最短路径算法之——Floyd算法介绍与实现
之前我们学习了图的最短路径算法之Dijkstra算法,知道此算法是用来求指定的两顶点间最短路径的(也称单源最短路径single-source),如果要求图中任意两顶点间的最短路径,怎么办呢?
当然可以通过对任意两点调用Dijkstra算法来实现。有没有更好的办法,运行一次就能求解出任意两顶点的距离呢?
这里我们介绍下Floyd算法(Floyd–Warshall、Roy–Warshall、Roy–Floyd都指同一种算法),就是专门用来求解此问题的。
我们先看下该算法的基本思想。如图示,我们有三个顶点 a b c
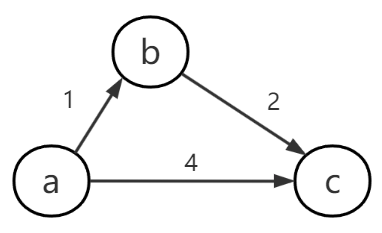
顶点a到c的直达路径为a-c,距离为4。为了探索其它更短路径,我们选择一个新的顶点b,看b是否能缩短a-c的距离,得知a-b距离为1,b-c距离为2, 1+2<4,说明经过b点是可以缩短距离的,即a-c的更短的距离等于a-b距离加上b-c的距离。
可以看到通过引入新的顶点,达到了缩短原有路程的目的。新的顶点我们可以理解为排除开始和结束两顶点,其他顶点的统称,通过依次引入这些顶点,判断开始点到此顶点距离加上此顶点到结束点的距离,如果小于开始和顶点间的原始距离,则更新为这个距离。
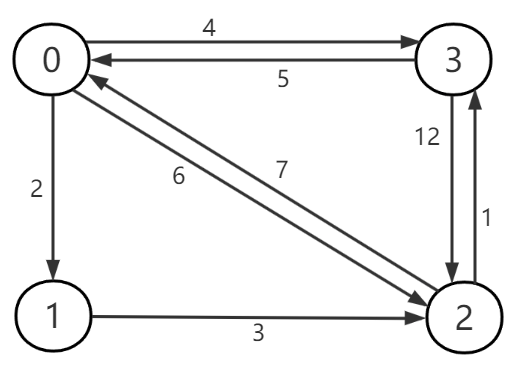
接下来我们就按照这个思路来编写代码。演示图顶点信息如下
代码
1 public class Floyd { 2 private static final int MAX_WEIGHT = 999; 3 private static final int NOT_EXISTS_PATH = -1; 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 //顶点个数 7 int vertexNum = 4; 8 //顶点数据 9 int[][] vertices = initVertex(vertexNum); 10 //路径默认数据 11 int[][] path = initPath(vertices); 12 print(vertices, "vertex"); 13 print(path, "path"); 14 15 //midVertex为中间顶点,判断加入此顶点后能否缩短原有距离。例如a至b的距离,则转换为a至midVertex距离加上midVertex至b的距离。 16 //每个顶点都需要做一次中间顶点,所以最外层为中间顶点 17 for (int midVertex = 0; midVertex < vertexNum; midVertex++) { 18 //顶点要两两判断,这样才能求解任意两个顶点的距离,因此是一个两层循环 19 for (int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++) { 20 for (int j = 0; j < vertexNum; j++) { 21 //i到j距离,对比i到midVertex距离加上midVertex到j的距离,小于则更新为这个midVertex顶点 22 if (vertices[i][j] > vertices[i][midVertex] + vertices[midVertex][j]) { 23 System.out.printf("midVertex %d %d-%d dist=%d>%d+%d ", midVertex, i, j, vertices[i][j], vertices[i][midVertex], vertices[midVertex][j]); 24 vertices[i][j] = vertices[i][midVertex] + vertices[midVertex][j]; 25 System.out.printf("path=%d\n", path[midVertex][j]); 26 //注意!直接前驱顶点不能直接设置为midVertex,而是取midVertex到结束顶点j的直接前驱顶点 27 path[i][j] = path[midVertex][j]; 28 } 29 } 30 } 31 } 32 33 print(vertices, "vertex"); 34 print(path, "path"); 35 //顶点3到2的最短路径经过的各个边 36 printShortestPath(3, 2, path); 37 } 38 39 private static void printShortestPath(int i, int j, int[][] path) { 40 System.out.printf("[path %d-%d]\n", i, j); 41 while (path[i][j] != NOT_EXISTS_PATH) { 42 System.out.printf("%d->%d\n", path[i][j], j); 43 j = path[i][j]; 44 } 45 } 46 47 private static int[][] initVertex(int vertexNum) { 48 int[][] vertex = new int[vertexNum][vertexNum]; 49 for (int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++) { 50 for (int j = 0; j < vertexNum; j++) { 51 if (i == j) { 52 vertex[i][i] = 0; 53 } else { 54 vertex[i][j] = MAX_WEIGHT; 55 } 56 } 57 } 58 