tableau项目实战-中国五城市六年pm2.5大数据可视化
中国五城市六年pm2.5大数据可视化
一,典型课题研究
中国五城市六年的pm2.5的值与那些因素有关,与PM2.5的变化
二,数据
1,数据源:https://www.kaggle.com/uciml/pm25-data-for-five-chinese-cities

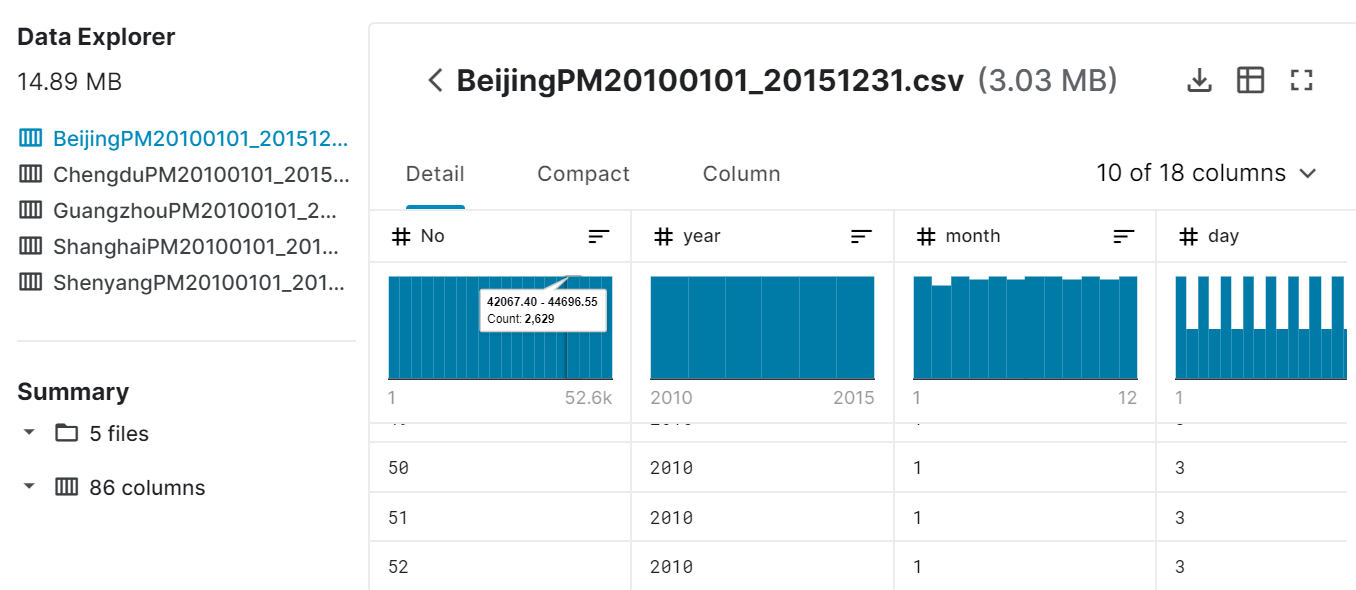
2,数据集介绍
Context
PM2.5 readings are often included in air quality reports from environmental authorities and companies. PM2.5 refers to atmospheric particulate matter (PM) that have a diameter less than 2.5 micrometers. In other words, it's used as a measure of pollution.
