nchu-software-oop-2022第6-8次作业(电信计费)总结
一、前言
最后三次大作业主要围绕电信计费相关计算展开。难度和之前点线形系列相比降了好几个档次,即便还是有难调的地方。考点仍然是类、继承与多态,还有java容器的使用。作为java巨型作业,这几次虽然在计算量上降了难度,但在细节上还是层层加码滴。三道电信计费大题都给了类图作为参考,很明显,照着类图写还是能方便很多的,但不知世事险恶的我第一题还是用自己的方法写的,那几个被半天调不出来的代码搞崩心态的夜晚简直劝退。好在最后还是圆满完成了作业。除了电信计费还有其它一些简单题,分分钟写完的那种,本次博客还是浅浅提一下。好,话不多说,咱直接开始吧!
二、设计与分析
电信计费部分
题目
实现一个简单的电信计费程序:
假设南昌市电信分公司针对市内座机用户采用的计费方式:
月租20元,接电话免费,市内拨打电话0.1元/分钟,省内长途0.3元/分钟,国内长途拨打0.6元/分钟。不足一分钟按一分钟计。
南昌市的区号:0791,江西省内各地市区号包括:0790~0799以及0701。
输入格式:
输入信息包括两种类型
1、逐行输入南昌市用户开户的信息,每行一个用户,
格式:u-号码 计费类型 (计费类型包括:0-座机 1-手机实时计费 2-手机A套餐)
例如:u-079186300001 0
座机号码除区号外由是7-8位数字组成。
本题只考虑计费类型0-座机计费,电信系列2、3题会逐步增加计费类型。
2、逐行输入本月某些用户的通讯信息,通讯信息格式:
座机呼叫座机:t-主叫号码 接听号码 起始时间 结束时间
t-079186330022 058686330022 2022.1.3 10:00:25 2022.1.3 10:05:11
以上四项内容之间以一个英文空格分隔,
时间必须符合"yyyy.MM.dd HH:mm:ss"格式。提示:使用SimpleDateFormat类。
以上两类信息,先输入所有开户信息,再输入所有通讯信息,最后一行以“end”结束。
注意:
本题非法输入只做格式非法的判断,不做内容是否合理的判断(时间除外,否则无法计算),比如:
1、输入的所有通讯信息均认为是同一个月的通讯信息,不做日期是否在同一个月还是多个月的判定,直接将通讯费用累加,因此月租只计算一次。
2、记录中如果同一电话号码的多条通话记录时间出现重合,这种情况也不做判断,直接 计算每条记录的费用并累加。
3、用户区号不为南昌市的区号也作为正常用户处理。
输出格式:
根据输入的详细通讯信息,计算所有已开户的用户的当月费用(精确到小数点后2位,
单位元)。假设每个用户初始余额是100元。
每条通讯信息单独计费后累加,不是将所有时间累计后统一计费。
格式:号码+英文空格符+总的话费+英文空格符+余额
每个用户一行,用户之间按号码字符从小到大排序。
错误处理:
输入数据中出现的不符合格式要求的行一律忽略。
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
u-079186300001 0
t-079186300001 058686330022 2022.1.3 10:00:25 2022.1.3 10:05:25
end
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
079186300001 3.0 77.0
电信计费系列第一题,自己的方法写的
先把类图祭上
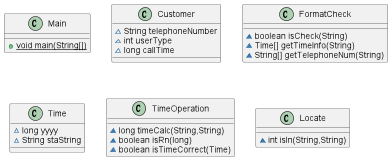
没有任何继承关系,当时还没这个概念。
Customer(客户类):原本想用来存客户信息,可惜后来没有用到
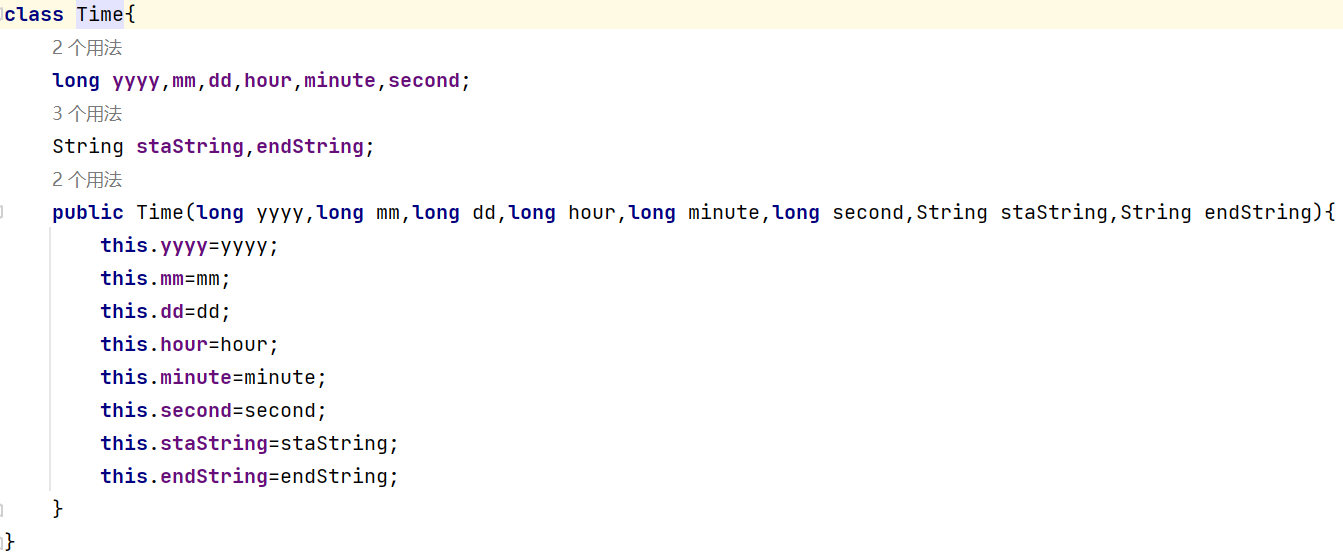
Time(时间类):储存时间信息,不会用date类型变量时想出的笨方法
TimeOperation(时间格式判断、计算类):
时间计算:研究了老久的计算方法,把所有时间转化为毫秒对就这么直接,然后后面减去前面。

时间判断就不贴了,无非是一天有几个小时、一个月有几天这样的判断。
Locate(地点判断类):按题意写就行

FormatCheck类:主要是输入格式正则表达式的格式判断。
![]()
剩下就没啥了。。
sourceMonitor分析:
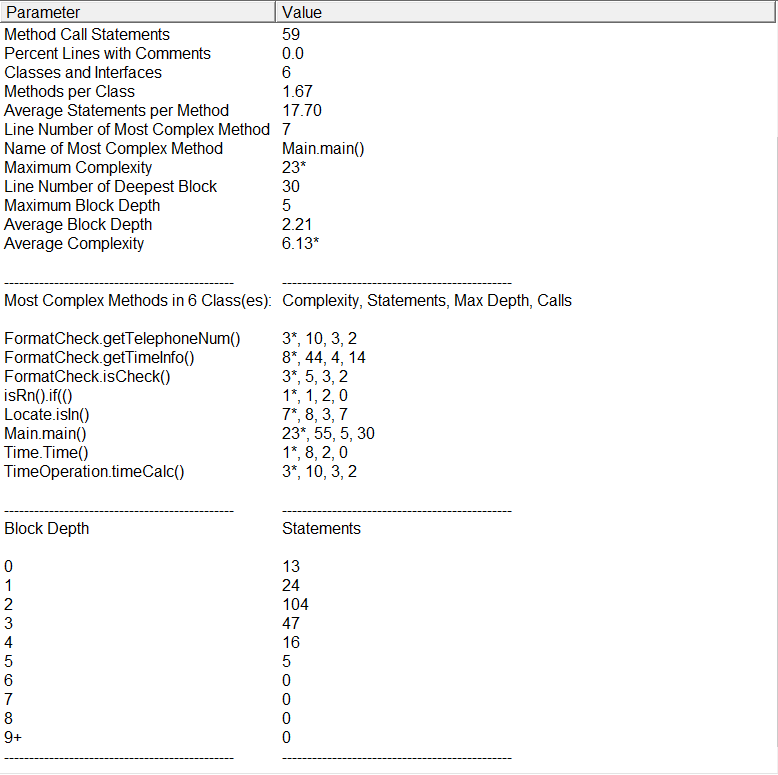

复杂度果然有亿点高,,深度还行。
代码:

