Python逆向(四)—— Python内置模块dis.py源码详解
一、前言
上一节我们对Python编译及反汇编做了讲解,大家知道dis模块可以将编译好的pyc文件中提取出来的PyCodeObject反汇编为可以阅读字节码形式。本节我们对dis模块中的源码进行详细的解读。
二、dis模块原理解析
官方文档说明:https://docs.python.org/2/library/dis.html
The dis module supports the analysis of CPython bytecode by disassembling it. The CPython bytecode which this module takes as an input is defined in the file Include/opcode.h and used by the compiler and the interpreter.
dis模块通过反汇编来支持对python字节码形式的分析。dis模块可以将编译好的二进制数据或者python源码当作模块的输入源。
dis模块可以将python源码文件、内存中的类或者方法、或者经过反序列化的PyCodeObject翻译为相应的字节码供分析。
2.1、dis反汇编源码文件:
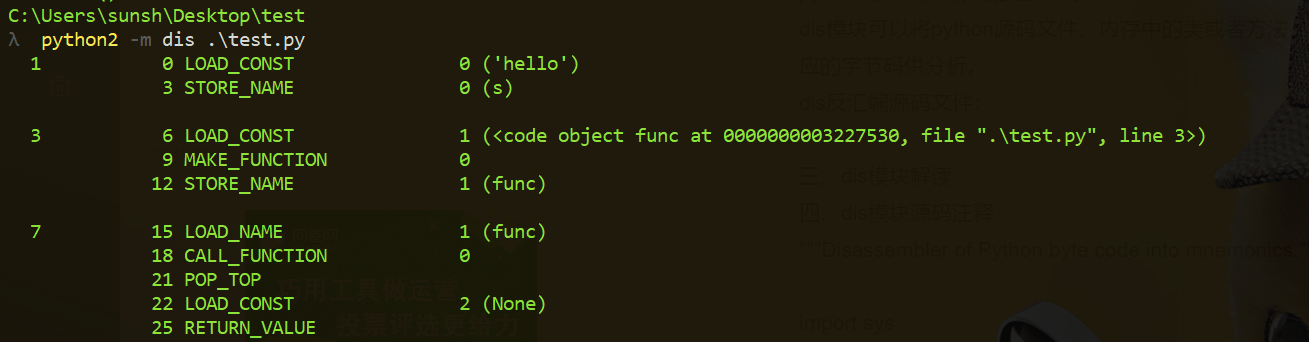
将源码文件作为dis模块的输入,dis模块将直接输入该源码文件编译后对应的字节码文本。
2.2、dis反汇编内存中的类或者函数:
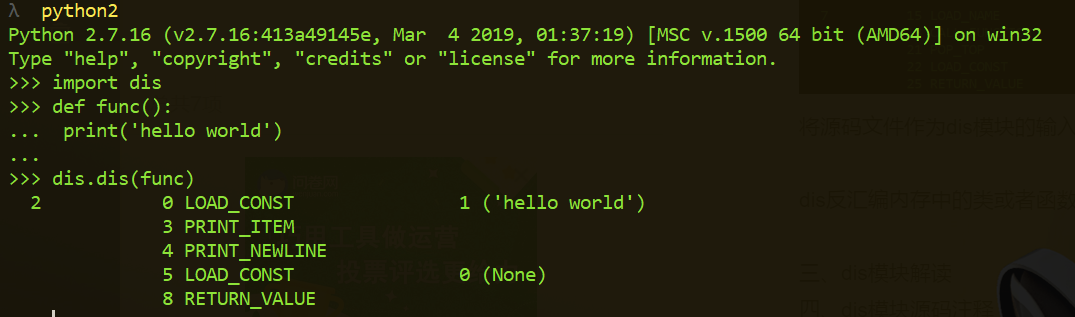
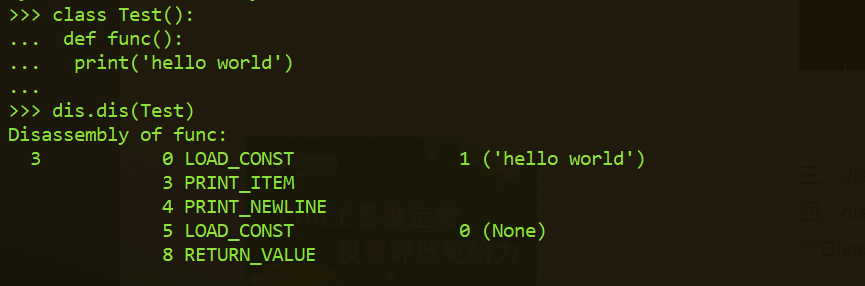
将内存中的类、函数,甚至时普通的变量作为参数传递给dis模块中的dis函数,也可以返回该类对应的编译后的字节码形式。
2.3、dis反汇编PyCodeObject对象:

这一类情况是我们在做python逆向或者pyc文件分析时常用到的形式。
2.4、dis无参数:

如果dis.dis无参数传入,该方法默认会返回当前python shell上次报错时堆栈中储存的内存信息的字节码形式。
三、dis模块解读
dis模块包含许多类和方法,具体用法如下表:
| 方法或者属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| dis.dis([bytesource]) | Disassemble the bytesource object. bytesource can denote either a module, a class, a method, a function, or a code object. For a module, it disassembles all functions. For a class, it disassembles all methods. For a single code sequence, it prints one line per bytecode instruction. If no object is provided, it disassembles the last traceback. |
| dis.distb([tb]) | Disassembles the top-of-stack function of a traceback, using the last traceback if none was passed. The instruction causing the exception is indicated. |
| dis.disassemble(code[, lasti]) | Disassembles a code object, indicating the last instruction if lasti was provided. |