vertex[0][1] = 2; 59 vertex[0][2] = 6; 60 vertex[0][3] = 4; 61 62 vertex[1][2] = 3; 63 64 vertex[2][0] = 7; 65 vertex[2][3] = 1; 66 67 vertex[3][0] = 5; 68 vertex[3][2] = 12; 69 return vertex; 70 } 71 72 private static int[][] initPath(int[][] vertices) { 73 int[][] path = new int[vertices.length][vertices.length]; 74 for (int i = 0; i < vertices.length; i++) { 75 for (int j = 0; j < vertices.length; j++) { 76 if (vertices[i][j] != MAX_WEIGHT && i != j) { 77 path[i][j] = i; 78 } else { 79 path[i][j] = NOT_EXISTS_PATH; 80 } 81 } 82 } 83 return path; 84 } 85 86 private static void print(int[][] vertices, String name) { 87 System.out.printf("[%s]\n", name); 88 System.out.print("+ "); 89 for (int i = 0; i < vertices.length; i++) { 90 System.out.printf("%d ", i); 91 } 92 System.out.println(); 93 int index = 0; 94 for (int[] ints : vertices) { 95 System.out.printf("%d ", index++); 96 for (int j = 0; j < vertices.length; j++) { 97 if (ints[j] == MAX_WEIGHT) { 98 System.out.print(" - "); 99 } else { 100 System.out.printf("%2d ", ints[j]); 101 } 102 } 103 System.out.println(); 104 } 105 } 106 }
输出
[vertex] #顶点信息,第一行、第一列都为下标数据方便数据查看。“-”为无穷大(内部用的999表示),可以认为是两个顶点间无直接路径 + 0 1 2 3 0 0 2 6 4 1 - 0 3 - 2 7 - 0 1 3 5 - 12 0 [path] #默认的各顶点直接前驱的顶点, -1为此路径不存在,即不存在前驱 + 0 1 2 3 0 -1 0 0 0 1 -1 -1 1 -1 2 2 -1 -1 2 3 3 -1 3 -1 midVertex 0 2-1 dist=999>7+2 path=0 #以顶点0为中间顶点,判断0的引入是否能缩短2-1间的路径,因为2-1没有直接路径相连,默认为无穷大,2-0长度为7,0-1长度为2,7+2小于无穷大(999),因此把2-1路径长度改为9,同时把顶点1的前驱改为顶点0 midVertex 0 3-1 dist=999>5+2 path=0 #同上判断3-0,0-1,相加后为7,小于无穷大,更新,同时把顶点1的直接前驱改为顶点0 midVertex 0 3-2 dist=12>5+6 path=0 midVertex 1 0-2 dist=6>2+3 path=1 midVertex 1 3-2 dist=11>7+3 path=1 midVertex 2 1-0 dist=999>3+7 path=2 midVertex 2 1-3 dist=999>3+1 path=2 midVertex 3 1-0 dist=10>4+5 path=3 midVertex 3 2-0 dist=7>1+5 path=3 midVertex 3 2-1 dist=9>1+7 path=0 #顶点1的直接前驱顶点改为0,注意这个0是中间顶点3-1对应的直接前驱顶点0 [vertex] #最终各个顶点间的最短路径 + 0 1 2 3 0 0 2 5 4 1 9 0 3 4 2 6 8 0 1 3 5 7 10 0 [path] #各顶点的直接前驱顶点 + 0 1 2 3 0 -1 0 1 0 1 3 -1 1 2 2 3 0 -1 2 3 3 0 1 -1 [path 3-2] #顶点3到2最短路径经过的边 1->2 0->1 3->0
可以看到Floyd算法的代码是相当简练的:最外层为要引入的中间顶点,即判断这个顶点的加入是否能缩短任意两个顶点间的距离,而任意一个顶点都可以当做中间顶点,再加上任意两个顶点的组合(两层循环),就构成了一个三层的循环。因此随着顶点数量的增多,循环的次数增长较快(假设顶点个数为N,则对应的循环次数为N*N*N=N3)。
参考资料
https://baike.baidu.com/item/Floyd%E7%AE%97%E6%B3%95/291990
https://brilliant.org/wiki/floyd-warshall-algorithm/
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1K5411f7G7
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1RK4y1d7ct


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号