NOIP比赛中如何加速c++的输入输出
NOIP比赛中如何加速c++的输入输出
在竞赛中,遇到大数据时,往往需要更快的读取方式。由于比赛中输出一般规模较小,本文只讨论输入如何加速.
现在我们生成1000000个随机数,构成1000*1000的矩阵,然后输入比较时间(Win 10系统)
#include<iostream>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<ctime>
using namespace std;
int main(){
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
freopen("out1.txt","w",stdout);
for(int i=1;i<=1000;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=1000;j++){
cout<<rand()<<' ';
}
cout<<endl;
}
}cin的速度
在比赛中,经常出现数据集超大造成 cin TLE的情况。这时候大部分人(包括原来我也是)认为这是cin的效率不及scanf的错
准确的说,cin在不优化的情况下效率是很低的,我们来测试一下
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<ctime>
using namespace std;
int a[1005][1005];
int main(){
freopen("out1.txt","r",stdin);
double s=clock();
for(int i=1;i<=1000;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=1000;j++){
cin>>a[i][j];
}
}
printf("time used=%.3fs\n",double(clock()-s)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
}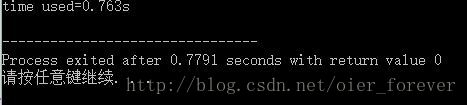
可以看出,cin的用时达到了惊人的0.763s!!!假如运行时间限制为1s,那么程序只剩下0.3秒来计算,是极容易TLE的
因此,遇到大数据时尽量避免用cin
有博客提到:
默认的时候,cin与stdin总是保持同步的,也就是说这两种方法可以混用,而不必担心文件指针混乱,同时cout和stdout也一样,两者混用不会输出顺序错乱。正因为这个兼容性的特性,导致cin有许多额外的开销,如何禁用这个特性呢?只需一个语句std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);,这样就可以取消cin与stdin的同步了
其实还有一个等价的写法
cin.tie(0);//取消cin的同步
cout.tie(0);//取消cout的同步我们来验证一下:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<ctime>
using namespace std;
int a[1005][1005];
int main(){
freopen("out1.txt","r",stdin);
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);//优化
double s=clock();
for(int i=1;i<=1000;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=1000;j++){
cin>>a[i][j];
}
}
printf("time used=%.3fs\n",double(clock()-s)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
}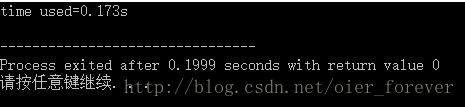
时间变成了0.173s,相比cin是飞跃性的优化
但是别急着高兴,本人亲测,在NOIP的评测机上这样子会爆0
因此,noip比赛中坚决不要写std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
爆0的原因如下
noip明确要求使用freopen,而freopen是stdio库中的,既然我们已经取消了iostream和stdio的同步,这样会造成文件指针混乱,进而导致RE
scanf的速度
既然noip比赛中坚决不要写std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false),那么我们可以用scanf
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<ctime>
using namespace std;
int a[1005][1005];
int main(){
freopen("out1.txt","r",stdin);
double s=clock();
for(int i=1;i<=1000;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=1000;j++){
scanf("%d",&a[i][j]);
}
}
printf("time used=%.3fs\n",double(clock()-s)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
}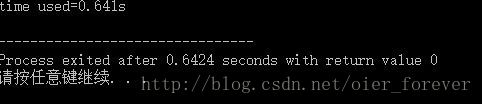
时间变成了0.641s,相比无优化的cin还是较快的
手写快速读入的速度
我们知道,getchar的速度是很快的,但它只能读取单个字符,因此,我们通过将字符转为整型来优化,同理可以转成long long
快速读入的代码NOIP初赛曾经考过
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<ctime>
using namespace std;
int a[1005][1005];
inline int read(){//非常重要的快速读入代码
int x=0,sign=1;
char c=getchar();
while(c>'9'||c<'0'){//判断符号
if(c=='-') sign=-1;
c=getchar();
}
while(c>='0'&&c<='9'){//转换数
x=x*10+c-'0';
c=getchar();
}
return x*sign;
}
int main(){
freopen("out1.txt","r",stdin);
double s=clock();
for(int i=1;i<=1000;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=1000;j++){
a[i][j]=read();
}
}
printf("time used=%.3fs\n",double(clock()-s)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
}运行后的结果如下:
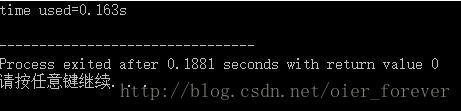
现在这个方法只需0.163s,比其他的方法都快,而且不会在评测机上出现问题,并且也没有调用许多函数
遇到数据量大的题,尽量用手写的快速读入来读取
总结
- 遇到大数据时尽量避免用cin
- noip比赛中写std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false)时,不能把scanf,printf和cin,cout混用
- 如果是double或输入格式较复杂用scanf
- 遇到数据量大的题,且是long long或int,尽量用手写的快速读入来读取


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号