005-shiro认证
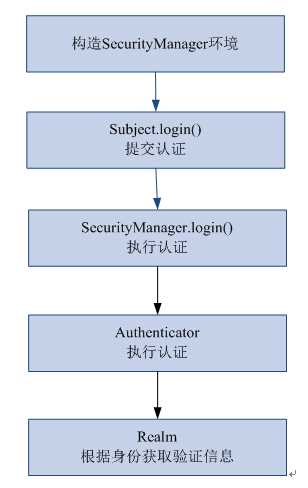
一、shiro认证流程
二、入门程序
1、代码:
2、配置shiro-first.ini
通过此配置文件创建securityManager工厂。
需要修改eclipse的ini的编辑器:

配置数据:
#对用户信息进行配置 [users] #用户账户和密码 zhangsan=111111 lisi=22222
用户登录和退出

// 用户登陆和退出 @Test public void testLoginAndLogout() { // 创建securityManager工厂,通过ini配置文件创建securityManager工厂 Factory<SecurityManager> factory = new IniSecurityManagerFactory( "classpath:shiro-first.ini"); // 创建SecurityManager SecurityManager securityManager = factory.getInstance(); // 将securityManager设置当前的运行环境中 SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager); // 从SecurityUtils里边创建一个subject Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); // 在认证提交前准备token(令牌) // 这里的账号和密码 将来是由用户输入进去 UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("zhangsan", "111111"); try { // 执行认证提交 subject.login(token); } catch (AuthenticationException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } // 是否认证通过 boolean isAuthenticated = subject.isAuthenticated(); System.out.println("是否认证通过:" + isAuthenticated); // 退出操作 subject.logout(); // 是否认证通过 isAuthenticated = subject.isAuthenticated(); System.out.println("是否认证通过:" + isAuthenticated); }
3、执行流程
1、通过ini配置文件创建securityManager
2、调用subject.login方法主体提交认证,提交的token
3、securityManager进行认证,securityManager最终由ModularRealmAuthenticator进行认证。
4、ModularRealmAuthenticator调用IniRealm(给realm传入token) 去ini配置文件中查询用户信息
5、IniRealm根据输入的token(UsernamePasswordToken)从 shiro-first.ini查询用户信息,根据账号查询用户信息(账号和密码)
如果查询到用户信息,就给ModularRealmAuthenticator返回用户信息(账号和密码)
如果查询不到,就给ModularRealmAuthenticator返回null
6、ModularRealmAuthenticator接收IniRealm返回Authentication认证信息
如果返回的认证信息是null,ModularRealmAuthenticator抛出异常(org.apache.shiro.authc.UnknownAccountException)
如果返回的认证信息不是null(说明inirealm找到了用户),对IniRealm返回用户密码 (在ini文件中存在)和 token中的密码 进行对比,如果不一致抛出异常(org.apache.shiro.authc.IncorrectCredentialsException)
4、小结
ModularRealmAuthenticator作用进行认证,需要调用realm查询用户信息(在数据库中存在用户信息)
ModularRealmAuthenticator进行密码对比(认证过程)。
realm:需要根据token中的身份信息去查询数据库(入门程序使用ini配置文件),如果查到用户返回认证信息,如果查询不到返回null。
三、自定义realm
实际开发需要realm从数据库中查询用户信息。
1、realm接口

2、自定义realm
com.lhx.shiro.realm.CustomRealm

package com.lhx.shiro.realm; import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException; import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationInfo; import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationToken; import org.apache.shiro.authc.SimpleAuthenticationInfo; import org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationInfo; import org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthorizingRealm; import org.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection; /** * * <p> * Title: CustomRealm * </p> * <p> * Description:自定义realm * </p> * @version 1.0 */ public class CustomRealm extends AuthorizingRealm { // 设置realm的名称 @Override public void setName(String name) { super.setName("customRealm"); } // 用于认证 @Override protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo( AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { // token是用户输入的 // 第一步从token中取出身份信息 String userCode = (String) token.getPrincipal(); // 第二步:根据用户输入的userCode从数据库查询 // .... // 如果查询不到返回null //数据库中用户账号是zhangsansan /*if(!userCode.equals("zhangsansan")){// return null; }*/ // 模拟从数据库查询到密码 String password = "111112"; // 如果查询到返回认证信息AuthenticationInfo SimpleAuthenticationInfo simpleAuthenticationInfo = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo( userCode, password, this.getName()); return simpleAuthenticationInfo; } // 用于授权 @Override protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo( PrincipalCollection principals) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } }
3、配置realm
需要在shiro-realm.ini配置realm注入到securityManager中。
[main] #自定义 realm customRealm=com.lhx.shiro.realm.CustomRealm #\将realm设置到securityManager相当于spring中注入 securityManager.realms=$customRealm
4、测试

