模拟处理机进程调度---简单循环轮转调度算法
简单循环轮转调度算法原理
当CPU空闲时,选取就绪队列队首元素,赋予时间片。当该进程时间片用完时,则释放CPU控制权,进入就绪队列的队尾,CPU控制权给下一个处于就绪队列首元素,原理如下图。
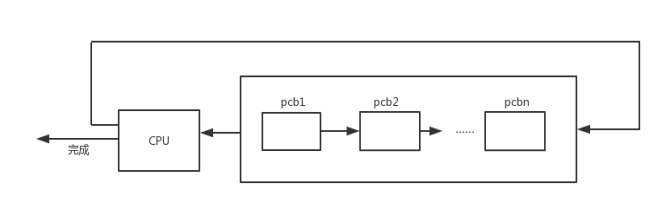
实现流程图

进程控制块PCB 的结构如下:
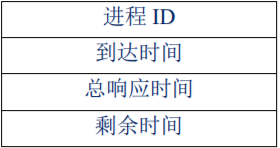
模拟实现
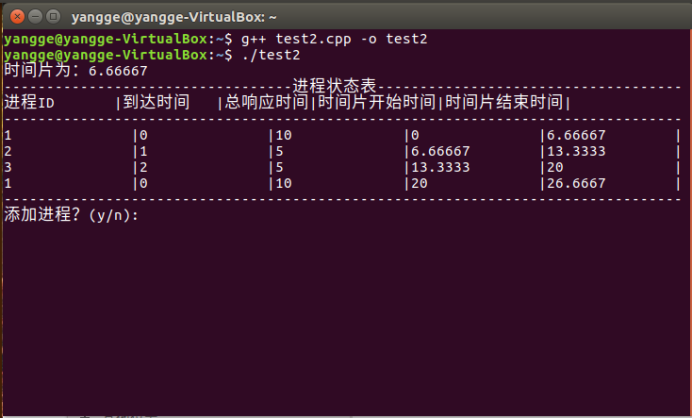
①时间片定义为:总相应时间/进程数;
②在屏幕上输出以下进程状态表(表中每一行代表一个进程对一个时间片的占用):
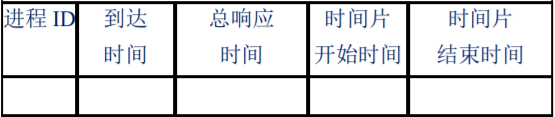
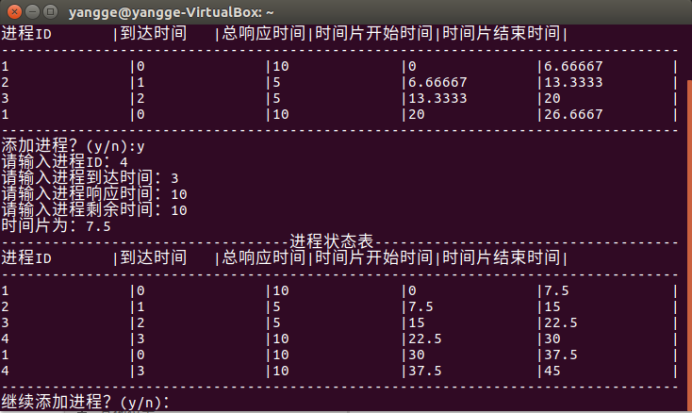
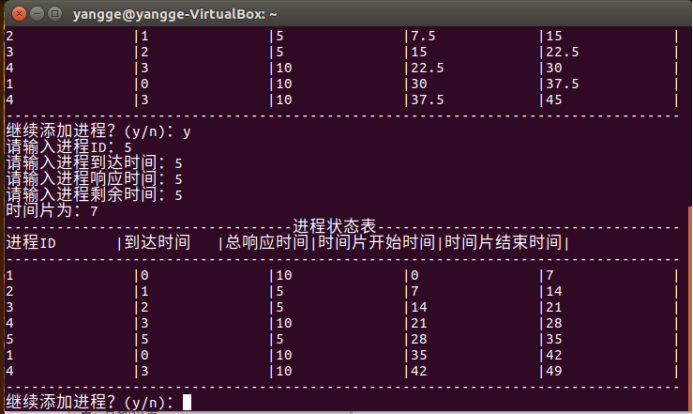
③可以通过键盘命令动态地增加作业(即增加一个 PCB 数 3 据结构项),增加进程后,进程状态表内容可更新查看。
算法代码
#include "stdafx.h" #include<queue> #include<math.h> #include<vector> #include<iostream> #include <iomanip> using namespace std; /*进程的数据结构*/ struct PCB { int ID;//进程ID double in_time;//进程的进入时间 double res_time;//进程的响应时间 double l_time;//进程的剩余时间 }; /*进程调度函数 */ /*输入:进程队列prs,时间片timeslice */ /*输出:进程状态表 */ void ProcessScheduling(queue<PCB>prs,double timeslice) { cout << left; queue<PCB>ex_prs;//就绪队列,该队列中的进程是等待执行的 ex_prs.push(prs.front());//第一个进程首先进入就绪队列 prs.pop();//将第一个进程退出进程队列 double slice_start;//时间片开始时间 double slice_end = 0;//时间片结束时间 cout << "----------------------------------进程状态表------------------------------------" << endl; cout <<setw(15)<<"进程ID" << "|" << setw(15) << "到达时间" << "|" <<setw(15) << "总响应时间" << "|" << setw(15) << "时间片开始时间"<<"|" << setw(15) <<"时间片结束时间"<<"|"<< endl; cout << "--------------------------------------------------------------------------------" << endl; while (!prs.empty()||!ex_prs.empty()) { slice_start = slice_end;//更新时间片开始与结束时间 slice_end += timeslice;//每次增加一个时间片的时间 while (!prs.empty()) //每次执行一个进程前,将能在此进程占用cpu期间进入就绪队列的进程加入就绪队列 { if (prs.front().in_time > slice_end)break; ex_prs.push(prs.front()); prs.pop(); if (ex_prs.size() == 1) { slice_start = slice_end; slice_end += timeslice; } } //如果就绪队列为空则继续while循环 if (ex_prs.empty())continue; //如果剩余时间小于或等于时间片 