PM2.5读数通常包含在环境部门和公司的空气质量报告中。PM2.5是指直径小于2.5微米的大气颗粒物(PM)。换句话说,它被用作污染的量度。
3,字段含义
- No: row number 行号
- year: year of data in this row 该行中数据的年份
- month: month of data in this row 该行中数据的月份
- day: day of data in this row 该行中数据的日期
- hour: hour of data in this row 该行中的小时数据
- season: season of data in this row 此行中的数据季节
- PM: PM2.5 concentration (ug/m^3) PM2.5浓度(ug / m ^ 3)
- DEWP: Dew Point (Celsius Degree) 露点(摄氏温度)
- TEMP: Temperature (Celsius Degree) 温度(摄氏温度)
- HUMI: Humidity (%) 湿度(%)
- PRES: Pressure (hPa) 压力(hPa)
- cbwd: Combined wind direction 组合风向
- Iws: Cumulated wind speed (m/s) 累积风速(m / s)
- precipitation: hourly precipitation (mm) 每小时降水量(毫米)
- Iprec: Cumulated precipitation (mm) 累积降水量(毫米)
三,提出问题
①各城市PM2.5的分布并找出其规律
②各城市PM2.5收什么影响,影响程度如何
③各城市一年的PM2.5的分布主要集中在哪些时间段PM2.5的值比较高
