Spring之Bean容器源码理解,Spring4.3.12.RELEASE版本
1、Spring容器创建以及初始化过程。Spring容器的refresh(),是容器的创建以及刷新功能。整个容器就是通过refresh()方法运行完成以后,实现容器创建、以及将所有的bean创建对象、初始化完成。this();是做预处理操作,register(annotatedClasses);是做解析操作。
1 package com.bie.main; 2 3 import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; 4 5 import com.bie.config.SpringApplicationConfig; 6 7 /** 8 * 9 * 10 * @Title: SpringTransactionApplication.java 11 * @Package com.bie.main 12 * @Description: TODO 13 * @author biehl 14 * @date 2019年12月19日 15 * @version V1.0 16 * 17 */ 18 public class SpringTransactionApplication { 19 20 public static void main(String[] args) { 21 // 创建IOC容器,new一个IOC容器。 22 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringApplicationConfig.class); 23 24 ac.close(); 25 } 26 27 }
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringApplicationConfig.class);点击进去,打好断点。
启动主启动类,进入断点。
点击Step Into(F5)进入断点。
prepareRefresh();刷新前的预处理工作。
1 @Override 2 public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { 3 // 线程安全的锁机制 4 synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { 5 // Prepare this context for refreshing. 6 // 刷新前的预处理工作。 7 prepareRefresh(); 8 9 // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. 10 // 获取Bean工厂 11 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); 12 13 // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. 14 // 对Bean工作做预处理操作,对beanFactory做一些设置 15 prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); 16 17 try { 18 // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. 19 // BeanFactory准备工作完成后进行的后置处理工作。 20 postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); 21 22 // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. 23 // 注册BeanFactoryPostProcessors即注册bean工厂的后置处理器,核心作用,就是执行beanFactoryPostProcessors的方法 24 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); 25 26 // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. 27 // 注册BeanPostProcessors,注册bean的后置处理器。 28 // 后置处理器是拦截bean的创建过程的。 29 registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); 30 31 // Initialize message source for this context. 32 // 初始化MessageSource组件(在SpringMVC中做国际化功能、消息绑定、消息解析功能的)。 33 initMessageSource(); 34 35 // Initialize event multicaster for this context. 36 // Spring容器创建,初始化事件派发器等。 37 initApplicationEventMulticaster(); 38 39 // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. 40 // 留给子容器(即子类),在子容器中初始化剩下指定的bean。 41 onRefresh(); 42 43 // Check for listener beans and register them. 44 // Spring容器创建监听器等。检查监听器或者注册监听器,给容器中将所有项目里面的ApplicationListener注册进来。 45 registerListeners(); 46 47 // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. 48 // 初始化所有剩下的单实例bean。Spring容器创建,创建Bean准备。 49 finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); 50 51 // Last step: publish corresponding event. 52 // 完成工厂的刷新工作。完成BeanFactory的初始化创建工作。此步骤完成,相当于IOC容器创建完成。 53 finishRefresh(); 54 } 55 56 catch (BeansException ex) { 57 if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { 58 logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " + 59 "cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex); 60 } 61 62 // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources. 63 // 64 destroyBeans(); 65 66 // Reset 'active' flag. 67 // 68 cancelRefresh(ex); 69 70 // Propagate exception to caller. 71 throw ex; 72 } 73 74 finally { 75 // Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we 76 // might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore... 77 resetCommonCaches(); 78 } 79 } 80 }
如下所示:
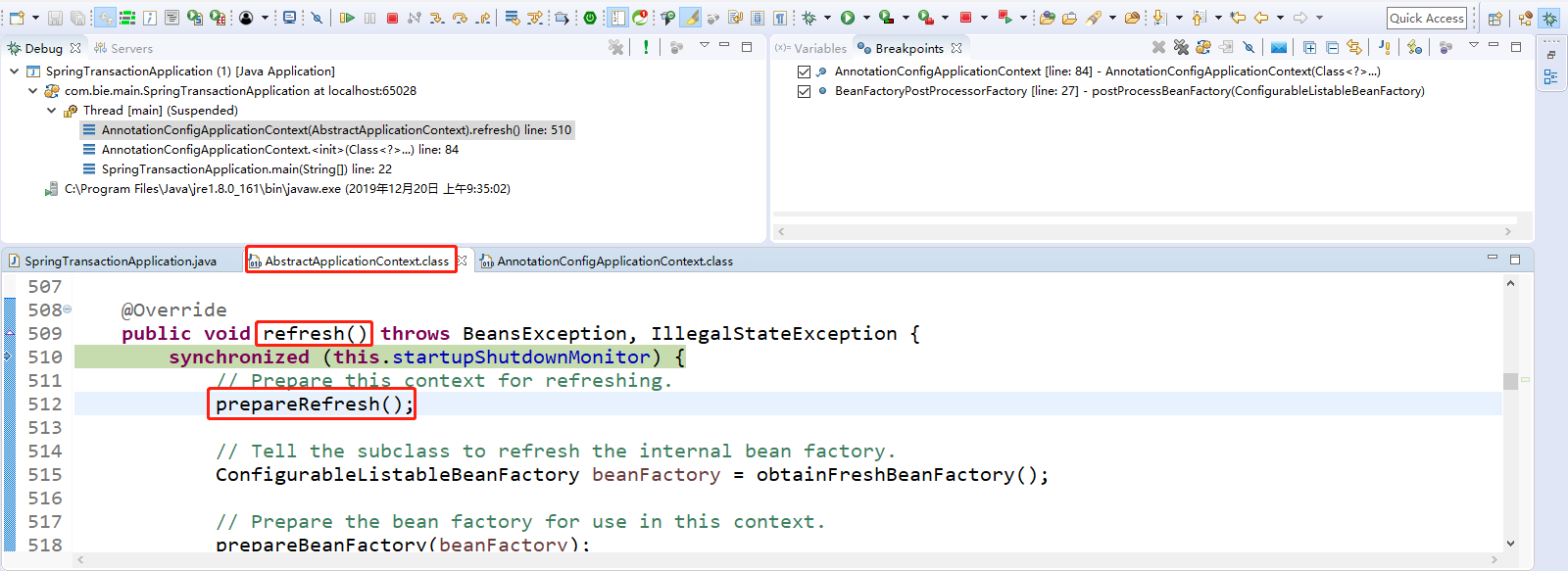
点击Step Into(F5)进入。prepareRefresh(); 刷新前的预处理工作。
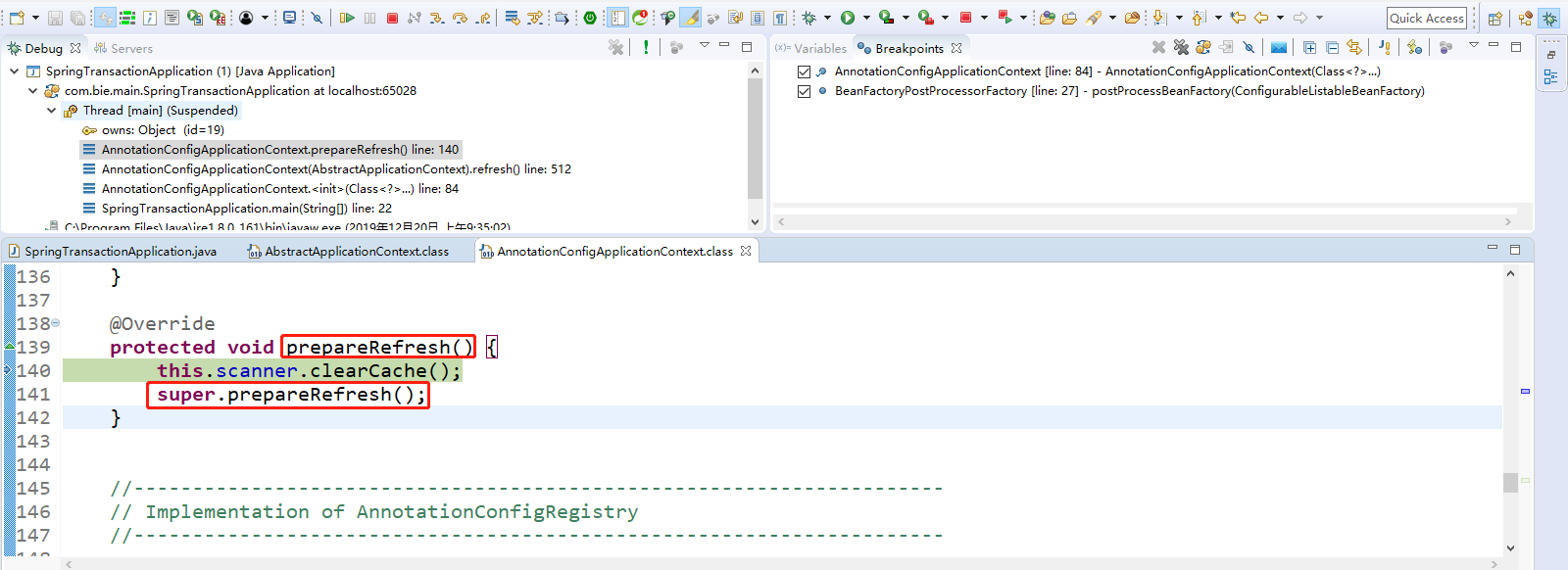
this.scanner.clearCache();清理缓存的工作。super.prepareRefresh();点击Step Into(F5)进入。
1 protected void prepareRefresh() { 2 // 记录时间 3 this.startupDate = System.currentTimeMillis(); 4 // 容器已经关闭了吗,设置为false 5 this.closed.set(false); 6 // 容器是否已经被激活,设置为true 7 this.active.set(true); 8 9 // 打印容器刷新日志 10 if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { 11 logger.info("Refreshing " + this); 12 } 13 14 // Initialize any placeholder property sources in the context environment 15 // 初始化一些属性设置 16 initPropertySources(); 17 18 // Validate that all properties marked as required are resolvable 19 // see ConfigurablePropertyResolver#setRequiredProperties 20 // 对自定义属性进行属性校验的。检验属性是否合法。 21 getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties(); 22 23 // Allow for the collection of early ApplicationEvents, 24 // to be published once the multicaster is available... 25 // 创建一个集合,保存容器中一些早期的事件,如果有事件发生存入这个集合中,方便在合适的时候使用事件派发器进行派发事件。 26 this.earlyApplicationEvents = new LinkedHashSet<ApplicationEvent>(); 27 }
如下所示:

点击Step Into(F5)进入。initPropertySources();初始化属性设置。

发现这个方法initPropertySources()是空的,是留给子类做事情的。子类自定义个性化的属性设置方法(自定义的时候有用哦)。
走到下一步,getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties();对自定义属性进行属性校验的。
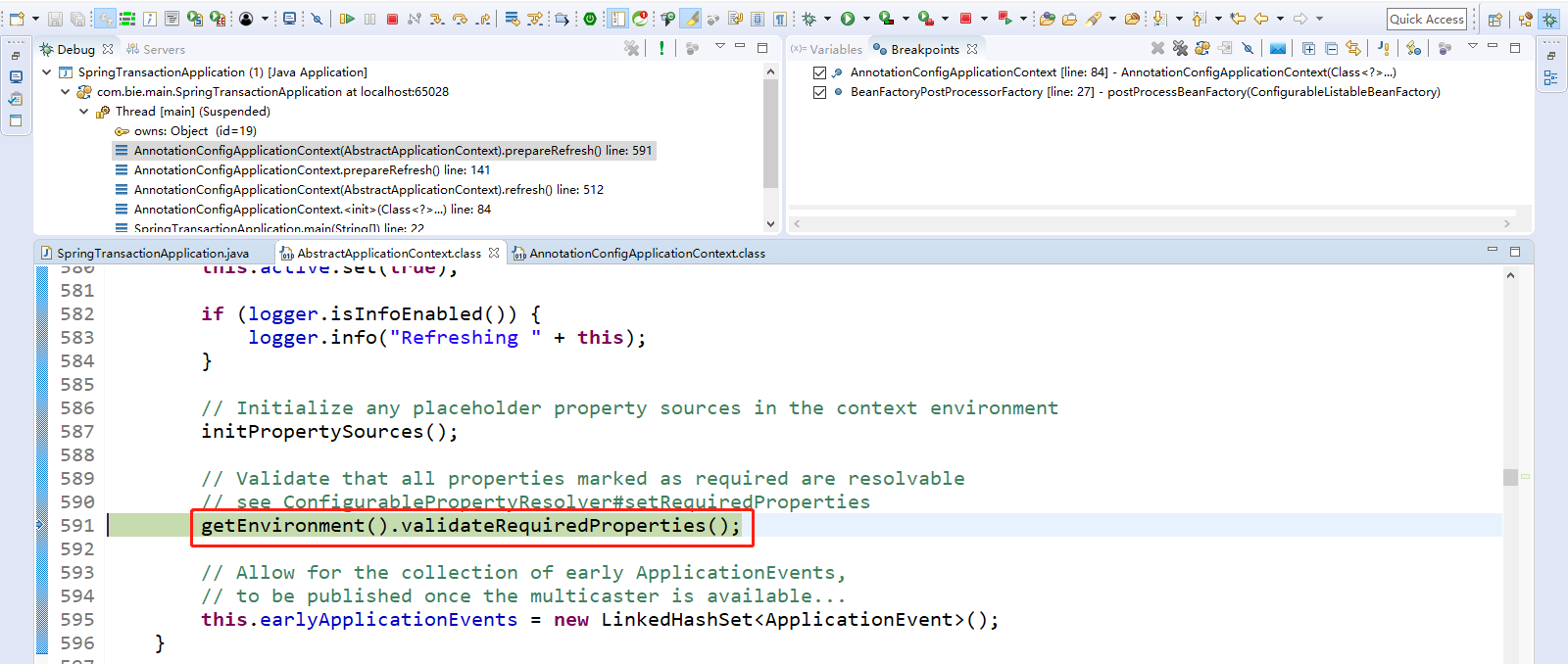
点击Step Into(F5)进入。getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties();自定义属性进行校验。
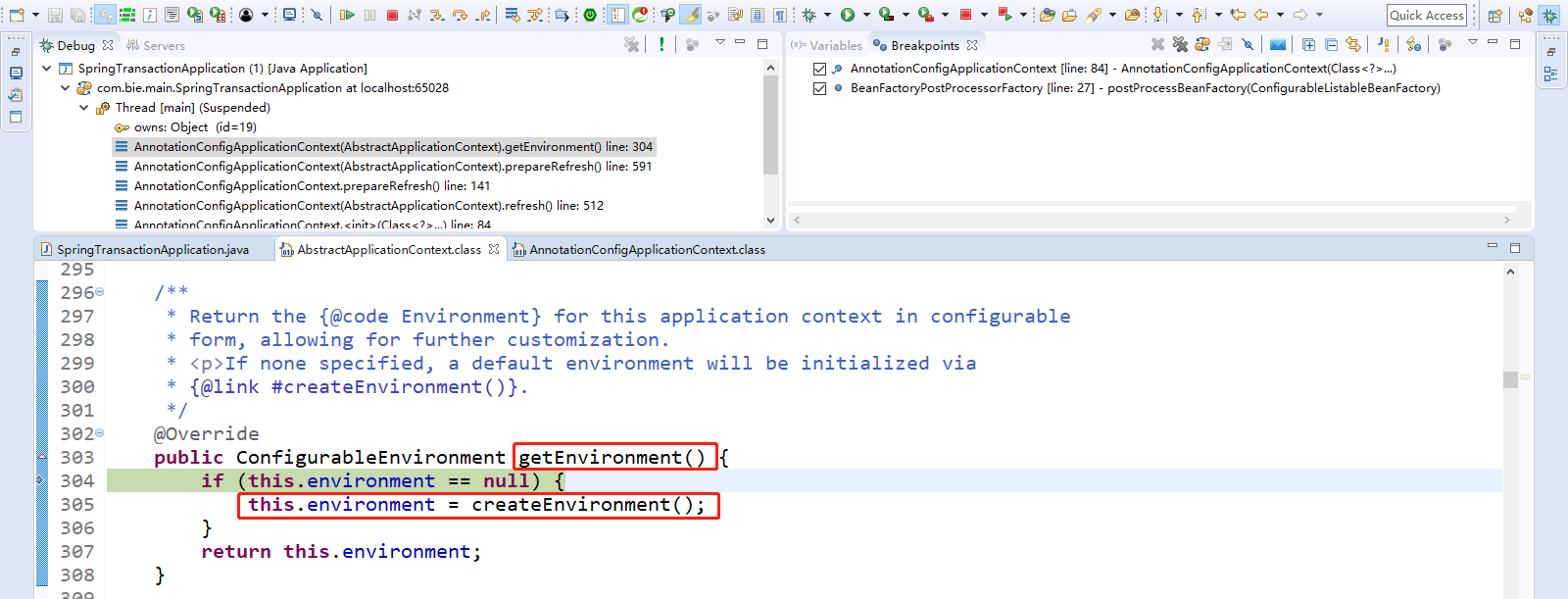
Step Over(F6)出去,再点击Step Into(F5)进入validateRequiredProperties();
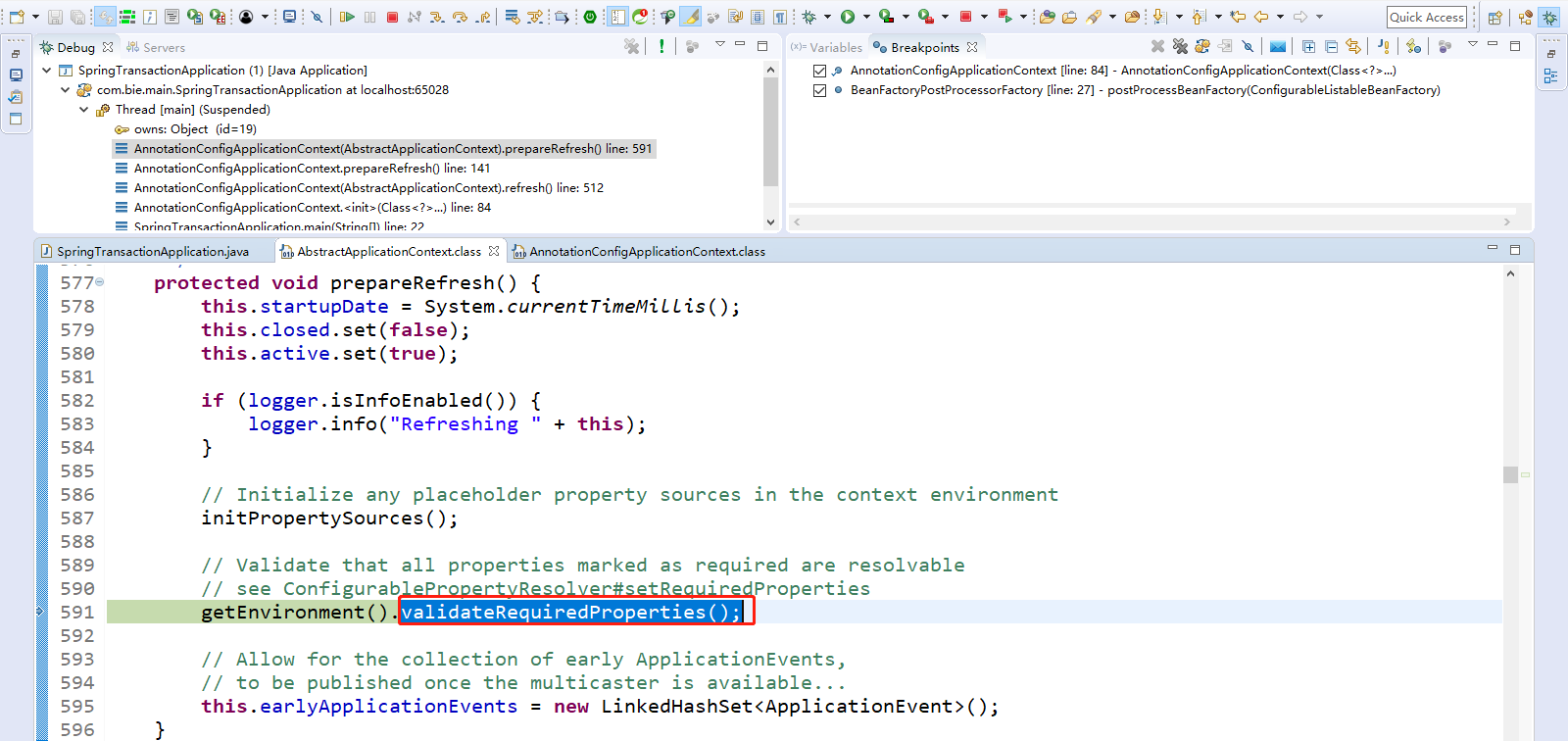
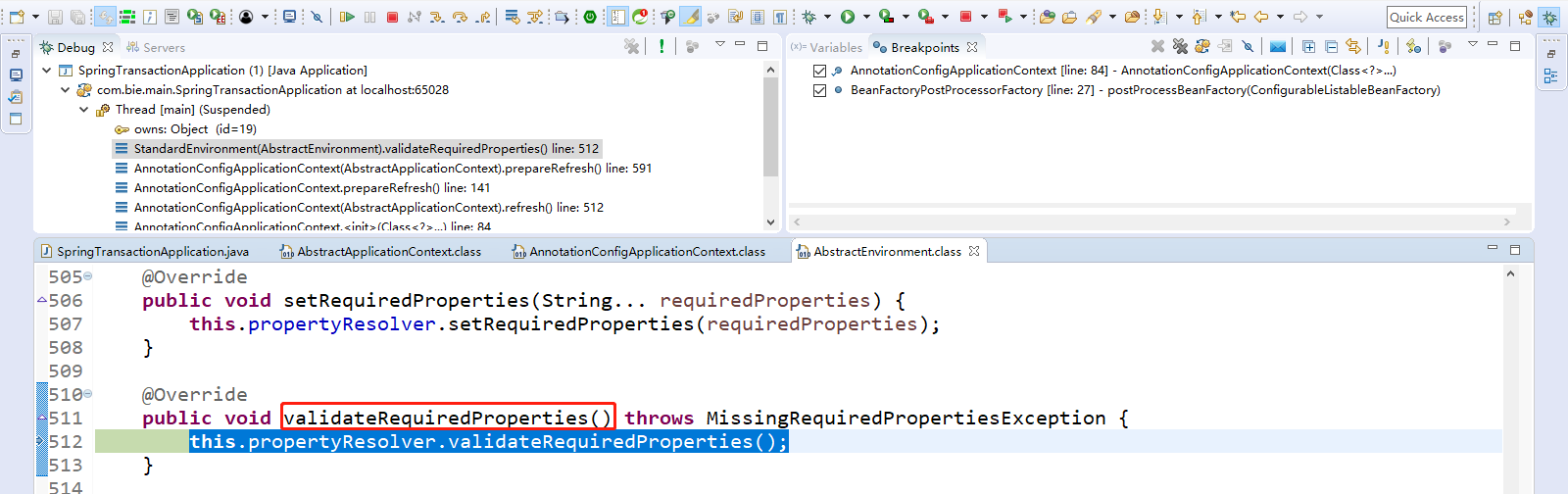
this.propertyResolver.validateRequiredProperties();属性解析器进行校验,自己可以点击Step Into(F5)进入看看。
点击Step Over(F6)下一步,创建一个集合,保存容器中一些早期的事件,如果有事件发生存入这个集合中,方便在合适的时候使用事件派发器进行派发事件。
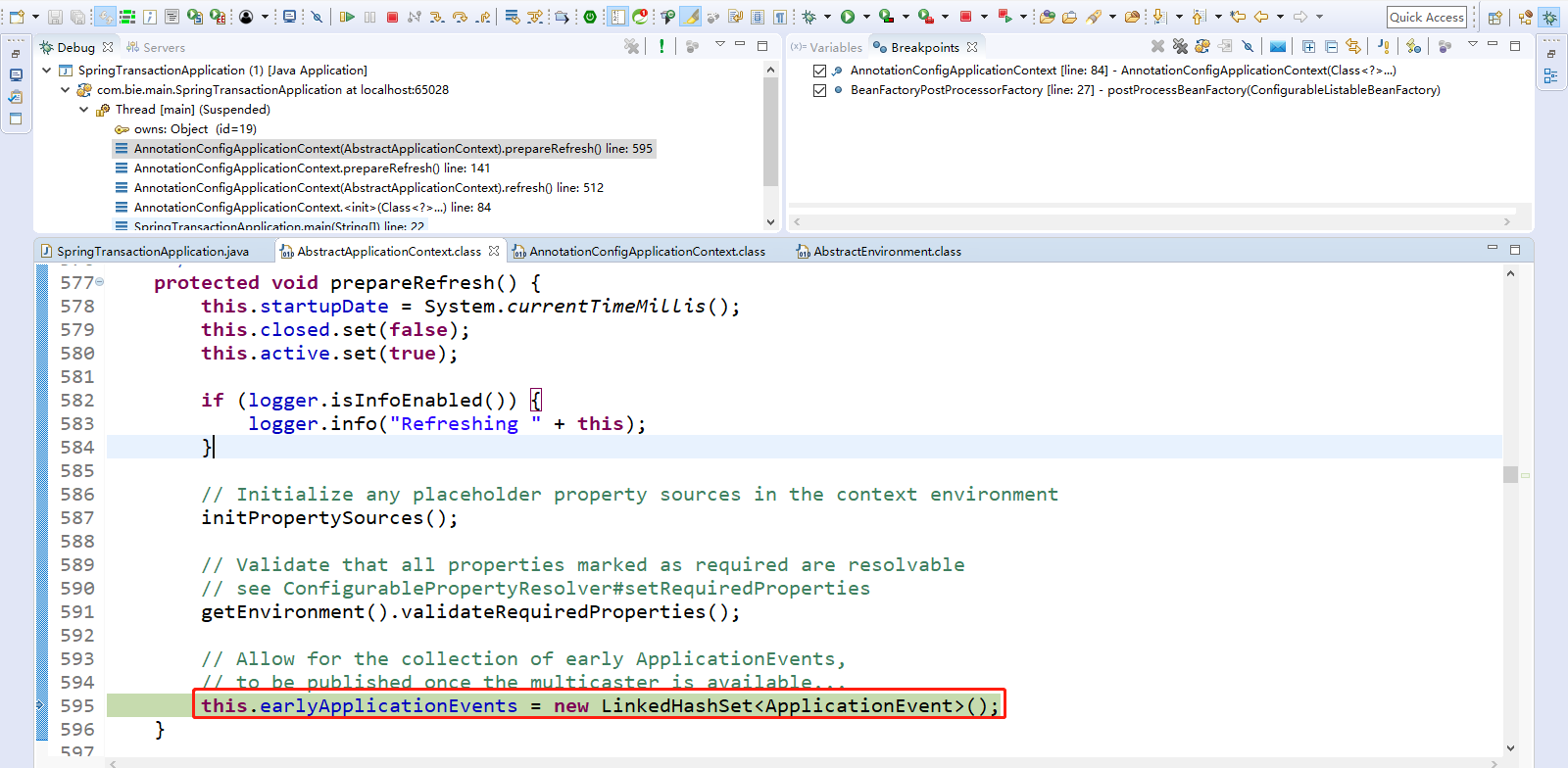
2、点击Step Over(F6)下一步,直到ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
点击Step Into(F5)进入obtainFreshBeanFactory();

refreshBeanFactory();刷新Bean工厂。
1 protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() { 2 // 刷新即创建Bean工厂(此时是创建了Bean工厂) 3 refreshBeanFactory(); 4 // 获取Bean工厂 5 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory(); 6 // 打印容器刷新日志 7 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 8 logger.debug("Bean factory for " + getDisplayName() + ": " + beanFactory); 9 } 10 // 返回Bean工厂 11 return beanFactory; 12 }
如下所示:

点击Step Into(F5)进入refreshBeanFactory();
