Demo
1 package LeetCode.test9_lianbiao; 2 3 public class ListNode { 4 int val; 5 ListNode next; 6 7 public ListNode() { 8 9 } 10 11 public ListNode(int val) { 12 this.val = val; 13 } 14 15 public ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { 16 this.val = val; 17 this.next = next; 18 } 19 }
1、反转链表
问题:
你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5]
输出:[5,4,3,2,1]
示例 2:
输入:head = [1,2]
输出:[2,1]
示例 3:
输入:head = []
输出:[]

1 package LeetCode.test9_lianbiao; 2 3 /** 4 * 思路1:先对原链表做头删操作,再对新链表做头插 5 * 思路2: _ 1->2->3 _ <-1 2->3 _ <-1 2->3 _ <-1 <-2 3 _ <-1 <-2 3 _ <-1 <-2 <-3 6 * p0 p1 p2 p0 p1 p2 p0 p1 p2 p0 p1 p2 p0 p1 p2 p0 p1 p2 p2=null 7 * p0 p1 p0 p1 p2 p0 p1 p0 p1 p2 p0 p1 p1=null 8 */ 9 public class ques_206_反转链表 { 10 public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) { 11 ListNode newHead = null; // 定义一个新的头结点 12 ListNode node; //定义一个临时中转站 13 while (head != null) { 14 //对之前的链表做头删 15 node = head; 16 head = head.next; 17 //对新链表做头插 (eg:1234) 18 node.next = newHead; 19 // node(1)->newHead(null) node(2)->newHead(1) node(3)->newHead(2)->(1) node(4)->newHead(3)->(1)->(1) 20 newHead = node; 21 // newHead(1) newHead(2) newHead(3) newHead(4) 22 } 23 return newHead; 24 } 25 26 public ListNode reverseList2(ListNode head) { 27 ListNode p0 = null; 28 ListNode p1 = head; 29 ListNode p2 = head.next; 30 while (p1 != null) { 31 p1.next = p0; 32 p0 = p1; 33 p1 = p2; 34 if (p2 != null) { 35 p2 = p2.next; 36 } 37 } 38 return p0; 39 } 40 } 41 42 class Test_206 { 43 public static void main(String[] args) { 44 int[] head = {1, 2}; 45 int index = 0; 46 ListNode listNode = create(head, index); 47 // PreOrder(listNode); 48 ques_206_反转链表 s = new ques_206_反转链表(); 49 // PreOrder(s.reverseList(listNode)); 50 PreOrder(s.reverseList2(listNode)); 51 } 52 53 private static ListNode create(int[] head, int index) { 54 ListNode listNode; 55 if (index >= head.length) { 56 return null; 57 } 58 listNode = new ListNode(head[index]); 59 listNode.next = create(head, index + 1); 60 return listNode; 61 } 62 63 private static void PreOrder(ListNode listNode) { 64 if (listNode == null) { 65 return; 66 } 67 System.out.print(listNode.val + " "); 68 PreOrder(listNode.next); 69 } 70 }
2、合并两个有序链表
问题:
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
示例 1:
输入:l1 = [1,2,4], l2 = [1,3,4]
输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4]
示例 2:
输入:l1 = [], l2 = []
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:l1 = [], l2 = [0]
输出:[0]

