SpringBoot原理深入及源码剖析(二) 自定义Starter及SpringBoot执行原理
自定义Starter
SpringBoot starter机制
SpringBoot由众多starter组成(一系列的自动化配置的starter插件),SpringBoot之所以流行,也是因为starter。
starter是SpringBoot非常重要的一部分,可以理解为一个可拔插式的插件,正是这些starter使得使用某个功能的开发者不需要关注各种依赖库的处理,不需要具体的配置信息,由SpringBoot自动通过classpath路径下的类发现需要的Bean,并植入相应的Bean。
例如,想用Redis插件,那么可以使用spring-boot-starter-redis;想用MongoDB插件,那么可以使用spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb。
为什么要自定义starter
开发过程中,经常会有一些独立于业务之外的配置模块。如果我们将这些可独立于业务代码之外的功能配置模块封装成一个个starter,复用的时候只需要将其在pom中引入依赖即可,SpringBoot将为我们完成自动装配。
自定义starter的命名规则
SpringBoot官方提供的starter是以spring-boot-starter-xxx的方式命名的。官方建议自定义的starter使用xxx-spring-boot-starter的命名规则,以区分SpringBoot生态提供的starter。
自定义starter
(1)新建maven jar工程,工程名为hardy-spring-boot-starter,导入依赖:
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-autoconfigure</artifactId> <version>2.5.0</version> </dependency> </dependencies>
(2)编写javaBean:
package com.hardy; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties; /** * @Author: HardyYao * @Date: 2021/6/6 */ @EnableConfigurationProperties(SimpleBean.class) @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "simplebean") public class SimpleBean { private int id; private String name; public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } @Override public String toString() { return "SimpleBean{" + "id=" + id + ", name='" + name + '\'' + '}'; } }
(3)编写配置类MyAutoConfiguration:
package com.hardy.config; import com.hardy.SimpleBean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnClass; /** * @Author: HardyYao * @Date: 2021/6/6 */ @Configuration @ConditionalOnClass // @ConditionalOnClass:当类路径classpath下有指定的类的情况下进行自动配置 public class MyAutoConfiguration { static { System.out.println("MyAutoConfiguration init...."); } @Bean public SimpleBean simpleBean(){ return new SimpleBean(); } }
(4)resources下创建/META-INF/spring.factories:
注意:META-INF是我们自己手动创建的目录,spring.factories也是我们自己手动创建的文件,在该文件中配置自己的自动配置类:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\ com.hardy.config.MyAutoConfiguration
使用自定义starter
(1)导入自定义starter的依赖:
<dependency> <groupId>com.hardy</groupId> <artifactId>hardy-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> </dependency>
(2)在全局配置文件中配置属性值:
simplebean.id=1 simplebean.name=自定义starter
(3)编写测试方法:
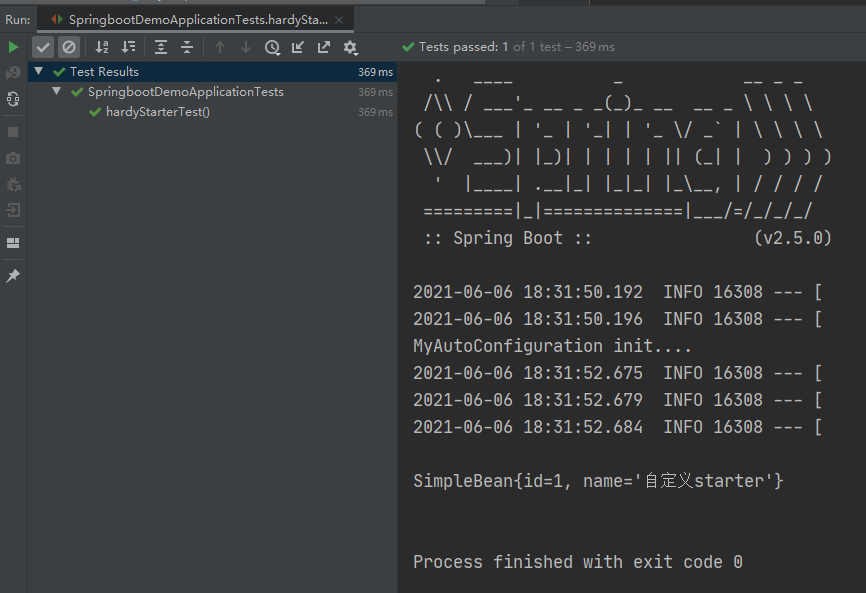
// 测试自定义starter @Autowired private SimpleBean simpleBean; @Test public void hardyStarterTest(){ System.out.println(simpleBean); }
(4)运行结果:
SpringBoot执行原理
每个SpringBoot项目都有一个主程序启动类,在主程序启动类中有一个启动项目的main()方法,在该方法中通过执行SpringApplication.run()即可启动整个SpringBoot项目。
问题:那么SpringApplication.run()方法到底是如何做到启动整个SpringBoot项目的呢?