1 // 定义beanFactory,这个Bean工厂对象 2 private final DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory; 3 4 // GenericApplicationContext无参构造器,创建对象的时候,创建Bean工厂this.beanFactory 5 public GenericApplicationContext() { 6 this.beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory(); 7 } 8 9 @Override 10 protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws IllegalStateException { 11 if (!this.refreshed.compareAndSet(false, true)) { 12 throw new IllegalStateException( 13 "GenericApplicationContext does not support multiple refresh attempts: just call 'refresh' once"); 14 } 15 // 给Bean工厂设置序列号id,序列化id标识 16 this.beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId()); 17 }
如下所示:
点击Step Over(F6)下一步,走到ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
点击Step Into(F5)进入getBeanFactory();
将上一步refreshBeanFactory();创建的Bean工厂返回回来。返回刚才GenericApplicationContext创建的Bean工厂对象。
Step Over(F6)下一步,走到ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
Step Over(F6)下一步,走到ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();获取到Bean工厂对象。将创建的Bean工厂返回给beanFactory ,默认叫做DefaultListableBeanFactory。
3、对Bean工作做预处理操作,对beanFactory做一些设置prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
点击Step Into(F5)进入prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
1 protected void prepareBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { 2 // Tell the internal bean factory to use the context's class loader etc. 3 // 把类加载器放入到beanFactory中 4 beanFactory.setBeanClassLoader(getClassLoader()); 5 // 把表达式语言解析器放入到beanFactory中 6 beanFactory.setBeanExpressionResolver(new StandardBeanExpressionResolver(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader())); 7 // 8 beanFactory.addPropertyEditorRegistrar(new ResourceEditorRegistrar(this, getEnvironment())); 9 10 // Configure the bean factory with context callbacks. 11 // 把BeanPostProcessor后置处理器放入到beanFactory中。添加部分BeanPostProcessor到beanFactory中,如ApplicationContextAwareProcessor。 12 beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this)); 13 // 设置忽略的自动装配的接口EnvironmentAware。即这些接口的实现类,不能通过这些接口类型自动注入哦。 14 beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EnvironmentAware.class); 15 // 设置忽略的自动装配的接口EmbeddedValueResolverAware 16 beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EmbeddedValueResolverAware.class); 17 // 设置忽略的自动装配的接口ResourceLoaderAware 18 beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ResourceLoaderAware.class); 19 // 设置忽略的自动装配的接口ApplicationEventPublisherAware 20 beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationEventPublisherAware.class); 21 // 设置忽略的自动装配的接口MessageSourceAware 22 beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(MessageSourceAware.class); 23 // 设置忽略的自动装配的接口ApplicationContextAware 24 beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationContextAware.class); 25 26 // BeanFactory interface not registered as resolvable type in a plain factory. 27 // MessageSource registered (and found for autowiring) as a bean. 28 // 注册可以解析的自动装配BeanFactory。所谓的可以解析的自动装配即可以在任何组件中写@Autowired进行自动装配。 29 beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(BeanFactory.class, beanFactory); 30 // 注册可以解析的自动装配ResourceLoader 31 beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ResourceLoader.class, this); 32 // 注册可以解析的自动装配ApplicationEventPublisher 33 beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationEventPublisher.class, this); 34 // 注册可以解析的自动装配ApplicationContext 35 beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationContext.class, this); 36 37 // Register early post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners. 38 // 设置后置处理器ApplicationListenerDetector到beanFactory中。 39 beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(this)); 40 41 // Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found. 42 // LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME=loadTimeWeaver。添加编译时的AspectJ的支持。默认是运行时的动态代理。 43 if (beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) { 44 beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory)); 45 // Set a temporary ClassLoader for type matching. 46 beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader())); 47 } 48 49 // Register default environment beans. 50 // ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME=environment。给容器中注册一些能用的组件,key=environment,值是当前的环境对象。 51 if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) { 52 beanFactory.registerSingleton(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment()); 53 } 54 // SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME = systemProperties。给容器中注册组件,key=systemProperties,值是当前的系统配置。 55 if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME)) { 56 beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemProperties()); 57 } 58 // SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME = systemEnvironment。给容器中注册组件,key=systemEnvironment,值是当前的系统环境对象。 59 if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) { 60 beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemEnvironment()); 61 } 62 }
如下所示:
4、Step Over(F6)下一步,直到运行到postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
点击Step Into(F5)进入postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); BeanFactory准备工作完成后进行的后置处理工作。
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);方法也是一个空实现的,留给子类进行实现,在beanFactory创建并准备好以后,可以重写该postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);方法的。对beanFactory做更进一步的设置。子类通过重写这个方法来在BeanFactory创建并预准备完成以后做进一步的设置。
Step Over(F6)下一步,再点击Step Into(F5)走到postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
注意:以上四步是BeanFactory的创建以及预准备工作。
5、继续执行Step Over(F6)下一步,走到invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
Spring容器创建,执行BeanFactoryPostProcessor(即BeanFactory的后置处理器,在BeanFactory标准初始化之后执行的,而标准初始化即上四步流程)。两个接口,BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口,BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor是BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的子接口。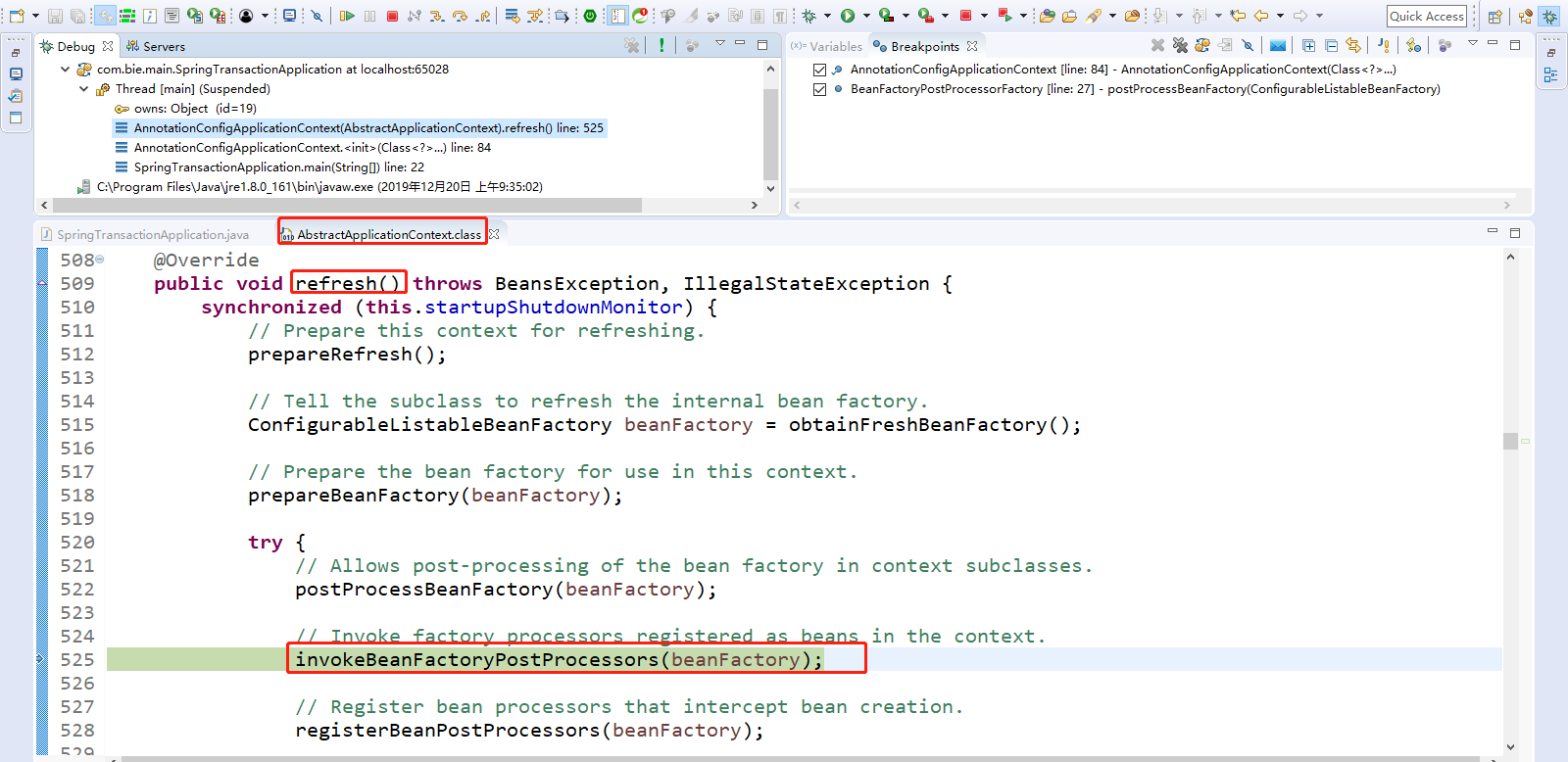
点击Step Into(F5)进入invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
