刷刷刷 Day 14| 二叉树的遍历
144. 二叉树的前序遍历
LeetCode题目要求
给你二叉树的根节点 root ,返回它节点值的 前序 遍历。
示例

输入:root = [1,null,2,3] 输出:[1,2,3]
解题思路
最重要的要明白什么是二叉树的前序遍历:即从中间节点开始到左节点再到右节点的遍历过程,可简称为【中左右】遍历
如下图标识的遍历过程,在过程中下面指向的 null ,就是说明到子节点了,如果这是我们知道左节点到了子节点,那就要从右节点开始。

上代码,递归实现
class Solution { public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) { // 前序遍历即:从中间节点开始到左节点再到右节点的遍历过程,可简称为【中左右】遍历 // 用 List 来存储遍历的结果 List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(); preorder(root, res); return res; } public void preorder(TreeNode curr, List<Integer> res) { // 1、先拿中节点, // 2、判断左节点,如果左不为空,那么又作为新的中节点,重复 1、2,直到节点为空 // 3、判断右节点,如果右不为空,那么又作为新的中节点,重复 1、3,直到节点为空 if (curr == null) { return; } res.add(curr.val); preorder(curr.left, res); preorder(curr.right, res); } }
上代码,迭代实现
class Solution { public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) { List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(); if (root == null) { return res; } // 通过栈来实现,将二叉树的以 中右左的顺序 压入栈中,出栈时的顺序才是中左右 Deque<TreeNode> stack = new ArrayDeque<>(); stack.push(root); // 开始遍历栈,如果栈不为空,就先出栈 while (!stack.isEmpty()) { TreeNode curr = stack.pop(); res.add(curr.val); if (curr.right != null) stack.push(curr.right); if (curr.left != null) stack.push(curr.left); } return res; } }
145. 二叉树的后序遍历
LeetCode题目要求
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值的 后序遍历 。
示例

输入:root = [1,null,2,3] 输出:[3,2,1]
解题思路
最重要的要明白什么是二叉树的后序遍历:即从左节点开始到右节点再到中间节点的遍历过程,可简称为【左右中】遍历
如下图标识的遍历过程,总是从最左节点开始的。
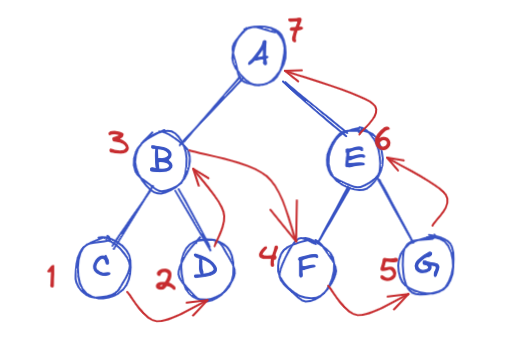
上代码,递归实现
class Solution { public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) { // 存储结果 List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(); postorder(root, res); return res; } public void postorder(TreeNode node, List<Integer> res) { if (node == null) { return; } // 从左节点开始递归,这里从root 开始一直到最左子节点,才能继续找右节点,但是右节点为空,那么就把当前左节点的值放入结果 postorder(node.left, res); // 从右节点开始递归 postorder(node.right, res); // 将当前节点值放入结果集 res.add(node.val); } }
上代码,迭代实现
class Solution { public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) { List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(); if (root == null) { return res; } Deque<TreeNode> stack = new ArrayDeque<>(); // 后序遍历: 左右中, 前序遍历的顺序是 中左右, // 那么可以在入栈时调整顺序变成 中左右,出栈顺序为 中右左, 然后再反转结果就是我们需要的 stack.push(root); while (!stack.isEmpty()) { TreeNode node = stack.pop(); res.add(node.val); if (node.left != null) stack.push(node.left); if (node.right != null) stack.push(node.right); } Collections.reverse(res); return res; } }
94. 二叉树的中序遍历
LeetCode题目要求
给定一个二叉树的根节点 root ,返回 它的 中序 遍历 。
示例

输入:root = [1,null,2,3] 输出:[1,3,2]
解题思路
最重要的要明白什么是二叉树的中序遍历:即从左节点开始到中间节点再到右节点的遍历过程,可简称为【左中右】遍历
如下图标识的遍历过程,总是从最左节点开始的。

上代码,递归实现
class Solution { public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) { List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(); inorder(root, res); return res; } public void inorder(TreeNode node, List<Integer> res) { if (node == null) { return; } // 左中右 inorder(node.left, res); res.add(node.val); inorder(node.right, res); } }
上代码,迭代实现
class Solution { public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) { List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(); if (root == null) { return res; } Deque<TreeNode> stack = new ArrayDeque<>(); TreeNode node = root; while (node != null || !stack.isEmpty()) { // 中序遍历的为 左中右,使用栈时,入栈时,从根一直遍历左节点,都入栈 if (node != null) { stack.push(node); node = node.left; } else { // 当上面的操作左节点都入栈后,此时栈不为空,开始出栈操作,就是左节点出栈并将其值入结果集,同时取右节点 node = stack.pop(); res.add(node.val); node = node.right; } } return res; } }
重难点
对于递归遍历来说,遍历二叉树代码写起来比较容易,但是递归的过程需要重点理解下。
而对于迭代法来说,弄明白入栈与出栈的过程就基本可以明白,可以通过模拟过程来理解,而中序遍历与前、后序遍历不太一样,需要着重理解了。
附:学习资料链接
分类:
算法





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 全程不用写代码,我用AI程序员写了一个飞机大战
· MongoDB 8.0这个新功能碉堡了,比商业数据库还牛
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· DeepSeek 开源周回顾「GitHub 热点速览」
· 白话解读 Dapr 1.15:你的「微服务管家」又秀新绝活了