Java字符串池
1. String类的两个构造方法
private final char value[]; private int hash; public String() { this.value = "".value; }
public String(String original) { this.value = original.value; this.hash = original.hash; }
2. new String中创建几个String对象?
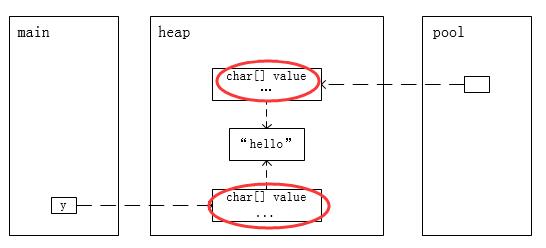
1)创建两个String对象
public static void main(String[] args) { String y = new String("hello"); }
内存模型如下:
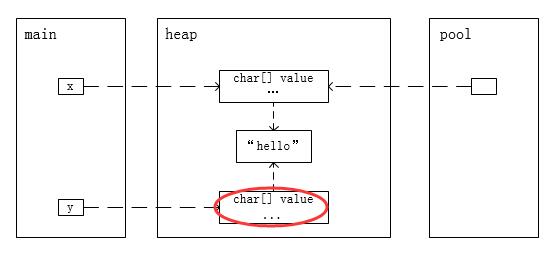
2)创建一个String对象
public static void main(String[] args) { String x = "hello"; String y = new String("hello"); }
内存模型如下:
3. String的intern方法
String类私有地维护着一个初始为空的字符串池,当调用intern方法时:
1. 若字符串池中已包含一个等于此String对象的字符串(用 equals方法确定),则返回池中的字符串。
2. 否则,将此String对象添加到字符串池中,并返回池中的字符串。
public native String intern();
字符串池中存放的是String对象的引用,而非String对象本身。
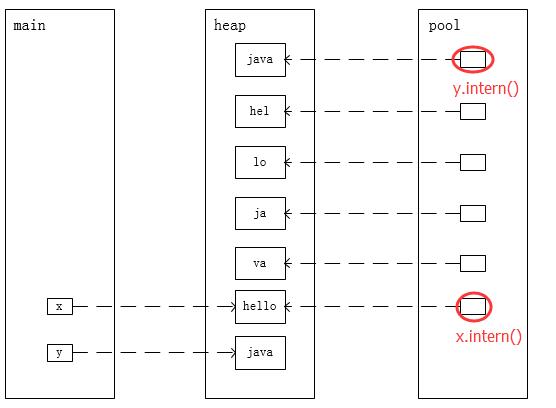
实验:
public static void main(String[] args) { String x = "hel"; x += "lo"; String y = "ja"; y += "va"; System.out.println(x == x.intern()); // true System.out.println(y == y.intern()); // false }
结论:字符串池中已包含一个等于"java"的字符串(JVM启动后在字符串池中加载的字符串还包括:"true"、"false"...)
内存模型如下:
intern()前
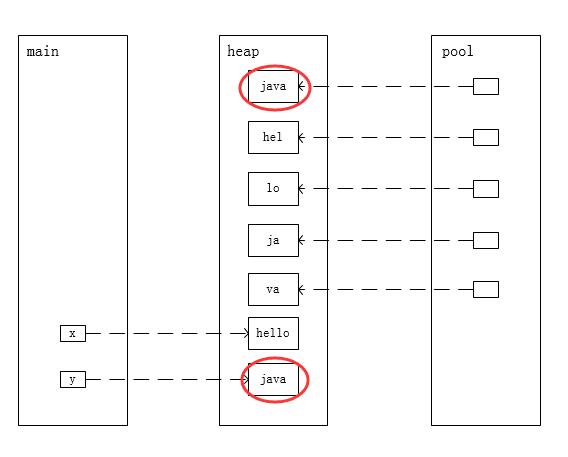
intern()后
4. 后记