Vuex とは何か?
Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式。它采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态,并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化。Vuex 也集成到 Vue 的官方调试工具 devtools extension,提供了诸如零配置的 time-travel 调试、状态快照导入导出等高级调试功能
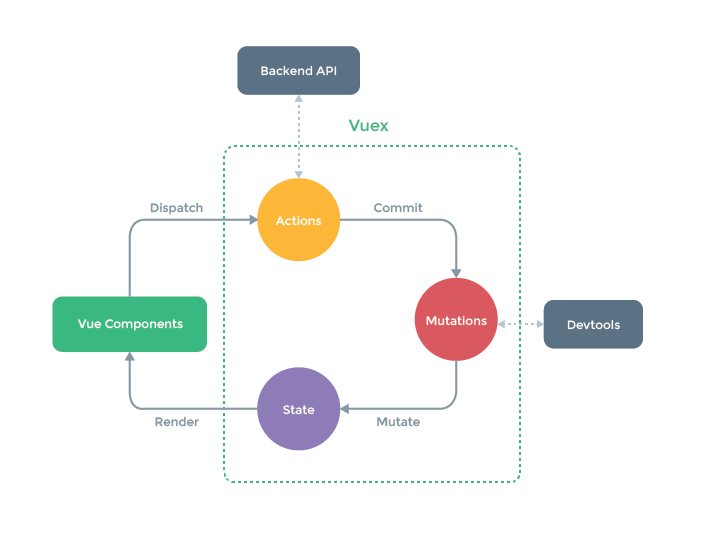
核心概念
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state:() => ({
// 定义属性
}),
getters: {
// store 的计算属性,类似于computed()
},
mutations: {
// commit
// 更改 store 中的状态,唯一方法是提交 mutation
},
actions: {
// dispatch
// action 提交的是 mutation,可以包含任意异步操作
},
modules: {
// store 分割成模块(module)。
// 每个模块拥有自己的 state、mutation、action、getter、甚至是嵌套子模块——从上至下进行同样方式的分割
}
})
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import store from './store'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
store,
render: function (h) { return h(App) }
}).$mount('#app')
State
// 首先我们在store仓库中定义一个状态
export default new Vuex.Store({
state:() => ({
counter: 10
}),
// ...
}
两个页面共享store仓库中的状态,所以显示的数据一致
<!-- 组件1 -->
<template>
<div id="component1">
<h1>{{$store.state.counter}}</h1> <!-- 10 -->
</div>
</template>
<!-- 组件2 -->
<template>
<div id="component2">
<h1>{{$store.state.counter}}</h1> <!-- 10 -->
</div>
</template>
Getters
有时候我们需要从 store 中的 state 中派生出一些状态,例如对列表进行过滤并计数:
export default new Vuex.Store({
state:() => ({
books: [
{
id: 1001,
title: 'Mysql',
price: 108,
totalNumber: 2000
},
{
id: 1002,
title: 'C++',
price: 66,
totalNumber: 3680
},
{
id: 1003,
title: 'JavaScript',
price: 99,
totalNumber: 980
}
]
}),
getters: {
filterPrice(state) {
return state.books.filter(book => { book.price > 100 }),
},
sumPrice(state, getters) {
// Getter 也可以接受其他 getter 作为第二个参数
const bookList =getters.filterPrice
return bookList.reduce((accumulator,currentValue )=> accumulator + currentValue.price, 0);
}
},
// ...
}
this.$store.getters 直接可以访问store中的Getters属性
<!-- 组件1 -->
<template>
<div id="component1">
<h1>{{$store.getters.filterPrice}}</h1> <!-- '{id: 1001,title: 'Mysql', price: 108, totalNumber: 2000}' -->
<h1>{{$store.getters.sumPrice}}</h1> <!-- 108 -->
</div>
</template>
<!-- 组件2 -->
<template>
<div id="component2">
<h1>{{$store.getters.filterPrice}}</h1> <!-- '{id: 1001,title: 'Mysql', price: 108, totalNumber: 2000}' -->
<h1>{{$store.getters.sumPrice}}</h1> <!-- 108 -->
</div>
</template>
Mutations
export default new Vuex.Store({
state:() => ({
softwareExperts: [{
name: 'James Gosling',
gender: '男',
countryCit: 'Canada',
birthday: '1955-05-19'
}]
}),
getters: {
getLength(state) {
return store.softwareExperts.length
}
},
mutations: {
inviteAnExperts(store, payload) {
store.softwareExperts.push( payload.info )
}
},
// ...
