ipython 是 jupyter notebook的前身并拥有ipython的全部功能
jupyter拥有 cell, markdown 整合的功能, 能同时运行代码, 而且是多组的. 同时也可以插入markdown这种多功能注释 包括图片(但支持很差).
写教程,写博客非常一流. 而且还可以上传到jupyterhub…据说要自己搭建
对于初学者来说, jupyter毕竟是一个web应用, 存储文件有不稳定的地方. 建议还是使用pycharm这类的软件编写代码. 如果是用于写博客, sublime可以安装插件copy as html jupyter对于copy的优化不够. 特别是离线图片保存起来是不可以显示的.
jupyter详细教程 http://blog.csdn.net/tina_ttl/article/details/51031113
Python·Jupyter Notebook各种使用方法记录·持续更新
标签(空格分隔): Python


Jupyter notebook )前身为IPython Notebook,学习时,可以找两者的教程
- Jupyter Project Documentation
- Jupyter Notebook Documentation
- Jupyter/IPython Notebook Quick Start Guide
- Old IPython Notebook Homepage

- 安装Jupyter Notebook的先决条件:已经安装了python(python 2.7 或者是python3.3)
具体的安装方法:
- 官方建议利用Anaconda安装Jupyter
- 安装完成Anaconda后,如果该Anaconda并不自带Jupyter Noterbook,那么,打开cmd,输入:conda install jupyter
- 这样安装完的jupyter不具有New a terminal的功能
经过各种查询才知道,原来是因为windows不具有terminal需要的TTY,所以,windows下的jupyter是不支持Terminal模式的,而且短期内也没有增加这种支持的计划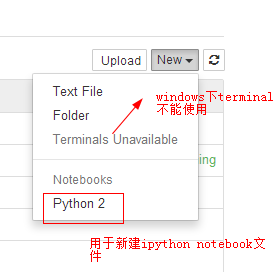
在其配置文件ipython_notebook_config.py中,有如下一句
