JDK 泛型之 Type
JDK 泛型之 Type
一、Type 接口
JDK 1.5 引入 Type,主要是为了泛型,没有泛型的之前,只有所谓的原始类型。此时,所有的原始类型都通过字节码文件类 Class 类进行抽象。Class 类的一个具体对象就代表一个指定的原始类型。
泛型出现后扩充了数据类型,从只有原始类型扩充了参数化类型、类型变量类型、泛型数组类型。Type 的子接口有:ParameterizedType、TypeVariable、GenericArrayType、WildcardType,实现类有 Class。
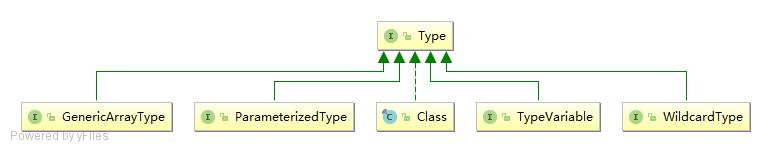
Type 体系中类型的包括:原始类型(Class)、基本类型(Class)、类型变量(TypeVariable)、参数化类型(ParameterizedType)、数组类型(GenericArrayType)。
- 原始类型(Class):不仅仅包含我们平常所指的类,还包括枚举、数组、注解等;
- 基本类型(Class):也就是我们所说的 java 的基本类型,即 int, float, double 等;
- 类型变量(TypeVariable):各种类型变量的公共父接口,就是泛型里面的类似 T、E,即泛型变量;
- 参数化类型(ParameterizedType):就是我们平常所用到的泛型 List、Map;
- 数组类型(GenericArrayType):并不是我们工作中所使用的数组 String[] 、byte[],而是泛型数组 T[] ;
// 1. 原始类型(Class)
Set set;
List aList;
String[] arr;
// 2. 参数化类型(ParameterizedType)
Map<String, Person> map;
Set<String> set;
Class<?> clazz;
List<String> list;
// 3. 类型变量(TypeVariable)
T t;
// 4. 数组类型(GenericArrayType)
Class<?>[] clazz;
Map<String, Person>[] clazz;
一、参数化类型(ParameterizedType)
ParameterizedType,参数化类型,形如:Object<T, K>,即常说的泛型,是 Type 的子接口。
public interface ParameterizedType extends Type {
// 1. 获得<>中实际类型
Type[] getActualTypeArguments();
// 2. 获得 <> 前面实际类型
Type getRawType();
// 3. 如果这个类型是某个类型所属,获得这个所有者类型,否则返回 null
Type getOwnerType();
}
(1) getActualTypeArguments
返回这个 Type 类型的参数的实际类型数组,即 <> 里的类型参数的类型,因为可能有多个类型参数,例如 Map<K, V>,所以返回的是一个 Type[] 数组。
【注意】无论 <> 中有几层 <> 嵌套,这个方法仅仅脱去最外层的 <>,之后剩下的内容就作为这个方法的返回值,所以其返回值类型不一定。
public class ParameterizedTypeTest<T> {
List<Set> a1; // 返回 Set,Class 类型
List<Set<String>> a2; // 返回 Set<String>,ParameterizedType 类型
List<T> a3; // 返回 T,TypeVariable 类型
List<? extends Set> a4; // 返回 WildcardType 类型
List<Set<String>[]> a5; // 返回 GenericArrayType 类型
@Test
public void test1() throws Exception {
Method method = getClass().getMethod("test", List.class);
Type[] types = method.getGenericParameterTypes();
ParameterizedType pType = (ParameterizedType) types[0];
Type[] type = pType.getActualTypeArguments();
// sun.reflect.generics.reflectiveObjects.GenericArrayTypeImpl
System.out.println(type[0].getClass().getName());
}
public void test(List<ArrayList<String>[]> a) {
}
}
(2) getRawType
返回的是当前这个 ParameterizedType 的类型,即最外层 <> 前面那个类型,如 Map<K ,V> 的 Map
Map.Entry<String, Integer> me;
@Test
public void rawTypeTest() throws Exception {
Field field = getClass().getDeclaredField("me");
ParameterizedType type = (ParameterizedType) field.getGenericType();
// java.util.Map$Entry
System.out.println(type.getRawType());
}
(3) getOwnerType
返回的是这个 ParameterizedType 所在的类的 Type。
Map.Entry<String, Integer> me;
@Test
public void ownerTypeTest() throws Exception {
Field field = getClass().getDeclaredField("me");
ParameterizedType type = (ParameterizedType) field.getGenericType();
// java.util.Map
System.out.println(type.getOwnerType());
}
三、TypeVariable(类型变量)
TypeVariable 描述所谓范型变量,也就是
public interface TypeVariable<D extends GenericDeclaration> extends Type, AnnotatedElement {
// 变量上边界数组,没有指定的话是 Object
Type[] getBounds();
// 获取变量被定义在什么 GenericDeclaration 上
D getGenericDeclaration();
// 获取变量名字
String getName();
// jdk 1.8
AnnotatedType[] getAnnotatedBounds();
}
getBounds得到上边界的 Type 数组,如 K 的上边界数组是 InputStream 和 Serializable。V 没有指定的话,上边界是 ObjectgetGenericDeclaration返回的是声明这个 Type 所在的类 的 TypegetName返回的是这个 type variable 的名称
(1) getBounds
获取泛型变量的上边界的 Type 数组,如果没有指定则是 Object。
@Test
public void test() {
// 1. 获取类上声明的泛型变量 getTypeParameters
TypeVariable<Class<TypeVariable>> typeVariable = TypeVariable.class.getTypeParameters()[0];
// 2. 获取泛型变量的上边界 java.lang.reflect.GenericDeclaration
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(typeVariable.getBounds()));
}
(2) getGenericDeclaration
GenericDeclaration 该接口用来定义哪些对象上是可以声明范型变量,目前实现 GenericDeclaration 接口的类包括 Class、Method、Constructor,也就是说只能在这几种对象上进行范型变量的声明(定义)。