| dis.disco(code[, lasti]) | A synonym for disassemble(). It is more convenient to type, and kept for compatibility with earlier Python releases. |
| dis.findlinestarts(code) | This generator function uses the co_firstlineno and co_lnotab attributes of the code object code to find the offsets which are starts of lines in the source code. They are generated as (offset, lineno) pairs. |
| dis.findlabels(code) | Detect all offsets in the code object code which are jump targets, and return a list of these offsets. |
| dis.opname | Sequence of operation names, indexable using the bytecode. |
| dis.opmap | Dictionary mapping operation names to bytecodes. |
| dis.cmp_op | Sequence of all compare operation names. |
| dis.hasconst | Sequence of bytecodes that access a constant. |
| dis.hasfree | Sequence of bytecodes that access a free variable. |
| dis.hasname | Sequence of bytecodes that access an attribute by name. |
| dis.hasjrel | Sequence of bytecodes that have a relative jump target. |
| dis.hasjabs | Sequence of bytecodes that have an absolute jump target. |
| dis.haslocal | Sequence of bytecodes that access a local variable. |
| dis.hascompare | Sequence of bytecodes of Boolean operations. |
| 上表摘自官方文档整理,对各个方法及属性进行了详细的说明。下文将对dis模块运行流程进行说明。 |
3.1
dis模块主函数为dis,所有对dis模块的调用默认都会将参数传送给dis.dis(不排除进阶玩家直接调用dis.disb等其他模块来完成特定功能)
3.2
dis.dis先进行参数检查,根据无参数、字典、PyCodeObject实例化对象,代码段等不同类型参数调用不同的方法。如果提交的参数是字典,dis模块会通过迭代,将字典中的每个键值作为参数传递给dis.dis
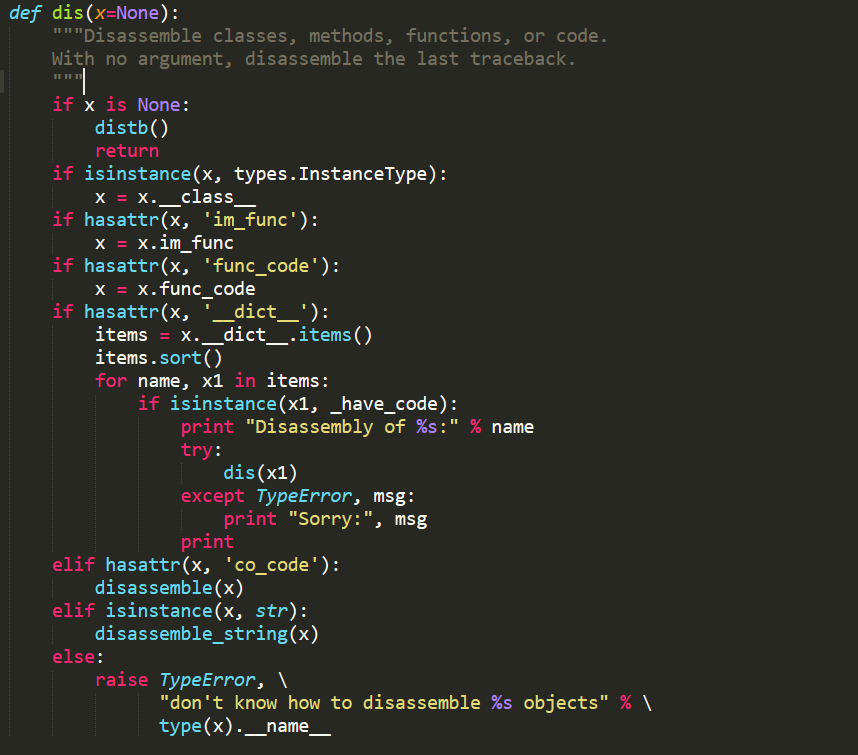
3.3
经过dis方法的处理,最终参数会被交给disassemble或者disassemble_string方法处理,disassemble方法负责对提交的对象进行反汇编,disassemble_string方法负责对代码段进行反汇编,因为disassemble_string方法代码类似于disassemble,不对disassemble_string进行解读。
3.4