# The directory to use for notebooks and kernels.
# c.NotebookApp.notebook_dir = u''
该句就是用来指定其工作空间的,例如,默认的工作空间是:用户名文件夹,例如,现在想要将工作空间变为D:\Jupyter,那么,需要做如下更改(要记得删掉注释#)
# The directory to use for notebooks and kernels.
c.NotebookApp.notebook_dir = u'D:\Jupyter'
这句话很容易抄错, ''前面是u ,还要去掉#号, 而且你要在本地建立一个文件夹, 如果文件夹不存在也会出错.
参考目录C:\Users\Administrator\.jupyter
- 在cmd中输入jupyter notebook --generate-config
- 如果该配置文件已经存在,那么,会出现如下信息,从中可以见到配置文件存在的位置,注意,此时,输入N,不要overwrite
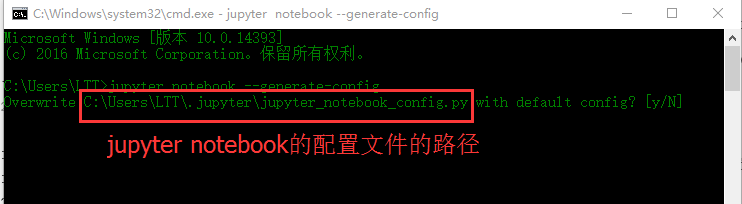
- 如果该配置文件不存在,那么,将会初始化产生一个配置文件
在cmd中输入:ipython profile create
可以找到关于jupyter的配置文件的位置- 执行当前cell,并自动跳到下一个cell:Shift Enter
- 执行当前cell,执行后不自动调转到下一个cell:Ctrl-Enter
- 是当前的cell进入编辑模式:Enter
- 退出当前cell的编辑模式:Esc
- 删除当前的cell:双D
- 为当前的cell加入line number:单L
- 将当前的cell转化为具有一级标题的maskdown:单1
- 将当前的cell转化为具有二级标题的maskdown:单2
- 将当前的cell转化为具有三级标题的maskdown:单3
- 为一行或者多行添加/取消注释:Crtl /
- 撤销对某个cell的删除:z
- 浏览器的各个Tab之间切换:Crtl PgUp和Crtl PgDn
- 快速跳转到首个cell:Crtl Home
- 快速跳转到最后一个cell:Crtl End
4.1 将本地的.py文件load到jupyter的一个cell中
问题背景:有一个test.py文件,需要将其载入到jupyter的一个cell中
test.py内容如下:SolverName = "/root/workspace"
sovler = caffe.AdamSolver(SolverName)
%load test.py #test.py是当前路径下的一个python文件
(2)运行该cell
