设计模式总结 - 行为型
对象的通信和流程的控制
Chain of Responsibility(职责链模式):为解除请求的发送者和接受者之间耦合,而使多个对象都有机会处理这个请求。将这些对象连成一条链,并沿着这条链传递该请求,直到有一个对象处理它。
Command(命令模式):将一个请求封装为一个对象,从而使你可以用不同的请求对客户进行参数化;对请求排队或记录请求日志,以及支持可取消的操作。
Interpreter(解释器模式):给定一个语言,定义它的文法的一种表示,并定义一个解释器,该解释器使用该表示来解释语言中的句子。
Iteartor(迭代器模式):提供一种方法顺序访问一个聚合对象中各个元素,而又不需暴露该对象的内部表示。
Mediator(中介者模式):用一个中介对象来封装一系列的对象交互。中介者使各对象不需要显式地相互引用,从而使器耦合松散,而且可以独立地改变它们之间的交互。
Memento(备忘录模式):在不破坏封装性的前提下,捕获一个对象的内部状态,并在该对象之外保存这个状态。这样以后就可以将该对象恢复到保存的状态。
Observer(观察者模式):定义对象间的一种一对多的依赖关系,以便当一个对象的状态发生改变时,所有依赖于它的对象都得到通知并自动刷新。
State(状态模式):允许一个对象在其内部状态改变时改变它的行为。对象看起来似乎修改了它所属的类。
Strategy(策略模式):定义一系列的算法,把它们一个个封装起来,并且使它们可相互替换。本模式使得算法的变化可独立于使用它的客户。
TemplateMethod(模板方法模式):定义一个操作中的算法的骨架,而将一些步骤延迟到子类中。Template Method使得子类可以不改变一个算法的结构即可重定义该算法的某些特定步骤。
Visitor(访问者模式):定义一个操作中的算法的骨架,而将一些步骤延迟到子类中。Template Method使得子类可以不改变一个算法的结构即可重定义该算法的某些特定步骤。
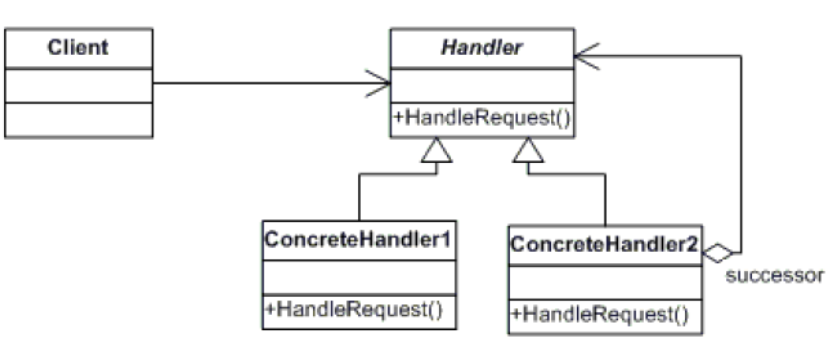
1、职责链模式
为解除请求的发送者和接受者之间耦合,而使多个对象都有机会处理这个请求。将这些对象连成一条链,并沿着这条链传递该请求,直到有一个对象处理它。
public class Chain
{
public static void Main1()
{
FlowElement Fa = new FlowElementA();
FlowElement Fb = new FlowElmentB();
FlowElement Fc = new FlowElmentC();
Fa.Next = Fb;
Fb.Next = Fc;
Fa.DoResult(10);
Console.Read();
}
}
public abstract class FlowElement
{
public virtual FlowElement Next { get; set; }
public abstract void DoResult(int condition);
}
public class FlowElementA : FlowElement
{
public override void DoResult(int condition)
{
Console.WriteLine("项目经理审批通过");
if (condition > 3 && Next!=null)
{
Next.DoResult(condition);
}
}
}
public class FlowElmentB : FlowElement
{
public override void DoResult(int condition)
{
Console.WriteLine("部门经理审批通过");
if (condition > 7 && Next != null)
{
Next.DoResult(condition);
}
}
}
public class FlowElmentC : FlowElement
{
public override void DoResult(int condition)
{
Console.WriteLine("总经理审批通过");
}
}
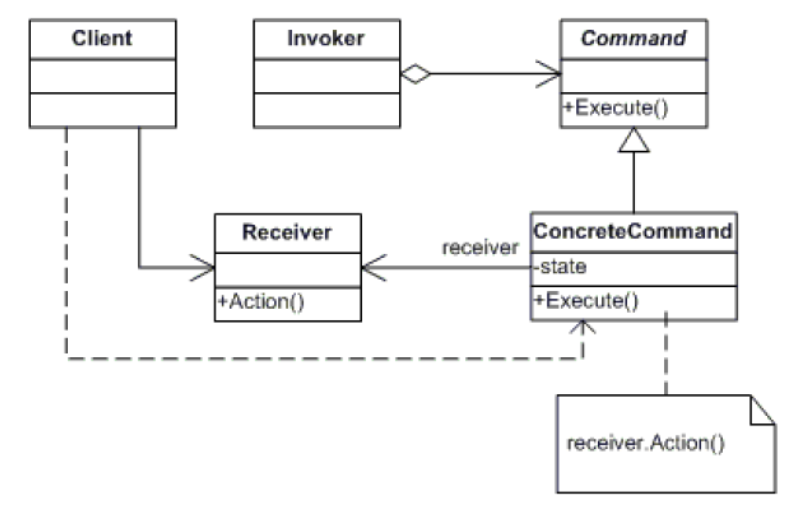
2、命令模式
将一个请求封装为一个对象,从而使你可以用不同的请求对客户进行参数化;对请求排队或记录请求日志,以及支持可取消的操作。
public class CommandTest { public static void Main1() { Invoker invoker = new Invoker(); invoker.Add(new CommandA() { Name="A"}); invoker.Add(new CommandB() { Name="B"}); invoker.Add(new CommandC() { Name="C"}); invoker.Add(new CommandD() { Name="D"}); ICommand cmd = null; try { for (int i = 0; i < invoker.List.Count; i++) { cmd = invoker.List[i]; cmd.Excecute(i); } } catch { if (cmd == null) return; invoker.Remove(cmd); } Console.Read(); } } public class Invoker { private List<ICommand> list; public Invoker() { list = new List<ICommand>(); } public void Add(ICommand cmd) { list.Add(cmd); } public void Remove(ICommand