1 // 核心作用,就是执行beanFactoryPostProcessors的方法 2 protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { 3 // 执行BeanFactoryPostProcessor的方法。getBeanFactoryPostProcessors()获取到beanFactoryPostProcessors。 4 PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors()); 5 6 // Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found in the meantime 7 // (e.g. through an @Bean method registered by ConfigurationClassPostProcessor) 8 if (beanFactory.getTempClassLoader() == null && beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) { 9 beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory)); 10 beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader())); 11 } 12 }
如下所示:
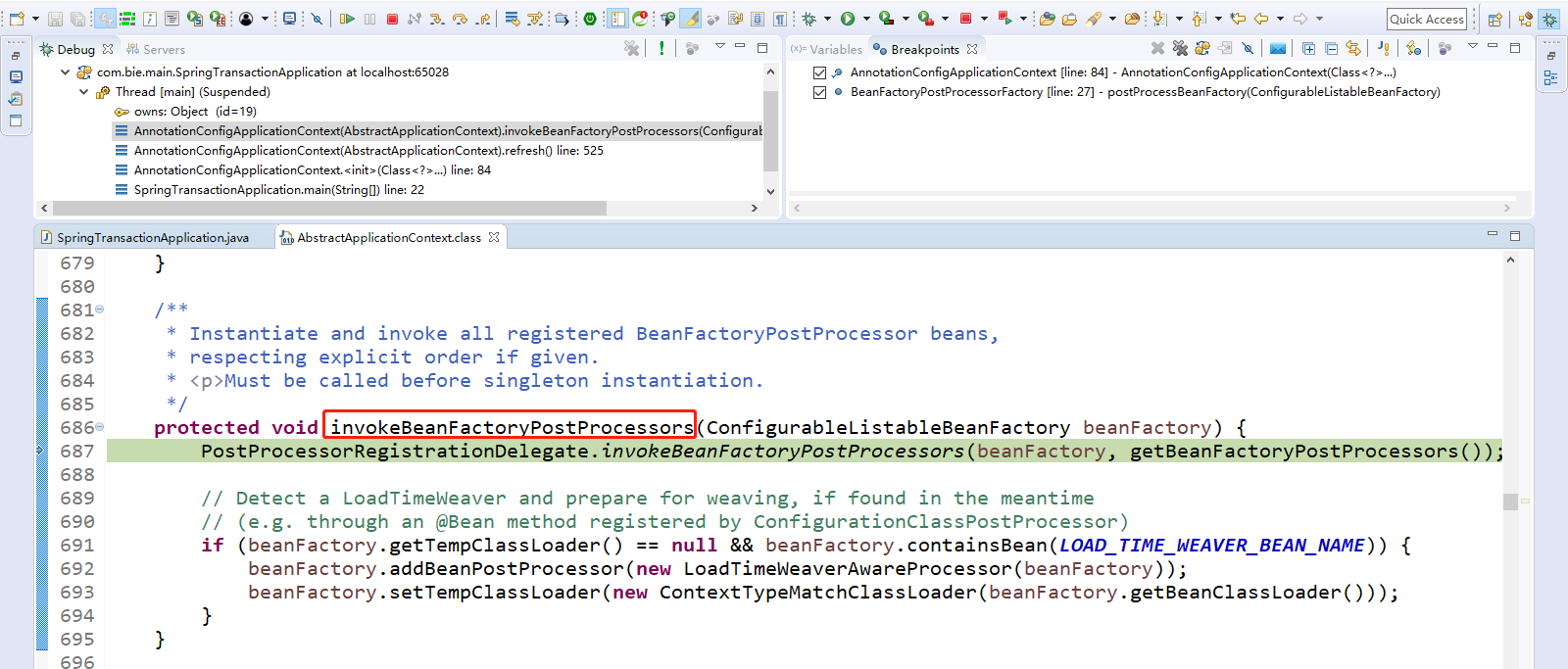
点击Step Into(F5)进入,PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors());
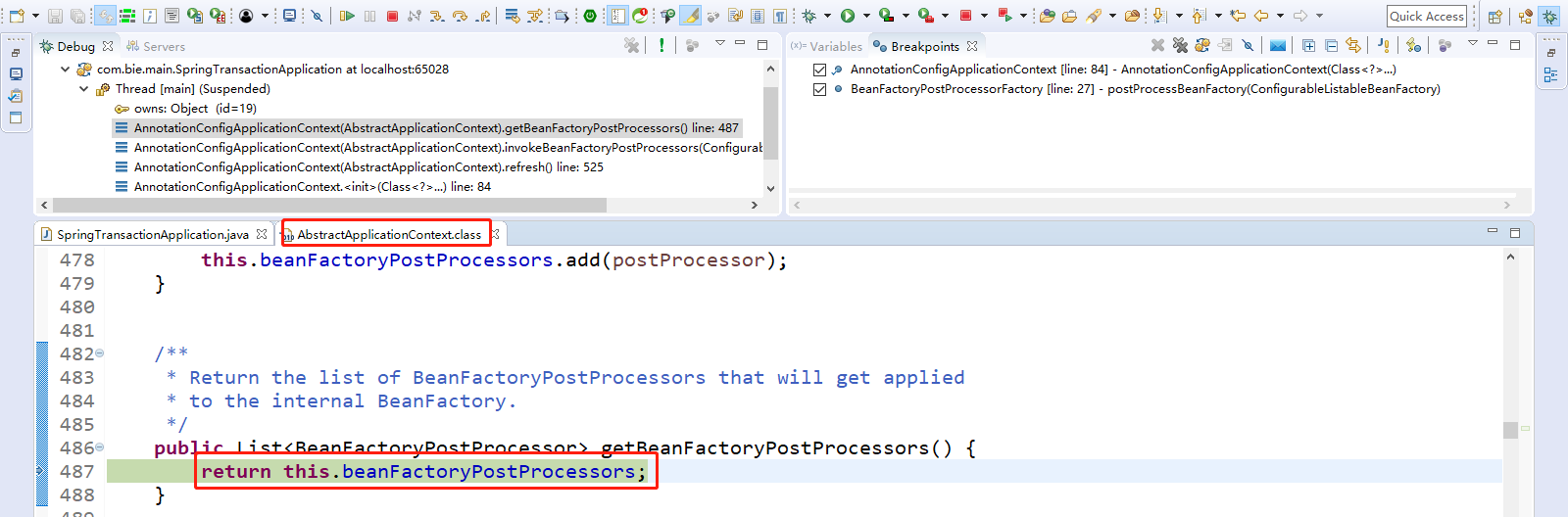
先获取到beanFactoryPostProcessors。Step Over(F6)下一步走到PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors());
执行invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法,点击Step Into(F5)进入。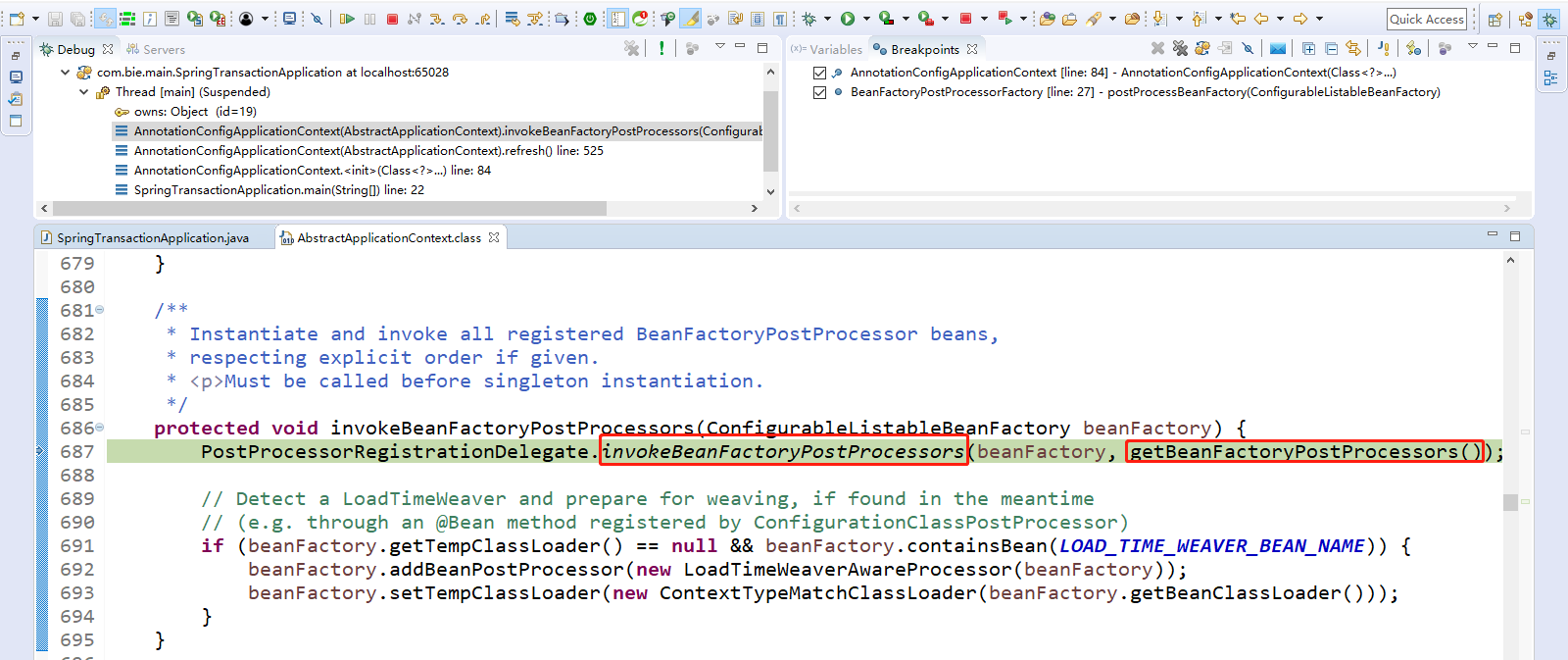
执行BeanFactoryPostProcessor的方法,即PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors()方法。
1 // 从容器中获取到所有的获取到beanFactoryPostProcessors 2 public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors( 3 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors) { 4 5 // Invoke BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors first, if any. 6 // 定义一个set集合存放processedBeans。 7 Set<String> processedBeans = new HashSet<String>(); 8 9 // 首先判断Bean工厂是否是BeanDefinitionRegistry类型的。DefaultListableBeanFactory就是BeanDefinitionRegistry类型的。 10 if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) { 11 // 将DefaultListableBeanFactory类型,强制转换为BeanDefinitionRegistry类型的。 12 BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory; 13 // 创建一个List集合,保存regularPostProcessors 14 List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> regularPostProcessors = new LinkedList<BeanFactoryPostProcessor>(); 15 // 创建一个List集合,保存registryProcessors 16 List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryProcessors = new LinkedList<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor>(); 17 18 // 遍历参数传递的beanFactoryPostProcessors,即上一步获取到的beanFactoryPostProcessors 19 for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) { 20 // 如果postProcessor是BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor类型的 21 if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) { 22 // 将postProcessor转换为BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor类型的。 23 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor = 24 (BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor; 25 // 将DefaultListableBeanFactory类型,强制转换为BeanDefinitionRegistry类型的。写入到registryProcessor 26 registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry); 27 // 将registryProcessor添加到registryProcessors 28 registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor); 29 } 30 else { 31 // 否则将postProcessor添加到regularPostProcessors 32 regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor); 33 } 34 } 35 36 // Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans 37 // uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them! 38 // Separate between BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement 39 // PriorityOrdered, Ordered, and the rest. 40 // 定义一个List集合currentRegistryProcessors 41 List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> currentRegistryProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor>(); 42 43 // First, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered. 44 // 第一步、获取到所有的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor类型的。BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor是BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的子接口。 45 // BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor子接口具有最高优先级 46 // 首先执行实现了PriorityOrdered优先级接口的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 47 String[] postProcessorNames = 48 beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false); 49 // 遍历获取到的这种BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor类型的 50 for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { 51 // 判断是否实现了PriorityOrdered优先级排序的接口。优先级排序有三种情况,这是第一种。 52 if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) { 53 // 将ppName添加到currentRegistryProcessors集合中 54 currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class)); 55 // 将ppName保存到全局的processedBeans集合中 56 processedBeans.add(ppName); 57 } 58 } 59 // 按照优先级进行排序操作 60 sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory); 61 // 将currentRegistryProcessors添加到集合registryProcessors中 62 registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors); 63 // 执行,调用方法遍历循环执行postProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry); 64 // 首先执行实现了PriorityOrdered优先级接口的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 65 invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry); 66 // 清除currentRegistryProcessors集合里面的内容 67 currentRegistryProcessors.clear(); 68 69 // Next, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement Ordered. 70 // 第二步,获取到所有的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor类型的。BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor是BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的子接口。 71 // 再执行实现了Ordered顺序接口的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 72 postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false); 73 // 遍历获取到的这种BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor类型的 74 for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { 75 // 如果processedBeans里面不包含ppName,并且判断是否实现了Ordered顺序的接口。 76 if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) { 77 // // 将ppName添加到currentRegistryProcessors集合中 78 currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class)); 79 // 将ppName保存到全局的processedBeans集合中 80 processedBeans.add(ppName); 81 } 82 } 83 // 按照顺序进行排序操作 84 sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory); 85 // 将currentRegistryProcessors添加到集合registryProcessors中 86 registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors); 87 // 执行,调用方法遍历循环执行postProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry); 88 // 再执行实现了Ordered顺序接口的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 89 invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry); 90 // 清除currentRegistryProcessors集合里面的内容 91 currentRegistryProcessors.clear(); 92 93 // Finally, invoke all other BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors until no further ones appear. 