import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.text.*; import java.util.*; import java.lang.*; import java.util.regex.*; public class Main{ public static void main(String[] args){ Scanner bjsn = new Scanner(System.in); FormatCheck formatCheck = new FormatCheck(); Customer customer = new Customer(); TimeOperation timeOperation = new TimeOperation(); HashMap<String,Double>map = new HashMap<>(); LinkedHashSet<String>set = new LinkedHashSet<>(); Locate locate = new Locate(); String[] userNote = new String[102]; String[] callNote = new String[102]; String s; int loc = 0; while(true){ s = bjsn.nextLine(); if(s.equals("end")){ break; } if(s.length()==0||!formatCheck.isCheck(s)){ continue; } if(s.matches("u-\\d{10,12} 0")){ String t=""; for(int i=2;s.charAt(i)!=' ';i++){ t+=s.charAt(i); } if(!map.containsKey(t)){ set.add(t); map.put(t,0.0); } } else{ callNote[loc++] = s; } } int ans = 0; while(ans < loc){ Time[] tt = formatCheck.getTimeInfo(callNote[ans]); String[] ss = formatCheck.getTelephoneNum(callNote[ans]); Time t1 = tt[0]; Time t2 = tt[1]; if(!timeOperation.isTimeCorrect(t1)||!timeOperation.isTimeCorrect(t2)||ss[0].length()<10||ss[0].length()>12||ss[1].length()<10||ss[1].length()>12){ ans++; continue; } String sta = tt[0].staString+" "+tt[0].endString; String end = tt[1].staString+" "+tt[1].endString; long t = timeOperation.timeCalc(sta,end); if(!map.containsKey(ss[0])||t<=0){ ans++; continue; } double tm=map.get(ss[0]); if(locate.isIn(ss[0],ss[1])==1){ tm+=0.1*t; } else if(locate.isIn(ss[0],ss[1])==0){ tm+=0.3*t; } else{ tm+=0.6*t; } map.put(ss[0],tm); ans++; } String[] res = new String[set.size()]; int pos=0; for(String tt:set){ res[pos++]=tt; } Arrays.sort(res); for(int i = 0; i < set.size() ;i++){ double tip = map.get(res[i]); System.out.print(res[i]+" "); System.out.println((float)tip+" "+(float)Math.max(80 - tip,0)); } } } class Customer{ String telephoneNumber; int userType; long callTime; } class FormatCheck{ boolean isCheck(String s){ String su = "u-\\d{11,12} 0"; String st="t-\\d{11,12} \\d{10,12} \\d{4}.\\d{1,2}.\\d{1,2} \\d{2}:\\d{2}:\\d{2} \\d{4}.\\d{1,2}.\\d{1,2} \\d{2}:\\d{2}:\\d{2}"; if(s.matches(su)||s.matches(st)){ return true; } return false; } Time[] getTimeInfo(String s){ Time[] res = new Time[2]; List<String>list = new ArrayList<>(); String regex = "\\d{4}.\\d{1,2}.\\d{1,2} \\d{2}:\\d{2}:\\d{2}"; Pattern p = Pattern.compile(regex); Matcher matcher = p.matcher(s); while (matcher.find()) { list.add(matcher.group(0)); } String s1 = list.get(0); String s2 = list.get(1); String ss1[] = s1.split(" "); String ss2[] = s2.split(" "); String str1[] = null; String str2[] = null; String str3[] = null; String str4[] = null; int t=0; for(String Str:ss1){ t++; if(t==1){ str1 = Str.split("\\."); } else{ str2 = Str.split(":"); } } t=0; for(String Str:ss2){ t++; if(t==1){ str3 = Str.split("\\."); } else{ str4 = Str.split(":"); } } long yyyy1=Long.parseLong(str1[0]); long mm1=Long.parseLong(str1[1]); long dd1=Long.parseLong(str1[2]); long hour1=Long.parseLong(str2[0]); long minute1=Long.parseLong(str2[1]); long second1=Long.parseLong(str2[2]); long yyyy2=Long.parseLong(str3[0]); long mm2=Long.parseLong(str3[1]); long dd2=Long.parseLong(str3[2]); long hour2=Long.parseLong(str4[0]); long minute2=Long.parseLong(str4[1]); long second2=Long.parseLong(str4[2]); res[0] = new Time(yyyy1,mm1,dd1,hour1,minute1,second1,ss1[0],ss1[1]); res[1] = new Time(yyyy2,mm2,dd2,hour2,minute2,second2,ss2[0],ss2[1]); return res; } String[] getTelephoneNum(String s){ String[] res = new String[2]; res[0]=""; res[1]=""; int i=2; for(i=2;s.charAt(i)!=' ';i++){ res[0]+=s.charAt(i); } i++; for(;s.charAt(i)!=' ';i++){ res[1]+=s.charAt(i); } return res; } } class Time{ long yyyy,mm,dd,hour,minute,second; String staString,endString; public Time(long yyyy,long mm,long dd,long hour,long minute,long second,String staString,String endString){ this.yyyy=yyyy; this.mm=mm; this.dd=dd; this.hour=hour; this.minute=minute; this.second=second; this.staString=staString; this.endString=endString; } } class TimeOperation{ long timeCalc(String str1,String str2){ if(str1.charAt(5)=='0'||str2.charAt(5)=='0'){ return -1; } SimpleDateFormat pattern = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy.MM.dd HH:mm:ss"); long nd=1000*60*60*24; long nh=1000*60*60; long nm=1000*60; long ns=1000; long t=0; try{ t=pattern.parse(str2).getTime()-pattern.parse(str1).getTime(); }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } if(t<=0){ return -1; } long dayNum=t/nd; long hourNum=t%nd/nh; long minuteNum=t%nd%nh/nm; long secondNum=t%nd%nh%nm/ns; long res=secondNum+minuteNum*60+hourNum*60*60+dayNum*60*60*24; long cnt=(res+59)/60; return cnt; } boolean isRn(long y){ if((y%4==0&&y%100!=0)||y%400==0){ return true; } return false; } boolean isTimeCorrect(Time startTime){ if(startTime.mm<1||startTime.mm>12||startTime.dd<1||startTime.hour<0||startTime.hour>23||startTime.minute<0||startTime.minute>59||startTime.second<0||startTime.second>59){ return false; } switch ((int)startTime.mm) { case 1: case 3: case 5: case 7: case 8: case 10: case 12: if (startTime.dd > 31) return false; break; case 2: if (isRn(startTime.yyyy)) { if (startTime.dd > 29) { return false; } } else { if (startTime.dd > 28) { return false; } } break; case 4: case 6: case 9: case 11: if(startTime.dd>30){ return false; } break; default: break; } return true; } } class Locate{ int isIn(String s1,String s2){ String ss1=s1.substring(0,4); String ss2=s2.substring(0,4); if(ss1.equals(ss2)){ return 1; } else if((ss2.substring(0,3).equals("079")||ss2.equals("0701"))&&(ss1.substring(0,3).equals("079")||ss1.equals("0701"))){ return 0; } else{ return -1; } } }
电信计费系列2-手机+座机计费
题面和上一题高度重合,重复的座机计费部分就不贴了。
针对手机用户采用实时计费方式:
月租15元,市内省内接电话均免费,市内拨打市内电话0.1元/分钟,市内拨打省内电话0.2元/分钟,市内拨打省外电话0.3元/分钟,省内漫游打电话0.3元/分钟,省外漫游接听0.3元/分钟,省外漫游拨打0.6元/分钟;
注:被叫电话属于市内、省内还是国内由被叫电话的接听地点区号决定,比如以下案例中,南昌市手机用户13307912264在区号为020的广州接听了电话,主叫号码应被计算为拨打了一个省外长途,同时,手机用户13307912264也要被计算省外接听漫游费:
u-13307912264 1
t-079186330022 13307912264 020 2022.1.3 10:00:25 2022.1.3 10:05:11
建议类图:
参见图1、2、3:
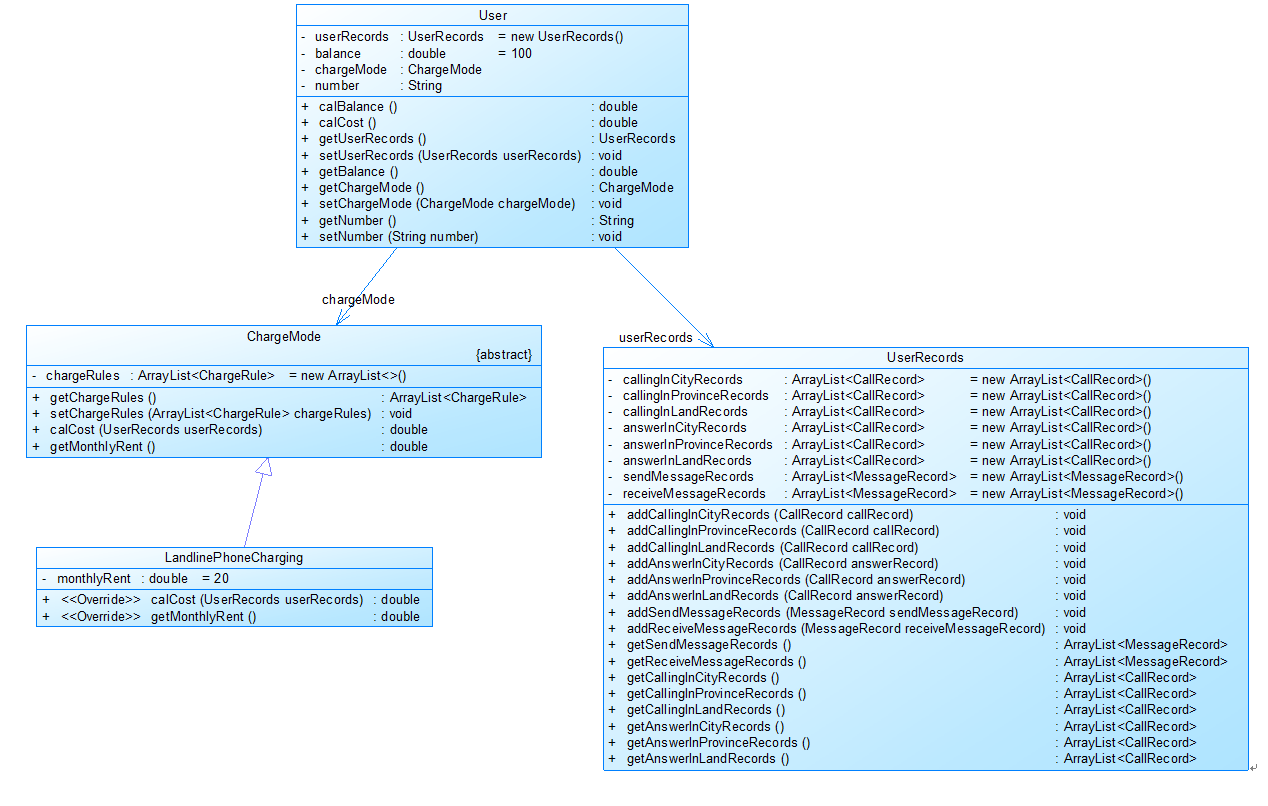
图1
图1中User是用户类,包括属性:
userRecords (用户记录)、balance(余额)、chargeMode(计费方式)、number(号码)。
ChargeMode是计费方式的抽象类:
chargeRules是计费方式所包含的各种计费规则的集合,ChargeRule类的定义见图3。
getMonthlyRent()方法用于返回月租(monthlyRent)。
UserRecords是用户记录类,保存用户各种通话、短信的记录,
各种计费规则将使用其中的部分或者全部记录。
其属性从上到下依次是:
市内拨打电话、省内(不含市内)拨打电话、省外拨打电话、
市内接听电话、省内(不含市内)接听电话、省外接听电话的记录
以及发送短信、接收短信的记录。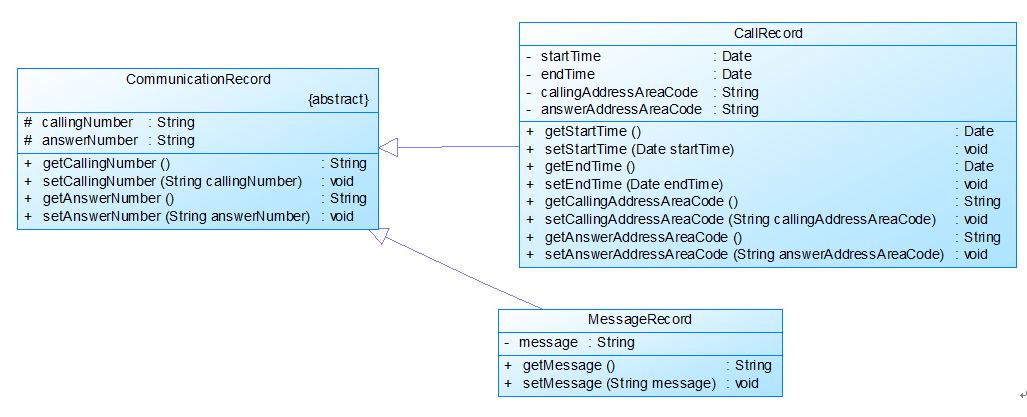
图2
图2中CommunicationRecord是抽象的通讯记录类:
包含callingNumber拨打号码、answerNumber接听号码两个属性。
CallRecord(通话记录)、MessageRecord(短信记录)是它的子类。CallRecord(通话记录类)包含属性:
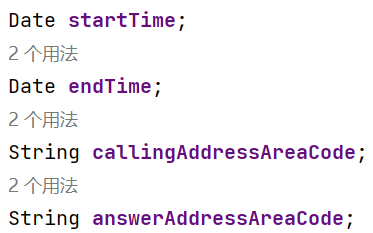
通话的起始、结束时间以及
拨号地点的区号(callingAddressAreaCode)、接听地点的区号(answerAddressAreaCode)。
区号用于记录在哪个地点拨打和接听的电话。座机无法移动,就是本机区号,如果是手机号,则会有差异。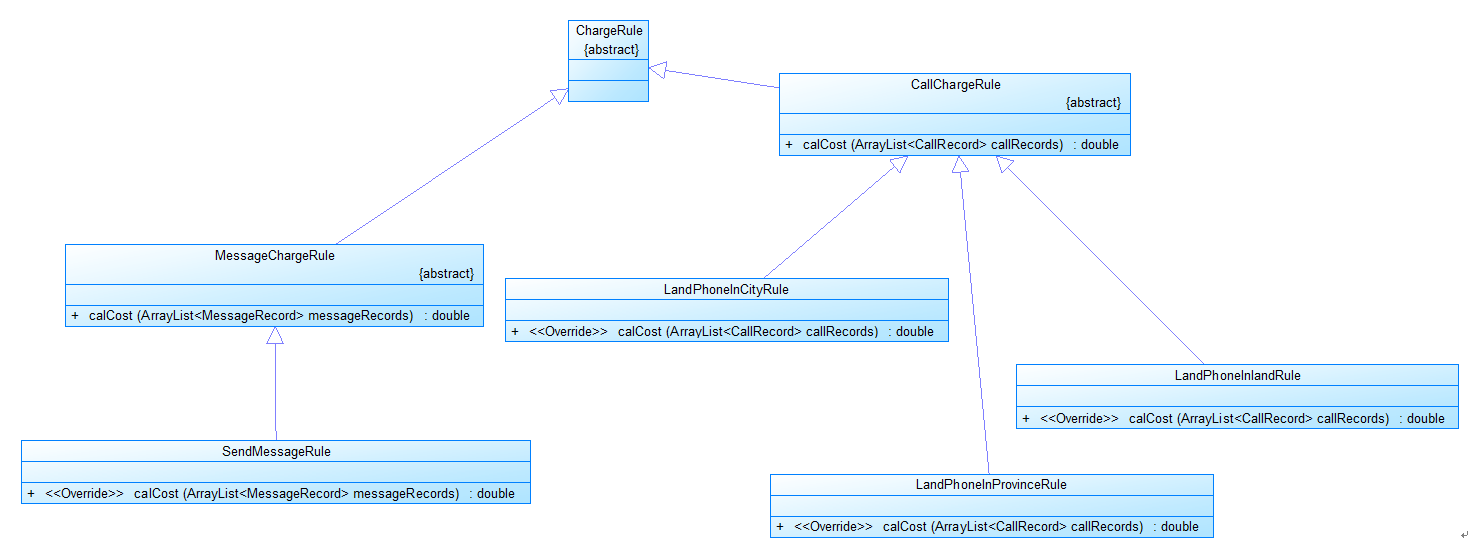
图3
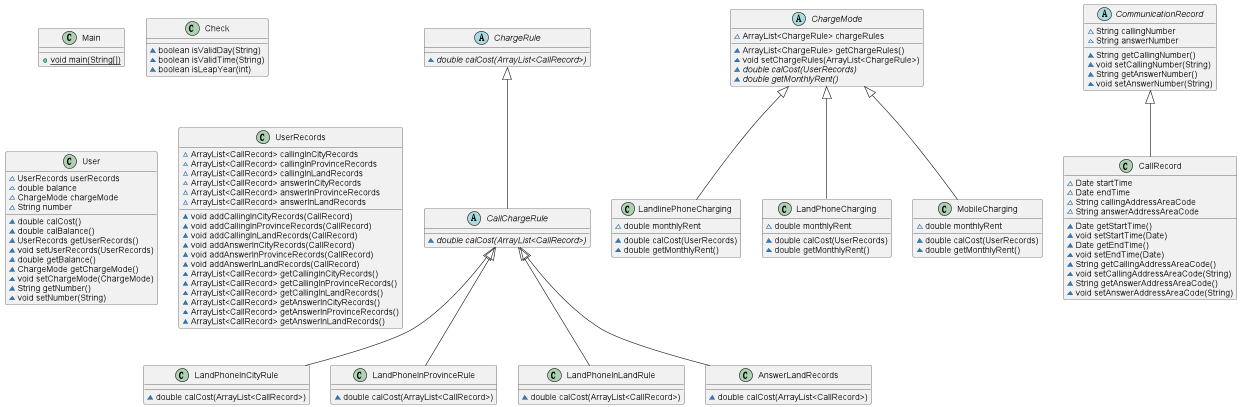
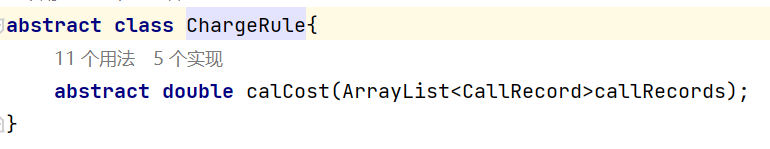
图3是计费规则的相关类,这些类的核心方法是:
calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords)。
该方法针根据输入参数callRecords中的所有记录计算某用户的某一项费用;如市话费。
输入参数callRecords的约束条件:必须是某一个用户的符合计费规则要求的所有记录。
SendMessageRule是发送短信的计费规则类,用于计算发送短信的费用。
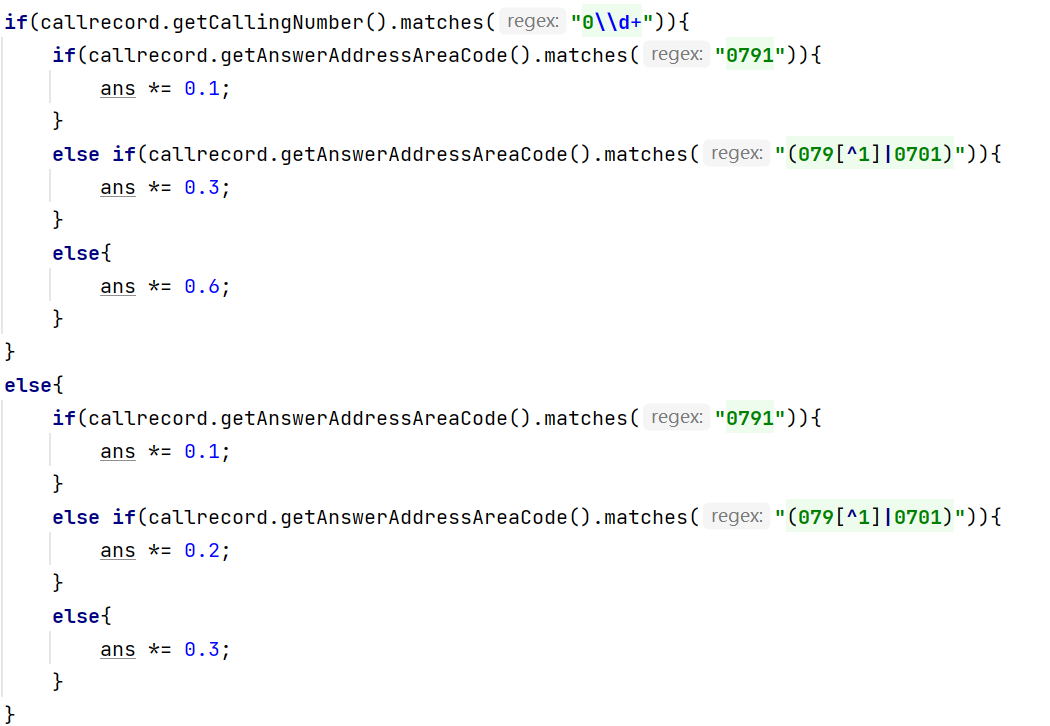
LandPhoneInCityRule、LandPhoneInProvinceRule、LandPhoneInLandRule三个类分别是座机拨打市内、省内、省外电话的计费规则类,用于实现这三种情况的费用计算。 (提示:可以从UserRecords类中获取各种类型的callRecords)。
注意:以上图中所定义的类不是限定要求,根据实际需要自行补充或修改。
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
u-13811111111 1
t-13811111111 0791 13811111110 020 2022.1.3 08:00:00 2022.1.3 08:09:20
end输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
13811111111 3.0 82.0先把类图祭上:
题目中类图一给,接下来就是看图写话。
Check类:判断输入是否符合要求,isValidDay判断日期,isVaildTime判断时间,isLeapYear判断是否闰年。
User类:用户信息类:主要包含如下信息:

userRecords存用户消费记录,chargeMode指消费模式,number为用户电话号码。函数部分主要为几个变量的修改和获取。
UserRecords类:用户消费记录,用arraylist容器储存通话信息。同样,函数部分修改或获取变量信息。

CommunicationRecord:通话记录类,callRecord以及下一题的sendMessageRecord继承。
CallRecord类:用于获取通话时间、通话双方所在位置。
ChargeRule类:缴费方式
CallChargeRule类:继承chargeRule类,指明缴费方案,计算由其继承者实现。
时间计算:
![]()
费用计算:
ChargeMode类:缴费形式,分座机缴费、手机缴费,以及市内、省内、国内计费。

正则表达式判断:
String patternStaStr = "u-0\\d{9,11}\\s0";
String patternStStr = "u-1\\d{10}\\s[12]";
String phoneToPhone = "t-0\\d{9,11}\\s0\\d{9,11}(\\s\\d{4}[.]([^0]|10|11|12)[.]\\d{1,2}\\s([01]\\d|20|21|22|23):[0-5]\\d:[0-5]\\d){2}";
String phoneToMobile = "t-0\\d{9,11}\\s1\\d{10}\\s0\\d{2,3}(\\s\\d{4}[.]([^0]|10|11|12)[.]\\d{1,2}\\s([01]\\d|20|21|22|23):[0-5]\\d:[0-5]\\d){2}";
String mobileToPhone = "t-1\\d{10}\\s0\\d{2,3}\\s0\\d{9,11}(\\s\\d{4}[.]([^0]|10|11|12)[.]\\d{1,2}\\s([01]\\d|20|21|22|23):[0-5]\\d:[0-5]\\d){2}";
String mobileToMobile = "t-1\\d{10}\\s0\\d{2,3}\\s1\\d{10}\\s0\\d{2,3}(\\s\\d{4}[.]([^0]|10|11|12)[.]\\d{1,2}\\s([01]\\d|20|21|22|23):[0-5]\\d:[0-5]\\d){2}";
String divideStr = "-|\\s";
String inProvince = "(079\\d|0701)";
sourceMonitor分析:


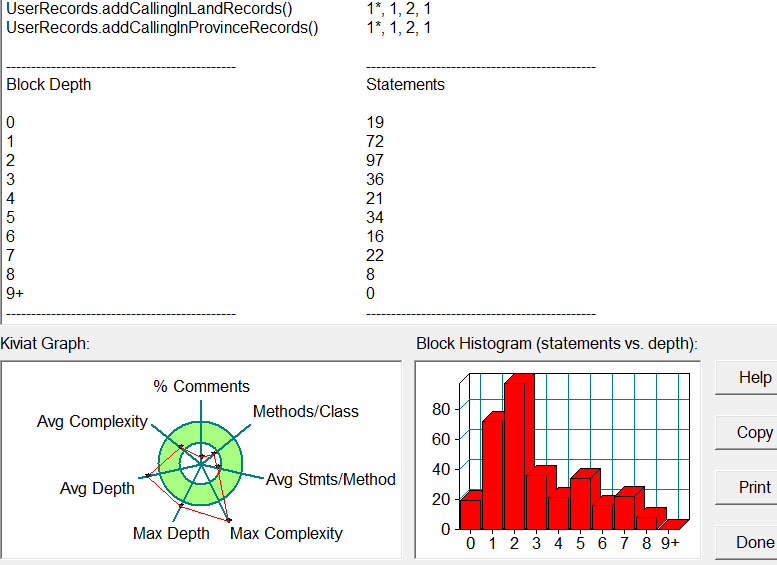
兄啊怎么最大复杂度这么高平均复杂度还是降了不少(喜)。
代码:

import java.lang.*; import java.text.*; import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args){ Scanner bjsn = new Scanner(System.in); Check check = new Check(); // ArrayList<User>user = new ArrayList<>(); Map<String,User>mp = new TreeMap<>(); SimpleDateFormat patternDateStr = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy.MM.dd HH:mm:ss"); String patternStaStr = "u-0\\d{9,11}\\s0"; String patternStStr = "u-1\\d{10}\\s[12]"; String phoneToPhone = "t-0\\d{9,11}\\s0\\d{9,11}(\\s\\d{4}[.]([^0]|10|11|12)[.]\\d{1,2}\\s([01]\\d|20|21|22|23):[0-5]\\d:[0-5]\\d){2}"; String phoneToMobile = "t-0\\d{9,11}\\s1\\d{10}\\s0\\d{2,3}(\\s\\d{4}[.]([^0]|10|11|12)[.]\\d{1,2}\\s([01]\\d|20|21|22|23):[0-5]\\d:[0-5]\\d){2}"; String mobileToPhone = "t-1\\d{10}\\s0\\d{2,3}\\s0\\d{9,11}(\\s\\d{4}[.]([^0]|10|11|12)[.]\\d{1,2}\\s([01]\\d|20|21|22|23):[0-5]\\d:[0-5]\\d){2}"; String mobileToMobile = "t-1\\d{10}\\s0\\d{2,3}\\s1\\d{10}\\s0\\d{2,3}(\\s\\d{4}[.]([^0]|10|11|12)[.]\\d{1,2}\\s([01]\\d|20|21|22|23):[0-5]\\d:[0-5]\\d){2}"; String divideStr = "-|\\s"; String inProvince = "(079\\d|0701)"; Date d1 = new Date(),d2 = new Date(); String info; while(true){ info = bjsn.nextLine(); if(info.equals("end")){ break; } if(info.matches(patternStaStr) | info.matches(patternStStr)){ String[] userInfo = info.split(divideStr); User user1 = new User(userInfo[2],userInfo[1]); // user.add(user1); mp.put(userInfo[1],user1); } else if(info.matches(phoneToPhone)){ String[] userInfo = info.split(divideStr); if(check.isValidDay(userInfo[3]) && check.isValidDay(userInfo[5]) && check.isValidTime(userInfo[4]) && check.isValidTime(userInfo[6])){ try { d1 = patternDateStr.parse(userInfo[3] + " " + userInfo[4]); d2 = patternDateStr.parse(userInfo[5] + " " + userInfo[6]); }catch (ParseException e){ } // for(int i=3;i<7;i++){ // System.out.println(userInfo[i]); // } // System.out.println(d1 + " " + d2); for(User tmp : mp.values()){ if(tmp.getNumber().equals(userInfo[1])){ CallRecord callRecord = new CallRecord(); callRecord.setStartTime(d1); callRecord.setEndTime(d2); callRecord.setCallingNumber(userInfo[1]); callRecord.setAnswerAddressAreaCode(userInfo[2].substring(0,4)); tmp.getUserRecords().addCallingInCityRecords(callRecord); } } } } else if(info.matches(phoneToMobile)){ String[] userInfo = info.split(divideStr); if(check.isValidDay(userInfo[4]) && check.isValidDay(userInfo[6]) && check.isValidTime(userInfo[5]) && check.isValidTime(userInfo[7])){ try { d1 = patternDateStr.parse(userInfo[4] + " " + userInfo[5]); d2 = patternDateStr.parse(userInfo[6] + " " + userInfo[7]); }catch (ParseException e){ } CallRecord callRecord = new CallRecord(); callRecord.setStartTime(d1); callRecord.setEndTime(d2); callRecord.setCallingNumber(userInfo[1]); callRecord.setAnswerNumber(userInfo[2]); callRecord.setCallingAddressAreaCode("0791"); callRecord.setAnswerAddressAreaCode(userInfo[3]); for(User tmp : mp.values()) { if (tmp.getNumber().equals(userInfo[1])) { tmp.getUserRecords().addCallingInCityRecords(callRecord); } } for(User tmp : mp.values()){ if(tmp.getNumber().equals(userInfo[2])){ if(!userInfo[3].matches(inProvince)){ tmp.getUserRecords().addAnswerInLandRecords(callRecord); } } } } } else if(info.matches(mobileToPhone)){ String[] userInfo = info.split(divideStr); if(check.isValidDay(userInfo[4]) && check.isValidDay(userInfo[6]) && check.isValidTime(userInfo[5]) && check.isValidTime(userInfo[7])){ try { d1 = patternDateStr.parse(userInfo[4] + " " + userInfo[5]); d2 = patternDateStr.parse(userInfo[6] + " " + userInfo[7]); }catch (ParseException e){ } for(User tmp : mp.values()){ if(tmp.getNumber().equals(userInfo[1])){ CallRecord callRecord = new CallRecord(); callRecord.setStartTime(d1); callRecord.setEndTime(d2); callRecord.setCallingNumber(userInfo[1]); callRecord.setAnswerNumber(userInfo[3]); callRecord.setCallingAddressAreaCode(userInfo[2]); callRecord.setAnswerAddressAreaCode(userInfo[3].substring(0,4)); if(userInfo[2].equals("0791")){ tmp.getUserRecords().addCallingInCityRecords(callRecord); } else if(userInfo[2].matches(inProvince)){ tmp.getUserRecords().addCallingInProvinceRecords(callRecord); } else{ tmp.getUserRecords().addCallingInLandRecords(callRecord); } } } } } else if(info.matches(mobileToMobile)){ // System.out.println("114514"); String[] userInfo = info.split(divideStr); if(check.isValidDay(userInfo[5]) && check.isValidDay(userInfo[7]) && check.isValidTime(userInfo[6]) && check.isValidTime(userInfo[8])){ try { d1 = patternDateStr.parse(userInfo[5] + " " + userInfo[6]); d2 = patternDateStr.parse(userInfo[7] + " " + userInfo[8]); }catch (ParseException e){ } // System.out.println(userInfo[5] + " " + userInfo[6] + " " + userInfo[7] + " " + userInfo[8]); // System.out.println(d1 + " " + d2); CallRecord callRecord = new CallRecord(); callRecord.setStartTime(d1); callRecord.setEndTime(d2); callRecord.setCallingNumber(userInfo[1]); callRecord.setAnswerNumber(userInfo[3]); callRecord.setCallingAddressAreaCode(userInfo[2]); callRecord.setAnswerAddressAreaCode(userInfo[4]); for(User tmp : mp.values()){ if(tmp.getNumber().equals(userInfo[1])){ if(userInfo[2].equals("0791")){ tmp.getUserRecords().addCallingInCityRecords(callRecord); } else if(userInfo[2].length() == 4 && userInfo[2].matches(inProvince)){ tmp.getUserRecords().addCallingInProvinceRecords(callRecord); } else{ tmp.getUserRecords().addCallingInLandRecords(callRecord); } } } for(User tmp : mp.values()){ if(tmp.getNumber().equals(userInfo[3])){ if(!userInfo[4].matches(inProvince)){ tmp.getUserRecords().addAnswerInLandRecords(callRecord); } } } } } } for(User tmp : mp.values()){ System.out.println(tmp.getNumber() + " " + (float)tmp.calCost() + " " + (float)tmp.calBalance()); } } } class Check{ boolean isValidDay(String s){ String[] temp = s.split("\\."); int yyyy = Integer.parseInt(temp[0]); int mm = Integer.parseInt(temp[1]); int dd = Integer.parseInt(temp[2]); if(mm < 1 || mm > 12 || dd < 1){ return false; } switch (mm){ case 1: case 3: case 5: case 7: case 8: case 10: case 12:if(dd > 31){ return false; } break; case 4: case 6: case 9: case 11:if(dd > 30){ return false; } break; case 2:if(isLeapYear(yyyy)){ if(dd > 29){ return false; } } else{ if(dd > 28){ return false; } } break; } return true; } boolean isValidTime(String s){ String[] temp = s.split(":"); int hh = Integer.parseInt(temp[0]); int mm = Integer.parseInt(temp[1]); int ss = Integer.parseInt(temp[2]); if(hh < 0 || hh > 23 || mm < 0 || mm > 59 || ss < 0 || ss > 59){ return false; } return true; } boolean isLeapYear(int yyyy){ if((yyyy % 4 == 0 && yyyy % 100 != 0) || yyyy % 400 == 0){ return true; } return false; } } class User{ UserRecords userRecords = new UserRecords(); double balance = 100; ChargeMode chargeMode; String number; public User(String t,String number){ this.number = number; if(t.equals("0")){ this.chargeMode = new LandlinePhoneCharging(); } else if(t.equals("1")){ this.chargeMode = new LandPhoneCharging(); } } double calCost(){ return chargeMode.calCost(userRecords); } double calBalance(){ return getBalance() - chargeMode.getMonthlyRent() - calCost(); } UserRecords getUserRecords(){ return userRecords; } void setUserRecords(UserRecords userRecords){ this.userRecords = userRecords; } double getBalance(){ return balance; } ChargeMode getChargeMode(){ return chargeMode; } void setChargeMode(ChargeMode chargeMode){ this.chargeMode = chargeMode; } String getNumber(){ return number; } void setNumber(String number){ this.number = number; } } abstract class ChargeRule{ abstract double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord>callRecords); } abstract class CallChargeRule extends ChargeRule{ abstract double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord>callRecords); } class LandPhoneInCityRule extends CallChargeRule{ @Override double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord>callRecords){ double cnt = 0; for(CallRecord callrecord : callRecords){ double ans = Math.ceil((callrecord.getEndTime().getTime() - callrecord.getStartTime().getTime()) / 60000.0); if(callrecord.getCallingNumber().matches("0\\d+")){ if(callrecord.getAnswerAddressAreaCode().matches("0791")){ ans *= 0.1; } else if(callrecord.getAnswerAddressAreaCode().matches("(079[^1]|0701)")){ ans *= 0.3; } else{ ans *= 0.6; } } else{ if(callrecord.getAnswerAddressAreaCode().matches("0791")){ ans *= 0.1; } else if(callrecord.getAnswerAddressAreaCode().matches("(079[^1]|0701)")){ ans *= 0.2; } else{ ans *= 0.3; } } cnt += ans; } return cnt; } } class LandPhoneInProvinceRule extends CallChargeRule{ double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord>callRecords){ double cnt = 0; for(CallRecord callrecord : callRecords){ double ans = Math.ceil((callrecord.getEndTime().getTime() - callrecord.getStartTime().getTime()) / 60000.0); cnt += ans; } return cnt * 0.3; } } class LandPhoneInLandRule extends CallChargeRule{ double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord>callRecords){ double cnt = 0; for(CallRecord callrecord : callRecords){ double d = Math.ceil((callrecord.getEndTime().getTime() - callrecord.getStartTime().getTime()) / 60000.0); cnt += d; } return cnt * 0.6; } } abstract class ChargeMode{ ArrayList<ChargeRule>chargeRules = new ArrayList<ChargeRule>(); public ChargeMode(){ chargeRules.add(new LandPhoneInCityRule()); chargeRules.add(new LandPhoneInProvinceRule()); chargeRules.add(new LandPhoneInLandRule()); chargeRules.add(new AnswerLandRecords()); } ArrayList<ChargeRule>getChargeRules(){ return chargeRules; } void setChargeRules(ArrayList<ChargeRule>chargeRules){ this.chargeRules = chargeRules; } abstract double calCost(UserRecords userRecords); abstract double getMonthlyRent(); } class LandlinePhoneCharging extends ChargeMode{ double monthlyRent = 20; public LandlinePhoneCharging(){ super(); // chargeRules.add(new LandPhoneInCityRule()); // chargeRules.add(new LandPhoneInProvinceRule()); // chargeRules.add(new LandPhoneInLandRule()); } double calCost(UserRecords userRecords){ double cnt = 0; cnt = getChargeRules().get(0).calCost(userRecords.getCallingInCityRecords()) + getChargeRules().get(1).calCost(userRecords.getCallingInProvinceRecords()) + getChargeRules().get(2).calCost(userRecords.getCallingInLandRecords()); return cnt; } double getMonthlyRent(){ return monthlyRent; } } class LandPhoneCharging extends ChargeMode{ double monthlyRent = 15; public LandPhoneCharging(){ super(); } double calCost(UserRecords userRecords){ double cnt = 0; cnt = getChargeRules().get(0).calCost(userRecords.getCallingInCityRecords()) + getChargeRules().get(1).calCost(userRecords.getCallingInProvinceRecords()) + getChargeRules().get(2).calCost(userRecords.getCallingInLandRecords()) + getChargeRules().get(3).calCost(userRecords.getAnswerInLandRecords()); return cnt; } double getMonthlyRent(){ return monthlyRent; } } class UserRecords{ ArrayList<CallRecord>callingInCityRecords = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList<CallRecord>callingInProvinceRecords = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList<CallRecord>callingInLandRecords = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList<CallRecord>answerInCityRecords = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList<CallRecord>answerInProvinceRecords = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList<CallRecord>answerInLandRecords = new ArrayList<>(); void addCallingInCityRecords(CallRecord callRecord){ callingInCityRecords.add(callRecord); } void addCallingInProvinceRecords(CallRecord callRecord){ callingInProvinceRecords.add(callRecord); } void addCallingInLandRecords(CallRecord callRecord){ callingInLandRecords.add(callRecord); } void addAnswerInCityRecords(CallRecord callRecord){ answerInCityRecords.add(callRecord); } void addAnswerInProvinceRecords(CallRecord callRecord){ answerInProvinceRecords.add(callRecord); } void addAnswerInLandRecords(CallRecord callRecord){ answerInLandRecords.add(callRecord); } ArrayList<CallRecord>getCallingInCityRecords(){ return callingInCityRecords; } ArrayList<CallRecord>getCallingInProvinceRecords(){ return callingInProvinceRecords; } ArrayList<CallRecord>getCallingInLandRecords(){ return callingInLandRecords; } ArrayList<CallRecord>getAnswerInCityRecords(){ return answerInCityRecords; } ArrayList<CallRecord>getAnswerInProvinceRecords(){ return answerInProvinceRecords; } ArrayList<CallRecord>getAnswerInLandRecords(){ return answerInLandRecords; } } abstract class CommunicationRecord{ String callingNumber; String answerNumber; String getCallingNumber(){ return callingNumber; } void setCallingNumber(String callingNumber){ this.callingNumber = callingNumber; } String getAnswerNumber(){ return answerNumber; } void setAnswerNumber(String answerNumber){ this.answerNumber = answerNumber; } } class CallRecord extends CommunicationRecord{ Date startTime; Date endTime; String callingAddressAreaCode; String answerAddressAreaCode; Date getStartTime(){ return startTime; } void setStartTime(Date startTime){ this.startTime = startTime; } Date getEndTime(){ return endTime; } void setEndTime(Date endTime){ this.endTime = endTime; } String getCallingAddressAreaCode(){ return callingAddressAreaCode; } void setCallingAddressAreaCode(String callingAddressAreaCode){ this.callingAddressAreaCode = callingAddressAreaCode; } String getAnswerAddressAreaCode(){ return answerAddressAreaCode; } void setAnswerAddressAreaCode(String answerAddressAreaCode){ this.answerAddressAreaCode = answerAddressAreaCode; } } class AnswerLandRecords extends CallChargeRule{ double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord>callRecords){ double cnt = 0; for(CallRecord tmp : callRecords){ double ans = Math.ceil((tmp.getEndTime().getTime() - tmp.getStartTime().getTime()) / 60000.0); cnt += ans; } return cnt * 0.3; } } class MobileCharging extends ChargeMode{ double monthlyRent = 15; public MobileCharging(){ super(); } double calCost(UserRecords userRecords){ return getChargeRules().get(0).calCost(userRecords.getCallingInCityRecords()) + getChargeRules().get(1).calCost(userRecords.getCallingInProvinceRecords()) + getChargeRules().get(2).calCost(userRecords.getCallingInLandRecords()) + getChargeRules().get(3).calCost(userRecords.getAnswerInLandRecords()); } double getMonthlyRent(){ return monthlyRent; } }
实现一个简单的电信计费程序,针对手机的短信采用如下计费方式:
1、接收短信免费,发送短信0.1元/条,超过3条0.2元/条,超过5条0.3元/条。
2、如果一次发送短信的字符数量超过10个,按每10个字符一条短信进行计算。
逐行输入本月某些用户的短信信息,短信的格式:
m-主叫号码,接收号码,短信内容 (短信内容只能由数字、字母、空格、英文逗号、英文句号组成)
m-18907910010 13305862264 welcome to jiangxi.
m-13305862264 18907910010 thank you.
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
u-18907910010 3
m-18907910010 13305862264 aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
end输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
18907910010 0.3 99.7

