Linux select 机制深入分析
Linux select 机制深入分析
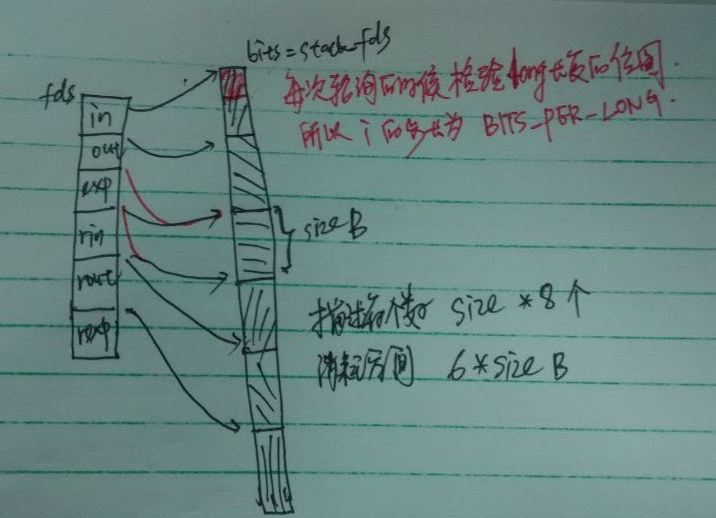
附图1:
作为IO复用的实现方式。select是提高了抽象和batch处理的级别,不是传统方式那样堵塞在真正IO读写的系统调用上。而是堵塞在select系统调用上,等待我们关注的描写叙述符就绪。当然如今更好的方式是epoll,比方Java中的NIO底层就是用的epoll。这篇文章仅仅是为了搞懂select机制的原理。不看源代码就不能说懂这些IO复用手法。也在面试过程中体会到了,不去实践就会发现知道的永远是皮毛。面试问题:select的最大描写叙述符限制能够改动吗?(有待深入)
用户层API语法:
/* According to POSIX.1-2001 */
#include <sys/select.h>
/* According to earlier standards */
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int select(int nfds, fd_set *readfds, fd_set *writefds,
fd_set *exceptfds, struct timeval *timeout);
void FD_CLR(int fd, fd_set *set);
int FD_ISSET(int fd, fd_set *set);
void FD_SET(int fd, fd_set *set);
void FD_ZERO(fd_set *set);
#include <sys/select.h>
int pselect(int nfds, fd_set *readfds, fd_set *writefds,
fd_set *exceptfds, const struct timespec *timeout,
const sigset_t *sigmask);注:这里的API发生了变化(參见UNPv1 P127),timeout值是同意更新的,这在内核中有体现。
select系统调用的内核源代码主要流程是:sys_select() -> core_sys_select() -> do_select() -> poll_select_copy_remaining。
可代码能够一目了然。
/*
* SYSCALL_DEFINE5宏的作用就是将其转成系统调用的常见形式,
* asmlinkage long sys_select(int n, fd_set __user *inp, fd_set __user *outp,fd_set __user *exp, struct timeval __user *tvp);
*/
SYSCALL_DEFINE5(select, int, n, fd_set __user *, inp, fd_set __user *, outp,
fd_set __user *, exp, struct timeval __user *, tvp)
{
struct timespec end_time, *to = NULL;
struct timeval tv;
int ret;
if (tvp) {//假设设置了超时阈值
if (copy_from_user(&tv, tvp, sizeof(tv)))
return -EFAULT;
to = &end_time;
// 从timeval(秒 微秒)转换为(秒 纳秒) 继而建立超时
if (poll_select_set_timeout(to,
tv.tv_sec + (tv.tv_usec / USEC_PER_SEC),
(tv.tv_usec % USEC_PER_SEC) * NSEC_PER_USEC))
return -EINVAL;
}
// 核心工作
ret = core_sys_select(n, inp, outp, exp, to);
//core_sys_select处理的fd_set 接下来更新timeout的值
ret = poll_select_copy_remaining(&end_time, tvp, 1, ret);
return ret;
}
/*
* We can actually return ERESTARTSYS instead of EINTR, but I'd
* like to be certain this leads to no problems. So I return
* EINTR just for safety.
*
* Update: ERESTARTSYS breaks at least the xview clock binary, so
* I'm trying ERESTARTNOHAND which restart only when you want to.