利用快捷键"Shift+Enter",可以看到如下结果: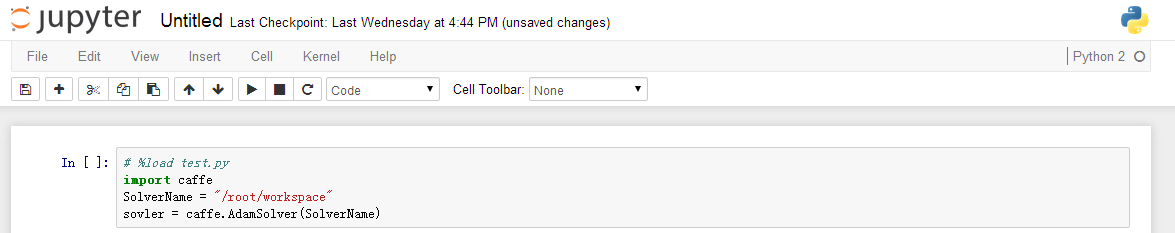
(3)可以看到,运行后,%load test.py被自动加入了注释符号#,test.py中的所有代码都被load到了当前的cell中
- 在cell中输入%load http://.....,然后运行该cell,就会将load后面所对应地址的代码load到当前的cell中;
首先,在想要导入该段代码的cell中输入
%load test.py #test.py是当前路径下的一个python文件
1
1
- 然后,Shift+Enter运行,可以看到如下结果:

可以看到,运行后,%load test.py被自动加入了注释符号#,test.py中的所有代码都被load到了当前的cell中
file.py为要运行的python程序,结果会显示在该cell中

6.1 jupyter的cell可以作为unix command使用
具体方法为:在unitx command前面加入一个感叹号"!"
例子:
查看python版本:!python --version
运行python文件:!python myfile.py还没有太明白,具体细节见The cell magics in IPython
6.3 获取current working directory
即当前运行的代码所在的路径
具体方法:current_path = %pwd
这样得到的current_path就是当前工作路径的字符转在Jupyter Notebook中,如果使用Matplotlib绘图,有时是弹不出图像框的,此时,可以在开头加入
- 原始的Jupyter是不支持markdown添加目录功能的
- 实际上,可以利用Jupyter notebook extensions去使得这种功能实现
具体方法:
- 利用Anaconda安装Jupyter Notebook extensions
conda install -c conda-forge jupyter_contrib_nbextensions
- 打开Jupyter Notebook,在它的(新增的)Nbextensions标签下勾选"Table of Contents(2)"
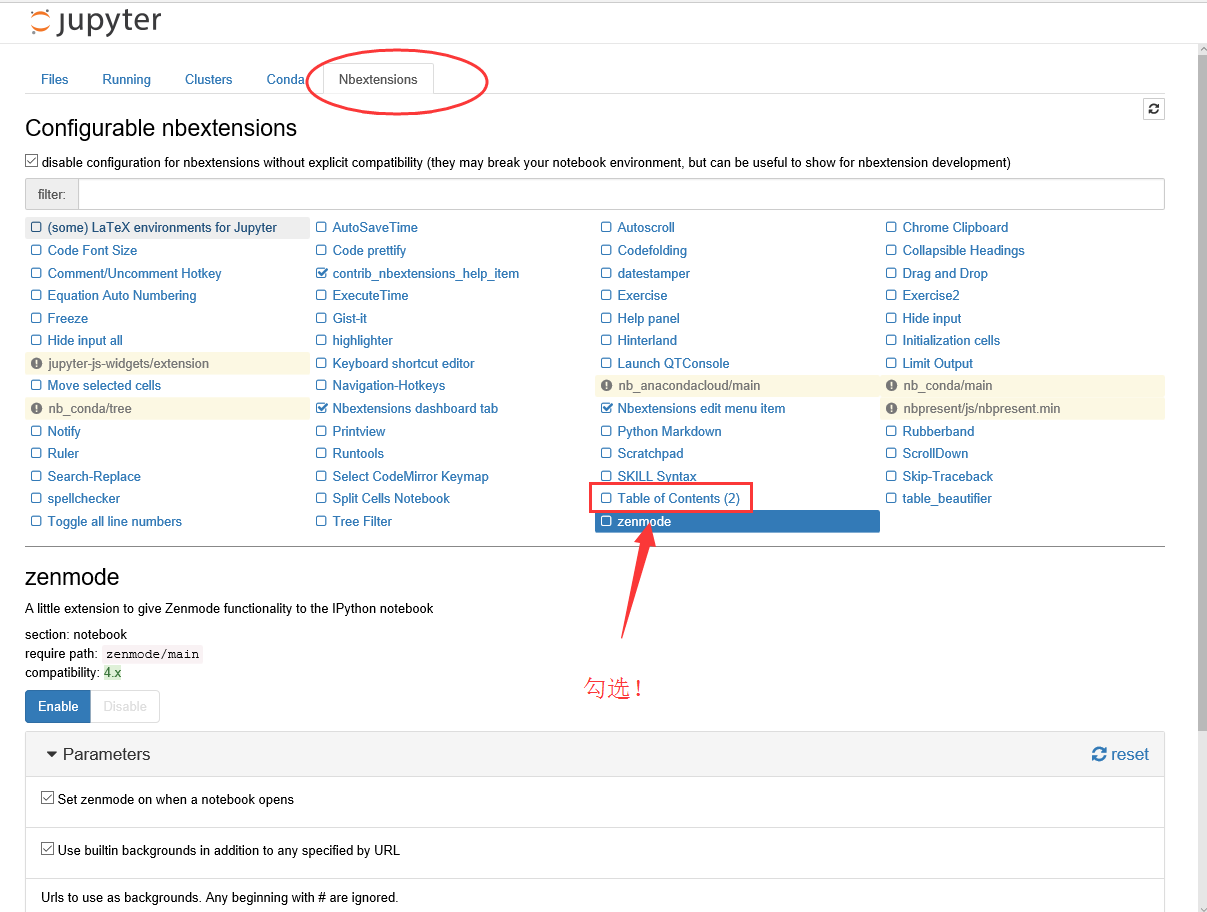
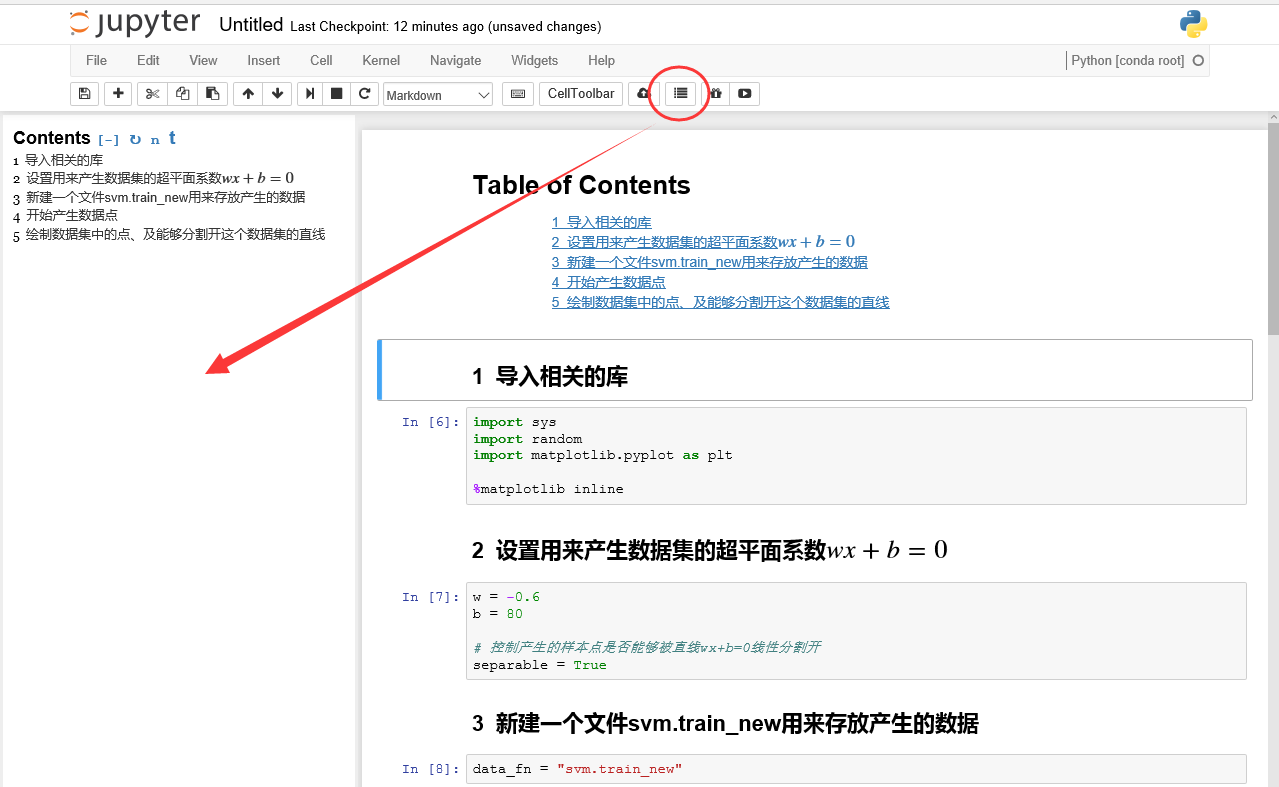
- 打开一个.jpynb文件,发现,目录功能可用了!

参考文献