public class TypeVariableTest<E> {
@Test
public void getGenericDeclarationTest() {
// 1. 类上声明泛型
TypeVariable<Class<TypeVariableTest>> classType = TypeVariableTest.class.getTypeParameters()[0];
Class<TypeVariableTest> clazzDeclaration = classType.getGenericDeclaration();
// class com.github.binarylei.spring01.day0728.test.TypeVariableTest
System.out.println(clazzDeclaration);
// 2. 方法上声明泛型
Method[] methods = TypeVariableTest.class.getMethods();
Method method = Arrays.stream(methods)
.filter(m -> m.getName().equals("test"))
.collect(Collectors.toList())
.get(0);
TypeVariable methodType = (TypeVariable) method.getGenericParameterTypes()[0];
GenericDeclaration methodDeclaration = methodType.getGenericDeclaration();
// public void com.github.binarylei.TypeVariableTest.test(java.lang.Object)
System.out.println(methodDeclaration);
// 3. 构造器上声明泛型
}
public <T> void test(T t) {
}
}
四、GenericArrayType(数组类型)
范型数组,组成数组的元素中有范型则实现了该接口;它的组成元素是 ParameterizedType 或 TypeVariable 类型
public interface GenericArrayType extends Type {
// 获得这个数组元素类型,即获得:A<T>(A<T>[])或T(T[])
Type getGenericComponentType();
}
下面我们一起来看一下例子:
classA<K>[][] key;
Type type = Main.class.getDeclaredField("key").getGenericType();
// com.github.binarylei..classA<K>[]
System.out.println(((GenericArrayType)type).getGenericComponentType());
五、WildcardType(通配符的类型)
WildcardType,通配符表达式,Type 子接口,但是在 Java 中并没有 WildcardType 类型。extends 用来指定上边界,没有指定的话上边界默认是 Object,super 用来指定下边界,没有指定的话为 null。
几个主要方法介绍:
public interface WildcardType extends Type {
Type[] getUpperBounds();
Type[] getLowerBounds();
}
-
getLowerBounds得到上边界 Type 的数组 -
getUpperBounds得到下边界 Type 的数组
下面一起来看一下例子:
public class WildcardTypeTest {
// 指定上界 Number,下边界默认为 []
private List<? extends Number> a;
// 指定下界 String,上边界默认是 Object
private List<? super String> b;
// 上界和下界都不指定,上边界默认是 Object,下边界默认为 []
private Class<?> clazz;
// 没有通配符,不是 WildcardType
private List<String> c;
@Test
public void test() throws Exception {
Field[] fields = WildcardTypeTest.class.getDeclaredFields();
for (int i = 0; i < fields.length; i++) {
Field field = fields[i];
Type type = field.getGenericType();
String nameString = field.getName();
//1. 先拿到范型类型
if (!(type instanceof ParameterizedType)) {
continue;
}
//2. 再从范型里拿到通配符类型
ParameterizedType parameterizedType = (ParameterizedType) type;
type = parameterizedType.getActualTypeArguments()[0];
if (!(type instanceof WildcardType)) {
continue;
}
System.out.println("-------------" + nameString + "--------------");
WildcardType wildcardType = (WildcardType) type;
Type[] lowerTypes = wildcardType.getLowerBounds();
if (lowerTypes != null) {
System.out.println("下边界:" + Arrays.toString(lowerTypes));
}
Type[] upTypes = wildcardType.getUpperBounds();
if (upTypes != null) {
System.out.println("上边界:" + Arrays.toString(upTypes));
}
}
}
}
六、GenericDeclaration
GenericDeclaration 该接口用来定义哪些对象上是可以声明范型变量,目前实现 GenericDeclaration 接口的类包括 Class、Method、Constructor,也就是说只能在这几种对象上进行范型变量的声明(定义)。
GenericDeclaration 的接口方法 getTypeParameters 用来逐个获取该 GenericDeclaration 的范型变量声明。
public interface GenericDeclaration extends AnnotatedElement {
// 用来获取该GenericDeclaration的范型变量声明
public TypeVariable<?>[] getTypeParameters();
}
(1) 泛型的声明
//1. 在类(Class)上声明
class A<T> { T a; }
// 2. 在方法上声明
// 类型变量声明不是在参数里边,而且必须在返回值之前,static 等修饰后
public <E> void test(E e) {}
// 3. 在构造器上声明
public <K> A(K k) {}
【注意】类型变量声明(定义)的时候不能有下限(既不能有 super),否则编译报错。为什么?T extends classA 表示泛型有上限 classA,当然可以,因为这样,每一个传进来的类型必定是 classA(具有 classA 的一切属性和方法),但若是 T super classA,传进来的类型不一定具有 classA 的属性和方法,当然就不适用于泛型,说的具体点:
class A<T super classA>{
T t;
public void test(){
// t 的子类是 classA,我们还是不知道 t 到底是什么类型,不知道 t 有那些方法
}
}
参考:
- 《Type - Java类型》:https://blog.csdn.net/a327369238/article/details/52621043
每天用心记录一点点。内容也许不重要,但习惯很重要!



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号