Java中HashSet和HashMap
Set中存储元素为什么不重复(即使hashCode相同)?

HashSet中存放自定义类型元素时候,需要重写对象中的hashCode方法和equals方法,
HashSet中存放自定义类型元素时候,需要重写对象中的hashCode方法和equals方法,建立自己的比较方式,才能保证HashSet集合中的对象唯
HashSet是单列集合

1 package com.biggw.day13.demo01; 2 3 import java.util.HashSet; 4 import java.util.Iterator; 5 import java.util.Set; 6 7 /** 8 * @author gw 9 * @date 2019/11/5 0005 下午 19:04 10 */ 11 12 /* 13 * java.util.Set接口 extends Collection接口 14 * Set接口的特点: 15 * 1.不允许存储重复的元素 16 * 2.没有索引,没有带索引的方法,也不能使用普通的for循环遍历 17 * 18 * java.util.HashSet集合 implements Set接口 19 * HashSet特点: 20 * 1.不允许存储重复的元素 21 * 2.没有索引,没有带索引的方法,也不允许使用普通的for循环遍历 22 * 3.是一个无序集合,存储元素和取出元素的顺序有可能不一致 23 * 4.底层是一个哈希表结构(存储速度非常快)【重要】 24 * 25 * 26 * JDK 1.8 之前,哈希表 = 数组+链表 27 * JDK 1.8及之后,哈希表 = 数组+链表(红黑树)(提高查询速度)【当链表长度超过8位,将链表改为红黑树】 28 * */ 29 public class HashSetTest { 30 public static void main(String[] args) { 31 Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>(); 32 set.add(1); 33 set.add(2); 34 set.add(3); 35 set.add(1); 36 37 // 使用迭代器遍历set集合 38 Iterator<Integer> iterator = set.iterator(); 39 while (iterator.hasNext()) { 40 Integer next = iterator.next(); 41 System.out.println("next = " + next); 42 } 43 44 // 使用增强for循环遍历set集合 45 for (Integer integer : set) { 46 System.out.println("integer = " + integer); 47 } 48 49 System.out.println("================"); 50 51 HashSet<String> strings = new HashSet<>(); 52 strings.add("重地"); 53 strings.add("通话"); 54 for (String s : strings) { 55 System.out.println("s = " + s); 56 } 57 } 58 }
HashMap是双列集合