[1] 为Jupyter Notebook添加目录- 上一篇theano安装(一)windows配置安装theano环境(非GPU版)、keras
下一篇Docker学习系列(二):Ubuntu14.04下安装Docker-2016.06.26更新版
相关文章推荐
猜你在找
Jupyter Notebook的27个秘诀,技巧和快捷键
文摘供稿

原文链接
翻译:姜范波
校对:毛丽 && 寒小阳Jupyter Notebook
Jupyther notebook ,也就是一般说的 Ipython notebook,是一个可以把代码、图像、注释、公式和作图集于一处,从而实现可读性分析的一种灵活的工具。
Jupyter延伸性很好,支持多种编程语言,可以很轻松地安装在个人电脑或者任何服务器上——只要有ssh或者http接入就可以啦。最棒的一点是,它完全免费哦。
Jupyter 界面默认情况下,Jupyter Notebook 使用Python内核,这就是为什么它原名 IPython Notebook。Jupyter notebook是Jupyter项目的产物——Jupyter这个名字是它要服务的三种语言的缩写:Julia,PYThon和R,这个名字与"木星(jupiter)"谐音。本文将介绍27个轻松使用Jupyter的小窍门和技巧。
1、快捷键
高手们都知道,快捷键可以节省很多时间。Jupyter在顶部菜单提供了一个快捷键列表:Help > Keyboard Shortcuts 。每次更新Jupyter的时候,一定要看看这个列表,因为不断地有新的快捷键加进来。另外一个方法是使用Cmd + Shift + P ( Linux 和 Windows下 Ctrl + Shift + P亦可)调出命令面板。这个对话框可以让你通过名称来运行任何命令——当你不知道某个操作的快捷键,或者那个操作没有快捷键的时候尤其有用。这个功能与苹果电脑上的Spotlight搜索很像,一旦开始使用,你会欲罢不能。
几个我的最爱:
- Esc + F 在代码中查找、替换,忽略输出。
- Esc + O 在cell和输出结果间切换。
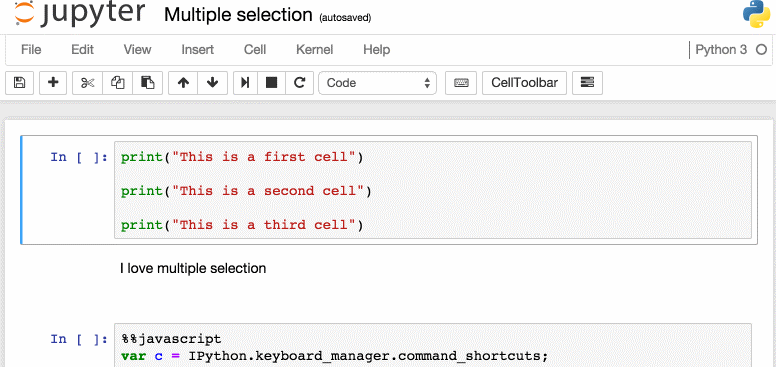
- 选择多个cell:
- Shift + J 或 Shift + Down 选择下一个cell。
- Shift + K 或 Shift + Up 选择上一个cell。
- 一旦选定cell,可以批量删除/拷贝/剪切/粘贴/运行。当你需要移动notebook的一部分时这个很有用。
- Shift + M 合并cell.

