003-Spring4 扩展分析-spring类初始化@PostConstruct > InitializingBean > init-method、ApplicationContext、BeanPostProcessor、BeanFactoryPostProcessor、BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
一、spring类初始化@PostConstruct > InitializingBean > init-method
InitializingBean接口为bean提供了初始化方法的方式,它只包括afterPropertiesSet方法,凡是继承该接口的子类,在初始化bean的时候会执行该方法。
示例
<bean id="myInitializingBean" class="com.paic.phssp.springtest.init.MyInitializingBean" init-method="testInit"></bean>
bean
/** * 继承InitializingBean接口的类,在初始化bean的时候会执行该方法 */ //@Component public class MyInitializingBean implements InitializingBean { public MyInitializingBean() { System.out.println("1MyInitializingBean...."); } @Override public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { System.out.println("3ceshi MyInitializingBean>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"); } @PostConstruct //功能上近似init-method,但加载时机不同 public void test(){ System.out.println("2PostConstruct >>>>>>>>>>>>"); } public void testInit(){ System.out.println("4ceshi init-method"); } }
结果:
1MyInitializingBean.... 2PostConstruct >>>>>>>>>>>> 3ceshi MyInitializingBean>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 4ceshi init-method
说明:
通过上述输出结果,三者的先后顺序:Constructor > @PostConstruct > InitializingBean > init-method
1.1、 InitializingBean > init-method 执行时机
spring初始化bean过程
002-创建型-03-单例模式(Singleton)【7种】、spring单例及原理 spring 单例
通过查看spring的加载bean的源码类(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory)可看出
如使用getBean方式创建:getBean→doGetBean→createBean→doCreateBean→initializeBean→invokeInitMethods
查看AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.invokeInitMethods

protected void invokeInitMethods(String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) throws Throwable { boolean isInitializingBean = (bean instanceof InitializingBean); if (isInitializingBean && (mbd == null || !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod("afterPropertiesSet"))) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Invoking afterPropertiesSet() on bean with name '" + beanName + "'"); } if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) { try { AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>) () -> { ((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet(); return null; }, getAccessControlContext()); } catch (PrivilegedActionException pae) { throw pae.getException(); } } else { ((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet(); } } if (mbd != null && bean.getClass() != NullBean.class) { String initMethodName = mbd.getInitMethodName(); if (StringUtils.hasLength(initMethodName) && !(isInitializingBean && "afterPropertiesSet".equals(initMethodName)) && !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod(initMethodName)) { invokeCustomInitMethod(beanName, bean, mbd); } } }
说明:
1.2、@PostConstruct加载过程
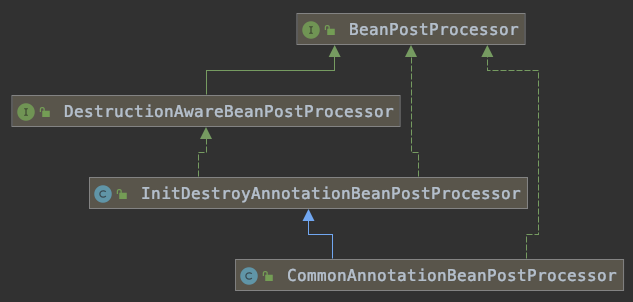
源码:InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class
@Override public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { LifecycleMetadata metadata = findLifecycleMetadata(bean.getClass()); try { metadata.invokeInitMethods(bean, beanName);//利用反射,执行注解方法 } catch (InvocationTargetException ex) { throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex.getTargetException()); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Failed to invoke init method", ex); } return bean; }
findLifecycleMetadata

private LifecycleMetadata findLifecycleMetadata(Class<?> clazz) { if (this.lifecycleMetadataCache == null) { // Happens after deserialization, during destruction... return buildLifecycleMetadata(clazz); } // Quick check on the concurrent map first, with minimal locking. LifecycleMetadata metadata = this.lifecycleMetadataCache.get(clazz); if (metadata == null) { synchronized (this.lifecycleMetadataCache) { metadata = this.lifecycleMetadataCache.get(clazz); if (metadata == null) { metadata = buildLifecycleMetadata(clazz); this.lifecycleMetadataCache.put(clazz, metadata); } return metadata; } } return metadata; }
buildLifecycleMetadata