1 package LeetCode.test9_lianbiao; 2 3 public class ques_21_合并两个有序链表 { 4 public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) { 5 ListNode newHead = new ListNode(0); 6 ListNode node = newHead; // 指针 7 while (list1 != null && list2 != null) { 8 if (list1.val <= list2.val) { 9 node.next = list1; 10 list1 = list1.next; 11 } else { 12 node.next = list2; 13 list2 = list2.next; 14 } 15 node = node.next; 16 } 17 if (node.next == list1) { //list1循环完了,把list2加在后面。 18 node.next = list2; 19 } else { //list2循环完了,把list1加在后面。 20 node.next = list1; 21 } 22 return newHead.next; 23 } 24 } 25 26 class Test_21 { 27 public static void main(String[] args) { 28 int[] head1 = {1, 2, 4}; 29 int[] head2 = {1, 3, 4}; 30 int index = 0; 31 ListNode list1 = create(head1, index); 32 ListNode list2 = create(head2, index); 33 ques_21_合并两个有序链表 s = new ques_21_合并两个有序链表(); 34 PreOrder(s.mergeTwoLists(list1, list2)); 35 } 36 37 private static ListNode create(int[] head, int index) { 38 ListNode listNode; 39 if (index >= head.length) { 40 return null; 41 } 42 listNode = new ListNode(head[index]); 43 listNode.next = create(head, index + 1); 44 return listNode; 45 } 46 47 private static void PreOrder(ListNode listNode) { 48 if (listNode == null) { 49 return; 50 } 51 System.out.print(listNode.val + " "); 52 PreOrder(listNode.next); 53 } 54 }
3、两两交换链表中的节点
问题:
给你一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后链表的头节点。你必须在不修改节点内部的值的情况下完成本题(即,只能进行节点交换)。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4]
输出:[2,1,4,3]
示例 2:
输入:head = []
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:head = [1]
输出:[1]

1 package LeetCode.test9_lianbiao; 2 3 /** 4 * 思路: 5 * 1-> 2 -> 3 -> 4 1 <- 2 3 -> 4 1 <- 2 3 <- 4 null <- 3 <- 4 6 * one two three one two three one two three(head)=null null <- 3 <- 4 <- 1 <- 2(two) 7 */ 8 public class ques_24_两两交换链表中的节点 { 9 public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) { 10 if (head == null || head.next == null) { 11 return head; 12 } 13 ListNode one = head; 14 ListNode two = one.next; 15 ListNode three = two.next; 16 17 two.next = one; 18 one.next = swapPairs(three); 19 20 return two; 21 } 22 } 23 24 class Test_24 { 25 public static void main(String[] args) { 26 int[] root = {1, 2, 3, 4}; 27 int index = 0; 28 ListNode head = create(root, index); 29 ques_24_两两交换链表中的节点 s = new ques_24_两两交换链表中的节点(); 30 PreOrder(s.swapPairs(head)); 31 } 32 33 private static ListNode create(int[] head, int index) { 34 ListNode listNode; 35 if (index >= head.length) { 36 return null; 37 } 38 listNode = new ListNode(head[index]); 39 listNode.next = create(head, index + 1); 40 return listNode; 41 } 42 43 private static void PreOrder(ListNode listNode) { 44 if (listNode == null) { 45 return; 46 } 47 System.out.print(listNode.val + " "); 48 PreOrder(listNode.next); 49 } 50 }
4、相交链表
问题:
给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表不存在相交节点,返回 null 。
题目数据 保证 整个链式结构中不存在环。
注意,函数返回结果后,链表必须 保持其原始结构 。
自定义评测:
评测系统 的输入如下(你设计的程序不适用此输入):
intersectVal - 相交的起始节点的值。如果不存在相交节点,这一值为 0
listA - 第一个链表
listB - 第二个链表
skipA - 在 listA 中(从头节点开始)跳到交叉节点的节点数
skipB - 在 listB 中(从头节点开始)跳到交叉节点的节点数
评测系统将根据这些输入创建链式数据结构,并将两个头节点 headA 和 headB 传递给你的程序。如果程序能够正确返回相交节点,那么你的解决方案将被 视作正确答案 。
示例 1:
输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,6,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
输出:Intersected at '8'
解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。
从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,6,1,8,4,5]。
在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
示例 2:
输入:intersectVal = 2, listA = [1,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
输出:Intersected at '2'
解释:相交节点的值为 2 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。
从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [1,9,1,2,4],链表 B 为 [3,2,4]。
在 A 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 1 个节点。
示例 3:
输入:intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
输出:null
解释:从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [2,6,4],链表 B 为 [1,5]。
由于这两个链表不相交,所以 intersectVal 必须为 0,而 skipA 和 skipB 可以是任意值。
这两个链表不相交,因此返回 null 。