2、变量的完美显示
有一点已经众所周知。把变量名称或没有定义输出结果的语句放在cell的最后一行,无需print语句,Jupyter也会显示变量值。当使用Pandas DataFrames时这一点尤其有用,因为输出结果为整齐的表格。
鲜为人知的是,你可以通过修改内核选项ast_note_interactivity,使得Jupyter对独占一行的所有变量或者语句都自动显示,这样你就可以马上看到多个语句的运行结果了。- 利用Anaconda安装Jupyter Notebook extensions
- In [1]: from IPython.core.interactiveshell import InteractiveShell
- InteractiveShell.ast_node_interactivity = "all"
- In [2]: from pydataset import data
- quakes = data('quakes')
- quakes.head()
- quakes.tail()
- Out[2]:
- lat long depth mag stations
- 1 -20.42 181.62 562 4.8 41
- 2 -20.62 181.03 650 4.2 15
- 3 -26.00 184.10 42 5.4 43
- 4 -17.97 181.66 626 4.1 19
- 5 -20.42 181.96 649 4.0 11
- Out[2]:
- lat long depth mag stations
- 996 -25.93 179.54 470 4.4 22
- 997 -12.28 167.06 248 4.7 35
- 998 -20.13 184.20 244 4.5 34
- 999 -17.40 187.80 40 4.5 14
- 1000 -21.59 170.56 165 6.0 119
如果你想在各种情形下(Notebook和Console)Jupyter都同样处理,用下面的几行简单的命令创建文件~/.ipython/profile_default/ipython_config.py即可实现:
- c = get_config()
- # Run all nodes interactively
- c.InteractiveShell.ast_node_interactivity = "all"
3、轻松链接到文档
在Help 菜单下,你可以找到常见库的在线文档链接,包括Numpy,Pandas,Scipy和Matplotlib等。
另外,在库、方法或变量的前面打上?,即可打开相关语法的帮助文档。
- In [3]: ?str.replace()

Docstring:
S.replace(old, new[, count]) -> str
Return a copy of S with all occurrences of substring
old replaced by new. If the optional argument count is
given, only the first count occurrences are replaced.