disassemble方法用来将PyCodeObject实例化对象翻译为可读字节码。首先调用findlabels和findlinestarts。findlabels将所有字节码跳转指向目的字节码地址存入堆栈。findlinestarts用来标记字节码对应的源码位置,官方注释说明findlinestarts会生成(offset, lineno)元组,其中offset为字节码偏移地址,lineno为源码偏移地址。
3.5
disassemble方法对字节码代码部分逐行翻译,并且添加必要变量及标志注释。
四、dis模块源码注释版本
"""Disassembler of Python byte code into mnemonics."""
import sys
import types
from opcode import *
from opcode import __all__ as _opcodes_all
__all__ = ["dis", "disassemble", "distb", "disco",
"findlinestarts", "findlabels"] + _opcodes_all
del _opcodes_all
_have_code = (types.MethodType, types.FunctionType, types.CodeType,
types.ClassType, type)
'''根据x所属type,判断对输入参数x执行何种反编译,其中co_code选项是
对pyc文件中提取的marshal数据进行反编译过程中常用的'''
def dis(x=None):
"""Disassemble classes, methods, functions, or code.
With no argument, disassemble the last traceback.
"""
if x is None:
distb()
return
if isinstance(x, types.InstanceType):
x = x.__class__
if hasattr(x, 'im_func'):
x = x.im_func
if hasattr(x, 'func_code'):
x = x.func_code
if hasattr(x, '__dict__'):
items = x.__dict__.items()
items.sort()
for name, x1 in items:
if isinstance(x1, _have_code):
print "Disassembly of %s:" % name
try:
dis(x1)
except TypeError, msg:
print "Sorry:", msg
print
elif hasattr(x, 'co_code'):
disassemble(x)
elif isinstance(x, str):
disassemble_string(x)
else:
raise TypeError, \
"don't know how to disassemble %s objects" % \
type(x).__name__
'''无参数x传入时,对上次报错的堆栈信息进行反编译'''
def distb(tb=None):
"""Disassemble a traceback (default: last traceback)."""
if tb is None:
try:
tb = sys.last_traceback
except AttributeError:
raise RuntimeError, "no last traceback to disassemble"
while tb.tb_next: tb = tb.tb_next
disassemble(tb.tb_frame.f_code, tb.tb_lasti)
'''反编译的主函数'''
def disassemble(co, lasti=-1):
"""Disassemble a code object."""