94 // 最后,执行所有未实现接口的任何优先级接口或者顺序接口的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 95 // 定义变量reiterate为true 96 boolean reiterate = true; 97 // 循环执行 98 while (reiterate) { 99 // 设置变量为false 100 reiterate = false; 101 // 获取到所有的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor类型的。BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor是BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的子接口。 102 postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false); 103 // 循环遍历postProcessorNames 104 for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { 105 // 如果processedBeans不包含ppName 106 if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) { 107 // // 将ppName添加到currentRegistryProcessors集合中 108 currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class)); 109 // 将ppName保存到全局的processedBeans集合中 110 processedBeans.add(ppName); 111 // 将变量reiterate设置为true 112 reiterate = true; 113 } 114 } 115 // 按照未实现接口的进行排序操作 116 sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory); 117 // 将currentRegistryProcessors添加到集合registryProcessors中 118 registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors); 119 // 执行,调用方法遍历循环执行postProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry); 120 // 未实现PriorityOrdered优先级接口、Ordered顺序接口的 121 invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry); 122 // 清除currentRegistryProcessors集合里面的内容 123 currentRegistryProcessors.clear(); 124 } 125 126 // Now, invoke the postProcessBeanFactory callback of all processors handled so far. 127 // 调用invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法,循环遍历postProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); 128 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory); 129 // 用invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法,循环遍历postProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); 130 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory); 131 } 132 133 else { 134 // Invoke factory processors registered with the context instance. 135 // 否则,执行beanFactoryPostProcessors 136 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactoryPostProcessors, beanFactory); 137 } 138 139 // Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans 140 // uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them! 141 // 获取到BeanFactoryPostProcessor方法。在bean工厂中按照类型获取到BeanFactoryPostProcessor。 142 // 下面的流程和上面的流程一致。 143 String[] postProcessorNames = 144 beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false); 145 146 // Separate between BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered, 147 // Ordered, and the rest. 148 // 创建List集合BeanFactoryPostProcessor 149 List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanFactoryPostProcessor>(); 150 // 创建List集合orderedPostProcessorNames 151 List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<String>(); 152 // 创建List集合nonOrderedPostProcessorNames 153 List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<String>(); 154 // 循环遍历postProcessorNames 155 for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { 156 // 如果processedBeans包含了ppName,跳过 157 if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) { 158 // skip - already processed in first phase above 159 } 160 // 否则,如果beanFactory是PriorityOrdered优先级顺序接口类型的。实现PriorityOrdered优先级接口的放入到priorityOrderedPostProcessors集合中。 161 else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) { 162 priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class)); 163 } 164 // 否则,如果beanFactory是Ordered顺序接口类型的。实现Ordered顺序接口的放入到orderedPostProcessorNames集合中 165 else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) { 166 orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName); 167 } 168 else { 169 // 否则,如果都不是,将ppName添加到nonOrderedPostProcessorNames。为实现接口的放到nonOrderedPostProcessorNames集合中。 170 nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName); 171 } 172 } 173 174 // First, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered. 175 // 按照优先级进行排序操作 176 sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); 177 // 执行,调用方法遍历循环执行postProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); 178 // 首先执行实现了PriorityOrdered优先级接口的BeanFactoryPostProcessor 179 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); 180 181 // Next, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement Ordered. 182 // 实现Ordered顺序接口的遍历添加到orderedPostProcessors集合中 183 List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanFactoryPostProcessor>(); 184 for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) { 185 orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class)); 186 } 187 // 按照顺序进行排序操作 188 sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); 189 // 执行,调用方法遍历循环执行postProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); 190 // 首先执行实现了Ordered顺序接口的BeanFactoryPostProcessor 191 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); 192 193 // Finally, invoke all other BeanFactoryPostProcessors. 194 // 最后,未实现PriorityOrdered接口、Ordered顺序接口的遍历添加到orderedPostProcessors集合中 195 List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanFactoryPostProcessor>(); 196 for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) { 197 nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class)); 198 } 199 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); 200 201 // Clear cached merged bean definitions since the post-processors might have 202 // modified the original metadata, e.g. replacing placeholders in values... 203 beanFactory.clearMetadataCache(); 204 }
如下所示:
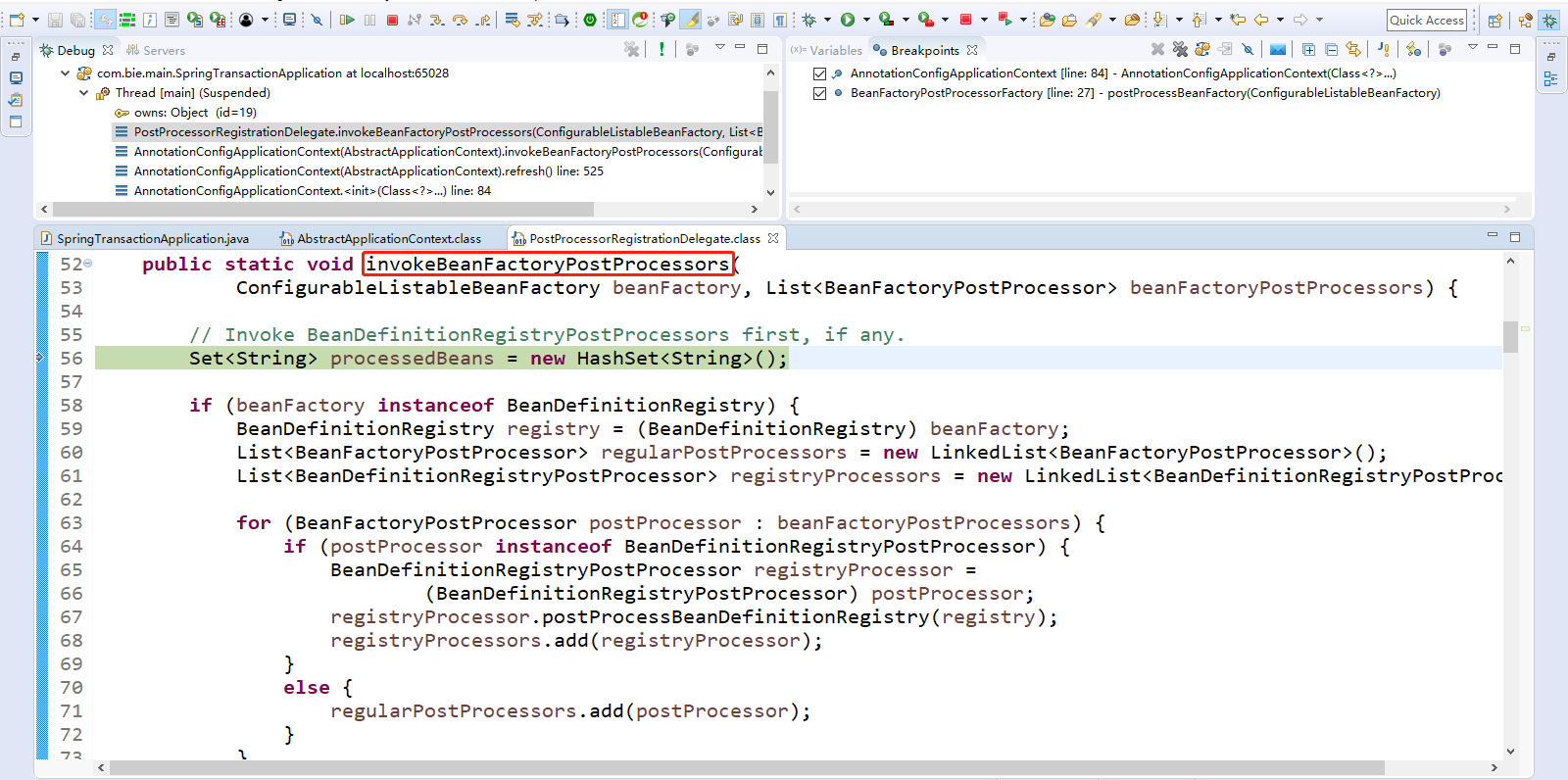
Step Over(F6)下一步,直到运行到invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);继续走Step Over(F6)下一步,走到registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
