博客系统|功能4:个人站点页面设计(ORM跨表与分组查询)
查询: 日期归档查询 date_format ============date,time,datetime=========== create table t_mul_new(d date,t time,dt datetime); insert into t_mul_new values(now(),now(),now()); select * from t_mul; mysql> select * from t_mul; +------------+----------+---------------------+ | d | t | dt | +------------+----------+---------------------+ | 2017-08-01 | 19:42:22 | 2017-08-01 19:42:22 | +------------+----------+---------------------+ row in set (0.00 sec) select date_format(dt,"%Y/%m/%d") from t_mul; extra extra(select=None, where=None, params=None, tables=None, order_by=None, select_params=None) 有些情况下,Django的查询语法难以简单的表达复杂的 WHERE 子句,对于这种情况, Django 提供了 extra() QuerySet修改机制 — 它能在 QuerySet生成的SQL从句中注入新子句 extra可以指定一个或多个 参数,例如 select, where or tables. 这些参数都不是必须的,但是你至少要使用一个!要注意这些额外的方式对不同的数据库引擎可能存在移植性问题.(因为你在显式的书写SQL语句),除非万不得已,尽量避免这样做 参数之select The select 参数可以让你在 SELECT 从句中添加其他字段信息,它应该是一个字典,存放着属性名到 SQL 从句的映射。 queryResult=models.Article .objects.extra(select={'is_recent': "create_time > '2017-09-05'"}) 结果集中每个 Entry 对象都有一个额外的属性is_recent, 它是一个布尔值,表示 Article对象的create_time 是否晚于2017-09-05. 练习: in sqlite: article_obj=models.Article.objects .extra(select={"standard_time":"strftime('%%Y-%%m-%%d',create_time)"}) .values("standard_time","nid","title") print(article_obj) # <QuerySet [{'title': 'MongoDb 入门教程', 'standard_time': '2017-09-03', 'nid': 1}]> 单表分组查询 ...... 日期归档查询的方式2 from django.db.models.functions import TruncMonth Sales.objects .annotate(month=TruncMonth('timestamp')) # Truncate to month and add to select list .values('month') # Group By month .annotate(c=Count('id')) # Select the count of the grouping .values('month', 'c') # (might be redundant, haven't tested) select month and count 总结
(1)用户未找到,404页面构建
# 个人站点页面设计
re_path(r'^(?P<username>\w+)$', views.home_site, name='home_site'),

not_found.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="/static/blog/bootstrap-3.3.7/css/bootstrap.css">
</head>
<body>
<div class="container" style="margin-top: 100px">
<div class="text-center">
<a href="http://www.cnblogs.com/"><img src="/static/img/logo_small.gif" alt="cnblogs"></a>
<p><b>404.</b> 抱歉! 您访问的资源不存在!</p>
<p class="d">请确认您输入的网址是否正确,如果问题持续存在,请发邮件至 404042726@qq.com 与 <strong style="font-size: 28px">老村长</strong> 联系。</p>
<p><a href="/">返回网站首页</a></p>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>

(2)查询当前站点对应的所有文章
def home_site(request,username):
'''
个人站点视图函数
:param request:
:return:
'''
user=UserInfo.objects.filter(username=username).first()
# 判断用户是否存在
if not user:
return render(request,'not_found.html')
# 当前用户或者当前站点所对应文章
blog=user.blog
print(blog)

# 方式一基于对象查询
# 作者和文章的关系---> 一对多(文章)
article_list=user.article_set.all()
# 方式二 基于双下划线 __ 跨表查询
article_list=models.Article.objects.filter(user=user)
return render(request, 'home_site.html')
2、个人站点标签与分类查询
# 跨表的分组查询的模型:
# 每一个后的表模型.objects.values("pk").annotate(聚合函数(关联表__统计字段)).values("表模型的所有字段以及统计字段") # 推荐pk字段查找
# 查询每一个分类名称以及对应的文章数
# 查询当前站点的每一个分类名称以及对应的文章数
# 查询当前站点的每一个标签名称以及对应的文章数
# 查询当前站点每一个年月的名称以及对应的文章数
from django.db.models import Avg, Max, Min, Sum, Count
# 补充知识点Emp.objects.all()-----select * from emp
# 补充知识点Emp.objects.all().values('name')-----select name from emp
# values('province')---values('group by的字段')

