1.目录结构:


2.pom文件:

Simple exmple:
package com.yuan.simple;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Haha {
String name() default "Haha lala";
}
package com.yuan.simple;
@Haha
public class Test {
public static void show(Class c){
System.out.println(c.getName());
boolean isExist=c.isAnnotationPresent(Haha.class);
if(isExist){
Haha haha=(Haha)c.getAnnotation(Haha.class);
System.out.println(haha.name());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test.show(Test.class);
}
}
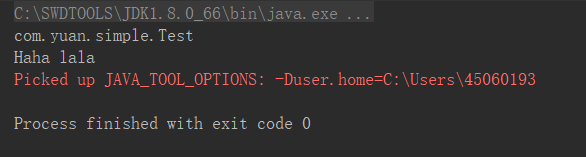
输出结果:
spring:
package com.yuan.springboot;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* Retention注解:定义被它所注解的注解保留多久(
* SOURCE:被编译器忽略
* ClASS:注解将会被保留在Class文件中,但在有耐性时并不会被VM保留。这是默认行为,所有没有用Retention注解的注解,都会采用这种策略。
* RUNtIME:保留至运行时。所以没有我们可以通过反射去获取注解信息
* )
* Target注解:用于描述杯盖注解标注的注解的作用范围(即:被描述的注解可以用在什么地方)
* 1.CONSTRUCTOR:用于描述构造器
* 2.FIELD:用于描述域
* 3.LOCAL_VARIABLE:用于描述局部变量
* 4.METHOD:用于描述方法
* 5.PACKAGE:用于描述包
* 6. PARAMETER: 用于描述参数
* 7. TYPE: 用于描述类、接口(包括注解类型) 或enum声明
*/
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.METHOD})
public @interface CheckType {
String value() default "";
package com.yuan.springboot;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.web.method.HandlerMethod;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class CheckTypeInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor{
@Value("${info.sys.checkType}")
private Integer checkType;//系统中配置的是否需要验证验证码
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
//当获取到的系统中的配置为null时,说明不校验。就放过
if (checkType==null){
return true;
}
//将被拦截的方法对象转成HandlerMethod对象
//关于HandlerMethod对象,是用来封装方法定义相关的信息(如:方法所属类,方法的参数,方法本身等)。可以理解成时具有了方法信息的一个实体类
HandlerMethod handlerMethod=(HandlerMethod) handler;
//调用getMethod()方法来获取方法本身
Method method=handlerMethod.getMethod();
//用方法本身来调用getAnnotation(x)方法来拿到参数中传如的注解类
//如果返回值不为空说明方法被该注解标记。否则没有被该注解标记
CheckType checkType=method.getAnnotation(CheckType.class);
if(checkType==null){
return true;
}
String value=checkType.value();
//根据传入的值来做一些业务相关判断
return false;
}
}
package com.yuan.springboot;
import com.yuan.springboot.CheckTypeInterceptor;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
/**
* 我们在自定义拦截器的时候,仅仅定义一个类实现HandlerInterceptor接口时不够的
* 我们还要将自定义的拦截器类注册到系统中并重写方法来告诉系统都需要拦截什么样的请求
* so 这里就是实现WebMvcConfigurger接口(此接口时spring boot中的)
* WebMvcConfigurer 接口时springboot定义配置的接口,相当于spring的.xml配置文件
*/
public class SmsConfiguration implements WebMvcConfigurer {
//@Bean 注解时将该方法产生的bean交给spring容器管理
@Bean
public CheckTypeInterceptor checkTypeInterceptor(){
return new CheckTypeInterceptor();
}
//addInterceptors是来注册拦截器的方法(如果不使用
//springboot 估计要在配置文件中配置了)
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
/**
* addInterceptor("xxx");方法死给注册具体的拦截器的,参数格式为:
* 自定义的注解的对象调用addPathPatterns("xxxx")方法,来为自定义拦截器添加拦截的请求,
* 另外一个方法registry.addInterceptor(checkTypeInterceptor()).addPathPatterns("xxx").excludePathPatterns("xxx","xxx","xxx",...)
* 这里的excludePathPatterns();方法是用来排除特定的请求的,比如首页等。所以一般的做饭是:先用addInterceptor("/**")方法来添加拦截所有的请求,
* 再用excludePathPatterns来排除不需要拦截器的请求即可
*
*/
registry.addInterceptor(checkTypeInterceptor()).addPathPatterns("/customer");
//这昂如果浏览器段的请求格式符合上述配置,那么就会被拦截到。就会进入上面自定义拦截器类中的preHande方法
}
}