6、点击Step Into(F5)进入registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
注册BeanPostProcessors,注册bean的后置处理器。后置处理器是拦截bean的创建过程的。

点击Step Into(F5)进入registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
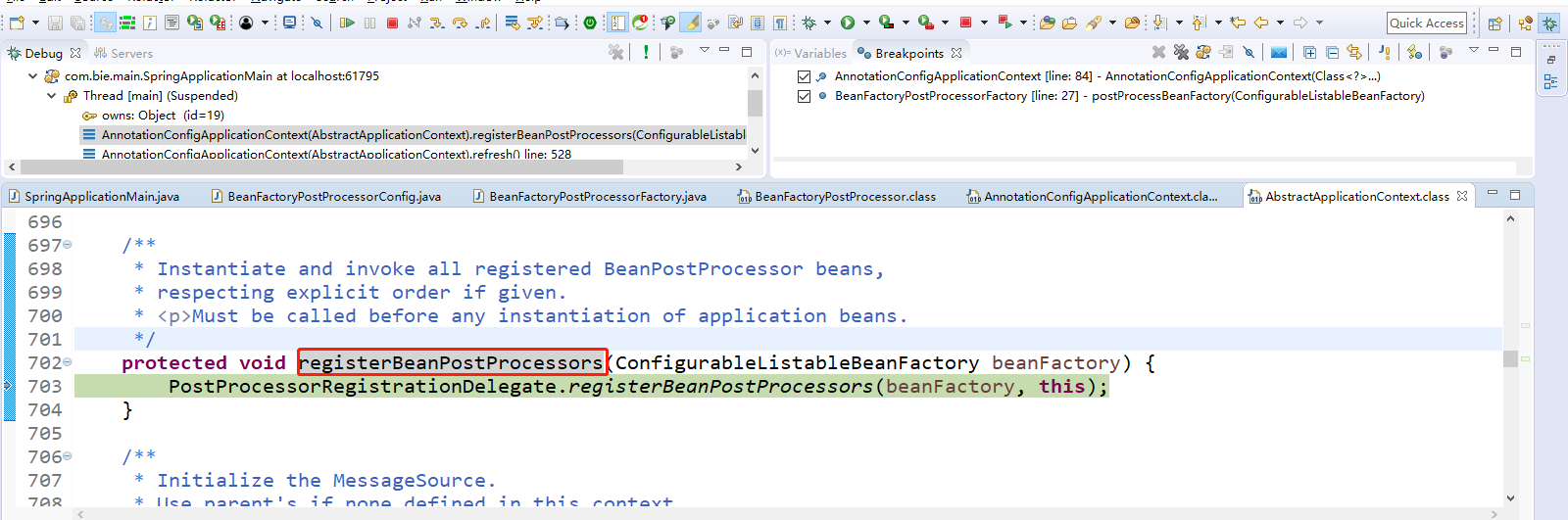
Step Into(F5)进入PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, this);调用此方法进行注册。
1 // 注册Bean的后置处理器,在Bean工厂中保存了Bean的后置处理器,而先不执行。 2 public static void registerBeanPostProcessors( 3 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext) { 4 // 不同接口类型的BeanPostProcessor,在bean创建前后执行时机是不一样的。 5 // BeanPostProcessor接口。 6 // DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor接口。 7 // InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口、SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口。SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口是的InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor子接口 8 // MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor接口。 9 // 根据类型从容器中获取BeanPostProcessor类型的(即后置处理器)。 10 String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanPostProcessor.class, true, false); 11 12 // Register BeanPostProcessorChecker that logs an info message when 13 // a bean is created during BeanPostProcessor instantiation, i.e. when 14 // a bean is not eligible for getting processed by all BeanPostProcessors. 15 // 统计获取beanFactory里面的BeanPostProcessor后置处理器的数量 16 int beanProcessorTargetCount = beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount() + 1 + postProcessorNames.length; 17 // 将BeanPostProcessorChecker后置处理器添加到bean工厂中。这个后置处理器是检查BeanPostProcessor的 18 beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new BeanPostProcessorChecker(beanFactory, beanProcessorTargetCount)); 19 20 21 // Separate between BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered, 22 // Ordered, and the rest. 23 // 后置处理器都默认可以通过PriorityOrdered接口、Ordered接口来指定优先级。 24 // 定义集合priorityOrderedPostProcessors 25 List<BeanPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>(); 26 // 定义集合internalPostProcessors 27 List<BeanPostProcessor> internalPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>(); 28 // 定义集合orderedPostProcessorNames 29 List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<String>(); 30 // 定义集合nonOrderedPostProcessorNames 31 List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<String>(); 32 // 遍历获取到的postProcessorNames后置处理器的名称 33 for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { 34 // 判断如果有PriorityOrdered优先级接口的 35 if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) { 36 // 从beanFactory获取到ppName 37 BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class); 38 // 将获取到的pp放入到集合中 39 priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp); 40 // 如果pp是这种类型的MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor 41 if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) { 42 // 将pp添加到internalPostProcessors集合中 43 internalPostProcessors.add(pp); 44 } 45 } 46 // 否则,如果有Ordered顺序接口优先级的 47 else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) { 48 // 将ppName添加到orderedPostProcessorNames集合中 49 orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName); 50 } 51 else { 52 // 否则,未实现PriorityOrdered、Ordered接口的。将ppName添加到nonOrderedPostProcessorNames集合中 53 nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName); 54 } 55 } 56 57 // First, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered. 58 // 按照优先级接口的进行排序操作 59 sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); 60 // 调用registerBeanPostProcessors方法,循环遍历beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(postProcessor);方法。即注册bean的后置处理器。 61 // 先注册PriorityOrdered优先级接口的BeanPostProcessor。把每一个BeanPostProcessor添加到BeanFactory中。 62 registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors); 63 64 // Next, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement Ordered. 65 // 定义集合orderedPostProcessors 66 List<BeanPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>(); 67 // 遍历获取到的实现Ordered接口的后置处理器 68 for (String ppName : orderedPostProcessorNames) { 69 // 从beanFactory获取到ppName 70 BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class); 71 // 将获取到的pp放入到集合中 72 orderedPostProcessors.add(pp); 73 // 如果pp是这种类型的MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor 74 if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) { 75 // 将pp添加到internalPostProcessors集合中 76 internalPostProcessors.add(pp); 77 } 78 } 79 // 按照顺序接口的进行排序操作 80 sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); 81 // 再注册Ordered接口的BeanPostProcessor。把每一个BeanPostProcessor添加到BeanFactory中。 82 registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors); 83 84 // Now, register all regular BeanPostProcessors. 85 List<BeanPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>(); 86 for (String ppName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) { 87 // 从beanFactory获取到ppName 88 BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class); 89 // 将获取到的pp放入到集合中 90 nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp); 91 // 如果pp是这种类型的MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor 92 if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) { 93 // 将pp添加到internalPostProcessors集合中 94 internalPostProcessors.add(pp); 95 } 96 } 97 // 最后注册未实现任何优先级接口的BeanPostProcessor。把每一个BeanPostProcessor添加到BeanFactory中。 98 registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, nonOrderedPostProcessors); 99 100 // Finally, re-register all internal BeanPostProcessors. 101 // 按照internal的进行排序操作 102 sortPostProcessors(internalPostProcessors, beanFactory); 103 // 最终注册MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor,这种类型的后置处理器 104 registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, internalPostProcessors); 105 106 // Re-register post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners, 107 // moving it to the end of the processor chain (for picking up proxies etc). 108 // 新增了一个后置处理器ApplicationListenerDetector,这个后置处理器在bean创建完成以后检查是否是ApplicationListener 109 // 如果是this.applicationContext.addApplicationListener((ApplicationListener<?>) bean); 110 beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(applicationContext)); 111 }