Type: method_descriptor
4、 在notebook里作图
在notebook里作图,有多个选择:
- matplotlib (事实标准),可通过%matplotlib inline 激活,详细链接
- %matplotlib notebook 提供交互性操作,但可能会有点慢,因为响应是在服务器端完成的。
- mpld3 提供matplotlib代码的替代性呈现(通过d3),虽然不完整,但很好。
- bokeh 生成可交互图像的更好选择。
- plot.ly 可以生成非常好的图,可惜是付费服务。
5、 Jupyter Magic命令
上文提到的%matplotlib inline 是Jupyter Magic命令之一。
推荐阅读Jupyter magic命令的相关文档,它一定会对你很有帮助。下面是我最爱的几个:
不必重启jupyter服务器进程,也可以管理notebook的环境变量。有的库(比如theano)使用环境变量来控制其行为,%env是最方便的途径。
In [55]: # Running %env without any arguments
# lists all environment variables
# The line below sets the environment
7、Jupyter Magic - %run: 运行python代码
In [56]: # this will execute and show the output from
# all code cells of the specified notebook
8、Jupyter Magic -%load:从外部脚本中插入代码
该操作用外部脚本替换当前cell。可以使用你的电脑中的一个文件作为来源,也可以使用URL。
9、Jupyter Magic - %store: 在notebook文件之间传递变量
%store 命令可以在两个notebook文件之间传递变量。
In [62]: data = 'this is the string I want to pass to different notebook'
del data # This has deleted the variable
this is the string I want to pass to different notebook
10、Jupyter Magic - %who: 列出所有的全局变量
不加任何参数, %who 命令可以列出所有的全局变量。加上参数 str 将只列出字符串型的全局变量。
three = "to get ready now go cat go"
time.sleep(0.01)# sleep for 0.01 seconds
CPU times: user 21.5 ms, sys: 14.8 ms, total: 36.3 ms
%%timeit 使用了Python的 timeit 模块,该模块运行某语句100,000次(默认值),然后提供最快的3次的平均值作为结果。
%timeit numpy.random.normal(size=100)
100000 loops, best of 3: 5.5 µs per loop
12、Jupyter Magic - %%writefile and %pycat:导出cell内容/显示外部脚本的内容
使用%%writefile magic可以保存cell的内容到外部文件。 而%pycat功能相反,把外部文件语法高亮显示(以弹出窗方式)。
In [7]: %%writefile pythoncode.py
def append_if_not_exists(arr, x):
def some_useless_slow_function():
x = numpy.random.randint(0, 10000)
def append_if_not_exists(arr, x):
def some_useless_slow_function():
x = numpy.random.randint(0, 10000)
13、Jupyter Magic - %prun: 告诉你程序中每个函数消耗的时间
使用%prun+函数声明会给你一个按顺序排列的表格,显示每个内部函数的耗时情况,每次调用函数的耗时情况,以及累计耗时。
In [47]: %prun some_useless_slow_function()
26324 function calls in 0.556 seconds
ncalls tottime percall cumtime percall filename:lineno(function)
10000 0.527 0.000 0.528 0.000 <ipython-input-46-b52343f1a2d5>:2(append_if_not_exists)
10000 0.022 0.000 0.022 0.000 {method 'randint' of 'mtrand.RandomState' objects}
1 0.006 0.006 0.556 0.556 <ipython-input-46-b52343f1a2d5>:6(some_useless_slow_function)
6320 0.001 0.000 0.001 0.000 {method 'append' of 'list' objects}
1 0.000 0.000 0.556 0.556 <string>:1(<module>)
1 0.000 0.000 0.556 0.556 {built-in method exec}
1 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 {method 'disable' of '_lsprof.Profiler' objects}
Jupyter 有自己的调试界面The Python Debugger (pdb),使得进入函数内部检查错误成为可能。
Pdb中可使用的命令见链接
In [ ]: %pdb
def pick_and_take():
picked = numpy.random.randint(0, 1000)
raise NotImplementedError()
pick_and_take()
Automatic pdb calling has been turned ON
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
NotImplementedError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-24-0f6b26649b2e> in <module>()
5 raise NotImplementedError()
6
----> 7 pick_and_take()
<ipython-input-24-0f6b26649b2e> in pick_and_take()
3 def pick_and_take():
4 picked = numpy.random.randint(0, 1000)
----> 5 raise NotImplementedError()
6
7 pick_and_take()
NotImplementedError:
> <ipython-input-24-0f6b26649b2e>(5)pick_and_take()
3 def pick_and_take():
4 picked = numpy.random.randint(0, 1000)
----> 5 raise NotImplementedError()
6
7 pick_and_take()
ipdb>
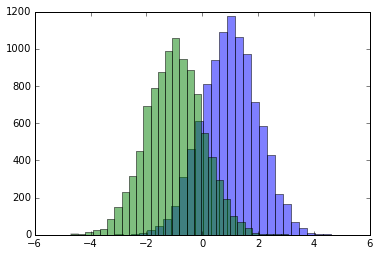
15、末句函数不输出
有时候不让末句的函数输出结果比较方便,比如在作图的时候,此时,只需在该函数末尾加上一个分号即可。
In [4]: %matplotlib inline
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy
x = numpy.linspace(0, 1, 1000)**1.5
In [5]: # Here you get the output of the function
plt.hist(x)
Out[5]:
(array([ 216., 126., 106., 95., 87., 81., 77., 73., 71., 68.]),
array([ 0. , 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9, 1. ]),
<a list of 10 Patch objects>)
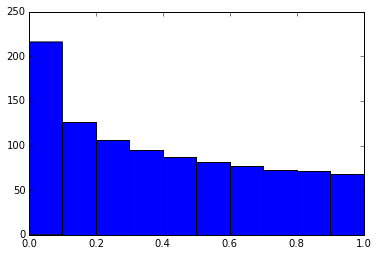
In [6]: # By adding a semicolon at the end, the output is suppressed.