private LifecycleMetadata buildLifecycleMetadata(final Class<?> clazz) { final boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled(); List<LifecycleElement> initMethods = new ArrayList<>(); List<LifecycleElement> destroyMethods = new ArrayList<>(); Class<?> targetClass = clazz; do { final List<LifecycleElement> currInitMethods = new ArrayList<>(); final List<LifecycleElement> currDestroyMethods = new ArrayList<>(); ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, method -> { if (this.initAnnotationType != null && method.isAnnotationPresent(this.initAnnotationType)) { LifecycleElement element = new LifecycleElement(method); currInitMethods.add(element); if (debug) { logger.debug("Found init method on class [" + clazz.getName() + "]: " + method); } } if (this.destroyAnnotationType != null && method.isAnnotationPresent(this.destroyAnnotationType)) { currDestroyMethods.add(new LifecycleElement(method)); if (debug) { logger.debug("Found destroy method on class [" + clazz.getName() + "]: " + method); } } }); initMethods.addAll(0, currInitMethods); destroyMethods.addAll(currDestroyMethods); targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass(); } while (targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class); return new LifecycleMetadata(clazz, initMethods, destroyMethods); }
判断指定类型注解
if (this.initAnnotationType != null && method.isAnnotationPresent(this.initAnnotationType)) {
方法:buildLifecycleMetadata(),判断是否是指定的注解类型,而这个属性,在CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class构造方法中被初始化为PostConstruct。
public CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor() { setOrder(Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE - 3); setInitAnnotationType(PostConstruct.class); setDestroyAnnotationType(PreDestroy.class); ignoreResourceType("javax.xml.ws.WebServiceContext"); }
1.3、 @PostConstruct > InitializingBean > init-method 执行时机
查看AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory的InitializingBean 方法
protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) { if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) { AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> { invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean); return null; }, getAccessControlContext()); } else { invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean); } Object wrappedBean = bean; if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) { wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName); } try { invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanCreationException( (mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null), beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex); } if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) { wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName); } return wrappedBean; }
查看标红的第一步applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization,第二部是 invokeInitMethods 【先执行了 ((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet(),进而执行了init-method自定义invokeCustomInitMethod(beanName, bean, mbd);】
--> 调用BeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法 (@PostConstruct在此)
--> 调用bean实例的初始化方法(invokeInitMethods-> InitializingBean->init-method)
--> 调用BeanPostProcessor的postProcessAfterInitialization方法
DisposableBean结束:https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaozhuanfeng/p/10415794.html
二、依赖注入ApplicationContext
方法一、@Autowired
创建一个User,内部使用ApplicationContext

@Component public class User { @Autowired private ApplicationContext applicationContext; public void show() { System.out.println("User:"+applicationContext.getClass()); } }
使用

public static void main(String[] args) { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext("com.lhx.spring.kuozhan"); System.out.println(context.getBean("user")); // System.out.println(context.getBean("createUser")); User bean = (User) context.getBean("user"); bean.show(); context.close(); }
方法二、实现ApplicationContextAware接口

@Component public class Book implements ApplicationContextAware{ private ApplicationContext ApplicationContext; @Override public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException { this.ApplicationContext=applicationContext; } public void show() { System.out.println("book:"+ApplicationContext.getClass()); } }
1)内部原理
接口BeanPostProcessor,内部方法,每一个bean初始化都会被执行
bean初始化属性完毕后,即依赖装配完成之后,postProcessBeforeInitialization
bean初始化在属性设置之后,Bean init之后触发的,postProcessAfterInitialization
作用:回调,返回代理对象等
如在postProcessBeforeInitialization中返回其他代理对象。
构建一个默认实现【两个方法不能返回null】

package com.lhx.spring.kuozhan; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class EchoBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor { @Override public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { System.out.println("--------------postProcessBeforeInitialization-------------" + "bean" + bean.getClass()); return bean; } @Override public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { System.out.println("--------------postProcessBeforeInitialization-------------" + "bean" + bean.getClass()); return bean; } }
2)示例
User类