1 package LeetCode.test9_lianbiao; 2 3 /** 4 * 思路:使用双指针法。 5 * 假设链表A的头节点到相交点的距离是a,链表B的头节点到相交点的距离是b,相交点到链表终点的距离为c。我们使用两个指针,分别指向两个链表的头节点, 6 * 并以相同的速度前进,若到达链表结尾,则移动到另一条链表的头节点继续前进。按照这种前进方法,两个指针会在a+b+c次前进后同时到达相交节点。 7 */ 8 public class ques_160_相交链表 { 9 public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) { 10 if (headA == null || headB == null) { 11 return null; 12 } 13 ListNode lA = headA; 14 ListNode lB = headB; 15 while (lA != lB) { 16 lA = (lA != null ? lA.next : headB); 17 lB = (lB != null ? lB.next : headA); 18 } 19 return lA; 20 } 21 } 22 23 class Test_160 { 24 public static void main(String[] args) { 25 int[] listA = {4, 1, 8, 4, 5}; 26 int[] listB = {5, 6, 1, 8, 4, 5}; 27 } 28 }
5、回文链表
问题:
给你一个单链表的头节点 head ,请你判断该链表是否为回文链表。如果是,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,2,1]
输出:true
示例 2:
输入:head = [1,2]
输出:false

1 package LeetCode.test9_lianbiao; 2 3 /** 4 * 链表中快慢指针的妙用: 5 * 1、找中间值:把一个链表看成一个跑道,假设a的速度是b的两倍,那么当a跑完全程后,b刚好跑一半,以此来达到找到中间节点的目的。 6 * 2、判断链表中的环 7 * 3、删除倒数第n个:删除倒数第n个节点,那就等于要先找出待删除元素前一个元素,也就是第n-1个节点。一开始就让fast指针比slow指针快n+1个元素, 8 * 接下来,两个指针都是一步一步来往下走。那么当fast指针走完时,slow指针就刚刚好停留在第(n-1)个元素上。 9 * 思路:先使用快慢指针找到链表中点,再把链表切成两半;然后把后半段翻转;最后比较两半是否相等。 10 */ 11 public class ques_234_回文链表 { 12 public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) { 13 if (head == null) { 14 return false; 15 } else if (head.next == null) { 16 return true; 17 } else if (head.next.next == null) { 18 if (head.val == head.next.val) { 19 return true; 20 } else { 21 return false; 22 } 23 } 24 ListNode fast = head; 25 ListNode slow = head; 26 while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) { 27 fast = fast.next.next; 28 slow = slow.next; 29 } 30 ListNode newHead = slow.next; // [2 1] -> [1 2] 31 32 ListNode afterHead = null; // 定义一个新的头结点 33 ListNode node; //定义一个临时中转站 34 while (newHead != null) { 35 //对之前的链表做头删 36 node = newHead; 37 newHead = newHead.next; 38 //对新链表做头插 39 node.next = afterHead; 40 afterHead = node; 41 } 42 ListNode beforeHead = head; 43 while (afterHead != null) { 44 if (afterHead.val != beforeHead.val) { 45 return false; 46 } 47 afterHead = afterHead.next; 48 beforeHead = beforeHead.next; 49 } 50 return true; 51 } 52 } 53 54 class Test_234 { 55 public static void main(String[] args) { 56 // int[] head = {1, 2, 3, 2, 1}; 57 // int[] head = {1, 2, 2, 1}; 58 // int[] head = {1, 2}; 59 // int[] head = {1}; 60 int[] head = {1, 1, 2, 1}; 61 int index = 0; 62 ListNode list = create(head, index); 63 // PreOrder(list); 64 ques_234_回文链表 s = new ques_234_回文链表(); 65 System.out.println(s.isPalindrome(list)); 66 67 } 68 69 private static ListNode create(int[] head, int index) { 70 ListNode listNode; 71 if (index >= head.length) { 72 return null; 73 } 74 listNode = new ListNode(head[index]); 75 listNode.next = create(head, index + 1); 76 return listNode; 77 } 78 79 private static void PreOrder(ListNode listNode) { 80 if (listNode == null) { 81 return; 82 } 83 System.out.print(listNode.val + " "); 84 PreOrder(listNode.next); 85 } 86 }
6、删除排序链表中的重复元素
问题:
给定一个已排序的链表的头 head , 删除所有重复的元素,使每个元素只出现一次 。返回 已排序的链表 。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,1,2]
输出:[1,2]
示例 2:
输入:head = [1,1,2,3,3]
输出:[1,2,3]