1 package com.biggw.day14.demo01; 2 3 import java.util.HashMap; 4 5 /** 6 * @author gw 7 * @date 2019/11/5 0005 下午 23:38 8 */ 9 10 /* 11 * HashMap 的底层实现是哈希表,所以查询速度特别快 12 * 1.public boolean containsKey(Object key); 判断是否含有该键,返回boolean值 13 * 2.public E get(Object key); 返回键对应的值,如果不存在,返回null 14 * 3.public E put(K key, V value); 添加键值对,返回添加之前的值 15 * 4.public V remove(Object key); 返回移除元素对应的值 16 * 17 * */ 18 public class Demo01HashMap { 19 public static void main(String[] args) { 20 funcPut(); 21 System.out.println("========"); 22 funcRemove(); 23 System.out.println("========"); 24 funcGet(); 25 System.out.println("========"); 26 funcContainsKey(); 27 } 28 29 private static void funcContainsKey() { 30 // public boolean containsKey(Object key); 判断集合中是否包含指定的值 31 // 包含返回true,不包含返回false 32 33 34 System.out.println("ContainsKey"); 35 HashMap<String, Integer> hashMap = new HashMap<>(); 36 // 用int类型接受,虽然我们的值是Integer类型,但是当我们第一次插入一对新键值对时候,由于键对应的值不存在,所以返回null 37 Object v1 = hashMap.put("小明", 23); 38 Object v2 = hashMap.put("小花", 24); 39 boolean v3 = hashMap.containsKey("小绿"); 40 System.out.println("v3 = " + v3); 41 boolean v4 = hashMap.containsKey("小花"); 42 System.out.println("v4 = " + v4); 43 44 } 45 46 private static void funcGet() { 47 // public V get(Object key) 48 // 如果key存在, 返回被删除的元素 49 // 如果key不存在,返回null,所以推荐使用Object接收 50 51 System.out.println("Get"); 52 HashMap<String, Integer> hashMap = new HashMap<>(); 53 // 用int类型接受,虽然我们的值是Integer类型,但是当我们第一次插入一对新键值对时候,由于键对应的值不存在,所以返回null 54 Object v1 = hashMap.put("小明", 23); 55 Object v2 = hashMap.put("小花", 24); 56 Integer v3 = hashMap.get("小绿"); 57 System.out.println("v3 = " + v3); 58 // 获取对应键对应的值 59 Integer v4 = hashMap.get("小花"); 60 System.out.println("v4 = " + v4); 61 } 62 63 public static void funcRemove() { 64 65 // public V remove(Object key) 把指定的键对应的值从map集合中删除,返回被删除的元素 66 // 如果key存在, 返回被删除的元素 67 // 如果key不存在,返回null,所以推荐使用Object接收 68 69 System.out.println("remove"); 70 HashMap<String, Integer> hashMap = new HashMap<>(); 71 // 用Integer类型接受,虽然我们的值是int类型,但是当我们第一次插入一对新键值对时候,由于键对应的值不存在,所以返回null 72 Object v1 = hashMap.put("小明", 23); 73 Object v2 = hashMap.put("小花", 24); 74 System.out.println("hashMap = " + hashMap); 75 Integer v3 = hashMap.remove("小白"); 76 System.out.println("v3 = " + v3); 77 Integer v4 = hashMap.remove("小花"); 78 System.out.println("v4 = " + v4); 79 } 80 81 public static void funcPut() { 82 // public V remove(Object key); 83 // 存储键值对的时候,key不重复,返回值为null 84 // 存储键值对的时候,key重复,会使用新的value替换掉map中的重复的value,并且返回被替换的value 85 86 System.out.println("Put"); 87 HashMap<String, Integer> hashMap = new HashMap<>(); 88 // 用int类型接受,虽然我们的值是Integer类型,但是当我们第一次插入一对新键值对时候,由于键对应的值不存在,所以返回null 89 Object v1 = hashMap.put("小明", 23); 90 Object v2 = hashMap.put("小花", 24); 91 // 我们还可以把put理解为修改键对应的值 92 Object v3 = hashMap.put("小花", 25); 93 System.out.println("v1 = " + v1); 94 System.out.println("v2 = " + v2); 95 System.out.println("v3 = " + v3); 96 System.out.println("hashMap = " + hashMap); 97 98 /*v1 = null 99 v2 = null 100 v3 = 24 101 hashMap = {小明=23, 小花=25}*/ 102 } 103 }
HashMap遍历方法1:keySet

