Java 自定义全局异常处理类
自定义全局异常处理类:优雅管理应用错误,告别杂乱代码
感觉本篇对你有帮助可以关注一下我的微信公众号(深入浅出谈java),会不定期更新知识和面试资料、技巧!!!

优点:
自定义全局异常处理类在开发中有以下几个主要用途和好处:
- 集中管理异常:通过自定义全局异常处理类,可以集中处理应用程序中所有的异常,而不需要在每个控制器中重复编写异常处理逻辑。这有助于代码的整洁性和可维护性。
- 统一的异常响应:全局异常处理类可以统一格式化异常的返回结果,确保前端接收到的一致性和规范性,这样在处理错误时,用户体验更加友好。
- 细粒度控制:可以根据不同类型的异常,定制不同的处理方式。例如,可以根据业务逻辑的需要返回不同的状态码和错误信息,方便前端进行处理。
- 记录日志:在全局异常处理类中,可以统一记录异常信息,便于后续的排查和分析。这有助于提高系统的监控和维护能力。
- 简化代码:通过自动化处理一些常见的异常(如请求参数异常、认证异常等),可以减少每个处理方法中的异常处理代码,使得业务逻辑更加清晰。
- 增强安全性:通过统一处理异常,可以有效避免敏感信息(如堆栈跟踪信息等)泄露到客户端,提高了应用程序的安全性。
全局异常处理实现原理
@ControllerAdvice:声明全局异常处理类,监控所有Controller的异常。@ExceptionHandler:标注具体处理异常的方法,支持按异常类型匹配。- 统一响应体:封装错误码、错误信息、数据等标准结构。
代码实现部分
2.1、定义全局异常处理类
在 Spring Boot 中,可以使用 @ControllerAdvice 注解来定义全局异常处理类
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.MethodArgumentNotValidException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
/**
* @Classname GlobalExceptionHandlerAdvice
* @Description 自定义全局异常处理类
* @Version 1.0.0
* @Date 2024/6/6 16:02
* @Created by Administrator
*/
@Slf4j
@ControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandlerAdvice {
/**-------- 通用异常处理方法 --------**/
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
@ResponseBody
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
public R error(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
log.error("全局异常捕获:" + e);
return R.fail(); // 通用异常结果
}
/**-------- 指定异常处理方法 --------**/
@ExceptionHandler(NullPointerException.class)
@ResponseBody
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
public R error(NullPointerException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
log.error("全局异常捕获:" + e);
return R.setResult(ResultCodeEnum.NULL_POINT);
}
/**-------- 下标越界处理方法 --------**/
@ExceptionHandler(IndexOutOfBoundsException.class)
@ResponseBody
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
public R error(IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
log.error("全局异常捕获:" + e);
return R.setResult(ResultCodeEnum.INDEX_OUT_OF_BOUNDS);
}
/**
* 方法参数校验
*/
@ExceptionHandler(MethodArgumentNotValidException.class)
@ResponseBody
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST)
public R handleMethodArgumentNotValidException(MethodArgumentNotValidException e) {
log.error(e.getMessage(), e);
return R.setResult(ResultCodeEnum.PARAM_ERROR).message(e.getBindingResult().getFieldError().getDefaultMessage());
}
/**-------- 自定义定异常处理方法 --------**/
@ExceptionHandler(UserException.class)
@ResponseBody
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK)
public R error(UserException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
log.error("全局异常捕获:" + e);
return R.fail().message(e.getMessage()).code(e.getCode());
}
}
2.2 自定义定异常处理方法
这里我们可以定义自己的异常方法(UserException 类),可后续在业务代码中使用
/**
* 自定义异常类
*
* @author admin
* @date 2018/10/15
*/
public class UserException extends RuntimeException {
private Integer code;
public UserException(String message) {
super(message);
this.code = ResultCodeEnum.CUSTOM_ERROR.getCode();
}
public UserException(Integer code, String message) {