code = co.co_code
labels = findlabels(code)
linestarts = dict(findlinestarts(co))
n = len(code)
i = 0
'''***'''
extended_arg = 0
free = None
while i < n:
c = code[i]
op = ord(c)
'''字节码对应源码偏移量标注'''
if i in linestarts:
if i > 0:
print
print "%3d" % linestarts[i],
else:
print ' ',
if i == lasti: print '-->',
else: print ' ',
'''标注跳转标记'''
if i in labels: print '>>',
else: print ' ',
'''标注字节码偏移和opcode名字'''
print repr(i).rjust(4),
print opname[op].ljust(20),
i = i+1
if op >= HAVE_ARGUMENT:
'''根据不同的变量类型进行变量标注'''
oparg = ord(code[i]) + ord(code[i+1])*256 + extended_arg
extended_arg = 0
i = i+2
if op == EXTENDED_ARG:
extended_arg = oparg*65536L
print repr(oparg).rjust(5),
if op in hasconst:
print '(' + repr(co.co_consts[oparg]) + ')',
elif op in hasname:
print '(' + co.co_names[oparg] + ')',
elif op in hasjrel:
print '(to ' + repr(i + oparg) + ')',
elif op in haslocal:
print '(' + co.co_varnames[oparg] + ')',
elif op in hascompare:
print '(' + cmp_op[oparg] + ')',
elif op in hasfree:
if free is None:
free = co.co_cellvars + co.co_freevars
print '(' + free[oparg] + ')',
print
'''字符串反编译的主函数'''
def disassemble_string(code, lasti=-1, varnames=None, names=None,
constants=None):
labels = findlabels(code)
n = len(code)
i = 0
while i < n:
c = code[i]
op = ord(c)
if i == lasti: print '-->',
else: print ' ',
if i in labels: print '>>',
else: print ' ',
print repr(i).rjust(4),
print opname[op].ljust(15),
i = i+1
if op >= HAVE_ARGUMENT:
oparg = ord(code[i]) + ord(code[i+1])*256
i = i+2
print repr(oparg).rjust(5),
if op in hasconst:
if constants:
print '(' + repr(constants[oparg]) + ')',
else:
print '(%d)'%oparg,
elif op in hasname:
if names is not None:
print '(' + names[oparg] + ')',
else:
print '(%d)'%oparg,
elif op in hasjrel:
print '(to ' + repr(i + oparg) + ')',
elif op in haslocal:
if varnames:
print '(' + varnames[oparg] + ')',
else:
print '(%d)' % oparg,
elif op in hascompare:
print '(' + cmp_op[oparg] + ')',
print
disco = disassemble # XXX For backwards compatibility
'''遍历寻找co_code中为跳转操作的opcode,并将跳转的目的地址(字节码的偏
移地址)存入labels中'''
def findlabels(code):
"""Detect all offsets in a byte code which are jump targets.
Return the list of offsets.
"""
labels = []
n = len(code)
i = 0
while i < n:
c = code[i]
op = ord(c)
i = i+1
if op >= HAVE_ARGUMENT:
'''计算argv表示的偏移地址'''
oparg = ord(code[i]) + ord(code[i+1])*256
i = i+2
label = -1
'''根据跳转类型将跳转后的地址加入数组labels中'''
if op in hasjrel:
label = i+oparg
elif op in hasjabs:
label = oparg
if label >= 0:
if label not in labels:
labels.append(label)
return labels
def findlinestarts(code):
"""Find the offsets in a byte code which are start of lines in the source.
Generate pairs (offset, lineno) as described in Python/compile.c.
"""
'''汇编偏移'''
byte_increments = [ord(c) for c in code.co_lnotab[0::2]]
'''源码偏移'''
line_increments = [ord(c) for c in code.co_lnotab[1::2]]
'''上一行源码的绝对地址'''
lastlineno = None
'''当前汇编对应源码的行'''
lineno = code.co_firstlineno
addr = 0
for byte_incr, line_incr in zip(byte_increments, line_increments):
if byte_incr:
if lineno != lastlineno:
yield (addr, lineno)
lastlineno = lineno
addr += byte_incr
lineno += line_incr
'''byte偏移量一定每次递增不为零,但是源码可能出现lambda类似
语句,因此不同区块的字节码可能对应于源码的同一行'''
if lineno != lastlineno:
yield (addr, lineno)
def _test():
"""Simple test program to disassemble a file."""
if sys.argv[1:]:
if sys.argv[2:]:
sys.stderr.write("usage: python dis.py [-|file]\n")
sys.exit(2)
fn = sys.argv[1]
if not fn or fn == "-":
fn = None
else:
fn = None
if fn is None:
f = sys.stdin
else:
f = open(fn)
source = f.read()
if fn is not None:
f.close()
else:
fn = "<stdin>"
code = compile(source, fn, "exec")
dis(code)
if __name__ == "__main__":
_test()


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号