新加的MessageRecord类:存储信息内容。

MessageCharge类:获取短信缴费信息。
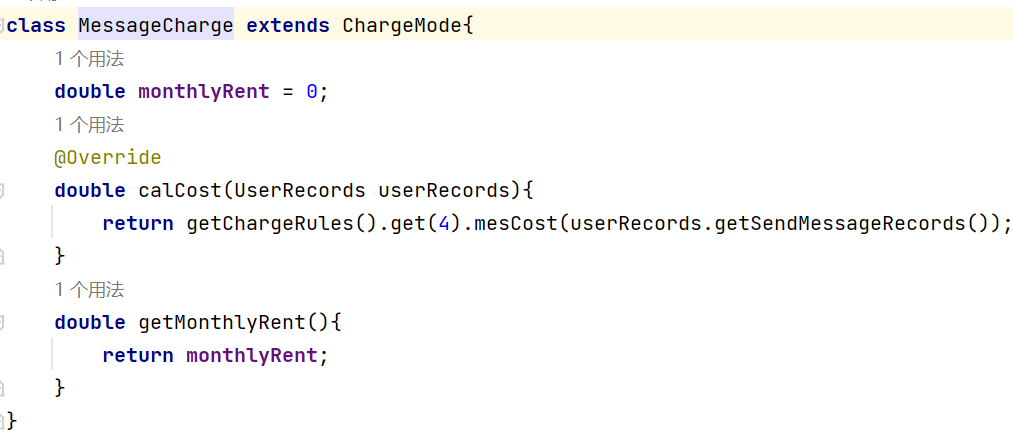
SendingMessageRule类:继承CommunicationRecord类, 用于计算费用。
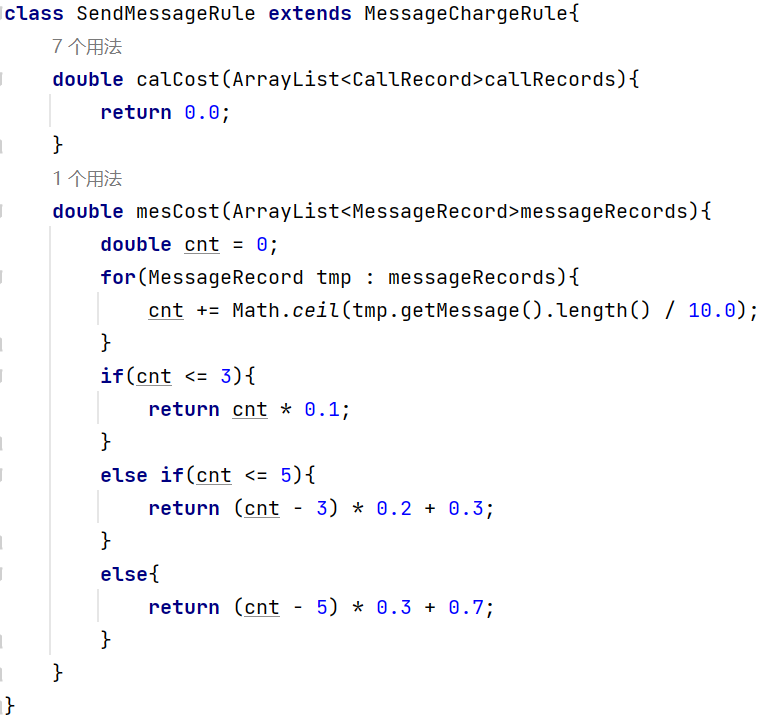
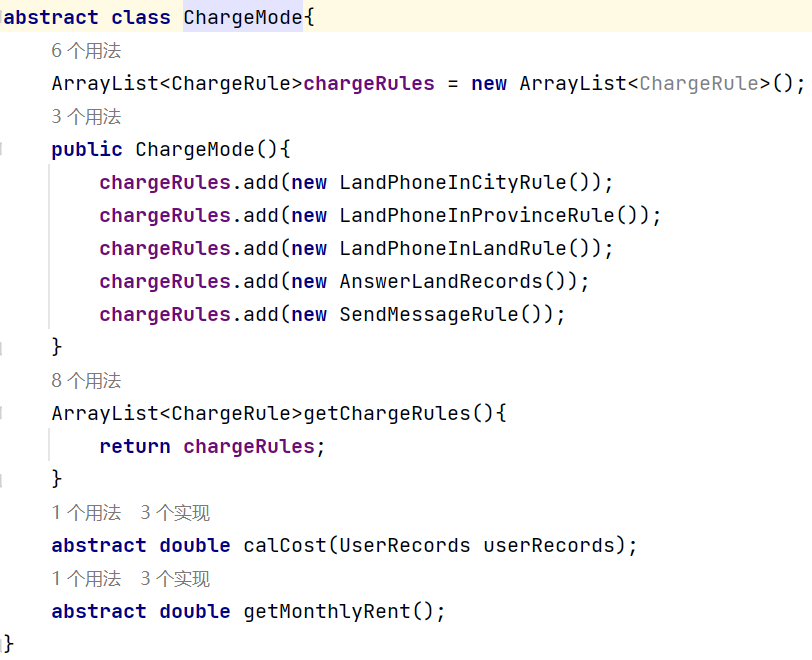
其它类作相应修改:
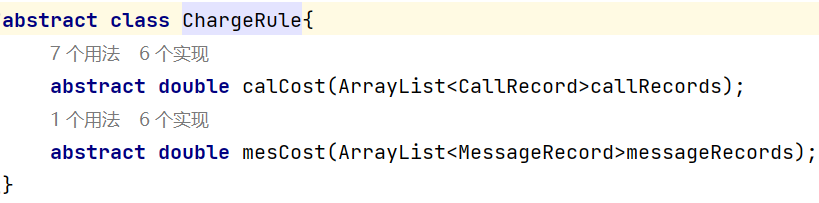
chargeRules加入SendMessageRule
ChargeRule新增mesCost返回短信计费信息
正则表达式判断:
String patternStStr = "u-1\\d{10}\\s[13]";
String mobileToPhone = "t-1\\d{10}\\s0\\d{2,3}\\s0\\d{9,11}(\\s\\d{4}[.]([^0]|10|11|12)[.]\\d{1,2}\\s([01]\\d|20|21|22|23):[0-5]\\d:[0-5]\\d){2}";
String mobileToMobile = "t-1\\d{10}\\s0\\d{2,3}\\s1\\d{10}\\s0\\d{2,3}(\\s\\d{4}[.]([^0]|10|11|12)[.]\\d{1,2}\\s([01]\\d|20|21|22|23):[0-5]\\d:[0-5]\\d){2}";
String messageSending = "m-1\\d{10}\\s1\\d{10}\\s(\\d|\\w|\\s|,|[.])+";
sourceMonitor分析:
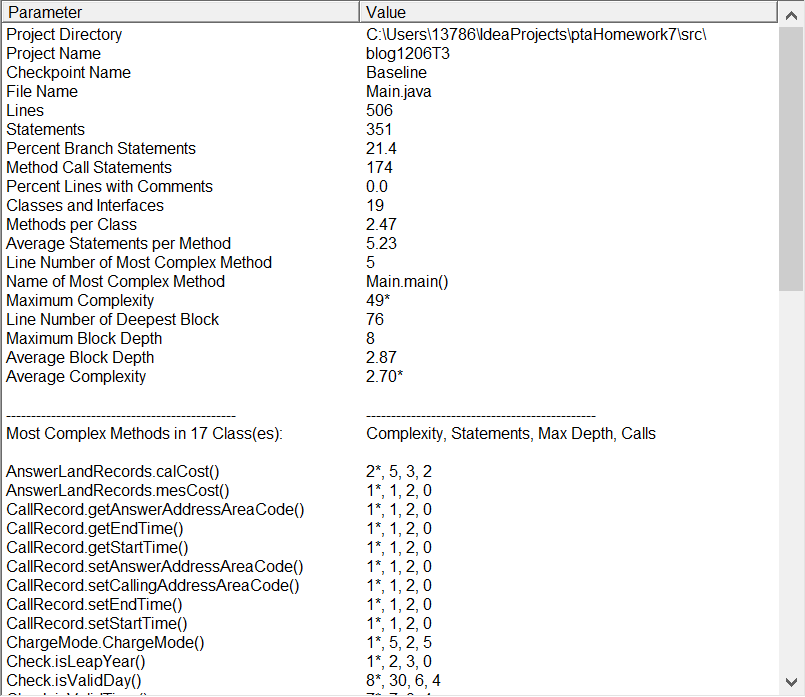

