ray tracing in one weekend - 2
add a sphere
球的公式
x2+y2+z2=r2
$(x,y,z)$ 在求的表面上
inside : $x^2 + y ^2 + z^2 < r^2$
outside : $x^2 + y ^2 + z^2 > r^2$
中心点 : $(C_{x}, C_{y},C_{z})$
(Cx−x)2+(Cy−y)2+(Cz−z)2=r2
使用向量来表示
$P=(x,y,z)$ , $C = (C_{x}, C_{y},C_{z})$
(C−P)⋅(C−P)=(Cx−x)2+(Cy−y)2+(Cz−z)2=r2
任意点P使得公式成立的就是在球上。如何判断光线是否和球相交呢?
(C−P(t))⋅(C−P(t))=r2
如果存在t是的公式成立表示 光线和球相交。
即
(C−(Q+td))⋅(C−(Q+td))=r2
我们只需要知道是否存在t,而不是解出公式
(−td+(C−Q))⋅(−td+(C−Q))=r2
t2d⋅d−2td⋅(C−Q)+(C−Q)⋅(C−Q)−r2=0
使用二次平方项可以得到。
a=d⋅d
b=−2d⋅(C−Q)
c=(C−Q)⋅(C−Q)−r2
只需要保证 $b^2 - 4ac >= 0$ 就可以保证光线和球相交,但是 有的时候 t 可能是复数。
the code
bool hit_sphere(const point3& center, double radius, const ray& r) {
vec3 oc = center - r.origin();
auto a = dot(r.direction(), r.direction());
auto b = -2.0 * dot(r.direction(), oc);
auto c = dot(oc, oc) - radius*radius;
auto discriminant = b*b - 4*a*c;
return (discriminant >= 0);
}
// 穿过为红色
color ray_color(const ray& r) {
if (hit_sphere(point3(0,0,-1), 0.5, r))
return color(1, 0, 0);
vec3 unit_direction = unit_vector(r.direction());
auto a = 0.5*(unit_direction.y() + 1.0);
return (1.0-a)*color(1.0, 1.0, 1.0) + a*color(0.5, 0.7, 1.0);
}
注意此时没有区分 前后。
法线和多个对象
在不需要的情况下,跳过规范化向量所涉及的昂贵的平方根运算是很有诱惑力的。然而,在实践中,有三个重要的观察结果。首先,如果需要单位长度的法向量,那么你最好先做一次,而不是一次又一次地做,以防每个需要单位长度的位置。其次,我们在一些地方确实需要单位长度的法向量。第三,如果你要求法向量为单位长度,那么你通常可以通过理解特定的几何形状来有效地生成该向量
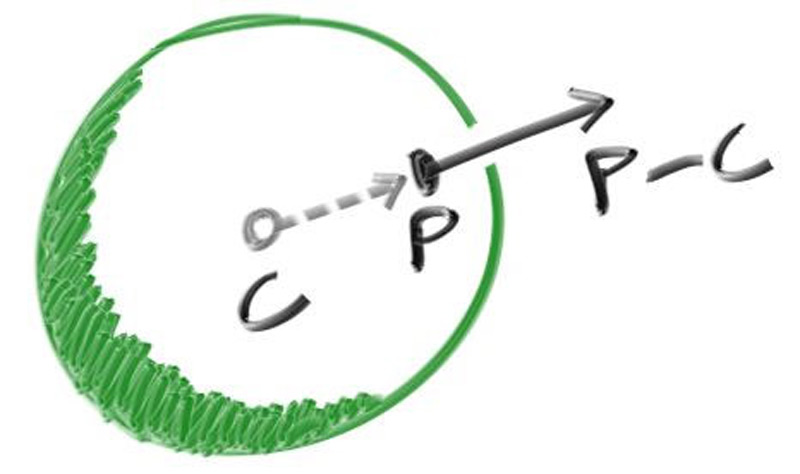
For a sphere, the outward normal is in the direction of the hit point minus the center
渲染法线贴图 法线范围 $-1<x<1$ 那么我们就可以用法线的三个值分别对应颜色。由于此时我们只有一个球,且在正前方。因此t必然 大于0, 且t的值就是那个较小的.