四,操作步骤
1,从kaggle中导出数据,并对数据进行清洗
①把分开的时间字符串通过periodIndex的方法转化为pandas的时间类型
②把datetime 设置为索引
③进行降采样
④处理缺失数据,删除缺失数据
# coding=utf-8 import pandas as pd from matplotlib import pyplot as plt file_path = "./PM2.5/BeijingPM20100101_20151231.csv" df = pd.read_csv(file_path) # 把分开的时间字符串通过periodIndex的方法转化为pandas的时间类型 period = pd.PeriodIndex(year=df["year"], month=df["month"], day=df["day"], hour=df["hour"], freq="H") df["datetime"] = period # print(df.head(10)) # 把datetime 设置为索引 df.set_index("datetime", inplace=True) # 进行降采样 df = df.resample("7D").mean() print(df.head()) # 处理缺失数据,删除缺失数据 # print(df["PM_US Post"]) data = df["PM_US Post"] data_china = df["PM_Nongzhanguan"] print(data_china.head(100)) # 画图 _x = data.index _x = [i.strftime("%Y%m%d") for i in _x] _x_china = [i.strftime("%Y%m%d") for i in data_china.index] print(len(_x_china), len(_x_china)) _y = data.values _y_china = data_china.values plt.figure(figsize=(20, 8), dpi=80) plt.plot(range(len(_x)), _y, label="US_POST", alpha=0.7) plt.plot(range(len(_x_china)), _y_china, label="CN_POST", alpha=0.7) plt.xticks(range(0, len(_x_china), 10), list(_x_china)[::10], rotation=45) plt.legend(loc="best") plt.show()
2,打开tableau连接数据源新生成文件
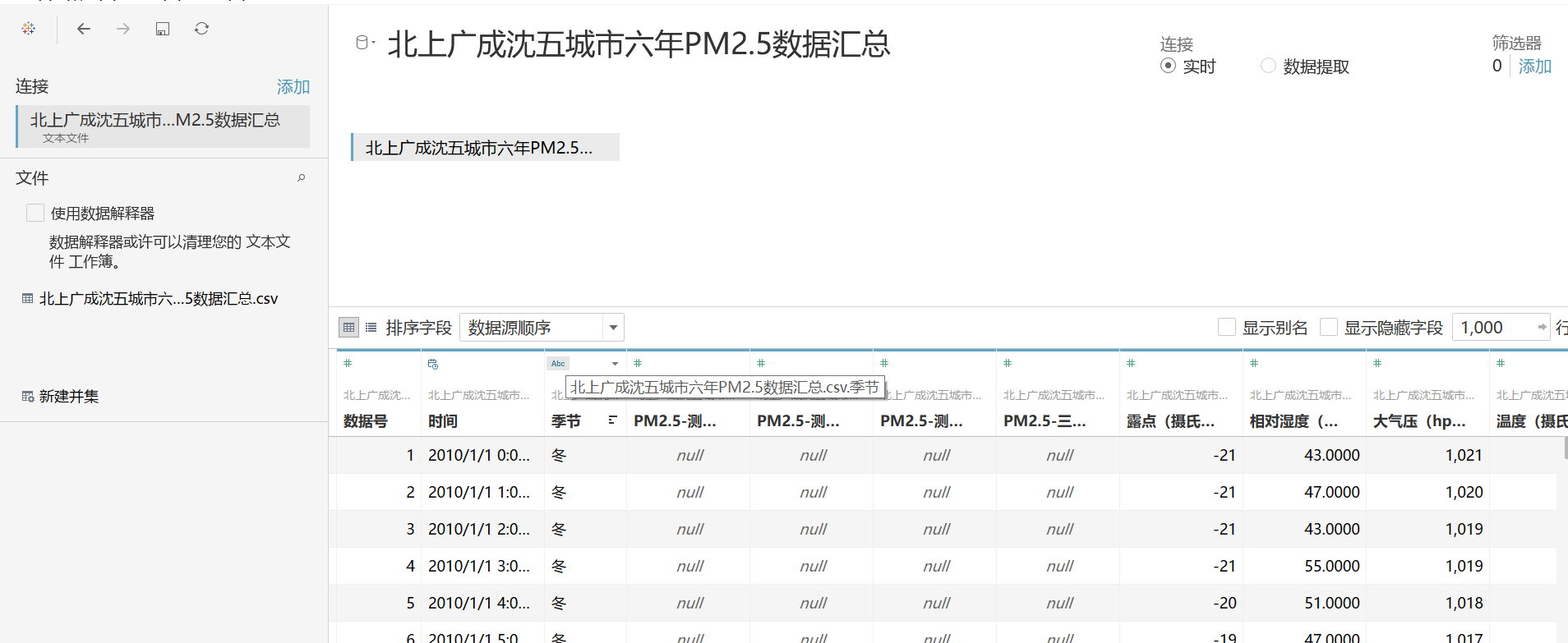
3,将城市转换为地理类型,并将经度纬度放入行和列中,将城市放入详细信息,三维PM2.5三个测点的平均值放入大小和颜色