cmd) { int index = list.IndexOf(cmd); for (; index >= 0; index--) { Console.WriteLine("正在撤销命令:{0}", list[index].Name); } list.Clear(); } public List<ICommand> List { get { return list; } } } public interface ICommand { string Name { get; set; } void Excecute(int v); } public class CommandA : ICommand { public void Excecute(int v) { Console.WriteLine(v); } public string Name { get; set; } } public class CommandB : ICommand { public void Excecute(int v) { Console.WriteLine(v); } public string Name { get; set; } } public class CommandC : ICommand { public void Excecute(int v) { throw new Exception(); } public string Name { get; set; } } public class CommandD : ICommand { public void Excecute(int v) { Console.WriteLine(v); } public string Name { get; set; } }
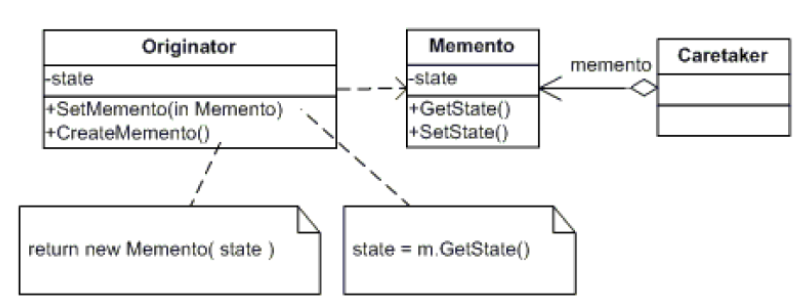
3、备忘录模式
Memento(备忘录模式):在不破坏封装性的前提下,捕获一个对象的内部状态,并在该对象之外保存这个状态。这样以后就可以将该对象恢复到保存的状态。
public class MementoCase { public static void Main1() { Params p = new Params() { Id = 1, Name = "binfire" }; Memento m = new Memento(p.Id, p.Name); Console.WriteLine(m.Id); p.Id = 2; Console.WriteLine(m.Id); Console.Read(); } } public class Params { public int Id { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } } public class Memento { private int _id; private string _name; public Memento(int id, string name) { this._id = id; this._name = name; } public int Id { get { return _id; } } public string Name { get { return _name; } } }
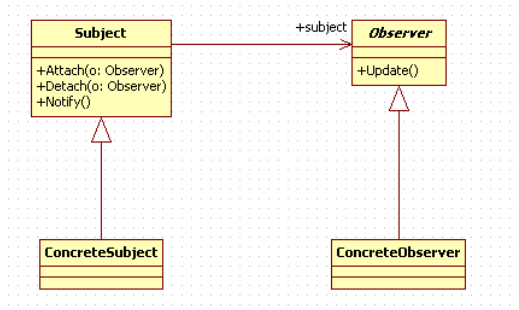
4、观察者模式
定义对象间的一种一对多的依赖关系,以便当一个对象的状态发生改变时,所有依赖于它的对象都得到通知并自动刷新
public class Observer { public static void Main1() { Boss b = new Boss("Tim"); Employee e = new Employee(b); e.Play(); b.Login(); Console.Read(); } } public sealed class ManEventArgs : EventArgs { private string _name; private DateTime _loginTime; public ManEventArgs(string name, DateTime loginTime) { this._name = name; this._loginTime = loginTime; } public string Name { get { return _name; } } public DateTime LoginTime { get { return _loginTime; } } } public class Boss { private string _name; private DateTime _loginTime; public Boss(string name) { this._name=name; } public delegate void LoginDelegate(ManEventArgs e); public event LoginDelegate OnLogin; public void Login() { _loginTime = DateTime.Now; Console.WriteLine("Boss:{0}在{1}进入了办公室.", _name, _loginTime); ManEventArgs e = new ManEventArgs(_name, _loginTime); Interlocked.CompareExchange(ref OnLogin, null, null); if (OnLogin != null) { OnLogin(e); } } } public class Employee { private Boss _boss; public Employee(Boss boss) { this._boss = boss; this._boss.OnLogin += _boss_OnLogin; } public void Play() { Console.WriteLine("在玩手机游戏"); } void _boss_OnLogin(ManEventArgs e) { Console.WriteLine("认真工作"); } }