如下所示: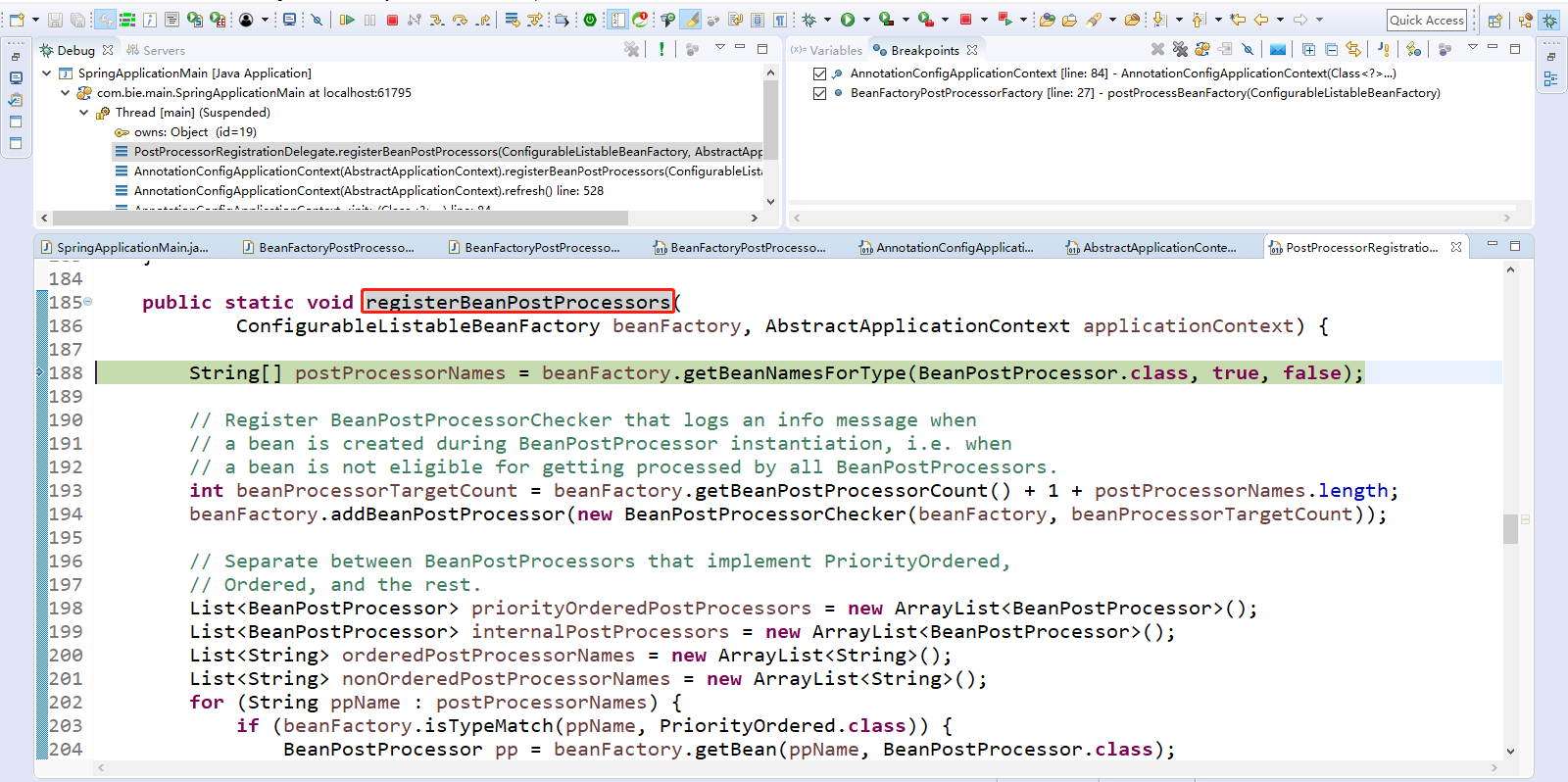
7、Step Over(F6)下一步,直到走到initMessageSource();
Spring容器创建,初始化MessageSource。初始化MessageSource组件(在SpringMVC中做国际化功能、消息绑定、消息解析功能的)。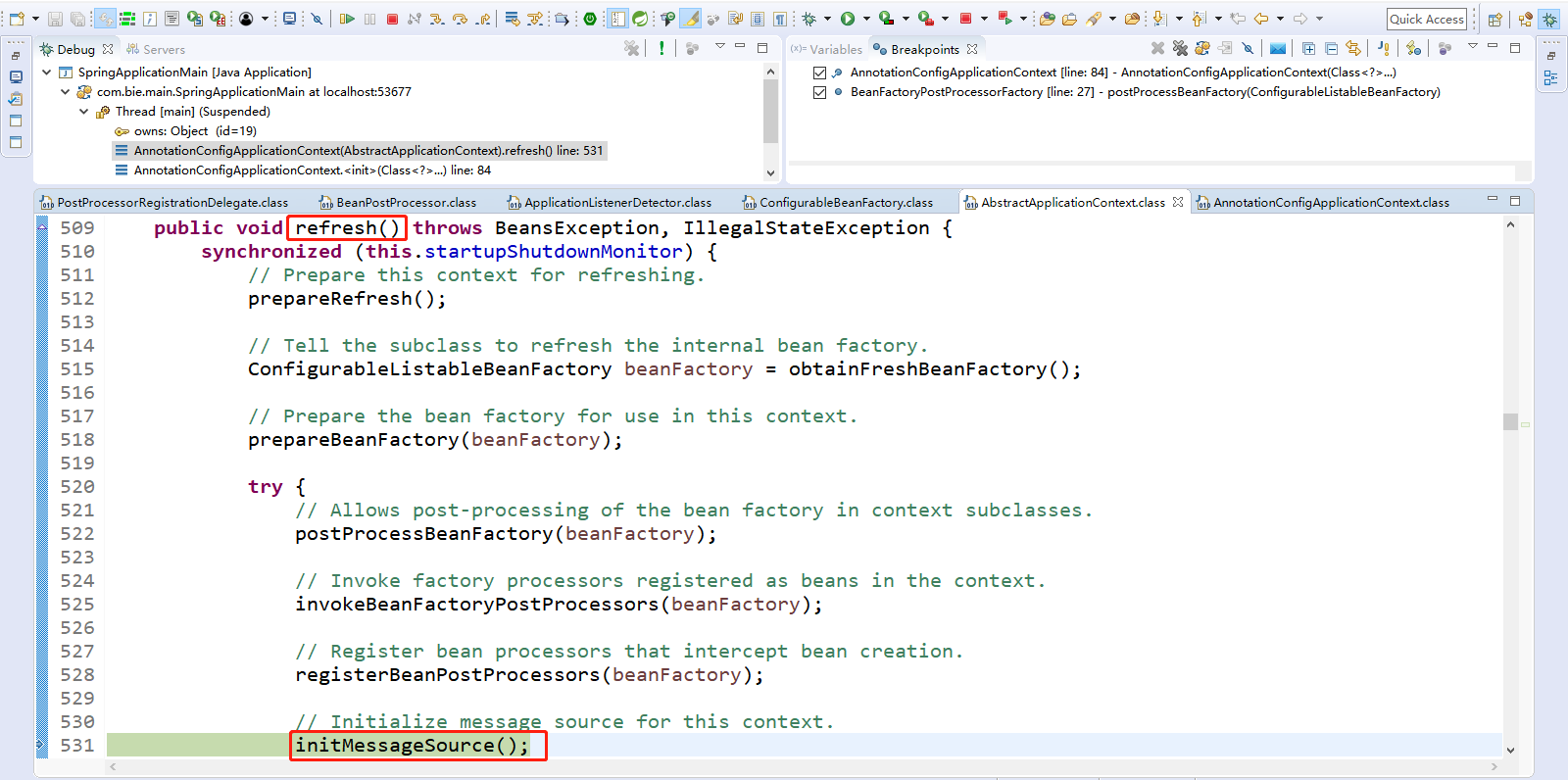
然后点击Step Into(F5)进入initMessageSource();
1 // MessageSource取出国际化配置文件中的某个key的值,能按照区域信息获取。 2 protected void initMessageSource() { 3 // 获取到Bean工厂 4 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory(); 5 // MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME = "messageSource"; 6 // 判断Bean工厂中是否存在id=messageSource。看容器中是否有id=messageSource的组件。 7 if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME)) { 8 // 如果有从beanFactory中获取到MessageSource的组件,赋值给messageSource属性 9 this.messageSource = beanFactory.getBean(MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME, MessageSource.class); 10 // Make MessageSource aware of parent MessageSource. 11 if (this.parent != null && this.messageSource instanceof HierarchicalMessageSource) { 12 HierarchicalMessageSource hms = (HierarchicalMessageSource) this.messageSource; 13 if (hms.getParentMessageSource() == null) { 14 // Only set parent context as parent MessageSource if no parent MessageSource 15 // registered already. 16 hms.setParentMessageSource(getInternalParentMessageSource()); 17 } 18 } 19 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 20 logger.debug("Using MessageSource [" + this.messageSource + "]"); 21 } 22 } 23 else { 24 // Use empty MessageSource to be able to accept getMessage calls. 25 // 如果Bean工厂中没有MessageSource组件,则创建一个默认的DelegatingMessageSource。 26 DelegatingMessageSource dms = new DelegatingMessageSource(); 27 // 28 dms.setParentMessageSource(getInternalParentMessageSource()); 29 this.messageSource = dms; 30 // 将创建好的MessageSource注册到容器中。以后获取国际化配置文件的值的时候,可以自动注入MessageSource 31 beanFactory.registerSingleton(MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME, this.messageSource); 32 // 打印日志信息 33 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 34 logger.debug("Unable to locate MessageSource with name '" + MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME + 35 "': using default [" + this.messageSource + "]"); 36 } 37 } 38 }
如下所示:

8、Step Over(F6)下一步,直到走到initApplicationEventMulticaster();Spring容器创建,初始化事件派发器、监听器等。
点击Step Into(F5)进入initApplicationEventMulticaster();
1 protected void initApplicationEventMulticaster() { 2 // 获取到Bean工厂 3 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory(); 4 // APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME = "applicationEventMulticaster"; 5 // 判断bean工厂中是否包含applicationEventMulticaster组件, 6 if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME)) { 7 // 从Bean工厂中获取applicationEventMulticaster的ApplicationEventMulticaster组件。可以自定义事件派发器的,在此可以进行获取。 8 this.applicationEventMulticaster = 9 beanFactory.getBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, ApplicationEventMulticaster.class); 10 // 打印日志信息 11 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 12 logger.debug("Using ApplicationEventMulticaster [" + this.applicationEventMulticaster + "]"); 13 } 14 } 15 else { 16 // 如果没有配置事件派发器。创建一个简单的事件派发器。用来帮助我们派发事件 17 this.applicationEventMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster(beanFactory); 18 // 将事件派发器注册到容器中,其他组件可以自动注入该组件。将创建的ApplicationEventMulticaster组件添加到bean工厂中即容器中,以后其他组件直接自动注入即可。 19 beanFactory.registerSingleton(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, this.applicationEventMulticaster); 20 // 打印日志信息 21 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 22 logger.debug("Unable to locate ApplicationEventMulticaster with name '" + 23 APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME + 24 "': using default [" + this.applicationEventMulticaster + "]"); 25 } 26 } 27 }
如下所示:
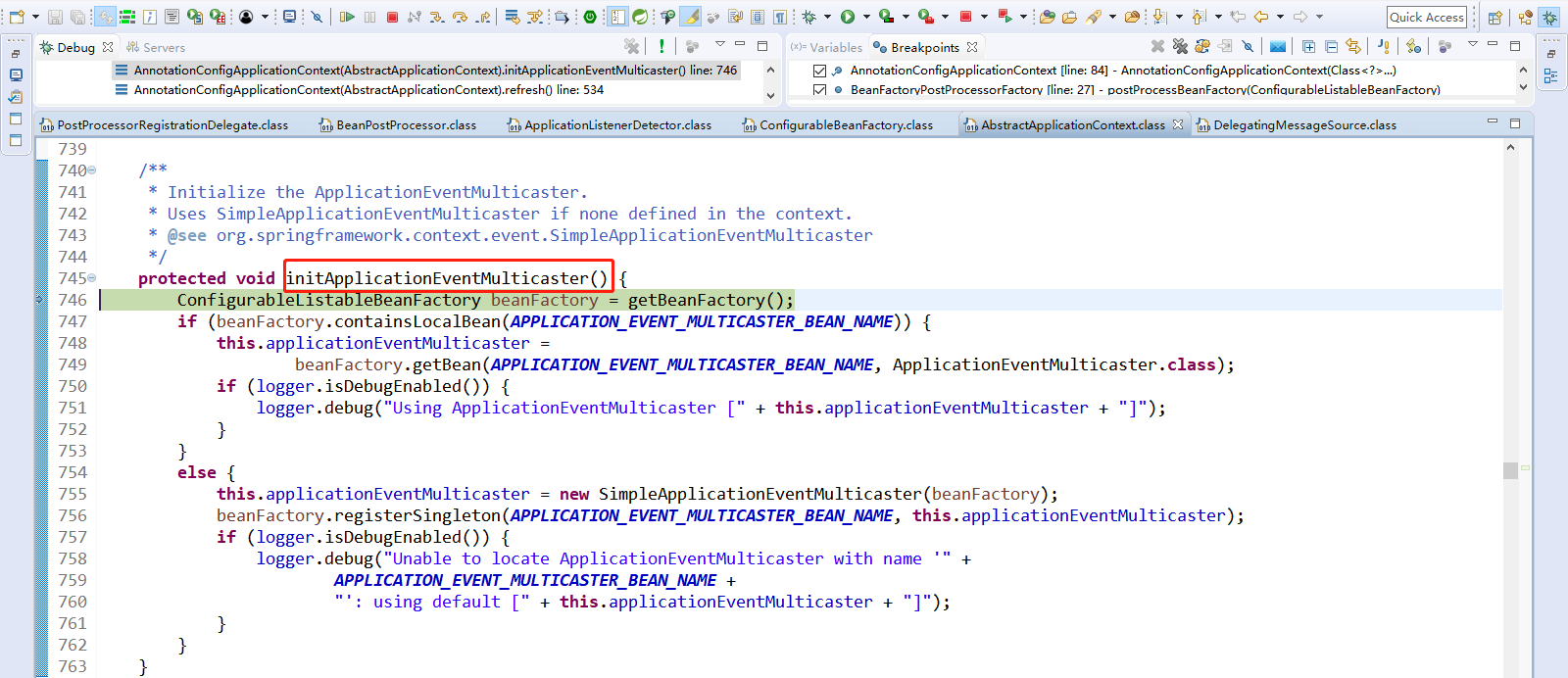
9、Step Over(F6)下一步,直到走到onRefresh(); 留给子容器(即子类),在子容器中初始化剩下指定的bean。

点击Step Into(F5)进入onRefresh();
onRefresh();空实现,这个是留给子类的,如果子类有需要刷新的,可以重写onRefresh();刷新方法。子类重写这个方法,在容器刷新的时候可以自定义逻辑。

10、Step Over(F6)下一步,直到走到registerListeners();
检查监听器或者注册监听器,给容器中将所有项目里面的ApplicationListener注册进来。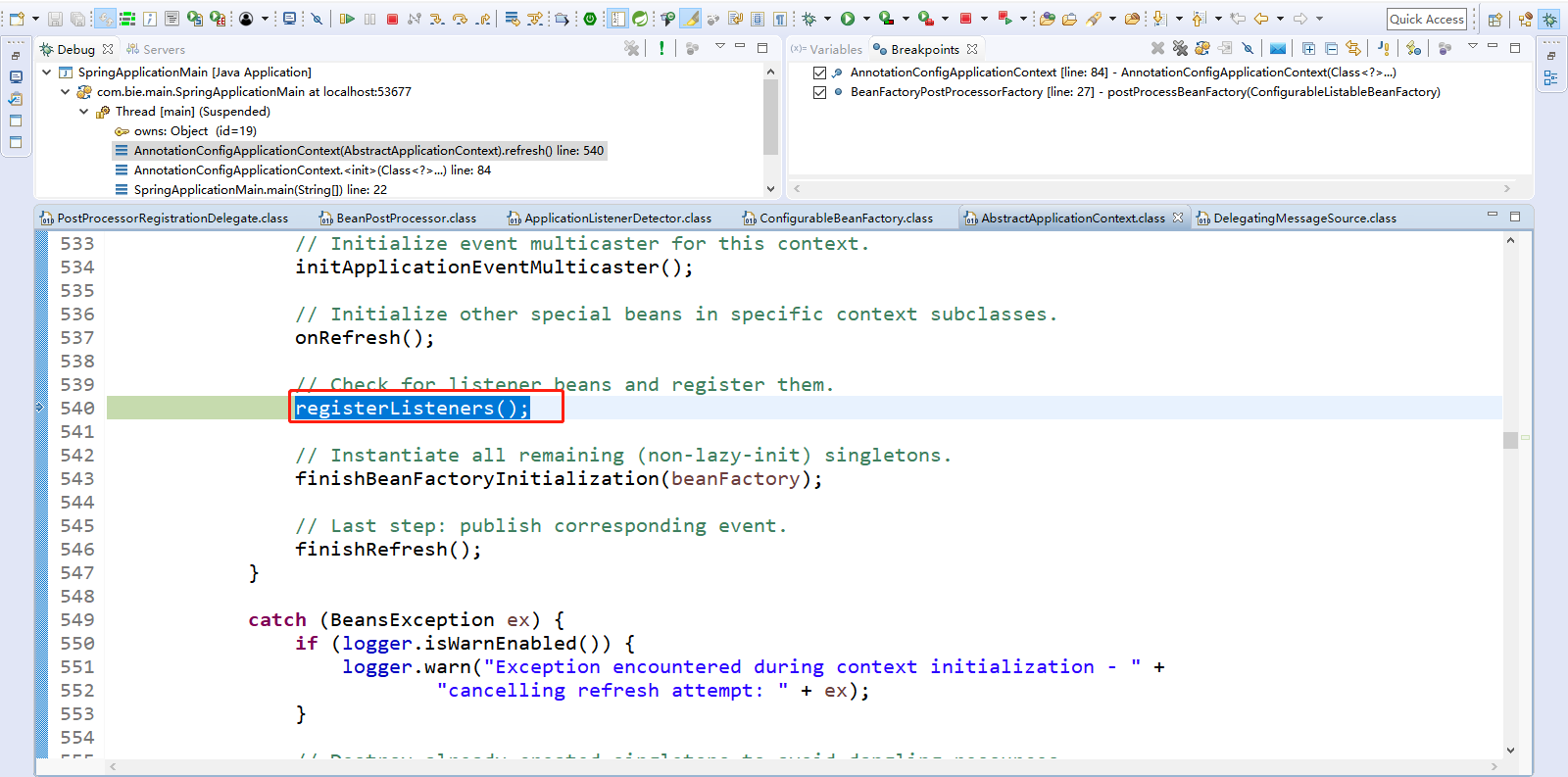
点击Step Into(F5)进入registerListeners();
1 protected void registerListeners() { 2 // Register statically specified listeners first. 3 // 获取到所有的applicationListeners,然后添加到事件派发器中。 4 for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners()) { 5 getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListener(listener); 6 } 7 8 // Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans 9 // uninitialized to let post-processors apply to them! 10 // 或者从容器中根据类型获取到所有的ApplicationListener类型的bean组件 11 String[] listenerBeanNames = getBeanNamesForType(ApplicationListener.class, true, false); 12 // 循环遍历ApplicationListener类型的bean组件。 13 for (String listenerBeanName : listenerBeanNames) { 14 // 将每个监听器添加到事件派发器中。 15 getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListenerBean(listenerBeanName); 16 } 17 18 // Publish early application events now that we finally have a multicaster... 19 // 派发之前步骤产生的事件 20 // 获取到之前产生的事件 21 Set<ApplicationEvent> earlyEventsToProcess = this.earlyApplicationEvents; 22 // 然后将之前产生的事件置为空null 23 this.earlyApplicationEvents = null; 24 // 如果之前产生的事件不为空 25 if (earlyEventsToProcess != null) { 26 // 循环遍历 27 for (ApplicationEvent earlyEvent : earlyEventsToProcess) { 28 getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(earlyEvent); 29 } 30 } 31 }
如下所示:
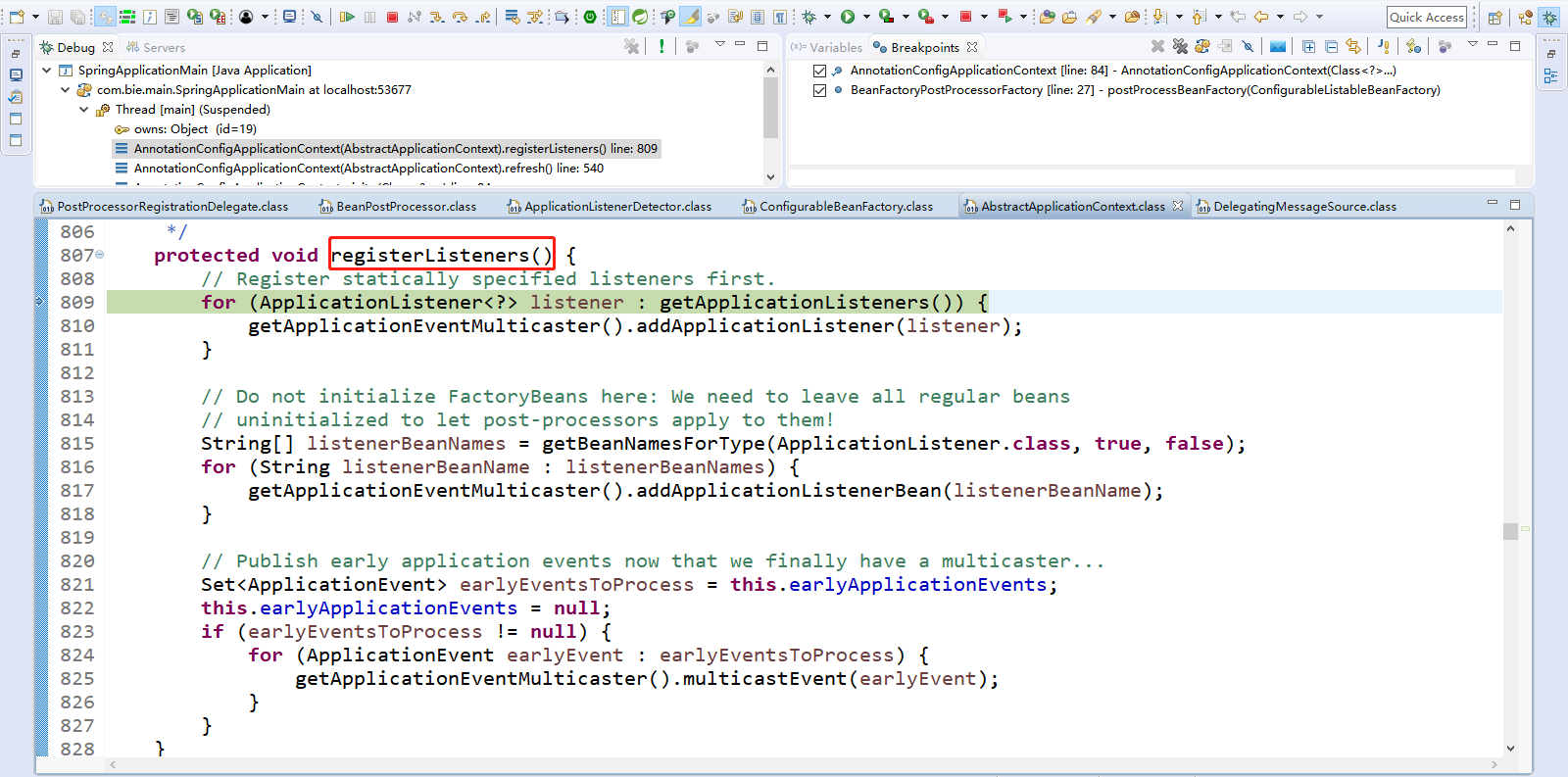
11、Step Over(F6)下一步,直到走到finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);初始化所有剩下的单实例bean。Spring容器创建,创建Bean准备。

点击Step Into(F5)进入finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