1 package LeetCode.test9_lianbiao; 2 3 public class ques_83_删除排序链表中的重复元素 { 4 public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) { 5 if (head == null) { 6 return null; 7 } 8 ListNode preNode = head; 9 ListNode curNode = head.next; 10 ListNode node; 11 while (curNode != null) { 12 if (preNode.val == curNode.val) { 13 if (curNode.next != null) { 14 node = curNode.next; 15 preNode.next = node; 16 curNode = node; 17 } else { 18 preNode.next = null; 19 curNode = null; 20 } 21 22 } else { 23 preNode = curNode; 24 curNode = curNode.next; 25 } 26 } 27 // PreOrder(head); 28 return head; 29 } 30 31 // 测试 32 private static void PreOrder(ListNode listNode) { 33 if (listNode == null) { 34 return; 35 } 36 System.out.print(listNode.val + " "); 37 PreOrder(listNode.next); 38 } 39 } 40 41 class Test_83 { 42 public static void main(String[] args) { 43 // int[] head = {1}; 44 // int[] head = {1, 1}; 45 // int[] head = {1, 2}; 46 // int[] head = {1, 1, 2}; 47 int[] head = {1, 1, 2, 2}; 48 int index = 0; 49 ListNode list = create(head, index); 50 ques_83_删除排序链表中的重复元素 s = new ques_83_删除排序链表中的重复元素(); 51 System.out.println(s.deleteDuplicates(list)); 52 53 } 54 55 private static ListNode create(int[] head, int index) { 56 ListNode listNode; 57 if (index >= head.length) { 58 return null; 59 } 60 listNode = new ListNode(head[index]); 61 listNode.next = create(head, index + 1); 62 return listNode; 63 } 64 }
补:
问题:删除有序链表中重复的元素-II
给出一个升序排序的链表,删除链表中的所有重复出现的元素,只保留原链表中只出现一次的元素。
示例 1:
输入:{1,2,2}
输出:{1}
示例 2:
输入:{}
输出:{}

1 import java.util.*; 2 3 public class Solution { 4 public ListNode deleteDuplicates (ListNode head) { 5 if(head==null){ 6 return null; 7 } 8 9 ListNode temp = new ListNode(-1); 10 ListNode res = temp; 11 temp.next = head; 12 13 ListNode preNode = head; 14 ListNode curNode = head.next; 15 ListNode node = null; 16 while(curNode!=null){ 17 if(preNode.val==curNode.val){ 18 if(curNode.next!=null){ 19 if(preNode.val==curNode.next.val){ 20 curNode = curNode.next; 21 }else{ 22 node = curNode.next; 23 temp.next = node; 24 preNode = node; 25 curNode = node.next; 26 } 27 }else{ 28 temp.next = null; 29 preNode = null; 30 curNode = null; // 终止条件 31 } 32 }else{ 33 temp = temp.next; 34 preNode = preNode.next; 35 curNode = curNode.next; 36 } 37 } 38 return res.next; 39 } 40 }
7、奇偶链表
问题:
给定单链表的头节点 head ,将所有索引为奇数的节点和索引为偶数的节点分别组合在一起,然后返回重新排序的列表。
第一个节点的索引被认为是 奇数 , 第二个节点的索引为 偶数 ,以此类推。
请注意,偶数组和奇数组内部的相对顺序应该与输入时保持一致。
你必须在 O(1) 的额外空间复杂度和 O(n) 的时间复杂度下解决这个问题。
示例 1:
输入: head = [1,2,3,4,5]
输出: [1,3,5,2,4]
示例 2:
输入: head = [2,1,3,5,6,4,7]
输出: [2,3,6,7,1,5,4]