values方法可以获取字段的字典列表。 values_list可以获取字段的元组列表。

(1)查询每一个分类名称以及对应的文章数
# 查询每一个分类名称以及对应的文章数
# annotate(聚合函数(关联表__统计字段)).values("表模型的所有字段以及统计字段")
# values('group by的字段')
ret=models.Category.objects.values('pk').annotate(c=Count('article__title')).values('title','c')
print(ret)
(2) 查询当前站点的每一个标签名称以及对应的文章数
# 查询当前站点的每一个分类名称以及对应的文章数
cate_list=models.Category.objects.filter(blog=blog).values('pk').annotate(c=Count('article__title')).values('title','c')
print(cate_list)
(3)每一个标签以及对应得文章数
# 每一个标签以及对应得文章数
tag_list=models.Tag.objects.filter(blog=blog).values('pk').annotate(count=Count('article')).values_list('title','count')
print('tag_list',tag_list)
(4)日期归档查询
知识点1date_format-(年月/文章数)
查询当前站点每一个年月的名称以及对应的文章数
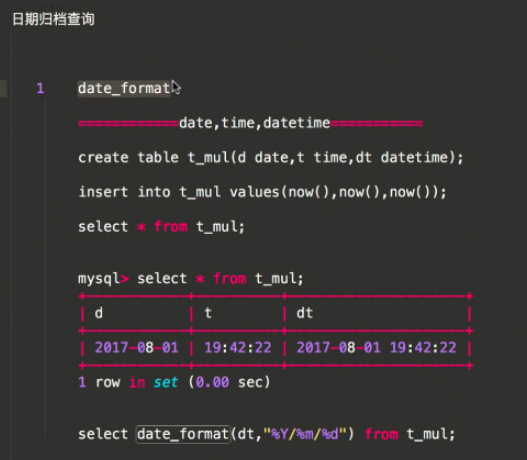
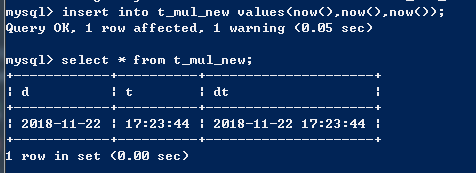
create table t_mul_new(d date,t time,dt datetime);
insert into t_mul_new values(now(),now(),now()); select * from t_mul_new;