plt.hist(x);
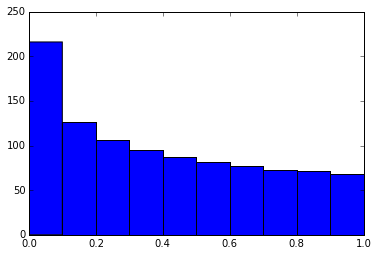
16、运行Shell命令
在notebook内部运行shell命令很简单,这样你就可以看到你的工作文件夹里有哪些数据集。
In [7]: !ls *.csv

nba_2016.csv titanic.csv
pixar_movies.csv whitehouse_employees.csv
17、用LaTex 写公式
当你在一个Markdown单元格里写LaTex时,它将用MathJax呈现公式:如
$$ P(A \mid B) = \frac{P(B \mid A) , P(A)}{P(B)} $$
会变成
18、在notebook内用不同的内核运行代码
如果你想要,其实可以把不同内核的代码结合到一个notebook里运行。
只需在每个单元格的起始,用Jupyter magics调用kernal的名称:
- %%bash
- %%HTML
- %%python2
- %%python3
- %%ruby
- %%perl
- In [6]: %%bash
- for i in {1..5}
- do
- echo "i is $i"
- done

i is 1
i is 2
i is 3
i is 4
i is 5
19、给Jupyter安装其他的内核
Jupyter的优良性能之一是可以运行不同语言的内核。下面以运行R内核为例说明:
简单的方法:通过Anaconda安装R内核
conda install -c r r-essentials
稍微麻烦的方法:手动安装R内核
如果你不是用Anaconda,过程会有点复杂,首先,你需要从CRAN安装R。
之后,启动R控制台,运行下面的语句:
install.packages(c('repr', 'IRdisplay', 'crayon', 'pbdZMQ', 'devtools'))
devtools::install_github('IRkernel/IRkernel')
IRkernel::installspec() # to register the kernel in the current R installation
20、在同一个notebook里运行R和Python
要这么做,最好的方法事安装rpy2(需要一个可以工作的R),用pip操作很简单:
pip install rpy2
然后,就可以同时使用两种语言了,甚至变量也可以在二者之间公用:
In [1]: %load_ext rpy2.ipython
In [2]: %R require(ggplot2)
Out[2]: array([1], dtype=int32)
In [3]: import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({
'Letter': ['a', 'a', 'a', 'b', 'b', 'b', 'c', 'c', 'c'],
'X': [4, 3, 5, 2, 1, 7, 7, 5, 9],
'Y': [0, 4, 3, 6, 7, 10, 11, 9, 13],
'Z': [1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3]
})
In [4]: %%R -i df
ggplot(data = df) + geom_point(aes(x = X, y= Y, color = Letter, size = Z))
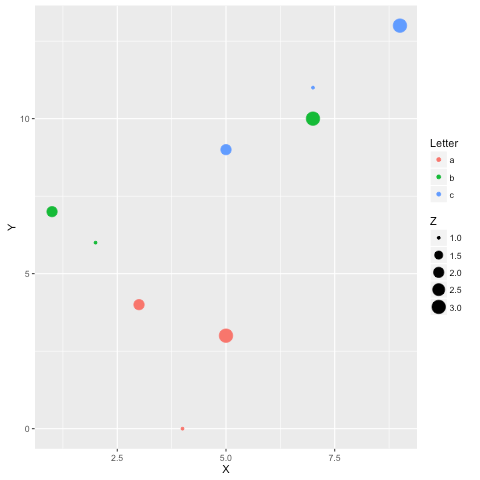
21、用其他语言写函数
有时候numpy的速度有点慢,我想写一些更快的代码。
原则上,你可以在动态库里编译函数,用python来封装…
但是如果这个无聊的过程不用自己干,岂不更好?