1 protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { 2 // Initialize conversion service for this context. 3 // CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME = "conversionService"; 4 // 和类型转换组件相关的代码 5 if (beanFactory.containsBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME) && 6 beanFactory.isTypeMatch(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class)) { 7 beanFactory.setConversionService( 8 beanFactory.getBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class)); 9 } 10 11 // Register a default embedded value resolver if no bean post-processor 12 // (such as a PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer bean) registered any before: 13 // at this point, primarily for resolution in annotation attribute values. 14 // 和值解析器相关的代码 15 if (!beanFactory.hasEmbeddedValueResolver()) { 16 beanFactory.addEmbeddedValueResolver(new StringValueResolver() { 17 @Override 18 public String resolveStringValue(String strVal) { 19 return getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(strVal); 20 } 21 }); 22 } 23 24 // Initialize LoadTimeWeaverAware beans early to allow for registering their transformers early. 25 // 和AspectJ相关的代码 26 String[] weaverAwareNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(LoadTimeWeaverAware.class, false, false); 27 for (String weaverAwareName : weaverAwareNames) { 28 getBean(weaverAwareName); 29 } 30 31 // Stop using the temporary ClassLoader for type matching. 32 // 33 beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(null); 34 35 // Allow for caching all bean definition metadata, not expecting further changes. 36 // 37 beanFactory.freezeConfiguration(); 38 39 // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. 40 // 初始化剩下的单实例bean 41 beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons(); 42 }
如下所示:

Step Over(F6)下一步,直到走到beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();初始化剩下的单实例bean。
1 @Override 2 public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException { 3 // 打印日志信息 4 if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 5 this.logger.debug("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this); 6 } 7 8 // Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions. 9 // While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine. 10 // 获取到所有的bean的定义信息,有的bean在之前的步骤已经创建完毕 11 List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<String>(this.beanDefinitionNames); 12 13 // Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans... 14 // 遍历拿到的所有bean的定义信息。获取容器中的所有bean,依次进行初始化和创建对象操作。 15 for (String beanName : beanNames) { 16 // 获取到bean的定义信息。 17 RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName); 18 // 判断该bean是否是抽象的,并且是单实例的,并且是否是懒加载的。 19 if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) { 20 // 不是抽象的、是单实例的、不是懒加载的。 21 // 判断是否是FactoryBean类型的。是否是工厂bean 22 if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) { 23 final FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName); 24 boolean isEagerInit; 25 if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) { 26 isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Boolean>() { 27 @Override 28 public Boolean run() { 29 return ((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit(); 30 } 31 }, getAccessControlContext()); 32 } 33 else { 34 isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean && 35 ((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit()); 36 } 37 if (isEagerInit) { 38 getBean(beanName); 39 } 40 } 41 else { 42 // 如果不是实现FactoryBean的Bean,即不是工厂bean,调用getBean(beanName);方法创建对象 43 getBean(beanName); 44 } 45 } 46 } 47 48 // Trigger post-initialization callback for all applicable beans... 49 // 触发初始化后置的回调方法。 50 // 循环遍历 51 for (String beanName : beanNames) { 52 // 获取到所有的bean对象。 53 Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName); 54 // 判断该对象是否是SmartInitializingSingleton类型的,是否实现了SmartInitializingSingleton接口。 55 if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) { 56 // 检查所有的bean是否是SmartInitializingSingleton接口的,如果是,执行smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated(); 57 final SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance; 58 if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) { 59 AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() { 60 @Override 61 public Object run() { 62 smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated(); 63 return null; 64 } 65 }, getAccessControlContext()); 66 } 67 else { 68 // 69 smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated(); 70 } 71 } 72 } 73 } 74 75 76 77 78 79 // isFactoryBean是上面方法引用的。 80 @Override 81 public boolean isFactoryBean(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException { 82 String beanName = transformedBeanName(name); 83 84 Object beanInstance = getSingleton(beanName, false); 85 if (beanInstance != null) { 86 // 判断是否是实现FactoryBean接口的Bean,是就返回true 87 return (beanInstance instanceof FactoryBean); 88 } 89 else if (containsSingleton(beanName)) { 90 // null instance registered 91 // 如果不是实现FactoryBean的Bean,返回false 92 return false; 93 } 94 95 // No singleton instance found -> check bean definition. 96 if (!containsBeanDefinition(beanName) && getParentBeanFactory() instanceof ConfigurableBeanFactory) { 97 // No bean definition found in this factory -> delegate to parent. 98 return ((ConfigurableBeanFactory) getParentBeanFactory()).isFactoryBean(name); 99 } 100 101 return isFactoryBean(beanName, getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName)); 102 }
如下所示:
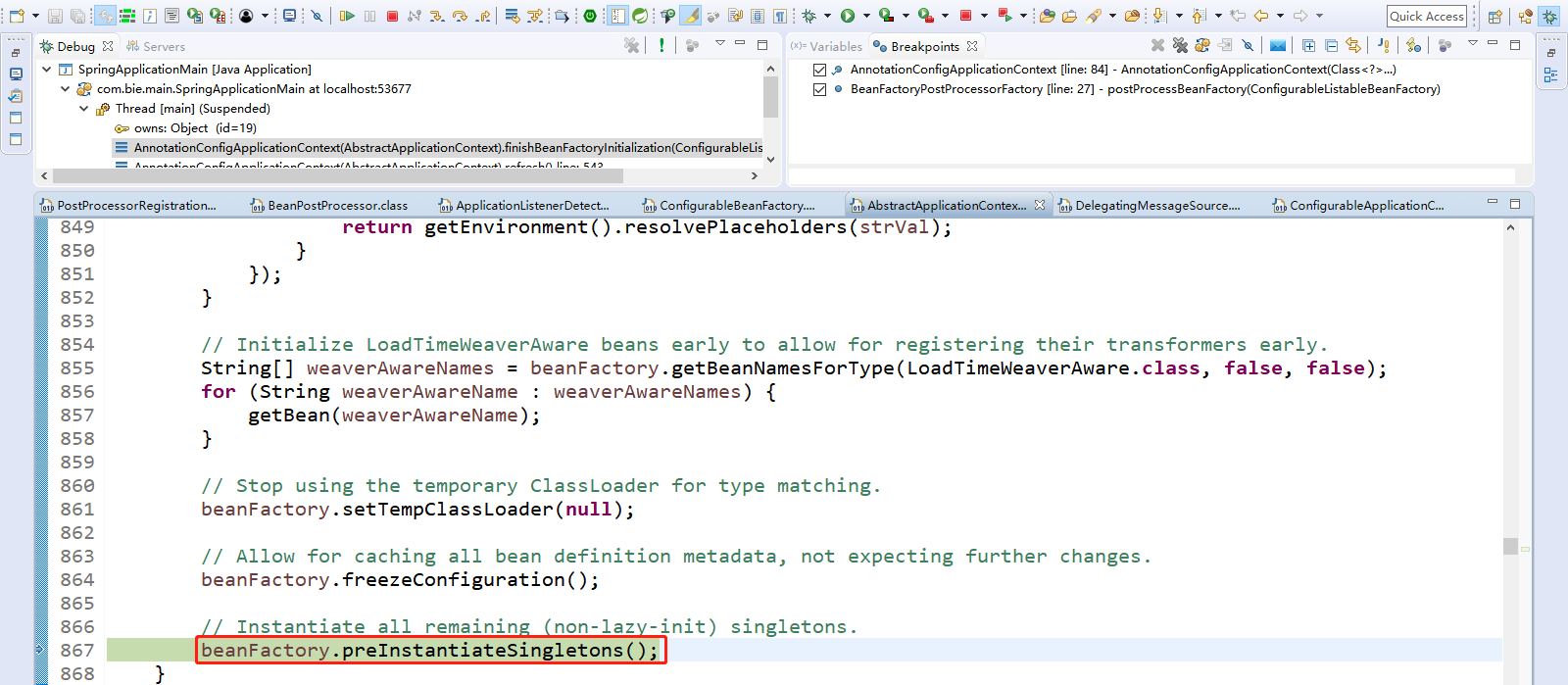
点击Step Into(F5)进入beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();
如下所示:
Step Over(F6)下一步,直到走到getBean(beanName);可以在此处打上断点,然后跳过默认创建的bean组件,走到自己创建的bean组件。
点击Step Into(F5)进入getBean(beanName);此处的getBean(beanName),就是测试的时候写的ac.getBean();的这个方法哦。
点击Step Into(F5)进入doGetBean(name, null, null, false);