1 package com.biggw.day14.demo01; 2 3 import java.util.HashMap; 4 import java.util.Iterator; 5 import java.util.Set; 6 7 /** 8 * @author gw 9 * @date 2019/11/6 0006 下午 13:24 10 */ 11 12 /* 13 * Map集合中的第一种遍历方式:通过键找值进行遍历 14 * 15 * Map集合中的方法: 16 * public Set<K> keySet(); 返回此映射中的键的set视图 17 * 18 * 实现步骤: 19 * 1.使用Map集合中的方法KeySet(),把Map集合中所有的key取出来,存储到一个Set集合中 20 * 2.使用Set集合的迭代器方法,获取Map集合中每一个key 21 * 3.通过Map集合中的方法get(key) 22 * 23 * 24 * */ 25 public class Demo02KeySet { 26 public static void main(String[] args) { 27 HashMap<String, Integer> hashMap = new HashMap<>(); 28 Object v1 = hashMap.put("小明", 23); 29 Object v2 = hashMap.put("小花", 24); 30 31 Set<String> keySet = hashMap.keySet(); 32 Iterator<String> iterator = keySet.iterator(); 33 while (iterator.hasNext()){ 34 String next = iterator.next(); 35 System.out.println("hashMap.get(next) = " + hashMap.get(next)); 36 } 37 38 for (String string : keySet) { 39 System.out.println("hashMap.get(string) = " + hashMap.get(string)); 40 } 41 42 for (String string : hashMap.keySet()) { 43 System.out.println("hashMap.get(string) = " + hashMap.get(string)); 44 } 45 } 46 }
HashMap遍历方法2:EntrySet
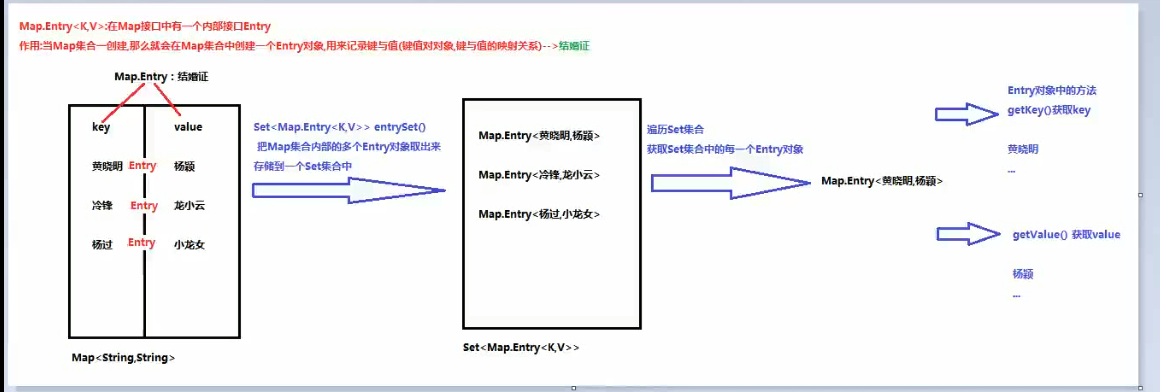

1 package com.biggw.day14.demo01; 2 3 import java.util.HashMap; 4 import java.util.Iterator; 5 import java.util.Map; 6 import java.util.Set; 7 8 /** 9 * @author gw 10 * @date 2019/11/6 0006 下午 13:53 11 */ 12 13 /* 14 * Map遍历集合的第二种方法:使用Entry对象遍历 15 * 16 * Map集合中的方法: 17 * Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet(); 返回此映射中包含的映射关系的Set视图 18 * 19 * 实现步骤: 20 * 1.使用Map集合中的方法enteySet(),把Map集合中多个Entry对象取出来,存储到一个Set集合中 21 * Entry对象:就是键值对组合(类似夫妻组合,黄晓明和baby) 22 * 2.遍历Set集合,获取每一个Entry对象 23 * 3.使用Entry对象中的方法getKey()和getValue()获取键和值 24 * 25 * */ 26 public class Demo03EntryKey { 27 public static void main(String[] args) { 28 HashMap<String, Integer> hashMap = new HashMap<>(); 29 Object v1 = hashMap.put("小明", 23); 30 Object v2 = hashMap.put("小花", 24); 31 32 Set<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> entrySet = hashMap.entrySet(); 33 Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> iterator = entrySet.iterator(); 34 35 while (iterator.hasNext()) { 36 Map.Entry<String, Integer> next = iterator.next(); 37 System.out.println("next.getKey()+next.getValue() = " + next.getKey() + next.getValue()); 38 } 39 40 for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> stringIntegerEntry : entrySet) { 41 System.out.println("next.getKey()+next.getValue() = " + stringIntegerEntry.getKey() + stringIntegerEntry.getValue()); 42 } 43 44 } 45 }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号