*/
int core_sys_select(int n, fd_set __user *inp, fd_set __user *outp,
fd_set __user *exp, struct timespec *end_time)
{
// poll.h :fd_set_bits包装了6个long *,代表三个描写叙述表集的值-结果
fd_set_bits fds;
void *bits;
int ret, max_fds;
unsigned int size;
struct fdtable *fdt;
/* Allocate small arguments on the stack to save memory and be faster
* 先是预分配256B的空间 大多数情况下可以满足须要 特殊情况在以下会分配空间
*/
long stack_fds[SELECT_STACK_ALLOC/sizeof(long)];
ret = -EINVAL;
if (n < 0)
goto out_nofds;
/* max_fds can increase, so grab it once to avoid race */
rcu_read_lock();
// 获得打开文件描写叙述符表(指针析取)
fdt = files_fdtable(current->files);
max_fds = fdt->max_fds;
rcu_read_unlock();
if (n > max_fds)
n = max_fds;//參数修正
/*
* 如今要监视的描写叙述符个数个size*8个对于每个都须要6个位来标示
* 它是否可以读写异常而且把结果写在res_in res_out res_exp中
* 所以构成了以下的内存布局(见图1)
*/
size = FDS_BYTES(n);
bits = stack_fds;
if (size > sizeof(stack_fds) / 6) {
/* Not enough space in on-stack array; must use kmalloc */
ret = -ENOMEM;
bits = kmalloc(6 * size, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!bits)
goto out_nofds;
}
fds.in = bits;
fds.out = bits + size;
fds.ex = bits + 2*size;
fds.res_in = bits + 3*size;
fds.res_out = bits + 4*size;
fds.res_ex = bits + 5*size;
// 从用户空间得到这些fd sets
if ((ret = get_fd_set(n, inp, fds.in)) ||
(ret = get_fd_set(n, outp, fds.out)) ||
(ret = get_fd_set(n, exp, fds.ex)))
goto out;
// 初始化这些结果參数为0
zero_fd_set(n, fds.res_in);
zero_fd_set(n, fds.res_out);
zero_fd_set(n, fds.res_ex);
// 到这里 一切准备工作都就绪了.....
ret = do_select(n, &fds, end_time);
if (ret < 0)
goto out;
if (!ret) {
ret = -ERESTARTNOHAND;
if (signal_pending(current))
goto out;
ret = 0;
}
// do_select正确返回后 通过copy_to_user将fds中的描写叙述符就绪结果參数
// 反馈到用户空间
if (set_fd_set(n, inp, fds.res_in) ||
set_fd_set(n, outp, fds.res_out) ||
set_fd_set(n, exp, fds.res_ex))
ret = -EFAULT;
out:
if (bits != stack_fds)
kfree(bits);
out_nofds:
return ret;
}
// select 的核心工作
int do_select(int n, fd_set_bits *fds, struct timespec *end_time)
{
ktime_t expire, *to = NULL;
struct poll_wqueues table;
poll_table *wait;
int retval, i, timed_out = 0;
unsigned long slack = 0;
unsigned int busy_flag = net_busy_loop_on() ? POLL_BUSY_LOOP : 0;
unsigned long busy_end = 0;
// 得到Select要监測的最大的描写叙述符值
rcu_read_lock();
retval = max_select_fd(n, fds);
rcu_read_unlock();
if (retval < 0)
return retval;
n = retval;
poll_initwait(&table);
wait = &table.pt;
// 定时器值(秒 纳秒)为0的话标示不等待
if (end_time && !end_time->tv_sec && !end_time->tv_nsec) {
wait->_qproc = NULL;
timed_out = 1;
}
if (end_time && !timed_out)
slack = select_estimate_accuracy(end_time);
// 以下会用到这个变量统计就绪的描写叙述符个数 所以先清0
retval = 0;
for (;;) {
unsigned long *rinp, *routp, *rexp, *inp, *outp, *exp;