1 package LeetCode.test9_lianbiao; 2 3 public class ques_328_奇偶链表 { 4 public ListNode oddEvenList(ListNode head) { 5 if (head == null) { 6 return null; 7 } else if (head.next == null) { 8 return head; 9 } 10 ListNode preNode = head; 11 ListNode curNode = head.next; 12 ListNode node; 13 ListNode newHead = new ListNode(-1); 14 ListNode newNode = newHead; 15 16 while (curNode != null) { 17 // 接在新链表下 18 newNode.next = curNode; 19 newNode = curNode; 20 21 node = curNode.next; 22 if (node != null) { 23 preNode.next = node; 24 preNode = node; 25 if (node.next != null) { 26 curNode = node.next; 27 } else { 28 curNode = null; 29 // 此时删除新链表最后一个节点 30 newNode.next = null; 31 } 32 33 } else { 34 preNode.next = null; 35 curNode = null; 36 } 37 } 38 preNode.next = newHead.next; 39 // PreOrder(head); 40 return head; 41 } 42 43 // 测试 44 private static void PreOrder(ListNode listNode) { 45 if (listNode == null) { 46 return; 47 } 48 System.out.print(listNode.val + " "); 49 PreOrder(listNode.next); 50 } 51 } 52 53 class Test_328 { 54 public static void main(String[] args) { 55 int[] head = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}; 56 // int[] head = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; 57 // int[] head = {1}; 58 int index = 0; 59 ListNode list = create(head, index); 60 ques_328_奇偶链表 s = new ques_328_奇偶链表(); 61 System.out.println(s.oddEvenList(list)); 62 63 } 64 65 private static ListNode create(int[] head, int index) { 66 ListNode listNode; 67 if (index >= head.length) { 68 return null; 69 } 70 listNode = new ListNode(head[index]); 71 listNode.next = create(head, index + 1); 72 return listNode; 73 } 74 }

1 import java.util.*; 2 3 public class Solution { 4 public ListNode oddEvenList (ListNode head) { 5 if(head==null){ 6 return null; 7 } 8 ListNode fastHead = head.next; 9 ListNode lowtail = head; 10 ListNode fasttail = fastHead; 11 while(fasttail!=null&&fasttail.next!=null){ 12 lowtail.next = fasttail.next; 13 lowtail = lowtail.next; 14 fasttail.next = lowtail.next; 15 fasttail = fasttail.next; 16 } 17 lowtail.next = fastHead; 18 return head; 19 } 20 }
8、删除链表的倒数第N个结点
问题:
给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2
输出:[1,2,3,5]
示例 2:
输入:head = [1], n = 1
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:head = [1,2], n = 1
输出:[1]