简化 hit 代码
before
double hit_sphere(const point3& center, double radius, const ray& r) {
vec3 oc = center - r.origin();
auto a = dot(r.direction(), r.direction());
auto b = -2.0 * dot(r.direction(), oc);
auto c = dot(oc, oc) - radius*radius;
auto discriminant = b*b - 4*a*c;
if (discriminant < 0) {
return -1.0;
} else {
return (-b - sqrt(discriminant) ) / (2.0*a);
}
}
向量点积自身,等于 自身长度的平方。 如果 b = -2h 则可以进一步简化
−b±√b2−4ac2a=h±√h2−aca
b=−2d(C−Q),b=−2h,h=d⋅(C−Q)
double hit_sphere(const point3& center, double radius, const ray& r) {
vec3 oc = center - r.origin();
auto a = r.direction().length_squared();
auto h = dot(r.direction(), oc);
auto c = oc.length_squared() - radius*radius;
auto discriminant = h*h - a*c;
if (discriminant < 0) {
return -1.0;
} else {
return (h - sqrt(discriminant)) / a;
}
}
对 hittable 对象的抽象
一个非常简洁的解决方案是为射线可能击中的任何东西创建一个抽象类,并创建一个球体和一个球体列表,只是可以被击中的东西。
hittable 对象 有一个方法 : 输入 ray。 添加 $t_{min} ,t_{max}$ 对于之后的计算是很方便的。只有在 $t_{min} < t < t_{max}$ 的时候 hit 才可以被计算。初始情况下 $t_{min}$ 为0 。 通常情况下 我们进行光线追踪的时候我们都需要用到法线,因此我们将需要的数据进行抽象化。
#ifndef HITTABLE_H
#define HITTABLE_H
#include "ray.h"
class hit_record {
public:
point3 p;
vec3 normal;
double t;
};
class hittable {
public:
virtual ~hittable() = default;
virtual bool hit(const ray& r, double ray_tmin, double ray_tmax, hit_record& rec) const = 0;
};
#endif
球体的抽象
#ifndef SPHERE_H
#define SPHERE_H
#include "hittable.h"
#include "vec3.h"
class sphere : public hittable {
public:
sphere(const point3& center, double radius) : center(center), radius(fmax(0,radius)) {}
bool hit(const ray& r, double ray_tmin, double ray_tmax, hit_record& rec) const override {
vec3 oc = center - r.origin();
auto a = r.direction().length_squared();
auto h = dot(r.direction(), oc);
auto c = oc.length_squared() - radius*radius;
auto discriminant = h*h - a*c;
if (discriminant < 0)
return false;
auto sqrtd = sqrt(discriminant);
// Find the nearest root that lies in the acceptable range.
auto root = (h - sqrtd) / a;
if (root <= ray_tmin || ray_tmax <= root) {
root = (h + sqrtd) / a;
if (root <= ray_tmin || ray_tmax <= root)
return false;
}
rec.t = root;
rec.p = r.at(rec.t);
rec.normal = (rec.p - center) / radius;
return true;
}
private:
point3 center;
double radius;
};
#endif
正面和背面
法线的第二个设计决策是它们是否应该总是指向。目前,找到的法线总是在中心到交点的方向(法线指向外)。如果射线从外面与球体相交法线对着射线的点。如果射线从内部与球体相交,法线(总是指向外)就指向射线。或者,我们可以让法线总是指向射线。如果射线在球外,法线将指向外,但如果射线在球内,法线将指向内。
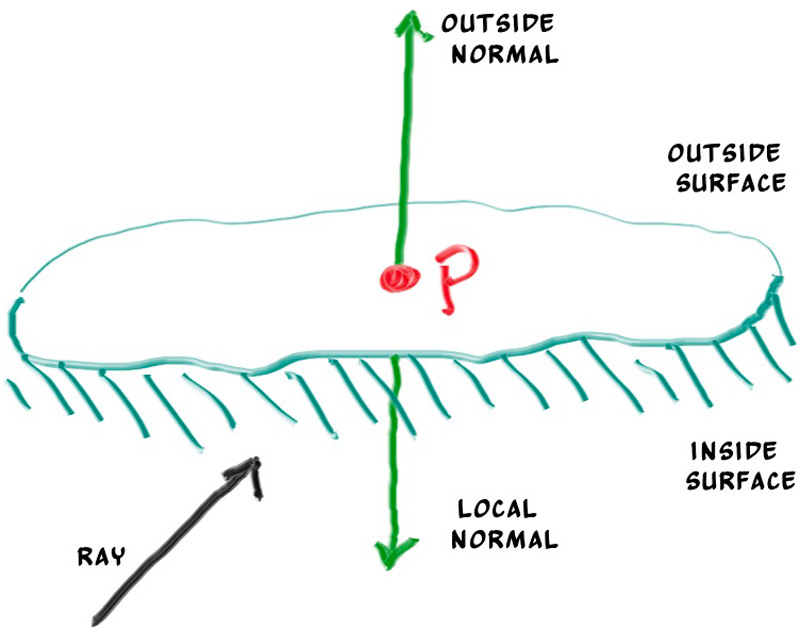
我们需要从这些可能性中选择一个因为我们最终想要确定射线来自曲面的哪一边。这对于每一面呈现不同的对象(如双面纸上的文本)或具有内外两面的对象(如玻璃球)非常重要。
如果我们决定法线总是指向外,那么当我们给它上色时,我们需要确定光线在哪一边。我们可以通过比较射线和法线来求出这个。如果射线与法线面的方向相同,则射线在物体内部,如果射线与法线面的方向相反,则射线在物体外部。这可以通过取这两个向量的点积来确定,如果它们的点积为正,则射线在球内。
if (dot(ray_direction, outward_normal) > 0.0) {
// ray is inside the sphere
...
