Java 同步代码块 - Synchronized Blocks
java锁实现原理:
http://blog.csdn.net/endlu/article/details/51249156
The synchronized keyword can be used to mark four different types of blocks:
- Instance methods
- Static methods
- Code blocks inside instance methods
- Code blocks inside static methods
Instance methods & Code blocks inside instance methods
Java实例方法同步是同步在拥有该方法的对象上
同步构造器中用括号括起来的对象叫做监视器对象

public class SyncBlockTest { public static void main(String[] args) { ExecutorService es = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2); final MySyncBlockClass syncBlockClass = new MySyncBlockClass(); es.submit(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { syncBlockClass.mehtod1(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }); es.submit(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { syncBlockClass.mehtod2(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }); es.shutdown(); } } class MySyncBlockClass { public synchronized void mehtod1() throws InterruptedException { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() + ":method1 run."); } public synchronized void mehtod2() throws InterruptedException { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4); System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() + ":method2 run."); } } // method1较method2延迟了2000ms // 1479350064132:method2 run. // 1479350066132:method1 run.

/** * method1 与method2等效 * 同步构造器中用括号括起来的对象叫做监视器对象 * * @throws InterruptedException */ public synchronized void mehtod1() throws InterruptedException { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() + ":method1 run."); } public synchronized void mehtod2() throws InterruptedException { synchronized (this) { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4); System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() + ":method2 run."); } }
Static methods & Code blocks inside static methods
静态方法的同步是指同步在该方法所在的类对象上。因为在Java虚拟机中一个类只能对应一个类对象,所以同时只允许一个线程执行同一个类中的静态同步方法。

public class SyncBlockTest { public static void main(String[] args) { ExecutorService es = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2); final MySyncBlockClass syncBlockClass1 = new MySyncBlockClass(); final MySyncBlockClass syncBlockClass2 = new MySyncBlockClass(); es.submit(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { syncBlockClass1.mehtod1(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }); es.submit(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { syncBlockClass2.mehtod2(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }); es.shutdown(); } } class MySyncBlockClass { public static synchronized void mehtod1() throws InterruptedException { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() + ":method1 run."); } public static synchronized void mehtod2() throws InterruptedException { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4); System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() + ":method2 run."); } } // method1较method2延迟了3000ms // 1479358310630:method1 run. // 1479358314631:method2 run.

/** * method1 与method2等效 * 静态方法中的同步块 * * @throws InterruptedException */ public static synchronized void mehtod1() throws InterruptedException { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() + ":method1 run."); } public static synchronized void mehtod2() throws InterruptedException { synchronized (MySyncBlockClass.class) { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4); System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() + ":method2 run."); } }
示例:
以下代码对应的Block关系如下:
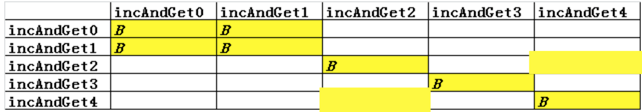
synchronized(class)与 static synchronized 等效

public class SyncMethod2 { private int value = 0; private final Object mutex = new Object(); public synchronized int incAndGet0() { try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("static synchronized void incAndGet0"); return ++value; } public int incAndGet1() { synchronized(this){ try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("static synchronized void incAndGet1"); return ++value; } } public int incAndGet2() { synchronized(SyncMethod.class){ ++value; try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("static synchronized void incAndGet4"); } return 0; } public int incAndGet3() { synchronized(mutex){ return ++value; } } public static synchronized void incAndGet4() { try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4); System.out.println("static synchronized void incAndGet4"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号