1 package LeetCode.test9_lianbiao; 2 3 public class ques_19_删除链表的倒数第N个结点 { 4 public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) { 5 ListNode temp = new ListNode(-1); 6 temp.next = head; 7 ListNode slow = temp; 8 ListNode fast = temp; 9 while (n != 0) { 10 fast = fast.next; 11 n--; 12 } 13 while (fast.next != null) { 14 slow = slow.next; 15 fast = fast.next; 16 } 17 ListNode node = slow.next.next; 18 if (node != null) { 19 slow.next = node; 20 } else { 21 slow.next = null; 22 } 23 // PreOrder(temp.next); 24 return temp.next; 25 } 26 27 private static void PreOrder(ListNode listNode) { 28 if (listNode == null) { 29 return; 30 } 31 System.out.print(listNode.val + " "); 32 PreOrder(listNode.next); 33 } 34 } 35 36 class Test_19 { 37 public static void main(String[] args) { 38 int[] head = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8}; 39 int n = 3; 40 // int[] head = {1,2}; 41 // int n = 2; 42 // int[] head = {1}; 43 // int n = 1; 44 int index = 0; 45 ListNode list = create(head, index); 46 ques_19_删除链表的倒数第N个结点 s = new ques_19_删除链表的倒数第N个结点(); 47 System.out.println(s.removeNthFromEnd(list, n)); 48 49 } 50 51 private static ListNode create(int[] head, int index) { 52 ListNode listNode; 53 if (index >= head.length) { 54 return null; 55 } 56 listNode = new ListNode(head[index]); 57 listNode.next = create(head, index + 1); 58 return listNode; 59 } 60 }
9、排序链表
问题:
给你链表的头结点 head ,请将其按 升序 排列并返回 排序后的链表 。
示例 1:
输入:head = [4,2,1,3]
输出:[1,2,3,4]
示例 2:
输入:head = [-1,5,3,4,0]
输出:[-1,0,3,4,5]
示例 3:
输入:head = []
输出:[]

1 package LeetCode.test9_lianbiao; 2 3 /** 4 * 利用快慢指针找到链表中点后,可以对链表进行归并排序。 5 */ 6 public class ques_148_排序链表 { 7 public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) { 8 PreOrder(merge_sort(head)); 9 return merge_sort(head); 10 } 11 12 public ListNode merge_sort(ListNode head) { 13 if (head == null) { 14 return head; 15 } 16 if (head.next == null) { // 递归终止条件 17 return head; 18 } 19 ListNode slow = head; 20 ListNode fast = head; 21 while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) { 22 fast = fast.next.next; 23 slow = slow.next; 24 } 25 ListNode mid = slow; 26 27 ListNode rightHead = mid.next; 28 mid.next = null; 29 30 ListNode left = merge_sort(head); 31 ListNode right = merge_sort(rightHead); 32 return merge(left, right); 33 } 34 35 public ListNode merge(ListNode left, ListNode right) { 36 ListNode node = new ListNode(-1); 37 ListNode temp = node; 38 ListNode temp1 = left; // 2 39 ListNode temp2 = right; // 1 40 while (temp1 != null && temp2 != null) { 41 if (temp1.val < temp2.val) { 42 temp.next = temp1; 43 temp1 = temp1.next; 44 } else { 45 temp.next = temp2; 46 temp2 = temp2.next; 47 } 48 temp = temp.next; // 注意!!! 49 } 50 if (temp1 != null) { // 2 51 temp.next = temp1; 52 } 53 if (temp2 != null) { 54 temp.next = temp2; 55 } 56 return node.next; 57 } 58 59 private static void PreOrder(ListNode listNode) { 60 if (listNode == null) { 61 return; 62 } 63 System.out.print(listNode.val + " "); 64 PreOrder(listNode.next); 65 } 66 } 67 68 class Test_148 { 69 public static void main(String[] args) { 70 // int[] head = {4, 2, 1, 3}; 71 // int[] head = {4, 2, 1}; 72 // int[] head = {-1,5,3,4,0}; 73 int[] head = {}; 74 int index = 0; 75 ListNode list = create(head, index); 76 ques_148_排序链表 s = new ques_148_排序链表(); 77 System.out.println(s.sortList(list)); 78 79 } 80 81 private static ListNode create(int[] head, int index) { 82 ListNode listNode; 83 if (index >= head.length) { 84 return null; 85 } 86 listNode = new ListNode(head[index]); 87 listNode.next = create(head, index + 1); 88 return listNode; 89 } 90 }