得出结论:北京空气质量最差,上海和广州空气质量最好,成都因地处四川盆地,工业污染难以被风吹散,空气质量较其它城市较差。
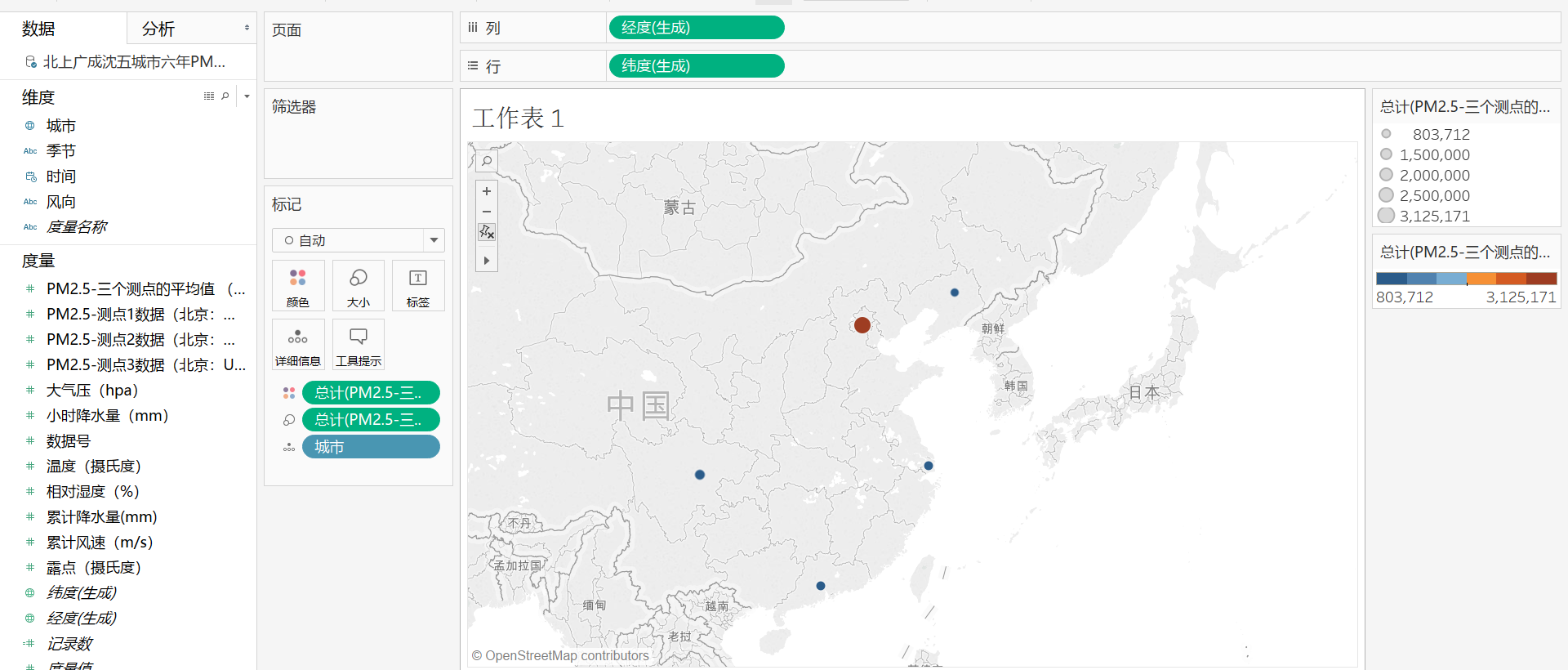
4,将城市和季节拖到列中,行中拖入PM2.5三个测量点的评价值,并将城市拖入到颜色中,并对其进行排序
得出结论:五个城市连续六年PM2.5大小在一年四季的分布,广州和上海的空气质量比较适宜
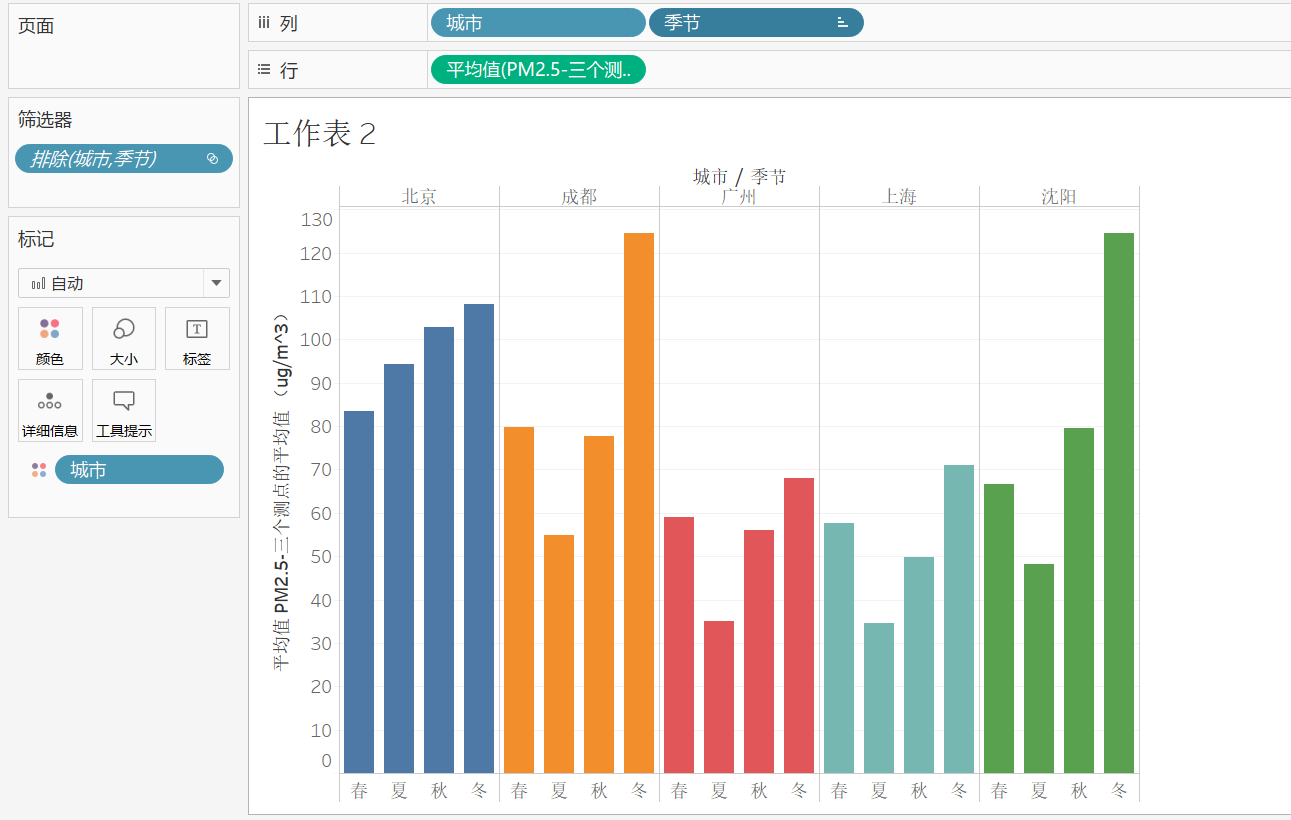
5,将时间放入列中,行中放入PM2.5的平均值,一次新建表,时间选择年,季度,月份,和小时,依次放入一个仪表盘
得出结论,PM2.5逐年计划和月份以及小时的变化
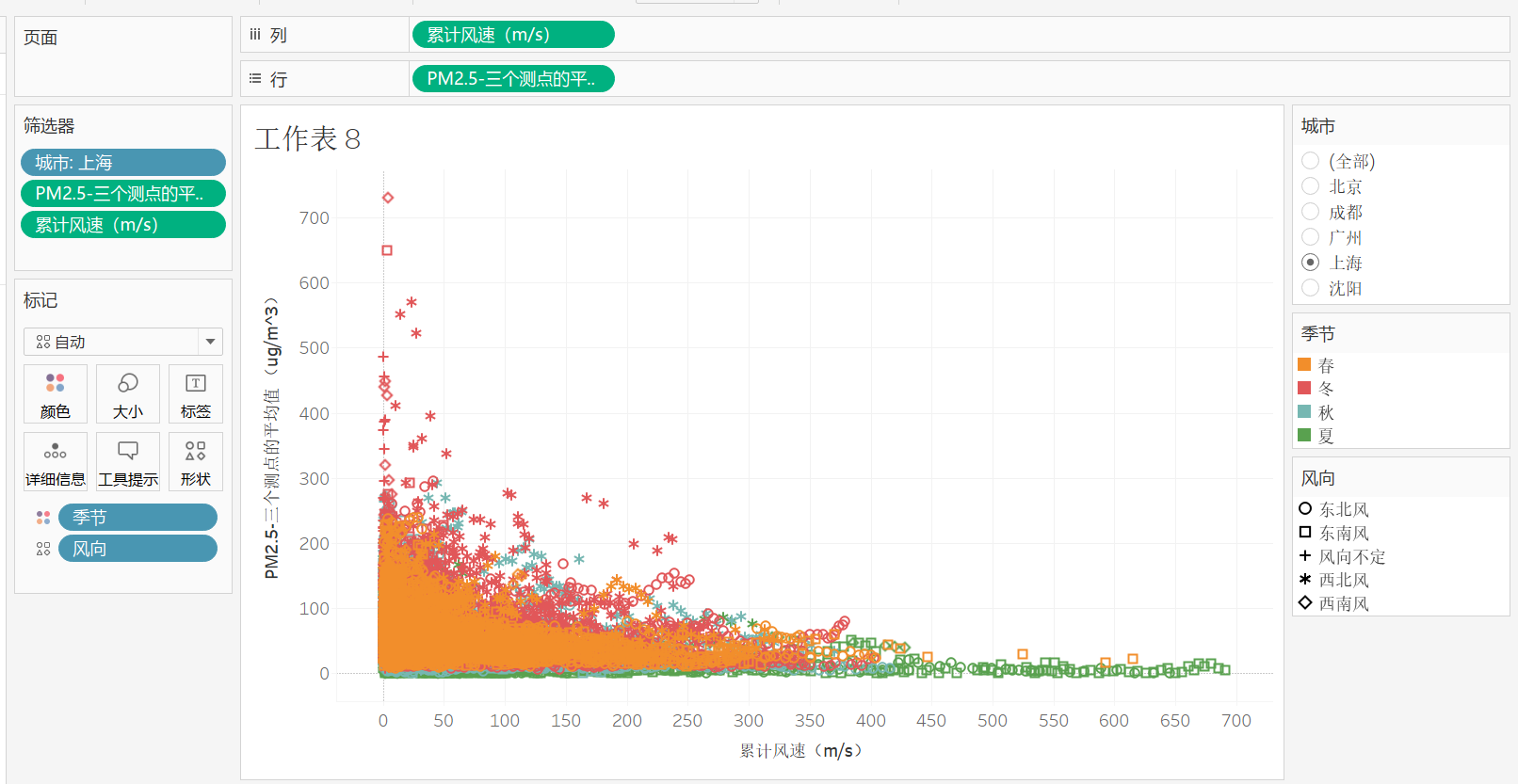
6,将累计风速,PM2.5三个测点的平均值分别放入列和行,选择维度数据本身,去掉重复值,将城市放入筛选器,季节放入颜色,风向放入形状选择一个城市