} else {
// ray is outside the sphere
...
}
如果我们决定法线总是指向射线,我们就不能用点积来确定射线在曲面的哪一边。相反,我们需要存储这些信息
bool front_face;
if (dot(ray_direction, outward_normal) > 0.0) {
// ray is inside the sphere
normal = -outward_normal;
front_face = false;
} else {
// ray is outside the sphere
normal = outward_normal;
front_face = true;
}
两种方式都可以。
我们会将是否在外侧存储在 hit_record 中, 并使用 se_face_normal 对 normal 进行修改。同时我们会假设 normal 是 单位向量。
class hit_record {
public:
point3 p;
vec3 normal;
double t;
bool front_face;
void set_face_normal(const ray& r, const vec3& outward_normal) {
// Sets the hit record normal vector.
// NOTE: the parameter `outward_normal` is assumed to have unit length.
front_face = dot(r.direction(), outward_normal) < 0;
normal = front_face ? outward_normal : -outward_normal;
}
};
//修改一下 sphere 类
class sphere : public hittable {
public:
...
bool hit(const ray& r, double ray_tmin, double ray_tmax, hit_record& rec) const {
...
rec.t = root;
rec.p = r.at(rec.t);
vec3 outward_normal = (rec.p - center) / radius;
rec.set_face_normal(r, outward_normal);
return true;
}
...
};
hittable list
#ifndef HITTABLE_LIST_H
#define HITTABLE_LIST_H
#include "hittable.h"
#include <memory>
#include <vector>
using std::make_shared;
using std::shared_ptr;
class hittable_list : public hittable {
public:
std::vector<shared_ptr<hittable>> objects;
hittable_list() {}
hittable_list(shared_ptr<hittable> object) { add(object); }
void clear() { objects.clear(); }
void add(shared_ptr<hittable> object) {
objects.push_back(object);
}
bool hit(const ray& r, double ray_tmin, double ray_tmax, hit_record& rec) const override {
hit_record temp_rec;
bool hit_anything = false;
auto closest_so_far = ray_tmax;
for (const auto& object : objects) {
if (object->hit(r, ray_tmin, closest_so_far, temp_rec)) {
hit_anything = true;
closest_so_far = temp_rec.t;
rec = temp_rec;
}
}
return hit_anything;
}
};
#endif
常用函数
#ifndef RTWEEKEND_H
#define RTWEEKEND_H
#include <cmath>
#include <iostream>
#include <limits>
#include <memory>
// C++ Std Usings
using std::make_shared;
using std::shared_ptr;
using std::sqrt;
// Constants
const double infinity = std::numeric_limits<double>::infinity();
const double pi = 3.1415926535897932385;
// Utility Functions
inline double degrees_to_radians(double degrees) {
return degrees * pi / 180.0;
}
// Common Headers
#include "color.h"
#include "ray.h"
#include "vec3.h"
#endif
管理 最大最小值
#ifndef INTERVAL_H
#define INTERVAL_H
class interval {
public:
double min, max;
interval() : min(+infinity), max(-infinity) {} // Default interval is empty
interval(double min, double max) : min(min), max(max) {}
double size() const {
return max - min;
}
bool contains(double x) const {
return min <= x && x <= max;
}
bool surrounds(double x) const {
return min < x && x < max;
}
static const interval empty, universe;
};
const interval interval::empty = interval(+infinity, -infinity);
const interval interval::universe = interval(-infinity, +infinity);
#endif
hittable 类 需要使用 这个类对最大最小值进行控制.
class hittable {
public:
...
virtual bool hit(const ray& r, interval ray_t, hit_record& rec) const = 0;
};
hittable_list 实现这个方法
class hittable_list : public hittable {
public:
...
bool hit(const ray& r, interval ray_t, hit_record& rec) const override {
hit_record temp_rec;
bool hit_anything = false;
auto closest_so_far = ray_t.max;
for (const auto& object : objects) {
if (object->hit(r, interval(ray_t.min, closest_so_far), temp_rec)) {
hit_anything = true;
closest_so_far = temp_rec.t;
rec = temp_rec;
}
}
return hit_anything;
}
...