if (ex_prs.front().l_time <= timeslice) { ex_prs.front().l_time = 0;//将进程的剩余时间置为0(可有可无) cout << setw(15) << ex_prs.front().ID << "|" << setw(15) << ex_prs.front().in_time << "|" << setw(15) << ex_prs.front().res_time << "|" << setw(15) << slice_start<<"|"<< setw(15) << slice_end<<"|"<< endl; ex_prs.pop(); } else { ex_prs.front().l_time -= timeslice;//将进程的剩余时间减少一个时间片 cout << setw(15) << ex_prs.front().ID << "|" << setw(15) << ex_prs.front().in_time << "|" << setw(15) << ex_prs.front().res_time << "|" << setw(15) << slice_start << "|" << setw(15) << slice_end <<"|"<< endl; //将队首进程置于队尾 PCB tmp_pr = ex_prs.front(); ex_prs.pop(); ex_prs.push(tmp_pr); } } cout << "--------------------------------------------------------------------------------" << endl; } int main() { queue<PCB>prs; //总响应时间 double allres_time = 0; //时间片 double timeslice = 0; PCB pr1, pr2, pr3; pr1 = { 1,0,10,10 }; pr2 = { 2,1,5,5 }; pr3 = { 3,2,5,5 }; allres_time += pr1.res_time + pr2.res_time + pr3.res_time; timeslice = allres_time / 3; prs.push(pr1); prs.push(pr2); prs.push(pr3); cout << "时间片为:" << timeslice << endl; ProcessScheduling(prs, timeslice); cout << "添加进程?(y/n):"; char i; cin >> i; while (i-'y'==0) { PCB pr; cout << "请输入进程ID:"; cin >> pr.ID; cout << "请输入进程到达时间:"; cin >> pr.in_time; cout << "请输入进程响应时间:"; cin >> pr.res_time; cout << "请输入进程剩余时间:"; cin >> pr.l_time; prs.push(pr); allres_time += pr.res_time; timeslice = allres_time / prs.size(); cout << "时间片为:" << timeslice << endl; ProcessScheduling(prs, timeslice); cout << "继续添加进程?(y/n):"; cin >> i; } return 0; }
运行结果截图
编译程序
运行程序
添加一个进程
继续添加一个进程
运行环境:Ubuntu
相关问题补充:
①C++输出一个表格
解决方法:首先用cout<<left设置左对齐,然后用setw()设置之后的文本宽度,如: cout << setw(12) << "Miles" ,设置其后的Miles宽为12个字母。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号