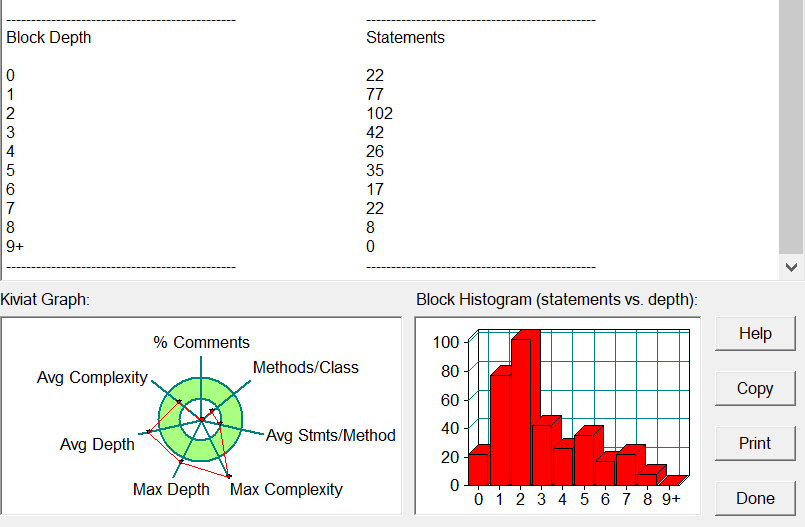
直接在第二题的基础上改的代码,各项指标十分甚至九分相似。。最大复杂度还是一如既往的大。
代码:

import java.lang.*; import java.text.*; import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args){ Scanner bjsn = new Scanner(System.in); Check check = new Check(); Map<String,User>mp = new TreeMap<>(); SimpleDateFormat patternDateStr = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy.MM.dd HH:mm:ss"); String patternStaStr = "u-0\\d{9,11}\\s0"; String patternStStr = "u-1\\d{10}\\s[13]"; String phoneToPhone = "t-0\\d{9,11}\\s0\\d{9,11}(\\s\\d{4}[.]([^0]|10|11|12)[.]\\d{1,2}\\s([01]\\d|20|21|22|23):[0-5]\\d:[0-5]\\d){2}"; String phoneToMobile = "t-0\\d{9,11}\\s1\\d{10}\\s0\\d{2,3}(\\s\\d{4}[.]([^0]|10|11|12)[.]\\d{1,2}\\s([01]\\d|20|21|22|23):[0-5]\\d:[0-5]\\d){2}"; String mobileToPhone = "t-1\\d{10}\\s0\\d{2,3}\\s0\\d{9,11}(\\s\\d{4}[.]([^0]|10|11|12)[.]\\d{1,2}\\s([01]\\d|20|21|22|23):[0-5]\\d:[0-5]\\d){2}"; String mobileToMobile = "t-1\\d{10}\\s0\\d{2,3}\\s1\\d{10}\\s0\\d{2,3}(\\s\\d{4}[.]([^0]|10|11|12)[.]\\d{1,2}\\s([01]\\d|20|21|22|23):[0-5]\\d:[0-5]\\d){2}"; String messageSending = "m-1\\d{10}\\s1\\d{10}\\s(\\d|\\w|\\s|,|[.])+"; String divideStr = "-|\\s"; String inProvince = "(079\\d|0701)"; Date d1 = new Date(),d2 = new Date(); String info; while(true){ info = bjsn.nextLine(); if(info.equals("end")){ break; } if(info.matches(patternStaStr) | info.matches(patternStStr)){ String[] userInfo = info.split(divideStr); User user1 = new User(userInfo[2],userInfo[1]); mp.put(userInfo[1],user1); } else if(info.matches(phoneToPhone)){ String[] userInfo = info.split(divideStr); if(check.isValidDay(userInfo[3]) && check.isValidDay(userInfo[5]) && check.isValidTime(userInfo[4]) && check.isValidTime(userInfo[6])){ try { d1 = patternDateStr.parse(userInfo[3] + " " + userInfo[4]); d2 = patternDateStr.parse(userInfo[5] + " " + userInfo[6]); }catch (ParseException e){ } for(User tmp : mp.values()){ if(tmp.getNumber().equals(userInfo[1])){ CallRecord callRecord = new CallRecord(); callRecord.setStartTime(d1); callRecord.setEndTime(d2); callRecord.setCallingNumber(userInfo[1]); callRecord.setAnswerAddressAreaCode(userInfo[2].substring(0,4)); tmp.getUserRecords().addCallingInCityRecords(callRecord); } } } } else if(info.matches(phoneToMobile)){ String[] userInfo = info.split(divideStr); if(check.isValidDay(userInfo[4]) && check.isValidDay(userInfo[6]) && check.isValidTime(userInfo[5]) && check.isValidTime(userInfo[7])){ try { d1 = patternDateStr.parse(userInfo[4] + " " + userInfo[5]); d2 = patternDateStr.parse(userInfo[6] + " " + userInfo[7]); }catch (ParseException e){ } CallRecord callRecord = new CallRecord(); callRecord.setStartTime(d1); callRecord.setEndTime(d2); callRecord.setCallingNumber(userInfo[1]); callRecord.setAnswerNumber(userInfo[2]); callRecord.setCallingAddressAreaCode("0791"); callRecord.setAnswerAddressAreaCode(userInfo[3]); for(User tmp : mp.values()) { if (tmp.getNumber().equals(userInfo[1])) { tmp.getUserRecords().addCallingInCityRecords(callRecord); } } for(User tmp : mp.values()){ if(tmp.getNumber().equals(userInfo[2])){ if(!userInfo[3].matches(inProvince)){ tmp.getUserRecords().addAnswerInLandRecords(callRecord); } } } } } else if(info.matches(mobileToPhone)){ String[] userInfo = info.split(divideStr); if(check.isValidDay(userInfo[4]) && check.isValidDay(userInfo[6]) && check.isValidTime(userInfo[5]) && check.isValidTime(userInfo[7])){ try { d1 = patternDateStr.parse(userInfo[4] + " " + userInfo[5]); d2 = patternDateStr.parse(userInfo[6] + " " + userInfo[7]); }catch (ParseException e){ } for(User tmp : mp.values()){ if(tmp.getNumber().equals(userInfo[1])){ CallRecord callRecord = new CallRecord(); callRecord.setStartTime(d1); callRecord.setEndTime(d2); callRecord.setCallingNumber(userInfo[1]); callRecord.setAnswerNumber(userInfo[3]); callRecord.setCallingAddressAreaCode(userInfo[2]); callRecord.setAnswerAddressAreaCode(userInfo[3].substring(0,4)); if(userInfo[2].equals("0791")){ tmp.getUserRecords().addCallingInCityRecords(callRecord); } else if(userInfo[2].matches(inProvince)){ tmp.getUserRecords().addCallingInProvinceRecords(callRecord); } else{ tmp.getUserRecords().addCallingInLandRecords(callRecord); } } } } } else if(info.matches(mobileToMobile)){ String[] userInfo = info.split(divideStr); if(check.isValidDay(userInfo[5]) && check.isValidDay(userInfo[7]) && check.isValidTime(userInfo[6]) && check.isValidTime(userInfo[8])){ try { d1 = patternDateStr.parse(userInfo[5] + " " + userInfo[6]); d2 = patternDateStr.parse(userInfo[7] + " " + userInfo[8]); }catch (ParseException e){ } CallRecord callRecord = new CallRecord(); callRecord.setStartTime(d1); callRecord.setEndTime(d2); callRecord.setCallingNumber(userInfo[1]); callRecord.setAnswerNumber(userInfo[3]); callRecord.setCallingAddressAreaCode(userInfo[2]); callRecord.setAnswerAddressAreaCode(userInfo[4]); for(User tmp : mp.values()){ if(tmp.getNumber().equals(userInfo[1])){ if(userInfo[2].equals("0791")){ tmp.getUserRecords().addCallingInCityRecords(callRecord); } else if(userInfo[2].length() == 4 && userInfo[2].matches(inProvince)){ tmp.getUserRecords().addCallingInProvinceRecords(callRecord); } else{ tmp.getUserRecords().addCallingInLandRecords(callRecord); } } } for(User tmp : mp.values()){ if(tmp.getNumber().equals(userInfo[3])){ if(!userInfo[4].matches(inProvince)){ tmp.getUserRecords().addAnswerInLandRecords(callRecord); } } } } } else if(info.matches(messageSending)){ String[] userInfo = info.split(divideStr); String messageInfo = info.substring(26); MessageRecord messageRecord = new MessageRecord(); messageRecord.setMessage(messageInfo); for(User tmp : mp.values()){ if(tmp.getNumber().equals(userInfo[1])){ tmp.getUserRecords().addSendMessageRecords(messageRecord); } } } } for(User tmp : mp.values()){ System.out.println(tmp.getNumber() + " " + (float)tmp.calCost() + " " + (float)tmp.calBalance()); } } } class Check{ boolean isValidDay(String s){ String[] temp = s.split("\\."); int yyyy = Integer.parseInt(temp[0]); int mm = Integer.parseInt(temp[1]); int dd = Integer.parseInt(temp[2]); if(mm < 1 || mm > 12 || dd < 1){ return false; } switch (mm){ case 1: case 3: case 5: case 7: case 8: case 10: case 12:if(dd > 31){ return false; } break; case 4: case 6: case 9: case 11:if(dd > 30){ return false; } break; case 2:if(isLeapYear(yyyy)){ if(dd > 29){ return false; } } else{ if(dd > 28){ return false; } } break; } return true; } boolean isValidTime(String s){ String[] temp = s.split(":"); int hh = Integer.parseInt(temp[0]); int mm = Integer.parseInt(temp[1]); int ss = Integer.parseInt(temp[2]); if(hh < 0 || hh > 23 || mm < 0 || mm > 59 || ss < 0 || ss > 59){ return false; } return true; } boolean isLeapYear(int yyyy){ if((yyyy % 4 == 0 && yyyy % 100 != 0) || yyyy % 400 == 0){ return true; } return false; } } class User{ UserRecords userRecords = new UserRecords(); double balance = 100; ChargeMode chargeMode; String number; public User(String t,String number){ this.number = number; if(t.equals("0")){ this.chargeMode = new LandlinePhoneCharging(); } else if(t.equals("1")){ this.chargeMode = new LandPhoneCharging(); } else if(t.equals("3")){ this.chargeMode = new MessageCharge(); } } double calCost(){ return chargeMode.calCost(userRecords); } double calBalance(){ return getBalance() - chargeMode.getMonthlyRent() - calCost(); } UserRecords getUserRecords(){ return userRecords; } double getBalance(){ return balance; } String getNumber(){ return number; } } abstract class ChargeRule{ abstract double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord>callRecords); abstract double mesCost(ArrayList<MessageRecord>messageRecords); } abstract class MessageChargeRule extends ChargeRule { abstract double mesCost(ArrayList<MessageRecord> messageChargeRules); } abstract class CallChargeRule extends ChargeRule{ abstract double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord>callRecords); } class LandPhoneInCityRule extends CallChargeRule{ @Override double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord>callRecords){ double cnt = 0; for(CallRecord callrecord : callRecords){ double ans = Math.ceil((callrecord.getEndTime().getTime() - callrecord.getStartTime().getTime()) / 60000.0); if(callrecord.getCallingNumber().matches("0\\d+")){ if(callrecord.getAnswerAddressAreaCode().matches("0791")){ ans *= 0.1; } else if(callrecord.getAnswerAddressAreaCode().matches("(079[^1]|0701)")){ ans *= 0.3; } else{ ans *= 0.6; } } else{ if(callrecord.getAnswerAddressAreaCode().matches("0791")){ ans *= 0.1; } else if(callrecord.getAnswerAddressAreaCode().matches("(079[^1]|0701)")){ ans *= 0.2; } else{ ans *= 0.3; } } cnt += ans; } return cnt; } double mesCost(ArrayList<MessageRecord>messageRecords){ return 0.0; } } class LandPhoneInProvinceRule extends CallChargeRule{ double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord>callRecords){ double cnt = 0; for(CallRecord callrecord : callRecords){ double ans = Math.ceil((callrecord.getEndTime().getTime() - callrecord.getStartTime().getTime()) / 60000.0); cnt += ans; } return cnt * 0.3; } double mesCost(ArrayList<MessageRecord>messageRecords){ return 0.0; } } class LandPhoneInLandRule extends CallChargeRule{ double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord>callRecords){ double cnt = 0; for(CallRecord callrecord : callRecords){ double d = Math.ceil((callrecord.getEndTime().getTime() - callrecord.getStartTime().getTime()) / 60000.0); cnt += d; } return cnt * 0.6; } double mesCost(ArrayList<MessageRecord>messageRecords){ return 0.0; } } abstract class ChargeMode{ ArrayList<ChargeRule>chargeRules = new ArrayList<ChargeRule>(); public ChargeMode(){ chargeRules.add(new LandPhoneInCityRule()); chargeRules.add(new LandPhoneInProvinceRule()); chargeRules.add(new LandPhoneInLandRule()); chargeRules.add(new AnswerLandRecords()); chargeRules.add(new SendMessageRule()); } ArrayList<ChargeRule>getChargeRules(){ return chargeRules; } abstract double calCost(UserRecords userRecords); abstract double getMonthlyRent(); } class LandlinePhoneCharging extends ChargeMode{ double monthlyRent = 20; public LandlinePhoneCharging(){ super(); } double calCost(UserRecords userRecords){ double cnt = 0; cnt = getChargeRules().get(0).calCost(userRecords.getCallingInCityRecords()) + getChargeRules().get(1).calCost(userRecords.getCallingInProvinceRecords()) + getChargeRules().get(2).calCost(userRecords.getCallingInLandRecords()); return cnt; } double getMonthlyRent(){ return monthlyRent; } } class LandPhoneCharging extends ChargeMode{ double monthlyRent = 15; public LandPhoneCharging(){ super(); } double calCost(UserRecords userRecords){ double cnt = 0; cnt = getChargeRules().get(0).calCost(userRecords.getCallingInCityRecords()) + getChargeRules().get(1).calCost(userRecords.getCallingInProvinceRecords()) + getChargeRules().get(2).calCost(userRecords.getCallingInLandRecords()) + getChargeRules().get(3).calCost(userRecords.getAnswerInLandRecords()); return cnt; } double getMonthlyRent(){ return monthlyRent; } } class UserRecords{ ArrayList<CallRecord>callingInCityRecords = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList<CallRecord>callingInProvinceRecords = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList<CallRecord>callingInLandRecords = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList<CallRecord>answerInCityRecords = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList<CallRecord>answerInProvinceRecords = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList<CallRecord>answerInLandRecords = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList<MessageRecord>sendMessageRecords = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList<MessageRecord>receiveMessagerecords = new ArrayList<>(); void addCallingInCityRecords(CallRecord callRecord){ callingInCityRecords.add(callRecord); } void addCallingInProvinceRecords(CallRecord callRecord){ callingInProvinceRecords.add(callRecord); } void addCallingInLandRecords(CallRecord callRecord){ callingInLandRecords.add(callRecord); } void addAnswerInLandRecords(CallRecord callRecord){ answerInLandRecords.add(callRecord); } void addSendMessageRecords(MessageRecord messageRecord){ sendMessageRecords.add(messageRecord); } ArrayList<MessageRecord>getSendMessageRecords(){ return sendMessageRecords; } ArrayList<CallRecord>getCallingInCityRecords(){ return callingInCityRecords; } ArrayList<CallRecord>getCallingInProvinceRecords(){ return callingInProvinceRecords; } ArrayList<CallRecord>getCallingInLandRecords(){ return callingInLandRecords; } ArrayList<CallRecord>getAnswerInLandRecords(){ return answerInLandRecords; } } abstract class CommunicationRecord{ String callingNumber; String answerNumber; String getCallingNumber(){ return callingNumber; } void setCallingNumber(String callingNumber){ this.callingNumber = callingNumber; } void setAnswerNumber(String answerNumber){ this.answerNumber = answerNumber; } } class CallRecord extends CommunicationRecord{ Date startTime; Date endTime; String callingAddressAreaCode; String answerAddressAreaCode; Date getStartTime(){ return startTime; } void setStartTime(Date startTime){ this.startTime = startTime; } Date getEndTime(){ return endTime; } void setEndTime(Date endTime){ this.endTime = endTime; } void setCallingAddressAreaCode(String callingAddressAreaCode){ this.callingAddressAreaCode = callingAddressAreaCode; } String getAnswerAddressAreaCode(){ return answerAddressAreaCode; } void setAnswerAddressAreaCode(String answerAddressAreaCode){ this.answerAddressAreaCode = answerAddressAreaCode; } } class MessageRecord extends CommunicationRecord{ String message; String getMessage(){ return message; } void setMessage(String message){ this.message = message; } } class MessageCharge extends ChargeMode{ double monthlyRent = 0; @Override double calCost(UserRecords userRecords){ return getChargeRules().get(4).mesCost(userRecords.getSendMessageRecords()); } double getMonthlyRent(){ return monthlyRent; } } class SendMessageRule extends MessageChargeRule{ double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord>callRecords){ return 0.0; } double mesCost(ArrayList<MessageRecord>messageRecords){ double cnt = 0; for(MessageRecord tmp : messageRecords){ cnt += Math.ceil(tmp.getMessage().length() / 10.0); } if(cnt <= 3){ return cnt * 0.1; } else if(cnt <= 5){ return (cnt - 3) * 0.2 + 0.3; } else{ return (cnt - 5) * 0.3 + 0.7; } } } class AnswerLandRecords extends CallChargeRule{ double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord>callRecords){ double cnt = 0; for(CallRecord tmp : callRecords){ double ans = Math.ceil((tmp.getEndTime().getTime() - tmp.getStartTime().getTime()) / 60000.0); cnt += ans; } return cnt * 0.3; } double mesCost(ArrayList<MessageRecord>messageRecords){ return 0.0; } }
电信计费系列完结撒花!
三次作业其它题目:
第六次T2
定义容器Container接口。模拟实现一个容器类层次结构,并进行接口的实现、抽象方法重写和多态机制测试。各容器类实现求表面积、体积的方法。
- 定义接口Container:
属性:
public static final double pi=3.1415926;
抽象方法:
public abstract double area();
public abstract double volume();
static double sumofArea(Container c[]);
static double sumofVolume(Container c[]);
其中两个静态方法分别计算返回容器数组中所有对象的面积之和、周长之和; - 定义Cube类、Cylinder类均实现自Container接口。
Cube类(属性:边长double类型)、Cylinder类(属性:底圆半径、高,double类型)。
输入格式:
第一行n表示对象个数,对象类型用cube、cylinder区分,cube表示立方体对象,后面输入边长,输入cylinder表示圆柱体对象,后面是底圆半径、高。
输出格式:
分别输出所有容器对象的表面积之和、体积之和,结果保留小数点后2位。
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
4
cube
15.7
cylinder
23.5 100
cube
46.8
cylinder
17.5 200输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
56771.13
472290.12水题,看看就好,没啥讲的。
代码:

import java.util.*; import java.lang.*; public class Main{ public static void main(String[] args){ Container container = new Container(); container.calc(); } } class Container{ boolean check(String s){ // int len = s.length(); if(s.charAt(1)=='u'){ return true; } return false; } void calc(){ Cube cube = new Cube(); Cylinder cylinder = new Cylinder(); double S=0,V=0; Scanner bjsn = new Scanner(System.in); int T = bjsn.nextInt(); for(int i = 0; i < T; i++) { String s = bjsn.next(); // System.out.println(s); if (check(s)) { double r = bjsn.nextDouble(); // System.out.println(r); S += cube.sumOfArea(r); V += cube.volume(r); } else { double r = bjsn.nextDouble(); double h = bjsn.nextDouble(); S += cylinder.sumOfArea(r, h); V += cylinder.volume(r, h); } } System.out.printf("%.2f\n%.2f",S,V); } } class Cube{ double sumOfArea(double r){ return 6*r*r; } double volume(double r){ return r*r*r; } } class Cylinder{ double pi=3.1415926; double sumOfArea(double r,double h){ return pi*r*r*2+2*pi*r*h; } double volume(double r,double h){ return pi*r*r*h; } }
第七次T2
经过不懈的努力,C~K终于当上了班主任。
现在他要统计班里学生的名单,但是C~K在教务系统中导出班级名单时出了问题,发现会有同学的信息重复,现在他想把重复的同学信息删掉,只保留一个,
但是工作量太大了,所以找到了会编程的你,你能帮他解决这个问题吗?
输入格式:
第一行输入一个N,代表C~K导出的名单共有N行(N<100000).
接下来的N行,每一行包括一个同学的信息,学号 姓名 年龄 性别。
输出格式:
第一行输出一个n,代表删除重复名字后C~K的班级共有几人。
接下来的n行,输出每一个同学的信息,输出按照学号从小到大的顺序。
输入样例:
6
0001 MeiK 20 M
0001 MeiK 20 M
0002 sdk2 21 M
0002 sdk2 21 M
0002 sdk2 21 M
0000 blf2 22 F输出样例:
3
0000 blf2 22 F
0001 MeiK 20 M
0002 sdk2 21 M代码:

import java.lang.*; import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args){ Scanner bjsn = new Scanner(System.in); int n = Integer.parseInt(bjsn.nextLine()); ArrayList<String>info = new ArrayList<>(); for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){ String t = bjsn.nextLine(); if(!info.contains(t)) { info.add(t); } } info.sort(new Comparator<String>() { @Override public int compare(String o1, String o2) { int id1 = Integer.parseInt(o1.substring(0,4)); int id2 = Integer.parseInt(o2.substring(0,4)); return id1 - id2; } }); System.out.println(info.size()); for(String stu : info){ System.out.println(stu); } } }
第六次T3
功能需求:
使用集合存储3个员工的信息(有序);
通过迭代器依次找出所有的员工。提示:学生复制以下代码到编程区,并按需求进行调试修改