@Component public class User { private ApplicationContext applicationContext; @Autowired public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) { this.applicationContext = applicationContext; } public void init() { System.out.println("User init"); } public void show() { System.out.println("User:" + applicationContext.getClass()); } }
UserConfig类

@Configuration public class MyConfig { @Bean(initMethod = "init") public User createUser() { return new User(); } }
调用
System.out.println(context.getBean("user"));
查看日志
User Set属性
--------------postProcessBeforeInitialization-------------beanclass com.lhx.spring.kuozhan.User
User init
--------------postProcessAfterInitialization-------------beanclass com.lhx.spring.kuozhan.User
3)自行实现ApplicationContextAware,这里起名为SpringContextAware,逻辑参考ApplicationContextAwareProcessor

public interface SpringContextAware { public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext); }
编写ContextBeanPostProcessor

package com.lhx.spring.kuozhan; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class ContextBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor { @Autowired private ApplicationContext applicationContext; @Override public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { if (bean instanceof SpringContextAware) { SpringContextAware sca = (SpringContextAware) bean; sca.setApplicationContext(applicationContext); } return bean; } @Override public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return bean; } }
实际类使用

package com.lhx.spring.kuozhan; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class Dog implements SpringContextAware { private ApplicationContext applicationContext; public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) { this.applicationContext = applicationContext; } public void show() { System.out.println("Dog:" + applicationContext.getClass()); } }
使用:
context.getBean(Dog.class).show();
4)查看ApplicationContextAware内部实现:
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext→GenericApplicationContext→AbstractApplicationContext
找打refresh方法,prepareBeanFactory,
// Configure the bean factory with context callbacks.
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this));
ApplicationContextAwareProcessor内部
class ApplicationContextAwareProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor
方法三、Spring 4.3 新特性,构造方法直接添加,有局限性,与构造方法直接相关

@Component public class Bank { private ApplicationContext applicationContext; //spring 4.3 提供,与构造方法调用有关 public Bank(ApplicationContext applicationContext) { this.applicationContext=applicationContext; } public void show() { System.out.println("book:"+applicationContext.getClass()); } }
二、容器扩展
2.1、BeanFactoryPostProcessor
在beanFactory之后,BeanFactoryPostProcessor容器初始化之后,只初始化一次,先于所有容器以及BeanPostProcessor
void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException;
示例代码扩展2
源码:
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext→GenericApplicationContext→AbstractApplicationContext
找打refresh方法

public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { // Prepare this context for refreshing. prepareRefresh(); // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try { // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Initialize message source for this context. initMessageSource(); // Initialize event multicaster for this context. initApplicationEventMulticaster(); // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. onRefresh(); // Check for listener beans and register them. registerListeners(); // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); // Last step: publish corresponding event. finishRefresh(); } catch (BeansException ex) { if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " + "cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex); } // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources. destroyBeans(); // Reset 'active' flag. cancelRefresh(ex); // Propagate exception to caller. throw ex; } finally { // Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we // might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore... resetCommonCaches(); } } }
2.2、BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
BeanFactoryPostProcessor的子类BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException;
注册一个Bean到Spring容器中,类似标注了@Componment
示例
新建一个Person类

public class Person { private String name; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } @Override public String toString() { return "Person [name=" + name + "]"; } }
MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor实现

package com.lhx.spring.kuozhan2; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory; import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionBuilder; import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistry; import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor { @Override public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } @Override public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { BeanDefinitionBuilder rootBeanDefinition = BeanDefinitionBuilder.rootBeanDefinition(Person.class); rootBeanDefinition.addPropertyValue("name", "admin" + i); registry.registerBeanDefinition("person" + i, rootBeanDefinition.getBeanDefinition()); } } }
使用
public static void main(String[] args) { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext("com.lhx.spring.kuozhan2"); System.out.println(context.getBean("person1")); context.getBeansOfType(Person.class).values().forEach(System.out::println); context.close(); }
当然在使用
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext("com.lhx.spring.kuozhan2");
使用context也可以注入
context.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, beanDefinition);
beanDefinition定义可以使用:BeanDefinitionBuilder rootBeanDefinition = BeanDefinitionBuilder.rootBeanDefinition(Person.class);