bool can_busy_loop = false;
inp = fds->in; outp = fds->out; exp = fds->ex;
rinp = fds->res_in; routp = fds->res_out; rexp = fds->res_ex;
for (i = 0; i < n; ++rinp, ++routp, ++rexp) {
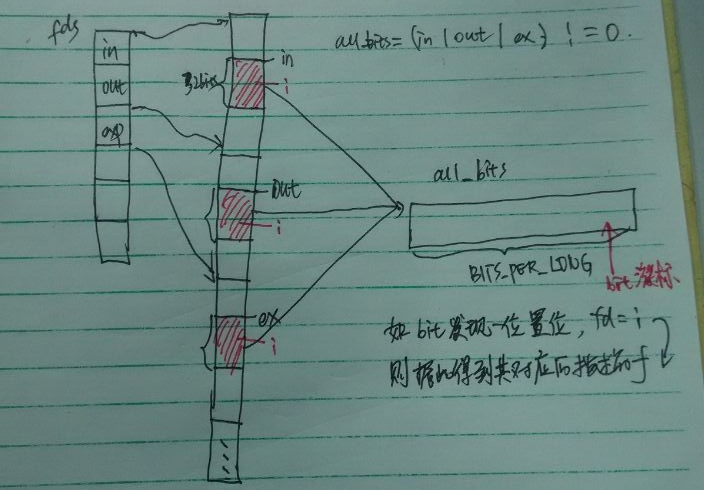
unsigned long in, out, ex, all_bits, bit = 1, mask, j;
unsigned long res_in = 0, res_out = 0, res_ex = 0;
in = *inp++; out = *outp++; ex = *exp++;
all_bits = in | out | ex;
// 要一次轮询这些这些位图 定位到某个有我们关心的fd的区间
// 否则以32bits步长前进
if (all_bits == 0) {
i += BITS_PER_LONG;
continue;
}
// 当前这个区间有我们关心的fd 所以深入细节追踪(图2)
for (j = 0; j < BITS_PER_LONG; ++j, ++i, bit <<= 1) {
struct fd f;
if (i >= n)
break;
if (!(bit & all_bits))
continue;
// 假设发现了当前区间的某一个bit为1 则说明相应的fd须要我们处理
// 此时此刻的i正是文件描写叙述符值
f = fdget(i);
if (f.file) {
const struct file_operations *f_op;
f_op = f.file->f_op;
mask = DEFAULT_POLLMASK;
//详细到文件操作结果中的poll函数指针 对于
if (f_op->poll) {
wait_key_set(wait, in, out,
bit, busy_flag);
mask = (*f_op->poll)(f.file, wait);// TODO
}
// 上面的fdget添加了file引用计数 所以这里恢复
fdput(f);
/* 推断关注的描写叙述符是否就绪 就绪的话就更新到结果參数中
* 而且添加就绪个数
*/
if ((mask & POLLIN_SET) && (in & bit)) {
res_in |= bit;
retval++;
wait->_qproc = NULL;
}
if ((mask & POLLOUT_SET) && (out & bit)) {
res_out |= bit;
retval++;
wait->_qproc = NULL;
}
if ((mask & POLLEX_SET) && (ex & bit)) {
res_ex |= bit;
retval++;
wait->_qproc = NULL;
}
/* got something, stop busy polling
* 停止忙循环
*/
if (retval) {
can_busy_loop = false;
busy_flag = 0;
/*
* only remember a returned
* POLL_BUSY_LOOP if we asked for it
*/
} else if (busy_flag & mask)
can_busy_loop = true;
}
}
// 这一轮的区间遍历完之后 更新结果參数
if (res_in)
*rinp = res_in;
if (res_out)
*routp = res_out;
if (res_ex)
*rexp = res_ex;
/* 进行一次调度 同意其它进程执行
* 后面有等待队列唤醒
*/
cond_resched();
}
// 一轮轮询之后
wait->_qproc = NULL;
// 假设有描写叙述符就绪 或者设置了超时 或者有待处理信号 则退出这个死循环
if (retval || timed_out || signal_pending(current))
break;
if (table.error) {
retval = table.error;
break;
}
/* only if found POLL_BUSY_LOOP sockets && not out of time */
if (can_busy_loop && !need_resched()) {
if (!busy_end) {
busy_end = busy_loop_end_time();
continue;
}
if (!busy_loop_timeout(busy_end))
continue;
}
busy_flag = 0;
/* 假设设置超时 而且这是首次循环(to==NULL) */
if (end_time && !to) {
// 从timespec转化为ktime类型(64位的有符号值)
expire = timespec_to_ktime(*end_time);
to = &expire;
}
/*设置该进程状态TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE 睡眠直到超时
* 返回到这里后进程 TASK_RUNNING
*/
if (!poll_schedule_timeout(&table, TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE, to, slack))
timed_out = 1;
}
// 释放该poll wait queue
poll_freewait(&table);
return retval;
}
附图2:
參考:
(1)Linux kernel 3.18 source code
(2)Linux man page
(3)UNPv1
耗时:3h



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号