}
点击Button,提交 mutations 更新state.softwareExperts的状态,component1,component2同时渲染,并且是响应式的
<!-- 组件1 -->
<template>
<div id="component1">
<h1>{{$store.getters.getLength}}</h1> <!-- 1 ------> @click ------ 2 -->
<button @click= "invite"> 邀请一位软件专家 </button>
</div>
</template>
<!-- 组件2 -->
<template>
<div id="component2">
<h1>{{$store.getters.getLength}}</h1> <!-- 1 ------> @click ------ 2 -->
</div>
</template>
export default {
// ...
methods: {
invite() {
const info = {
name: 'Bill Gates',
gender: '男',
countryCit: 'United States',
birthday: '1955-10-28'
}
this.$store.commit({
type: 'inviteAnExperts',
info
})
},
// ...
}
Actions
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state:() => ({
count: 0
}),
mutations: {
increment(state) {
state.count++
}
},
actions: {
//异步
incrementAsync(context) {
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('increment')
}, 1000)
}
// context 解构 { ... dispatch, commit, state ... }
},
})
action 提交的是 mutation,而不是直接变更状态,它可以包含任意异步操作
<!-- 组件1 -->
<template>
<div id="component1">
<h1>{{$store.state.count}}</h1> <!-- 0 ------> @click ------ 1 -->
<button @click= "accumulate"> count++ </button>
</div>
</template>
<!-- 组件2 -->
<template>
<div id="component2">
<h1>{{$store.state.count}}</h1> <!-- 0 ------> @click ------ 1 -->
</div>
</template>
export default {
// ...
methods: {
accumulate() {
this.$store.dispatch('incrementAsync')
},
// ...
}
Modules
const moduleA = {
state: () => ({ ... }),
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... },
getters: { ... }
}
const moduleB = {
state: () => ({ ... }),
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... }
}
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
a: moduleA,
b: moduleB
}
})
store.state.a // -> moduleA 的状态
store.state.b // -> moduleB 的状态
模块的局部状态
const moduleA = {
state: () => ({
count: 0
}),
getters: {
doubleCount (state) {
return state.count * 2
},
sumWithRootCount (state, getters, rootState) {
// rootState: 根仓库store
return state.count + rootState.count
}
},
mutations: {
increment (state) {
// 这里的 `state` 对象是模块的局部状态 {}
state.count++
}
},
actions: {
incrementIfOddOnRootSum ({ state, commit, rootState }) {
// rootState: 根仓库store
if ((state.count + rootState.count) % 2 === 1) {
commit('increment')
}
}
}
}
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: () => ({
count: 10
}),
modules: {
a: moduleA
}
})
<template>
<div id="component1">
<h1>{{$store.state.a.getters.sumWithRootCount}}</h1> <!-- 10 -->
</div>
</template>
export default {
methods: {
// ...
submitModuleA() {
// 向moduleA 提交mutations、actions 和 根store提交方式一样
this.$store.commit('increment')
this.$store.dispatch('incrementIfOddOnRootSum ')
}
}
}
进阶
项目结构
├── index.html
├── main.js
├── api
│ └── ... # 抽取出API请求
├── components
│ ├── App.vue
│ └── ...
└── store
├── index.js # 我们组装模块并导出 store 的地方
├── getters.js # 根级别的 getters
├── actions.js # 根级别的 action
├── mutations.js # 根级别的 mutation
└── modules
├── cart.js # 购物车模块
└── products.js # 产品模块
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import {getters} from './store/getters'
import {mutations} from './store/mutations'
import {actions} from './store/actions'
import {actions} from './store/actions'
import {cart} from './store/modules/cart'
import {products} from './store/modules/products'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const state = {
// ...
}
export default new Vuex.Store({
state,
getters,
mutations,
actions,
modules: {
cart,
products
}
})
灵活使用
// 使用常量替代 Mutation 事件类型
export const SOME_MUTATION = 'SOME_MUTATION'
export const SOME_ACTION = 'SOME_ACTIO'
import { SOME_MUTATION } from './mutation-types'
expotr default {
// ...
methods: {
submitMutations() {
this.$store.commit( SOME_MUTATION )
},
submitActions() {
this.$store.dispatch( SOME_ACTIVE).then(res => {console.log(res)})
}
}
}
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import { SOME_MUTATION } from './mutation-types'
import { SOME_ACTION } from './ACTION-types'
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: { ... },
mutations: {
// 我们可以使用 ES2015 风格的计算属性命名功能来使用一个常量作为函数名
[SOME_MUTATION](state) {
// mutate state
})
}
},
actions: {
[SOME_ACTION]({ commit }) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
commit(SOME_MUTATION)
reslove(...)
})
}
}
})


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号