下面我们来看run()方法内部的源码,核心代码具体如下:
@SpringBootApplication public class SpringbootDemoApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringbootDemoApplication.class, args); } }
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?> primarySource, String... args) { return run(new Class[]{primarySource}, args); } public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) { return (new SpringApplication(primarySources)).run(args); }
从上述源码可以看出,SpringApplication.run()方法内部执行了两个操作,分别是SpringApplication实例的初始化创建和调用run()方法启动项目,这两个阶段的实现具体说明如下:
1、SpringApplication实例的初始化创建
查看SpringApplication实例对象初始化创建的源码信息,核心代码如下:
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) { this.sources = new LinkedHashSet(); this.bannerMode = Mode.CONSOLE; this.logStartupInfo = true; this.addCommandLineProperties = true; this.addConversionService = true; this.headless = true; this.registerShutdownHook = true; this.additionalProfiles = Collections.emptySet(); this.isCustomEnvironment = false; this.lazyInitialization = false; this.applicationContextFactory = ApplicationContextFactory.DEFAULT; this.applicationStartup = ApplicationStartup.DEFAULT; this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader; Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null"); // 把项目启动类.class设置为属性存储起来 this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet(Arrays.asList(primarySources)); // 判断当前webApplicationType应用的类型 this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath(); this.bootstrapRegistryInitializers = this.getBootstrapRegistryInitializersFromSpringFactories(); // 设置初始化器(Initializer),最后会调用这些初始化器 this.setInitializers(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class)); // 设置监听器(Listener) this.setListeners(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class)); // 用于推断并设置项目main()方法启动的主程序启动类 this.mainApplicationClass = this.deduceMainApplicationClass(); }
从上述源码可以看出,SpringApplication的初始化过程主要包括四部分,具体说明如下所示:
(1)this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath()
用于判断当前webApplicationType应用的类型。deduceFromClasspath()方法用于查看Classpath类路径下是否存在某个特征类,从而判断当前webApplicationType类型是SERVLET应用(Spring5之前的传统MVC应用)还是REACTIVE应用(Spring5之后的WebFlux交互式应用)。
(2)this.setInitializers(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class))
用于SpringApplication应用的初始化器设置。在初始化器设置过程中,会使用Spring类加载器SpringFactoriesLoader从META-INF类路径下的spring.factories文件中获取所有可用的应用初始化器类ApplicationContextInitializer。
(3)this.setListeners(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class))
用于SpringApplication应用的监听器设置。监听器设置的过程与上一步初始化器设置的过程基本一样,也是使用SpringFactoriesLoader从META-INF类路径下的spring.factories文件中获取所有可用的监听器类ApplicationListener。
(4)this.mainApplicationClass = this.deduceMainApplicationClass()
用于推断并设置项目main()方法启动的主程序启动类。
2、项目的初始化启动
分析完(new SpringApplication(primarySources)).run(args)源码前一部分SpringApplication实例对象的初始化创建后,我们来查看run(args)方法执行的项目初始化启动过程,其核心代码具体如下:
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) { StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch(); stopWatch.start(); DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = this.createBootstrapContext(); ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null; this.configureHeadlessProperty(); // 1、获取并启动监听器 SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = this.getRunListeners(args); listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass); try { ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args); // 2、根据SpringApplicationRunListeners以及参数来准备环境 ConfigurableEnvironment environment = this.prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments); this.configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment); // 准备Banner打印器——即启动SpringBoot的时候打印在控制台的ASCII艺术字体 Banner printedBanner = this.printBanner(environment); // 3、创建Spring容器 context = this.createApplicationContext(); context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup); // 4、Spring容器前置处理 this.prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner); // 5、刷新容器 this.refreshContext(context); // 6、Spring容器后置处理 this.afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments); stopWatch.stop(); if (this.logStartupInfo) { (new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)).logStarted(this.getApplicationLog(), stopWatch); } // 7、发出结束执行的事件 listeners.started(context); // 8、执行Runners,返回容器 this.callRunners(context, applicationArguments); } catch (Throwable var10) { this.handleRunFailure(context, var10, listeners); throw new IllegalStateException(var10); } try { listeners.running(context); return context; } catch (Throwable var9) { this.handleRunFailure(context, var9, (SpringApplicationRunListeners)null); throw new IllegalStateException(var9); } }
1、获取并启动监听器
this.getRunListeners(args)和listeners.starting()方法主要用于获取SpringApplication实例初始化过程中 初始化的SpringApplicationRunListener监听器并运行。
2、根据SpringApplicationRunListeners以及参数来准备环境
this.prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments)方法主要用于对项目运行环境进行预设值,同时通过this.configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment)方法排除一些不需要的运行环境。
3、创建Spring容器
根据webApplicationType进行判断,确定容器类型,如果该类型为SERVLET类型,会通过反射加载对应的字节码,也就是AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext,接着使用之前初始化设置的context(应用上下文环境)、environment(项目运行环境)、listeners(运行监听器)、applicationArguments(项目参数)和 printedBanner(项目图标信息)进行上下文的组装配置,并刷新配置。
4、Spring容器前置处理
这一步主要是在容器刷新之前的准备动作。设置容器环境,包括各种变量等等,其中包含一个非常关键的操作:将启动类注入容器,为后续开启自动化配置奠定基础。
5、刷新容器
开启刷新Spring容器,通过refresh方法对整个IOC容器的初始化(包括bean资源的定位、解析、注册等等),同时向JVM运行时注册一个关机钩子(shutdown hook),在JVM关机时会关闭这个上下文,除非当时它已经关闭。
6、Spring容器后置处理
扩展接口,设计模式中的模板方法,默认为空实现。如果有自定义需求,可以重写该方法。比如打印一些启动结束log,或者一些其他的后置处理。
7、发出结束执行的事件
获取EventPublishingRunListener监听器,并执行其started方法,并且将创建的Spring容器传送进去,创建一个ApplicationStartedEvent事件,并执行ConfigurableApplicationContext的publishEvent方法,也就是说这里是在Spring容器中发布事件,并不是在SpringApplication中发布事件,和前面的starting是不同的,前面的starting是直接向SpringApplication中的监听器发布启动事件。
8、执行Runners
用于调用项目中自定义的执行器XxxRunner类,使得在项目启动完成后立即执行一些特定程序。其中,SpringBoot提供的执行器接口有ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner两种,在使用时只需要自定义一个执行器类实现其中一个接口并重写对应的run()方法接口,然后SpringBoot项目启动后立即执行这些特定程序。
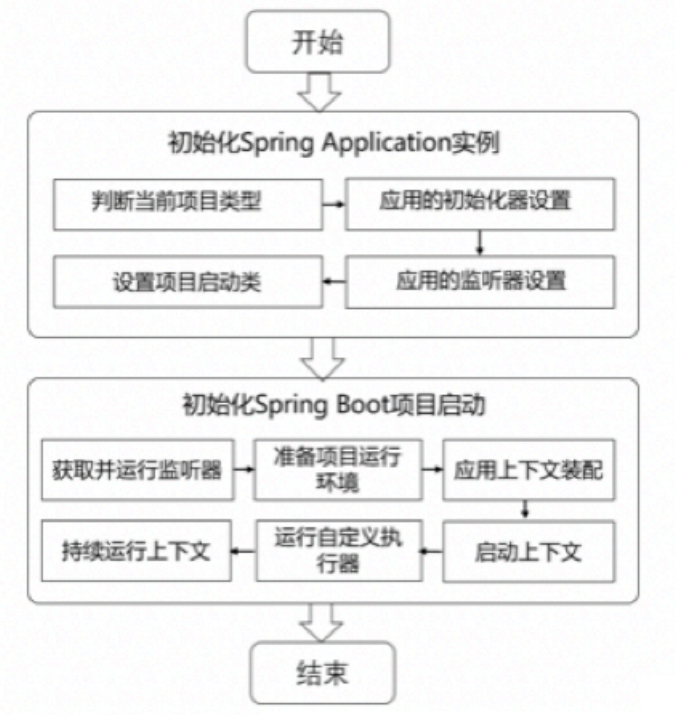
下图是SpringBoot执行的流程图,通过下图,可以直观地了解SpringBoot的整体执行流程和主要启动阶段:
出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/blayn/
版权:本文版权归作者和博客园共有
转载:欢迎转载,但未经作者同意,必须保留此段声明;必须在文章中给出原文连接;否则必究法律责任







【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 探究高空视频全景AR技术的实现原理
· 理解Rust引用及其生命周期标识(上)
· DeepSeek 开源周回顾「GitHub 热点速览」
· 物流快递公司核心技术能力-地址解析分单基础技术分享
· .NET 10首个预览版发布:重大改进与新特性概览!
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 单线程的Redis速度为什么快?