5、状态模式
允许一个对象在其内部状态改变时改变它的行为。对象看起来似乎修改了它所属的类。
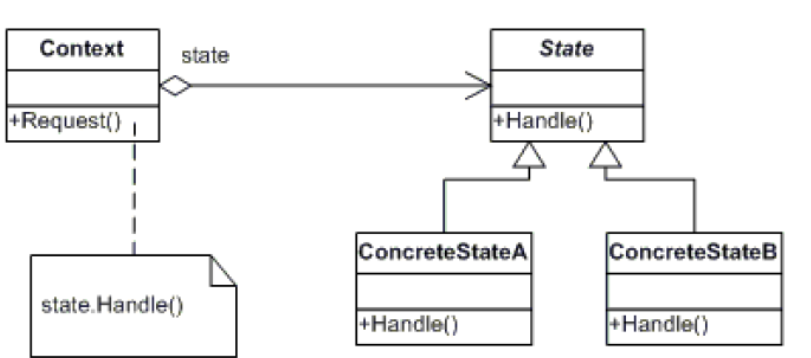
public class State { public static void Main1() { Context context = new Context(new LowerStatus()); context.GetPasswordSafeLevel("abc"); context.GetPasswordSafeLevel("abcdef"); context.GetPasswordSafeLevel("abcdefghi"); Console.Read(); } } public class Context { private StatusBase _statusBase; public Context(StatusBase statusBase) { _statusBase = statusBase; } public void GetPasswordSafeLevel(string password) { _statusBase.TestPassword(this, password); } public StatusBase Status { get { return _statusBase; } set { _statusBase = value; } } } public abstract class StatusBase { public abstract void TestPassword(Context context, string password); } public class LowerStatus : StatusBase { public override void TestPassword(Context context, string password) { context.Status = new NormalStatus(); } } public class NormalStatus : StatusBase { public override void TestPassword(Context context, string password) { context.Status = new LowerStatus(); } }
6、策略模式
定义一系列的算法,把它们一个个封装起来,并且使它们可相互替换。本模式使得算法的变化可独立于使用它的客户
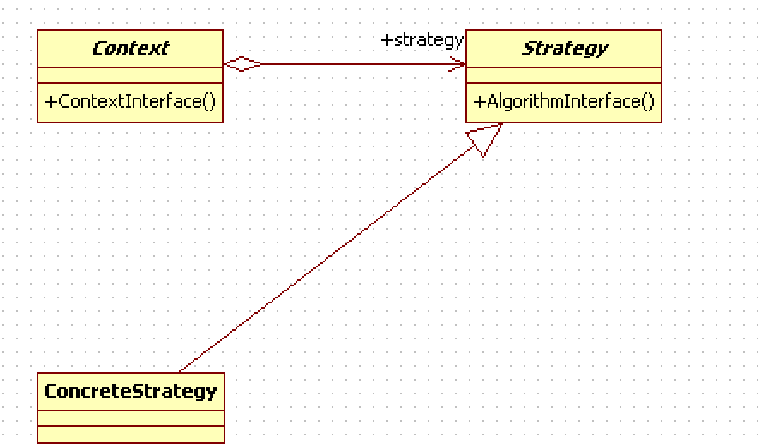
public class StrategyTest { public static void Main1() { StrategyContext context = new StrategyContext(new StrategyA()); context.Operate(); //策略B context = new StrategyContext(new StrategyB()); context.Operate(); Console.Read(); } } /// <summary> /// 外界调用Context完全不清楚实际上是实现策略的功能 /// </summary> public class StrategyContext { //Fields private Strategy _Strategy; public StrategyContext(Strategy Strategy) //**精华,封装不同的策略 { _Strategy = Strategy; } public void Operate() { _Strategy.Operate(); } } public abstract class Strategy { public abstract void Operate(); } public class StrategyA : Strategy { public override void Operate() { Console.WriteLine("算法A实现"); } } public class StrategyB : Strategy { public override void Operate() { Console.WriteLine("算法B实现"); } }
7、模板方法模式
定义一个操作中的算法的骨架,而将一些步骤延迟到子类中。Template Method使得子类可以不改变一个算法的结构即可重定义该算法的某些特定步骤
public abstract class AbstractTemplate { public abstract void Action1(); public abstract void Action2(); public virtual void ActionAll() { Action1(); Action2(); } } public class TemplateImpl1 : AbstractTemplate { public override void Action1() { throw new NotImplementedException(); } public override void Action2() { throw new NotImplementedException(); } }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号