005-Spring Boot配置分析-配置文件application、Environment、PropertySource、@Value、EnvironmentPostProcessor、Profiles
一、配置文件application
springboot配置文件,默认配置文件application.propertie或者application.yml,可同时存在。
基础使用
application.propertie增加配置:local.ip=192.168.1.1
application.yml增加配置【使用缩进】:
jdbc:
name: lhx
默认位置:classpath、classpath:/config、file:/、file:config下
注意:application.properties==application-default.properties
1.1、读取方式
方式一、Environment方式读取
context.getEnvironment().getProperty("local.ip","默认值")

@SpringBootApplication public class App { @Bean public Runnable createRunnable() { return () -> { System.out.println("spring boot is running"); }; } public static void main(String[] args) { ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(App.class, args); context.getBean(Runnable.class).run(); System.out.println(context.getEnvironment().getProperty("local.ip")); context.close(); } }
其实相当于自定义注入Environment ,然后使用env.getProperty("local.ip")即可

@Component public class UserConfig { @Autowired private Environment env; public void show() { System.out.println("local.ip=" + env.getProperty("local.ip")); } }
另一种设置默认值方式
HashMap<String, Object> defaultProperties = new HashMap<>(); defaultProperties.put("server.host", "127.0.0.1"); application.setDefaultProperties(defaultProperties);
方式二、使用@Value注解
@Value("${local.port}")
private String localPort;
默认必须有配置项,如果没有配置项可以增加默认值
@Value("${tomcat.port:9090}")
private String tomcatPort2;
这种的:@Value("tomcat.port") 也可以使用。具体没查
方式三、使用@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="ds")
在application配置文件中增加ds.url=jdbc:mysql://spring
增加读取类

@Component @ConfigurationProperties(prefix="ds") public class DataSourceProperties { private String url; public void show() { System.out.println("url"+url); } public String getUrl() { return url; } public void setUrl(String url) { this.url = url; } }
其他处使用即可。
注意:@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="ds")也支持指定具体路径文件配置@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="ds",localtions="classpath:/ds.properties")
注入数组、集合,在配置文件中增加
ds.host[0]=192.168.1.1 ds.host[1]=192.168.1.2 ds.host[2]=192.168.1.3
代码中
private List<String> hosts = new ArrayList<>();
即可,注意增加getter,setter,
注:支持配置引用配置
name=springboot
aap.name=this is ${name}
1.2、指定具体名称配置
如不使用application.properties,改为app.proerties.
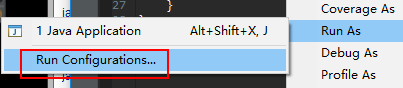
方式一、启动参数中修改:
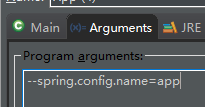
--spring.config.name=app
或者 有路径的 --spring.config.location=classpath:cong/app.propertis
或者 多个用逗号隔开
或者 file目录 --spring.config.location=classpath:cong/app.propertis,file:E:/app.properties
方式二、文件注解@PropertySource
增加jdbc.properties配置文件
增加Config配置类
@Configuration @PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties") public class FileConfig { }
然后使用即可 PropertySource 可以列多个
或者多个可以使用 @PropertySources({@PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties")})
@PropertySource: 用于引入外部属性配置,和Environment 配合一起使用。其中ignoreResourceNotFound 表示没有找到文件是否会报错,默认为false,就是会报错,一般开发情况应该使用默认值,设置为true相当于生吞异常,增加排查问题的复杂性.
引入PropertySource,注入Environment,然后就能用environment 获取配置文件中的value值。
二、EnvironmentPostProcessor配置文件扩展
 View Code
View Code需要注册到META-INF/spring.factories文件
1.增加此文件,并增加内容
org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessor=com.lhx.spring.springboot_config.MyEnvironmentPostProcessor
2.增加实现类文件MyEnvironmentPostProcessor
 View Code
View Code三、Profiles
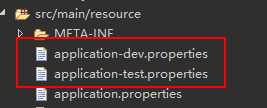
增加两个配置文件
方式一、程序读取
在application-dev.properties中添加
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1/spring_dev
在application-test.properties中添加
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1/spring_test
程序使用
SpringApplication app = new SpringApplication(App3.class);
app.setAdditionalProfiles("test");//test 读取application-test.properties
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = app.run(args);
context.getBean(Runnable.class).run();
System.out.println(context.getEnvironment().getProperty("jdbc.url"));
context.close();
注:可在setAdditionalProfiles配置多个,会被覆盖
方式二、参数配置
启动参数增加,多个使用逗号分割,配置多个 多个同时生效
--spring.profiles.active=test
使用
执行java -jar xxx.jar,可以观察到服务端口被设置为8001,也就是默认的开发环境(dev)
执行java -jar xxx.jar --spring.profiles.active=test,可以观察到服务端口被设置为8002,也就是测试环境的配置(test)
执行java -jar xxx.jar --spring.profiles.active=prod,可以观察到服务端口被设置为8003,也就是生产环境的配置(prod)
总结多环境的配置思路:
application.properties中配置通用内容,并设置spring.profiles.active=dev,以开发环境为默认配置
application-{profile}.properties中配置各个环境不同的内容
通过命令行方式去激活不同环境的配置
方式三、@Profile注解
@SpringBootConfiguration
public class MyConfig {
@Bean
public Runnable createRunnable() {
System.out.println("--------1--------");
return ()->{};
}
@Bean
@Profile("dev")
public Runnable createRunnable2() {
System.out.println("--------2--------");
return ()->{};
}
@Bean
@Profile("test")
public Runnable createRunnable3() {
System.out.println("--------3--------");
return ()->{};
}
}
启动对应环境时候生效



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号