1 import java.util.*; 2 3 public class Solution { 4 public ListNode sortInList (ListNode head) { 5 // write code here 6 if(head==null||head.next==null){ 7 return head; 8 } 9 // 奇数个节点找到中点,偶数个节点找到中心左边的节点 10 ListNode fast = head.next; //!!!!!!!!! 11 ListNode slow = head; 12 while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){ 13 fast = fast.next.next; 14 slow = slow.next; 15 } 16 ListNode mid = slow; 17 ListNode rightHead = mid.next; 18 mid.next = null; 19 20 ListNode left = sortInList(head); 21 ListNode right = sortInList(rightHead); 22 23 ListNode newHead = new ListNode(-1); 24 ListNode node = newHead; 25 while(left!=null&&right!=null){ 26 if(left.val<right.val){ 27 node.next = left; 28 left = left.next; 29 }else{ 30 node.next = right; 31 right = right.next; 32 33 } 34 node = node.next; 35 } 36 if(left!=null){ 37 node.next = left; 38 } 39 if(right!=null){ 40 node.next = right; 41 } 42 return newHead.next; 43 } 44 }
10、链表内指定区间反转
问题:
将一个节点数为 size 链表 m 位置到 n 位置之间的区间反转,要求时间复杂度 O(n),空间复杂度 O(1)。
示例 1:
输入:{1,2,3,4,5},2,4
输出:{1,4,3,2,5}
示例 2:
输入:{5},1,1
输出:{5}

1 import java.util.*; 2 3 public class Solution { 4 public ListNode reverseBetween (ListNode head, int m, int n) { 5 // write code here 6 ListNode newHead = new ListNode(-1); 7 newHead.next = head; 8 9 ListNode preLeft = newHead; 10 for(int i = 0; i < m-1; i++){ 11 preLeft = preLeft.next; 12 } 13 ListNode leftNode = preLeft.next; 14 15 ListNode curRight = preLeft; 16 for(int i = 0; i< n-m+1; i++){ 17 curRight = curRight.next; 18 } 19 ListNode rightNode = curRight; 20 21 curRight = curRight.next; 22 23 //截取 24 preLeft.next = null; 25 rightNode.next = null; 26 27 //反转 28 ListNode newSonHead = reverseList(leftNode); 29 preLeft.next = newSonHead; 30 leftNode.next = curRight; 31 32 return newHead.next; 33 } 34 35 public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head){ 36 ListNode newSonHead = null; 37 ListNode node = null; 38 while(head!=null){ 39 node = head; 40 head = head.next; 41 node.next = newSonHead; 42 newSonHead = node; 43 } 44 return newSonHead; 45 } 46 }
11、链表中的节点每k个一组翻转
问题:
将给出的链表中的节点每 k 个一组翻转,返回翻转后的链表
如果链表中的节点数不是 k 的倍数,将最后剩下的节点保持原样
你不能更改节点中的值,只能更改节点本身。
示例 1:
输入:{1,2,3,4,5},2
输出:{2,1,4,3,5}
示例 2:
输入:{},1
输出:{}