你可以在cython或fortran里写函数,然后在python代码里直接调用。
首先,你要先安装:
!pip install cython fortran-magic
In [ ]: %load_ext Cython
In [ ]: %%cython
def myltiply_by_2(float x):
return 2.0 * x
In [ ]: myltiply_by_2(23.)
我个人比较喜欢用Fortran,它在写数值计算函数时十分方便。更多的细节在这里。
In [ ]: %load_ext fortranmagic
In [ ]: %%fortran
subroutine compute_fortran(x, y, z)
real, intent(in) :: x(:), y(:)
real, intent(out) :: z(size(x, 1))
z = sin(x + y)
end subroutine compute_fortran
In [ ]: compute_fortran([1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6])
还有一些别的跳转系统可以加速python 代码。更多的例子见链接:
22、支持多指针
Jupyter支持多个指针同步编辑,类似Sublime Text编辑器。按下Alt键并拖拽鼠标即可实现。

23、Jupyter外接拓展
Jupyter-contrib extensions是一些给予Jupyter更多更能的延伸程序,包括jupyter spell-checker和code-formatter之类.
下面的命令安装这些延伸程序,同时也安装一个菜单形式的配置器,可以从Jupyter的主屏幕浏览和激活延伸程序。
!pip install https://github.com/ipython-contrib/jupyter_contrib_nbextensions/tarball/master
!pip install jupyter_nbextensions_configurator
!jupyter contrib nbextension install --user
!jupyter nbextensions_configurator enable --user

24、从Jupyter notebook创建演示稿
Damian Avila的RISE允许你从已有的notebook创建一个powerpoint形式的演示稿。
你可以用conda来安装RISE:
conda install -c damianavila82 rise
jupyter-nbextension install rise --py --sys-prefix
jupyter-nbextension enable rise --py --sys-prefix
Notebook本身以HTML的形式显示,单元格输出也可以是HTML形式的,所以你可以输出任何东西:视频/音频/图像。
这个例子是浏览我所有的图片,并显示前五张图的缩略图。
from IPython.display import display, Image
names = [f for f in os.listdir('../images/ml_demonstrations/') if f.endswith('.png')]
display(Image('../images/ml_demonstrations/' + name, width=100))
我们也可以用bash命令创建一个相同的列表,因为magics和bash运行函数后返回的是python 变量:
In [10]: names = !ls ../images/ml_demonstrations/*.png
Out[10]: ['../images/ml_demonstrations/colah_embeddings.png',
'../images/ml_demonstrations/convnetjs.png',
'../images/ml_demonstrations/decision_tree.png',
'../images/ml_demonstrations/decision_tree_in_course.png',
'../images/ml_demonstrations/dream_mnist.png']
ipyparallel(之前叫 ipython cluster) 是一个在python中进行简单的map-reduce运算的良好选择。我们在rep中使用它来并行训练很多机器学习模型。
- spark-sql magic %%sql
27、分享notebook
分享notebook最方便的方法是使用notebook文件(.ipynb),但是对那些不使用notebook的人,你还有这些选择:
- 通过File > Download as > HTML 菜单转换到html文件。
- 如果你把自己的notebook文件上传到github的仓库,可以使用很便利的Mybinder服务,允许另一个人进行半个小时的Jupyter交互连接到你的仓库。
将你的notebook存储在像dropbox这样的网站上,然后把链接放在nbviewer,nbviewer可以呈现任意来源的notebook。
用菜单File > Download as > PDF 保存notebook为PDF文件。如果你选择本方法,我强烈建议你读一读Julius Schulz的文章
- 用Pelican从你的notebook创建一篇博客。
















 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号