// 自定义realm @Test public void testCustomRealm() { // 创建securityManager工厂,通过ini配置文件创建securityManager工厂 Factory<SecurityManager> factory = new IniSecurityManagerFactory( "classpath:shiro-realm.ini"); // 创建SecurityManager SecurityManager securityManager = factory.getInstance(); // 将securityManager设置当前的运行环境中 SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager); // 从SecurityUtils里边创建一个subject Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); // 在认证提交前准备token(令牌) // 这里的账号和密码 将来是由用户输入进去 UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("zhangsan", "111111"); try { // 执行认证提交 subject.login(token); } catch (AuthenticationException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } // 是否认证通过 boolean isAuthenticated = subject.isAuthenticated(); System.out.println("是否认证通过:" + isAuthenticated); }
四、散列算法
通常需要对密码 进行散列,常用的有md5、sha
MD5
对密码md5,如果知道散列后的值可以通过穷举算法,得到md5密码对应的明文。
建议对md5进行散列时加salt(盐),进行加密相当 于对原始密码+盐进行散列
正常使用时散列方法:
在程序中对原始密码+盐进行散列,将散列值存储到数据库中,并且还要将盐也要存储在数据库中。
如果进行密码对比时,使用相同 方法,将原始密码+盐进行散列,进行比对。
1、MD5消息摘要测试程序

package com.lhx.shiro.authentication; import org.apache.shiro.crypto.hash.Md5Hash; import org.apache.shiro.crypto.hash.SimpleHash; /** * * <p>Title: MD5Test</p> * <p>Description: </p> * @version 1.0 */ public class MD5Test { public static void main(String[] args) { //原始 密码 String source = "111111"; //盐 String salt = "qwerty"; //散列次数 int hashIterations = 2; //上边散列1次:f3694f162729b7d0254c6e40260bf15c //上边散列2次:36f2dfa24d0a9fa97276abbe13e596fc //构造方法中: //第一个参数:明文,原始密码 //第二个参数:盐,通过使用随机数 //第三个参数:散列的次数,比如散列两次,相当 于md5(md5('')) Md5Hash md5Hash = new Md5Hash(source, salt, hashIterations); String password_md5 = md5Hash.toString(); System.out.println(password_md5); //同上面一样,只是多了一个参数名 //第一个参数:散列算法 SimpleHash simpleHash = new SimpleHash("md5", source, salt, hashIterations); System.out.println(simpleHash.toString()); } }
2、自定义realm支持散列算法
需求:实际开发时realm要进行md5值(明文散列后的值)的对比。
2.1、新建realm(CustomRealmMd5)

package com.lhx.shiro.realm; import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException; import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationInfo; import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationToken; import org.apache.shiro.authc.SimpleAuthenticationInfo; import org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationInfo; import org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthorizingRealm; import org.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection; import org.apache.shiro.util.ByteSource; /** * * <p> * Title: CustomRealm * </p> * <p> * Description:自定义realm * </p> * * @version 1.0 */ public class CustomRealmMd5 extends AuthorizingRealm { // 设置realm的名称 @Override public void setName(String name) { super.setName("customRealmMd5"); } // 用于认证 @Override protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { // token是用户输入的 // 第一步从token中取出身份信息 String userCode = (String) token.getPrincipal(); // 第二步:根据用户输入的userCode从数据库查询 // .... // 如果查询不到返回null // 数据库中用户账号是zhangsansan /* * if(!userCode.equals("zhangsansan")){// return null; } */ // 模拟从数据库查询到密码,散列值 String password = "f3694f162729b7d0254c6e40260bf15c"; // 从数据库获取salt String salt = "qwerty"; // 上边散列值和盐对应的明文:111111 // 如果查询到返回认证信息AuthenticationInfo SimpleAuthenticationInfo simpleAuthenticationInfo = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(userCode, password, ByteSource.Util.bytes(salt), this.getName()); return simpleAuthenticationInfo; } // 用于授权 @Override protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } }
2.2、在realm中配置凭证匹配器
[main] #定义凭证匹配器 credentialsMatcher=org.apache.shiro.authc.credential.HashedCredentialsMatcher #散列算法 credentialsMatcher.hashAlgorithmName=md5 #散列次数 credentialsMatcher.hashIterations=1 #将凭证匹配器设置到realm customRealm=cn.itcast.shiro.realm.CustomRealmMd5 customRealm.credentialsMatcher=$credentialsMatcher securityManager.realms=$customRealm
2.3、代码中测试即可

// 自定义realm实现散列值匹配 @Test public void testCustomRealmMd5() { // 创建securityManager工厂,通过ini配置文件创建securityManager工厂 Factory<SecurityManager> factory = new IniSecurityManagerFactory( "classpath:shiro-realm-md5.ini"); // 创建SecurityManager SecurityManager securityManager = factory.getInstance(); // 将securityManager设置当前的运行环境中 SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager); // 从SecurityUtils里边创建一个subject Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); // 在认证提交前准备token(令牌) // 这里的账号和密码 将来是由用户输入进去 UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("zhangsan", "222222"); try { // 执行认证提交 subject.login(token); } catch (AuthenticationException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } // 是否认证通过 boolean isAuthenticated = subject.isAuthenticated(); System.out.println("是否认证通过:" + isAuthenticated); }