super(message);
this.code = code;
}
public UserException(ResultCodeEnum resultCodeEnum) {
super(resultCodeEnum.getMessage());
this.code = resultCodeEnum.getCode();
}
public String toString() {
return "UserException{code=" + this.code + ", message=" + this.getMessage() + '}';
}
public Integer getCode() {
return this.code;
}
public void setCode(final Integer code) {
this.code = code;
}
public boolean equals(final Object o) {
if (o == this) {
return true;
} else if (!(o instanceof UserException)) {
return false;
} else {
UserException other = (UserException)o;
if (!other.canEqual(this)) {
return false;
} else {
Object this$code = this.getCode();
Object other$code = other.getCode();
if (this$code == null) {
if (other$code != null) {
return false;
}
} else if (!this$code.equals(other$code)) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
}
protected boolean canEqual(final Object other) {
return other instanceof UserException;
}
public int hashCode() {
int result = 1;
Object $code = this.getCode();
result = result * 59 + ($code == null ? 43 : $code.hashCode());
return result;
}
}
2.3、状态码枚举类
定义要用的状态枚举类,可做到统一的返回格式,这里也是可以自己定义和修改,只不过我提供的 UserException有用到该枚举类
public enum ResultCodeEnum {
SUCCESS(true, 0, "成功"),
UNKNOWN_ERROR(false, 999999, "未知错误"),
DAO_INSERT_ERROR(false, 100000, "插入数据异常"),
DAO_SELECT_ERROR(false, 100001, "查询数据异常"),
DAO_UPDATE_ERROR(false, 100002, "更新数据异常"),
DAO_DELETE_ERROR(false, 100003, "删除数据异常"),
NULL_POINT(false, 100004, "空指针异常"),
INDEX_OUT_OF_BOUNDS(false, 100005, "下标越界异常"),
REQUEST_TIMEOUT(false, 100006, "请求超时"),
PARAM_ERROR(false, 100007, "参数错误"),
NOT_INIT_DATA(false, 100008, "数据未初始化"),
CUSTOM_ERROR(false, 200000, "自定义错误"),
USER_FORBIDDEN(false, 200001, "用户被禁用"),
NOT_LOGIN_ERROR(false, 200002, "未登录");
private Boolean success;
private Integer code;
private String message;
private ResultCodeEnum(boolean success, Integer code, String message) {
this.success = success;
this.code = code;
this.message = message;
}
public Boolean getSuccess() {
return this.success;
}
public Integer getCode() {
return this.code;
}
public String getMessage() {
return this.message;
}
}
3、使用方法
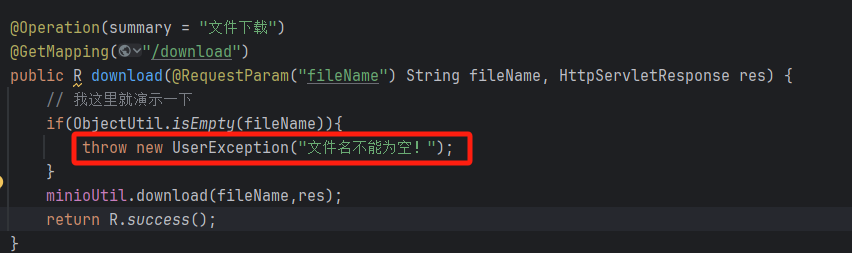
在需要地方代码中使用:throw new UserException()
@Operation(summary = "文件下载")
@GetMapping("/download")
public R download(@RequestParam("fileName") String fileName, HttpServletResponse res) {
// 我这里就演示一下
if(ObjectUtil.isEmpty(fileName)){
throw new UserException("文件名不能为空!");
}
minioUtil.download(fileName,res);
return R.success();
}
4、测试结果
控制台打印:
2024-09-27T10:12:29.042+08:00 ERROR 20732 --- [eip] [nio-8069-exec-4] c.e.e.c.GlobalExceptionHandlerAdvice : 全局异常捕获:UserException{code=200000, message=文件名不能为空!}
Disconnected from the target VM, address: '127.0.0.1:62663', transport: 'socket'
参数为空,返回前端就会提示定义的消息
{
"success": false,
"code": 200000,
"message": "文件名不能为空!",
"data": null,
"dataList": null,
"total": 0
}
最后文章有啥不对,欢迎大佬在评论区指点!!!
如果感觉对你有帮助就点赞推荐或者关注一下吧!!!
 ****
****




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号