---

知识点2:extra

extra(select=None, where=None, params=None, tables=None, order_by=None, select_params=None)
有些情况下,Django的查询语法难以简单的表达复杂的 WHERE 子句,对于这种情况, Django 提供了 extra() QuerySet修改机制 — 它能在 QuerySet生成的SQL从句中注入新子句
extra可以指定一个或多个 参数,例如 select, where or tables. 这些参数都不是必须的,但是你至少要使用一个!要注意这些额外的方式对不同的数据库引擎可能存在移植性问题.
(因为你在显式的书写SQL语句),除非万不得已,尽量避免这样做
参数之select
The select 参数可以让你在 SELECT 从句中添加其他字段信息,它应该是一个字典,存放着属性名到 SQL 从句的映射。
queryResult=models.Article
.objects.extra(select={'is_recent': "create_time > '2017-09-05'"})
结果集中每个 Entry 对象都有一个额外的属性is_recent, 它是一个布尔值,表示 Article对象的create_time 是否晚于2017-09-05.
# 查询当前站点每一个年月的名称以及对应的文章数
# 查看最近发布的文章
ret1 = models.Article.objects.extra(select={'is_recent':"create_time > 2018-07-28"}).values('title', 'is_recent')
# print(ret1)
# 查看这个月发布的文章
ret1 = models.Article.objects.extra(select={'y_m_date':"date_format(create_time,'%%Y-%%m')"}).values('title', 'y_m_date')
# print(ret1)
# 统计年月日
ret1 = models.Article.objects.extra(select={'y_m_date':"date_format(create_time,'%%Y-%%m')"}).values('y_m_date').annotate(c=Count('nid')).values_list('y_m_date', 'c')
#(只统计本站点,用户的)
ret1 = models.Article.objects.filter(user=user_obj).extra(select={'y_m_date':"date_format(create_time,'%%Y-%%m')"}).values('y_m_date').annotate(c=Count('nid')).values_list('y_m_date', 'c')
print(ret1)
def homesite(request,username,**kwargs):
# 当前站点得用户对象
user = UserInfo.objects.filter(username=username).first()
if not user:
return HttpResponse('404')
# 当前站点对象
blog = user.blog
# 查询当前站点对应得文章,以及分类,标签,日期归档得文章
if not kwargs:
article_list = Article.objects.filter(user=user)
else:
condition = kwargs.get('condition')
param = kwargs.get('param')
if condition == 'cate':
article_list = Article.objects.filter(user=user, category__title=param)
elif condition == 'tag':
article_list = Article.objects.filter(user=user, tags__title=param)
else:
year, month = param.split('-')
article_list = Article.objects.filter(user=user).filter(create_time__year=year, create_time__month=month)
# 查询站点所有每一个分类 以及 对应得文章数 分组!!
from django.db.models import Count
# 查询站点所有每一个分类 以及 对应得文章数 分组!!
cate_list = Category.objects.filter(blog=blog).annotate(count = Count('article')).values('title','count')
# 每一个标签以及对应得文章数
tag_list = Tag.objects.filter(blog=blog).annotate(count=Count('article')).values_list('title', 'count')
# 日期归档
date_list = Article.objects.filter(user=user).extra(
select={"create_ym": "DATE_FORMAT(create_time,'%%Y-%%m')"}).values('create_ym').annotate(
c=Count('nid')).values_list('create_ym', 'c')
return render(request,'homesite.html',locals())
日期归档查询2:利于Django中TruncMonth模块
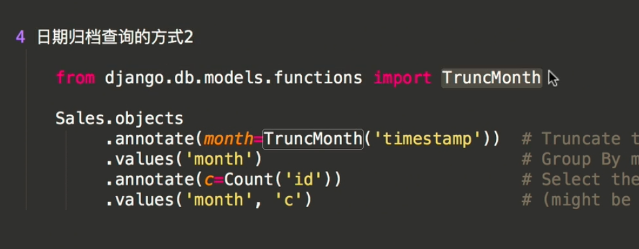
4 日期归档查询的方式2
from django.db.models.functions import TruncMonth
Sales.objects
.annotate(month=TruncMonth('timestamp')) # Truncate to month and add to select list
.values('month') # Group By month
.annotate(c=Count('id')) # Select the count of the grouping
.values('month', 'c') # (might be redundant, haven't tested) select month and count
-------------------------------------------------------------
# 方式二
from django.db.models.functions import TruncMonth
ret2=models.Article.objects.filter(user=user_obj).annotate(month=TruncMonth('create_time')).values('month').annotate(c=Count('nid')).values('month','c')
print(ret2)


views视图完整代码
def home_site(request, username): """ 个人站点视图函数 :param request: :return: """ # print("username", username) user_obj = models.UserInfo.objects.filter(username=username).first() # 判断用户是否存在 if not user_obj: return render(request, "blog/not_found.html") # 查询当前站点对象 blog = user_obj.blog # 当前用户或者当前站点对应的所有文章 # 方式1:基于对象查询 article_list = user_obj.article_set.all() # 方式2:基于__ article_list = models.Article.objects.filter(user=user_obj) # 跨表的分组查询的模型: # 每一个后的表模型.objects.values("pk").annotate(聚合函数(关联表__统计字段)).values("表模型的所有字段以及统计字段") # 推荐pk字段查找 from django.db.models import Avg, Max, Min, Count, F, Q # 查询每一个分类名称以及对应的文章数 # 全部blog的 ret1 = models.Category.objects.values('pk').annotate(c=Count("article__title")).values("title", 'c') # print(ret1) # 查询当前站点的每一个分类名称以及对应的文章数 # 只取当前用户站点的 # ret1 = models.Category.objects.filter(blog=blog).values('pk').annotate(c=Count("article__title")).values("title",'c') cate_list = models.Category.objects.filter(blog=blog).values('pk').annotate(c=Count("article__title")).values_list("title", 'c') # print(ret1) # 查询当前站点的每一个标签名称以及对应的文章数 ret = models.Tag.objects.values('pk').annotate(c=Count('article')).values_list('title','c') tag_list = models.Tag.objects.filter(blog=blog).values('pk').annotate(c=Count('article')).values_list('title','c') # print(ret) # print(ret1) # 查询当前站点每一个年月的名称以及对应的文章数 # 查看最近发布的文章 ret1 = models.Article.objects.extra(select={'is_recent':"create_time > 2018-07-28"}).values('title', 'is_recent') # print(ret1) # 查看这个月发布的文章 ret1 = models.Article.objects.extra(select={'y_m_date':"date_format(create_time,'%%Y-%%m')"}).values('title', 'y_m_date') # print(ret1) # 统计年月日 ret1 = models.Article.objects.extra(select={'y_m_date':"date_format(create_time,'%%Y-%%m')"}).values('y_m_date').annotate(c=Count('nid')).values_list('y_m_date', 'c') #(只统计本站点,用户的) date_list = models.Article.objects.filter(user=user_obj).extra(select={'y_m_date':"date_format(create_time,'%%Y-%%m')"}).values('y_m_date').annotate(c=Count('nid')).values_list('y_m_date', 'c') # print(ret1) # 方式2: from django.db.models.functions import TruncMonth models.Article.objects.filter(user=user_obj).annotate(month=TruncMonth('create_time')).values('month').annotate(c=Count('nid')).values_list('month','c') return render(request, 'blog/home_site.html', {'blog':blog,'article_list':article_list,"tag_list":tag_list,"date_list":date_list, "cate_list":cate_list})
个人站点页面渲染
bootstrap加面板
home_list.html中的tag_list,cate_list、date_list、article_list和试图中的def home_list()一一对应
{% for tag in tag_list %}
<p>{{ tag.0 }}({{ tag.1 }})</p>
{% endfor %}