结论:通过可视化可以得出PM2.5与风速的关系,点击查看单个城市的情况,风速越大,PM2.5越低,比如北京,刮大风总是会刮西北风
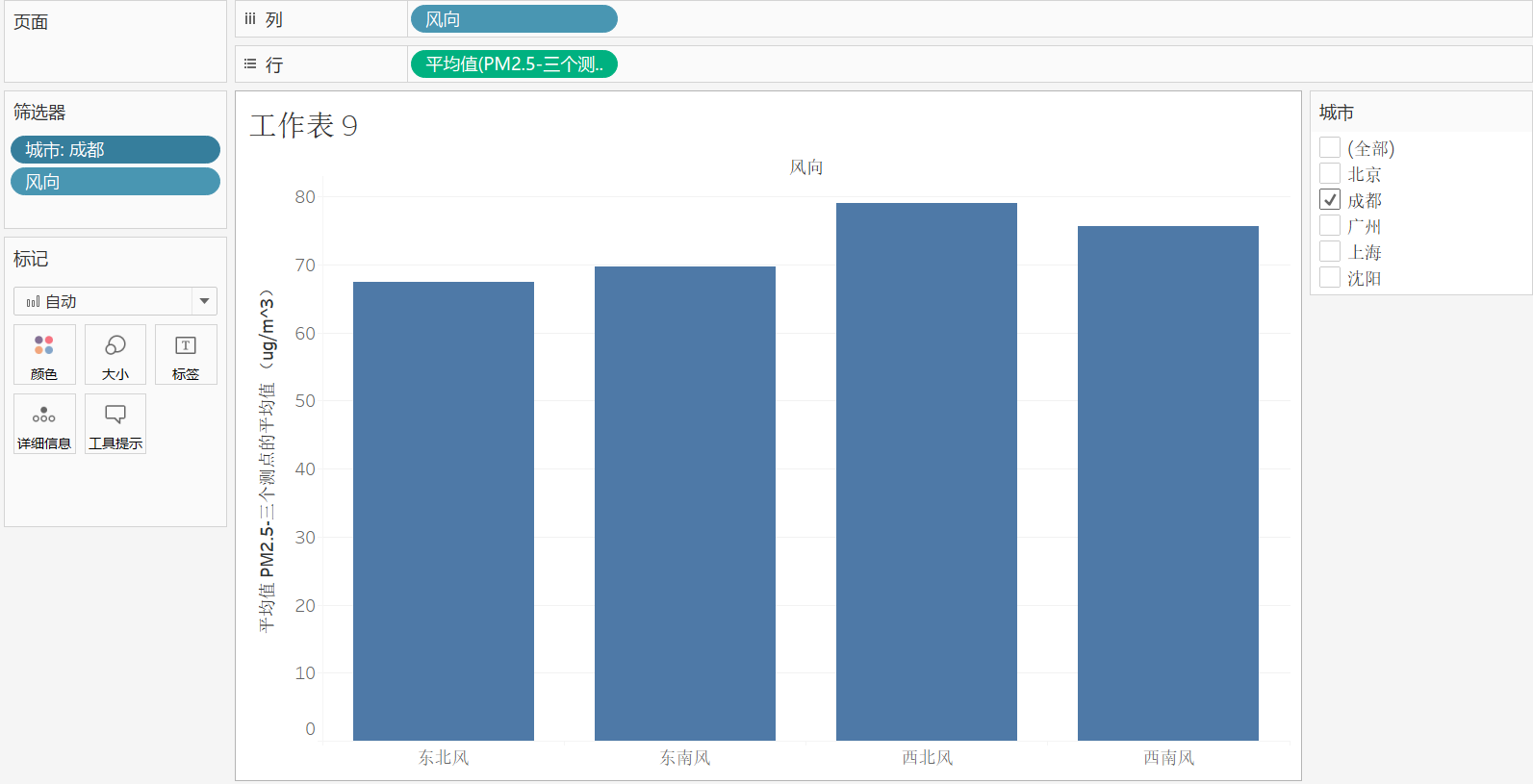
7,将风向放入列,三个点的平均值放入行中,城市放入筛选器,观察不同城市PM2.5大小与风向的关系
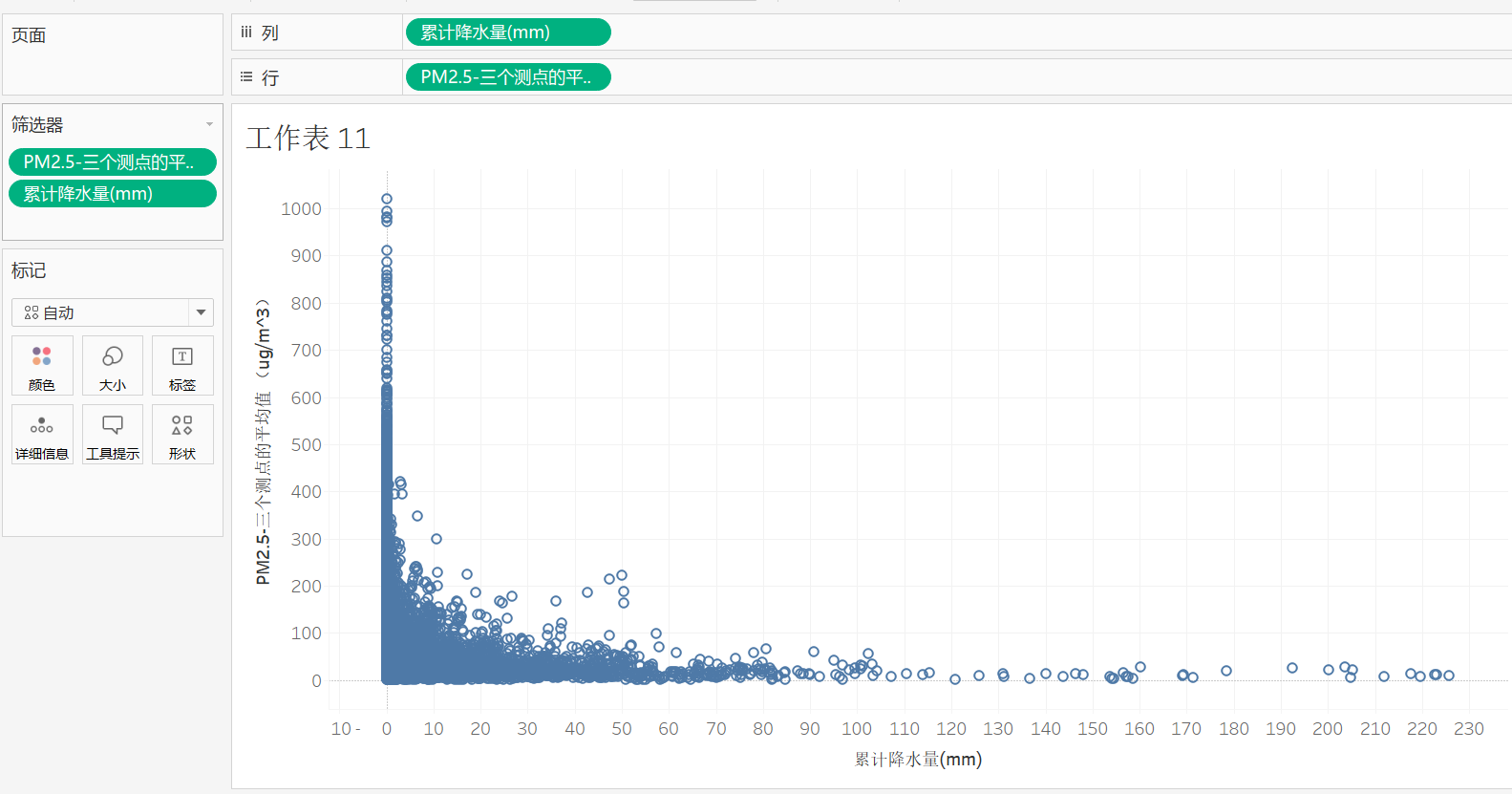
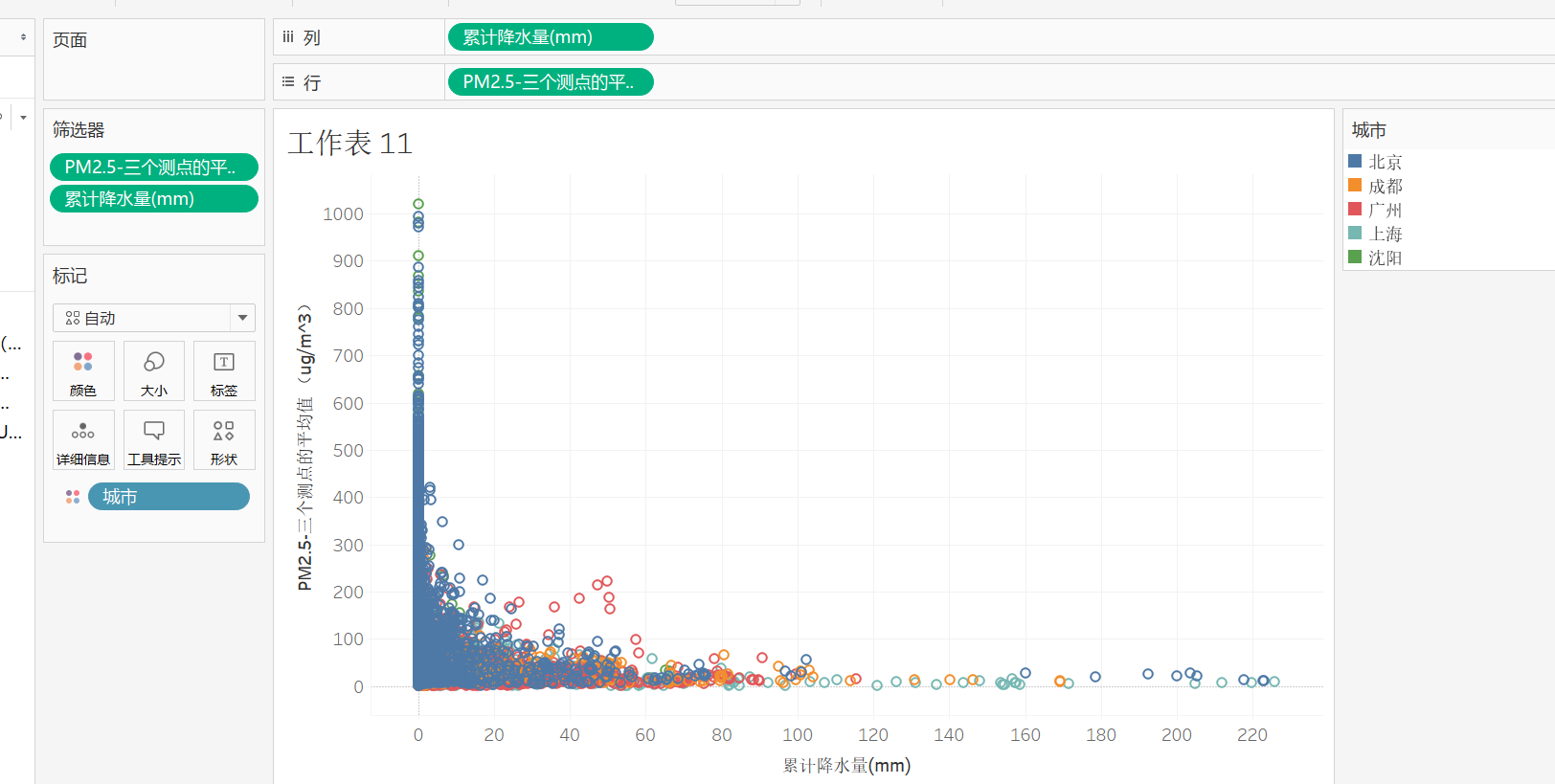
8,观察降水量与PM2.5的多少,可以得出结论,降水量越大,PM2.5越低
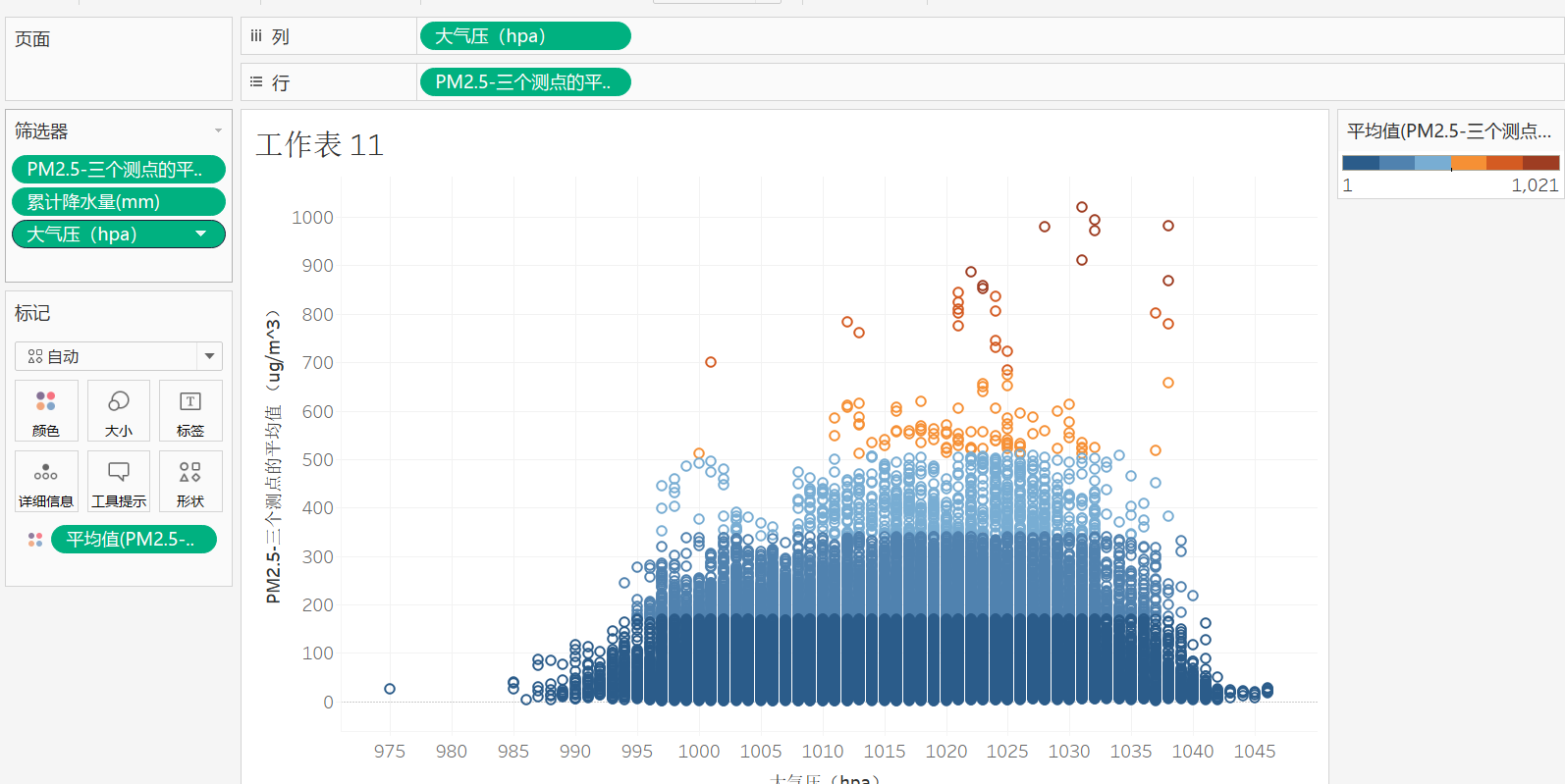
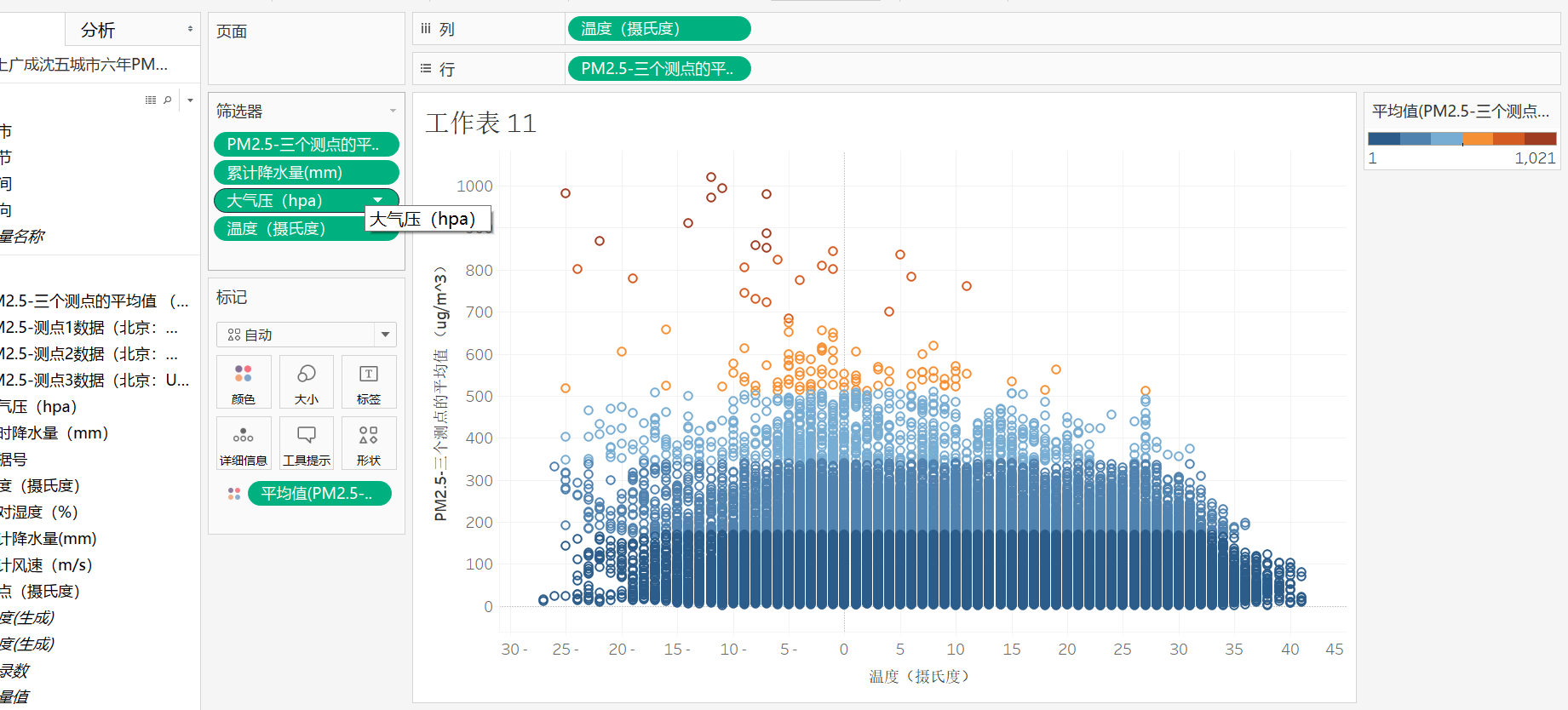
9,依次将大气压,相对湿度,温度等都会对其PM2.5的多少产生影响