// 1、导入相关包 //定义员工类 class Employee { private String name; private int age; public Employee() { super(); } public Employee(String name, int age) { super(); this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } } //主函数 public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { // 1、创建有序集合对象 Collection c ; // 创建3个员工元素对象 for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); String employeeName = sc.nextLine(); int employeeAge = sc.nextInt(); Employee employee = new Employee(employeeName, employeeAge); c.add(employee); } // 2、创建迭代器遍历集合 Iterator it; //3、遍历 while (it.hasnext) { //4、集合中对象未知,向下转型 Employee e = it.next(); System.out.println(e.getName() + "---" + e.getAge()); } } }
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
zs
10
ls
20
ww
30输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
zs---10
ls---20
ww---30这题有点阴间。。
代码:

import java.util.Collection; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.Iterator; // 1、导入相关包 //定义员工类 class Employee { private String name; private String age; public Employee() { super(); } public Employee(String name, String age) { super(); this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(String age) { this.age = age; } } //主函数 public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { // 1、创建有序集合对象 Collection c = new ArrayList<Employee>(); Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); // 创建3个员工元素对象 for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { String employeeName = sc.next(); String employeeAge = sc.next(); Employee employee = new Employee(employeeName, employeeAge); c.add(employee); } // 2、创建迭代器遍历集合 Iterator it = c.iterator(); //3、遍历 int pos = 0; while (it.hasNext()) { //4、集合中对象未知,向下转型 Employee e = (Employee)it.next(); int age = Integer.parseInt(e.getAge()); pos++; if(pos < 3) System.out.println(e.getName() + "---" + age); else System.out.print(e.getName() + "---" + age); } } }
第八次作业T2
编写一个类Shop(商店),该类中有一个成员内部类InnerCoupons(内部购物券),可以用于购买该商店的牛奶(假设每箱牛奶售价为50元)。要求如下:
(1)Shop类中有私有属性milkCount(牛奶的箱数,int类型)、公有的成员方法setMilkCount( )和getMilkCount( )分别用于设置和获取牛奶的箱数。
(2)成员内部类InnerCoupons,有公有属性value(面值,int类型),一个带参数的构造方法可以设定购物券的面值value,一个公有的成员方法buy( )要求输出使用了面值为多少的购物券进行支付,同时使商店牛奶的箱数减少value/50。
(3)Shop类中还有成员变量coupons50(面值为50元的内部购物券,类型为InnerCoupons)、coupons100(面值为100元的内部购物券,类型为InnerCoupons)。
(4)在Shop类的构造方法中,调用内部类InnerCoupons的带参数的构造方法分别创建上面的购物券coupons50、coupons100。
在测试类Main中,创建一个Shop类的对象myshop,从键盘输入一个整数(大于或等于3),将其设置为牛奶的箱数。假定有顾客分别使用了该商店面值为50的购物券、面值为100的购物券各消费一次,分别输出消费后商店剩下的牛奶箱数。
输入格式:
输入一个大于或等于3的整数。
输出格式:
使用了面值为50的购物券进行支付
牛奶还剩XX箱
使用了面值为100的购物券进行支付
牛奶还剩XX箱
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
5输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
使用了面值为50的购物券进行支付
牛奶还剩4箱
使用了面值为100的购物券进行支付
牛奶还剩2箱代码:

import java.util.*; import java.lang.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args){ Scanner bjsn = new Scanner(System.in); int n = bjsn.nextInt(); Shop shop = new Shop(n); shop.coupons50.buy(); System.out.println("牛奶还剩" + shop.getMilkCount() + "箱"); shop.coupons100.buy(); System.out.println("牛奶还剩" + shop.getMilkCount() + "箱"); } } class Shop{ private int milkCount; void setMilkCount(int milkCount){ this.milkCount = milkCount; } int getMilkCount(){ return this.milkCount; } public Shop(int milkCount){ super(); this.milkCount = milkCount; } InnerCoupons coupons50 = new InnerCoupons(50); InnerCoupons coupons100 = new InnerCoupons(100); class InnerCoupons{ public int value; public InnerCoupons(int value){ // super(); this.value = value; } void buy(){ System.out.println("使用了面值为" + value + "的购物券进行支付"); milkCount -= value / 50; } } }
第八次作业T3
设计一个动物发生模拟器,用于模拟不同动物的叫声。比如狮吼、虎啸、狗旺旺、猫喵喵……。
定义抽象类Animal,包含两个抽象方法:获取动物类别getAnimalClass()、动物叫shout();
然后基于抽象类Animal定义狗类Dog、猫类Cat和山羊Goat,用getAnimalClass()方法返回不同的动物类别(比如猫,狗,山羊),用shout()方法分别输出不同的叫声(比如喵喵、汪汪、咩咩)。
最后编写AnimalShoutTest类测试,输出:
猫的叫声:喵喵
狗的叫声:汪汪
山羊的叫声:咩咩
其中,在AnimalShoutTestMain类中,用speak(Animal animal){}方法输出动物animal的叫声,在main()方法中调用speak()方法,分别输出猫、狗和山羊对象的叫声。
请在下面的【】处添加代码。
//动物发生模拟器. 请在下面的【】处添加代码。
public class AnimalShoutTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cat cat = new Cat();
Dog dog = new Dog();
Goat goat = new Goat();
speak(cat);
speak(dog);
speak(goat);
}
//定义静态方法speak()
【】
}
//定义抽象类Animal
【】class Animal{
【】
}
//基于Animal类,定义猫类Cat,并重写两个抽象方法
class Cat 【】{
【】
【】
}
//基于Animal类,定义狗类Dog,并重写两个抽象方法
class Dog 【】{
【】
【】
}
//基于Animal类,定义山羊类Goat,并重写两个抽象方法
class Goat 【】{
【】
【】
}输入样例:
输出样例:
猫的叫声:喵喵
狗的叫声:汪汪
山羊的叫声:咩咩代码:

import java.util.*; import java.lang.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args){ Cat cat = new Cat(); Dog dog = new Dog(); Goat goat = new Goat(); speak(cat); speak(dog); speak(goat); } static void speak(Animal animal){ System.out.println(animal.getAnimalClass() + "的叫声:" + animal.shout()); } } //动物发生模拟器. 请在下面的【】处添加代码。 class AnimalShoutTest2 { public static void main(String[] args) { } //定义静态方法speak() } //定义抽象类Animal abstract class Animal{ abstract String getAnimalClass(); abstract String shout(); } //基于Animal类,定义猫类Cat,并重写两个抽象方法 class Cat extends Animal{ String getAnimalClass(){ return "猫"; } String shout(){ return "喵喵"; } } //基于Animal类,定义狗类Dog,并重写两个抽象方法 class Dog extends Animal{ String getAnimalClass(){ return "狗"; } String shout(){ return "汪汪"; } } //基于Animal类,定义山羊类Goat,并重写两个抽象方法 class Goat extends Animal{ String getAnimalClass(){ return "山羊"; } String shout(){ return "咩咩"; } }
三、踩坑心得
最后三次作业比较简单,坑也没踩多少。下面来简单地罗列一遍吧~
(1)区号有可能是三位
(2)日期中月份不能带前缀0(如1919年8月10日必须写成1919.8.10而不能写成1919.08.10)

因为这两个点爆WA无数发。。话说PTA评测机上午到中午这段时间抖动挺厉害的啊,同一代码时隔几十秒提交,分数能差个二三十分(部分测试点运行超时)。
(3)Date的getTime()真好用啊。。单位是毫秒,转化为分钟要除以60000.0。
(4)第七次作业T2,改代码的那道,防不胜防的格式错误。。(最后一行不能继续换行)
四、改进建议
经历了点线形系列的摧残,这三次大作业难度都算不上啥了。果然代码平均复杂度低、sourceMonitor分析数据好看还得靠老师给的推荐类图带。下面说几点我认为还可以优化的地方:
(1) 从sourceMonitor分析结果来看,虽然平均复杂度降低了,但最大复杂度还是惊人的高。这怕是main函数的锅。
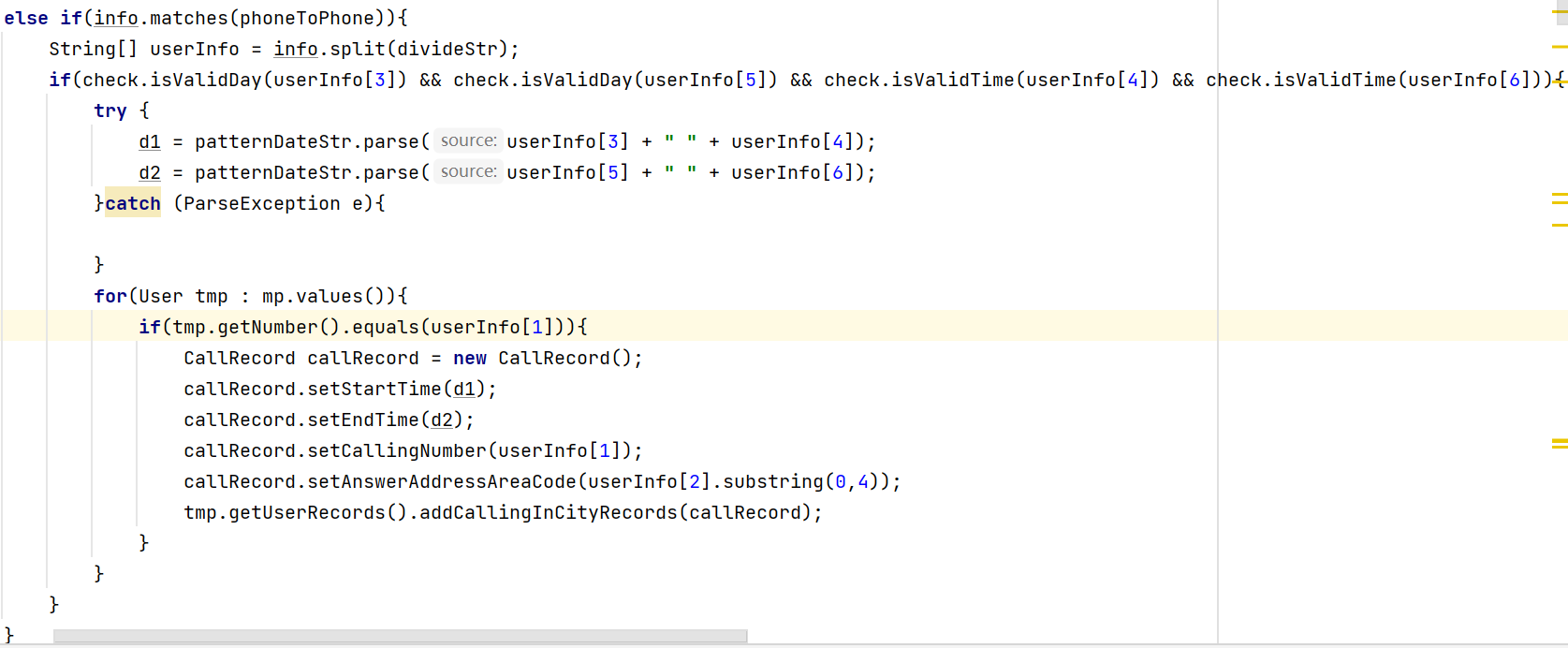
截一小块过来,可以看出存在较多if嵌套。将其中部分改写为switch,case(如正则式匹配),或多写几个函数、类并引用,估计会好一些。
(2)可以把市内、省内、国内三种形式的通话计费方式写成独立的类,方便代码修改及复用。
五、总结
这三次大作业虽然难度不大,但也让我学到了很多。从自己硬写高复杂度的烂代码,到从类图中提取有效信息,按照类图来写高质量代码,并由此更深刻地体会到面向对象的魅力、面向对象编程所带来的简洁、代码修改的方便,java的学习让我编程时的思路更加清晰、明朗。
期末考试的顺利结束,意味着这个学期的java学习正式告一段落。这是本学期的最后一篇java博客,也是java课的最后一个任务。我在这个学期的java学习过程中,遇到了大大小小的困难,被一次次地搞心态,但是最后还是挺过来了。学习嘛,不遇到几次困难你永远不知道自己几斤几两,也永远不会进步。java课程的结束,并不意味着java学习的结束。技术发展日新月异,我们在短短一学期内所学到的,永远只是java宇宙的冰山一角。其它的学科也一样。学习也不能局限于学校里学的知识。同时,对于我们这种计算机类专业,在学习了理论知识以后要多多动手实践,只有自己用代码敲出来才能对知识点有更深刻的理解。学习不是一蹴而就的过程,更要的是博识多学、坚持不懈。千淘万漉虽辛苦,吹尽狂沙始到金。人生也是这样,克服所遇到的困难,让自己闪现出金子般的光芒!最后,在此感谢老师同学们对我java学习所提供的帮助!