跳转过滤功能



url--路由设计
re_path("^(?P<username>\w+)/$", views.home_site), # home_site(reqeust,username="yuan")
#个人站点下的跳转
re_path("^(?P<username>\w+)/(?P<condition>tag|category|archive)/(?P<param>.*)/$", views.home_site),
# home_site(reqeust,username="yuan",condition='tag',param='python')
试图设计def home_site()


2、判断是否传入kwargs
def home_site(request, username, **kwargs):
print("kwargs",kwargs)
user_obj = models.UserInfo.objects.filter(username=username).first()
# 判断用户是否存在
if not user_obj:
return render(request, "not_found.html")
# 查询当前站点对象
blog = user_obj.blog
# 当前用户或者当前站点对应的所有文章
article_list = models.Article.objects.filter(user=user_obj)
# 判断是否跳转到其他地方

if kwargs:
condition = kwargs.get("condition") # 标签\分类\归档
param = kwargs.get("param") # 具体的哪一个
if condition == "category":
article_list = models.Article.objects.filter(user=user_obj).filter(category__title=param)
elif condition == "tag":
article_list = models.Article.objects.filter(user=user_obj).filter(tags__title=param)
print(article_list)
else:
year,month = param.split('-')
print(year,month)
article_list = models.Article.objects.filter(user=user_obj).filter(create_time__year=year,create_time__month=month)
print(article_list)

----


视图跳转
访问个人站点和个人站点过滤的站点


<div class="col-md-3">
<div class="panel panel-warning">
<div class="panel-heading">我的标签</div>
<div class="panel-body">
{% for tag in tag_list %}
<p><a href="/{{ username }}/tag/{{ tag.0 }}">{{ tag.0 }}({{ tag.1 }})</a></p>
{% endfor %}
</div>
</div>
<div class="panel panel-warning">
<div class="panel-heading">随笔分类</div>
<div class="panel-body">
{% for cate in cate_list %}
<p><a href="/{{ username }}/category/{{ cate.0 }}">{{ cate.0 }}({{ cate.1 }})</a></p>
{% endfor %}
</div>
</div>
<div class="panel panel-warning">
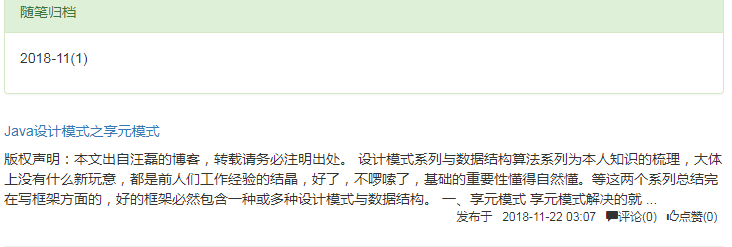
<div class="panel-heading">随笔归档</div>
<div class="panel-body">
{% for date in date_list %}
<p><a href="/{{ username }}/archive/{{ date.0 }}">{{ date.0 }}({{ date.1 }})</a></p>
{% endfor %}
</div>
</div>
</div>