1 import java.util.*; 2 3 public class Solution { 4 public ListNode reverseKGroup (ListNode head, int k) { 5 ListNode virtualHead = new ListNode(-1); 6 ListNode result = virtualHead; 7 Stack<ListNode> st = new Stack(); 8 9 while(true){ 10 if(head==null){ // 取完链表或者空链表 11 break; 12 } 13 for(int i=0;i<k;i++){ 14 st.add(head); 15 head = head.next; 16 if(head==null){ //少于k个退出for循环 17 break; 18 } 19 } 20 if(st.size()==k){ 21 while(!st.isEmpty()){ 22 virtualHead.next = st.pop(); 23 virtualHead = virtualHead.next; 24 } 25 } 26 } 27 28 ListNode endNode = null; 29 while(!st.isEmpty()){ 30 endNode = st.pop(); 31 } 32 virtualHead.next = endNode; 33 return result.next; 34 } 35 }
12、链表中环的入口结点
问题:
给一个长度为n链表,若其中包含环,请找出该链表的环的入口结点,否则,返回null。
例如,输入{1,2},{3,4,5}时,对应的环形链表如下图所示:
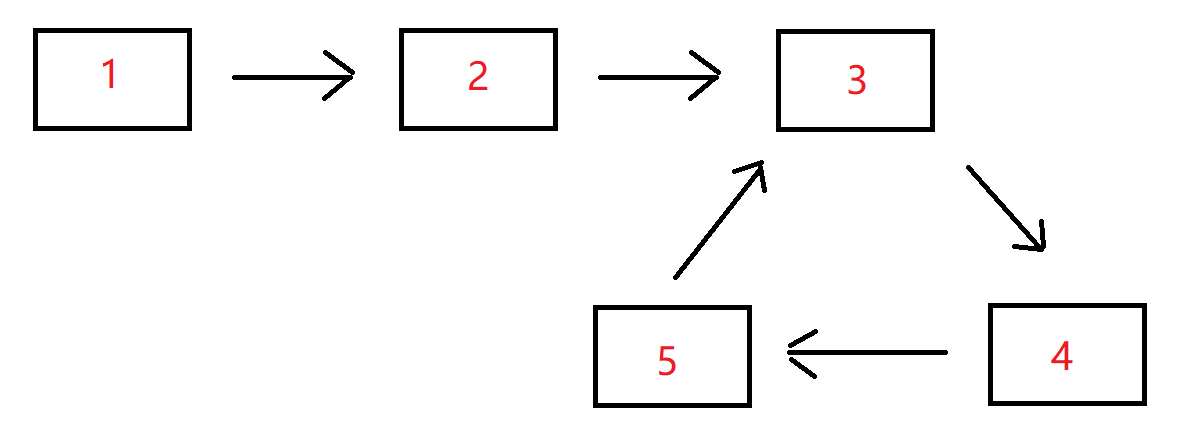
示例 1:
输入:{1,2},{3,4,5}
输出:3
示例 2:
输入:{1},{}
输出:"null"
示例 3:
输入:{},{2}
输出:2

1 import java.util.*; 2 3 public class Solution { 4 public ListNode EntryNodeOfLoop(ListNode pHead) { 5 ListNode fast = pHead; 6 ListNode slow = pHead; 7 while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){ 8 fast = fast.next.next; 9 slow = slow.next; 10 if(fast == slow){ 11 break; 12 } 13 } 14 if(fast == null||fast.next == null){ 15 return null; 16 } 17 fast = pHead; 18 while(fast!=slow){ 19 fast = fast.next; 20 slow = slow.next; 21 } 22 return fast; 23 } 24 }
13、链表相加(二)
问题:
示例 1:
输入:[9,3,7],[6,3]
输出:{1,0,0,0}
示例 2:
输入:[0],[6,3]
输出:{6,3}

1 import java.util.*; 2 3 public class Solution { 4 public ListNode addInList (ListNode head1, ListNode head2) { 5 // write code here 6 if(head1==null){ 7 return head2; 8 } 9 if(head2==null){ 10 return head1; 11 } 12 Stack<ListNode> st1 = new Stack<>(); 13 Stack<ListNode> st2 = new Stack<>(); 14 while(head1!=null){ 15 st1.add(head1); 16 head1 = head1.next; 17 } 18 while(head2!=null){ 19 st2.add(head2); 20 head2 = head2.next; 21 } 22 int tmp = 0; //进位 23 ListNode newHead = null; 24 //ListNode head = new ListNode(-1); 25 //ListNode newHead = head.next; 26 27 while(!st1.isEmpty()||!st2.isEmpty()){ 28 int num = tmp; 29 if(!st1.isEmpty()){ 30 num += st1.pop().val; 31 } 32 if(!st2.isEmpty()){ 33 num += st2.pop().val; 34 } 35 tmp = num / 10; 36 ListNode node = new ListNode(num%10); 37 node.next = newHead; 38 newHead = node; 39 } 40 if(tmp>0){ 41 ListNode node = new ListNode(tmp); 42 node.next = newHead; 43 newHead = node; 44 } 45 return newHead; 46 } 47 }







【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术
· 字符编码:从基础到乱码解决
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结