(ed[i].w != 0 && Depth[ed[i].v] == Depth[u] + 1) { delta = Dinic(ed[i].v, min(cap, ed[i].w)); if(delta > 0) { ed[i].w -= delta; ed[i^1].w += delta; return delta; } } } return 0; } int main() { n = read(), m = read(), s = read(), t = read(); static int x, y, z; for(register int i=1; i<=m; i++) { x = read(), y = read(), z = read(); addedge(x, y, z), addedge(y, x, 0); } while (BFS()) Ans += Dinic(s, INF); printf("%d\n", Ans); }
来源:http://www.cnblogs.com/bljfy
说明:客官~~您如果觉得写得好的话,记得给我点赞哦。如果要转载的请在合适的地方注明出处。谢
谢您的合作。您要是有什么有疑问的地方可以在下面给我评论。也可以直接私信我哦
声明:本作品由Mystical-W采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 4.0 国
际许可协议进行许可


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号