};
对一些行为进行修改
class sphere : public hittable {
public:
...
bool hit(const ray& r, interval ray_t, hit_record& rec) const override {
...
// Find the nearest root that lies in the acceptable range.
auto root = (h - sqrtd) / a;
if (!ray_t.surrounds(root)) {
root = (h + sqrtd) / a;
if (!ray_t.surrounds(root))
return false;
}
...
}
...
};
Camera
类需要包含的作用 :
- 构建并发射 rays
- 利用 rays 构建 需要渲染的东西
因此 有两个 public 方法 : initialize render 两个 pirvate 方法 get_ray ray_color
#ifndef CAMERA_H
#define CAMERA_H
#include "rtweekend.h"
#include "hittable.h"
class camera {
public:
/* Public Camera Parameters Here */
void render(const hittable& world) {
...
}
private:
/* Private Camera Variables Here */
void initialize() {
...
}
color ray_color(const ray& r, const hittable& world) const {
...
}
};
#endif
基础代码结构,之后将 main 中的代码搬移过来
class camera {
public:
double aspect_ratio = 1.0; // Ratio of image width over height
int image_width = 100; // Rendered image width in pixel count
void render(const hittable& world) {
initialize();
std::cout << "P3\n" << image_width << ' ' << image_height << "\n255\n";
for (int j = 0; j < image_height; j++) {
std::clog << "\rScanlines remaining: " << (image_height - j) << ' ' << std::flush;
for (int i = 0; i < image_width; i++) {
auto pixel_center = pixel00_loc + (i * pixel_delta_u) + (j * pixel_delta_v);
auto ray_direction = pixel_center - center;
ray r(center, ray_direction);
color pixel_color = ray_color(r, world);
write_color(std::cout, pixel_color);
}
}
std::clog << "\rDone. \n";
}
private:
int image_height; // Rendered image height
point3 center; // Camera center
point3 pixel00_loc; // Location of pixel 0, 0
vec3 pixel_delta_u; // Offset to pixel to the right
vec3 pixel_delta_v; // Offset to pixel below
void initialize() {
image_height = int(image_width / aspect_ratio);
image_height = (image_height < 1) ? 1 : image_height;
center = point3(0, 0, 0);
// Determine viewport dimensions.
auto focal_length = 1.0;
auto viewport_height = 2.0;
auto viewport_width = viewport_height * (double(image_width)/image_height);
// Calculate the vectors across the horizontal and down the vertical viewport edges.
auto viewport_u = vec3(viewport_width, 0, 0);
auto viewport_v = vec3(0, -viewport_height, 0);
// Calculate the horizontal and vertical delta vectors from pixel to pixel.
pixel_delta_u = viewport_u / image_width;
pixel_delta_v = viewport_v / image_height;
// Calculate the location of the upper left pixel.
auto viewport_upper_left =
center - vec3(0, 0, focal_length) - viewport_u/2 - viewport_v/2;
pixel00_loc = viewport_upper_left + 0.5 * (pixel_delta_u + pixel_delta_v);
}
color ray_color(const ray& r, const hittable& world) const {
...
}
};
#endif
此时 main 的代码就可以简化了
#include "rtweekend.h"
#include "camera.h"
#include "hittable.h"
#include "hittable_list.h"
#include "sphere.h"
int main() {
hittable_list world;
world.add(make_shared<sphere>(point3(0,0,-1), 0.5));
world.add(make_shared<sphere>(point3(0,-100.5,-1), 100));
camera cam;
cam.aspect_ratio = 16.0 / 9.0;
cam.image_width = 400;
cam.render(world);
}
作者:bigsharker
出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/bigsharker/p/18198534
版权:本作品采用「署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 4.0 国际」许可协议进行许可。



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· Docker 太简单,K8s 太复杂?w7panel 让容器管理更轻松!