1 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 2 protected <T> T doGetBean( 3 final String name, final Class<T> requiredType, final Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly) 4 throws BeansException { 5 6 // 获取到参数传递进去的name 7 final String beanName = transformedBeanName(name); 8 // 定义Object类型的变量bean 9 Object bean; 10 11 // Eagerly check singleton cache for manually registered singletons. 12 // 如果之前已经有bean被创建成功就会被缓存起来。 13 // 这里先获取bean组件,sharedInstance是指共享的bean。 14 // 先获取缓存中保存的单实例Bean,如果能获取到说明这个bean之前被创建过(所有创建过的单实例bean都会被缓存起来的)。 15 // private final Map<String, Object> singletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object>(256);缓存所有的单实例bean,按照bean的名称和bean的实例对象。 16 // 从缓存中获取单实例bean对象实例 17 Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName); 18 // 如果从缓存中获取到了bean实例对象 19 if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) { 20 // 打印日志信息 21 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 22 if (isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) { 23 logger.debug("Returning eagerly cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + 24 "' that is not fully initialized yet - a consequence of a circular reference"); 25 } 26 else { 27 logger.debug("Returning cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'"); 28 } 29 } 30 // 按照类型从容器中获取到对应的bean实例 31 bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, null); 32 } 33 // 如果从缓存中获取不到 34 else { 35 // Fail if we're already creating this bean instance: 36 // We're assumably within a circular reference. 37 // 38 if (isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) { 39 throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName); 40 } 41 42 // Check if bean definition exists in this factory. 43 // 缓存中获取不到,开始Bean的创建对象流程。首先获取到父工厂,看是否存在父工厂。 44 BeanFactory parentBeanFactory = getParentBeanFactory(); 45 // 如果有父工厂的话 46 if (parentBeanFactory != null && !containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) { 47 // Not found -> check parent. 48 String nameToLookup = originalBeanName(name); 49 if (args != null) { 50 // Delegation to parent with explicit args. 51 return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, args); 52 } 53 else { 54 // No args -> delegate to standard getBean method. 55 return parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, requiredType); 56 } 57 } 58 59 // 先来标记该bean已经被创建了,防止多线程的情况下,两个线程同时都来创建同一个bean,就不是单实例的了。 60 if (!typeCheckOnly) { 61 // 标记该bean已经被创建了 62 markBeanAsCreated(beanName); 63 } 64 65 try { 66 // 获取到bean的定义信息。 67 final RootBeanDefinition mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName); 68 // 检查获取到的bean的定义信息 69 checkMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanName, args); 70 71 // Guarantee initialization of beans that the current bean depends on. 72 // 获取当前bean依赖的其他bean。如果有按照getBean()把依赖的Bean先创建出来。 73 String[] dependsOn = mbd.getDependsOn(); 74 // 如果当前bean依赖的其他bean不为null 75 if (dependsOn != null) { 76 // 遍历当前bean依赖的其他bean 77 for (String dep : dependsOn) { 78 // 打印日志信息 79 if (isDependent(beanName, dep)) { 80 throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, 81 "Circular depends-on relationship between '" + beanName + "' and '" + dep + "'"); 82 } 83 // 注册到依赖的bean组件中 84 registerDependentBean(dep, beanName); 85 // 如果有按照getBean()把依赖的Bean先创建出来。 86 getBean(dep); 87 } 88 } 89 90 // Create bean instance. 91 // 如果是单实例的就进行创建 92 if (mbd.isSingleton()) { 93 // 启动单实例Bean的创建流程。beanName是bean的名称,new ObjectFactory<Object>()是bean的工厂。 94 sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, new ObjectFactory<Object>() { 95 // 使用new ObjectFactory<Object>()工厂的getObject()方法创建bean。 96 @Override 97 public Object getObject() throws BeansException { 98 try { 99 // 调用createBean(beanName, mbd, args);创建bean。 100 // 创建成功bean以后直接返回。 101 return createBean(beanName, mbd, args); 102 } 103 catch (BeansException ex) { 104 // Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there 105 // eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution. 106 // Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean. 107 destroySingleton(beanName); 108 throw ex; 109 } 110 } 111 }); 112 bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd); 113 } 114 // 否则,如果是多实例的bean对象。 115 else if (mbd.isPrototype()) { 116 // It's a prototype -> create a new instance. 117 Object prototypeInstance = null; 118 try { 119 beforePrototypeCreation(beanName); 120 // 创建bean对象,自己可以跟进去研究一下。 121 prototypeInstance = createBean(beanName, mbd, args); 122 } 123 finally { 124 afterPrototypeCreation(beanName); 125 } 126 bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(prototypeInstance, name, beanName, mbd); 127 } 128 129 else { 130 String scopeName = mbd.getScope(); 131 final Scope scope = this.scopes.get(scopeName); 132 if (scope == null) { 133 throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope name '" + scopeName + "'"); 134 } 135 try { 136 Object scopedInstance = scope.get(beanName, new ObjectFactory<Object>() { 137 @Override 138 public Object getObject() throws BeansException { 139 beforePrototypeCreation(beanName); 140 try { 141 return createBean(beanName, mbd, args); 142 } 143 finally { 144 afterPrototypeCreation(beanName); 145 } 146 } 147 }); 148 bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(scopedInstance, name, beanName, mbd); 149 } 150 catch (IllegalStateException ex) { 151 throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, 152 "Scope '" + scopeName + "' is not active for the current thread; consider " + 153 "defining a scoped proxy for this bean if you intend to refer to it from a singleton", 154 ex); 155 } 156 } 157 } 158 catch (BeansException ex) { 159 cleanupAfterBeanCreationFailure(beanName); 160 throw ex; 161 } 162 } 163 164 // Check if required type matches the type of the actual bean instance. 165 if (requiredType != null && bean != null && !requiredType.isInstance(bean)) { 166 try { 167 return getTypeConverter().convertIfNecessary(bean, requiredType); 168 } 169 catch (TypeMismatchException ex) { 170 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 171 logger.debug("Failed to convert bean '" + name + "' to required type '" + 172 ClassUtils.getQualifiedName(requiredType) + "'", ex); 173 } 174 throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass()); 175 } 176 } 177 return (T) bean; 178 }
如下所示:
Step Over(F6)下一步,直到走到Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName); 可以点击Step Into(F5)进入getSingleton(beanName);
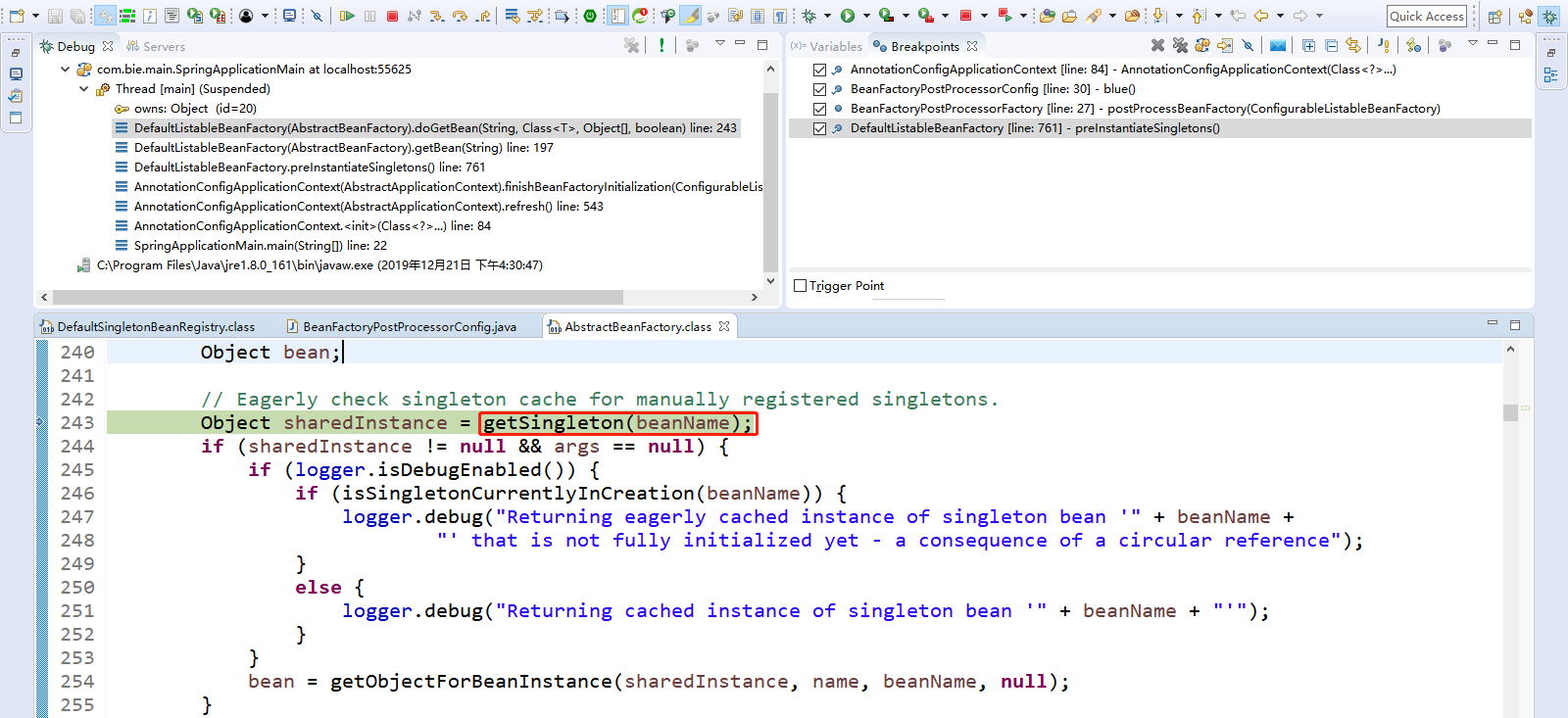
可以看到private final Map<String, Object> singletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object>(256);
singletonObjects对象缓存所有的单实例bean,按照bean的名称和bean的实例对象。
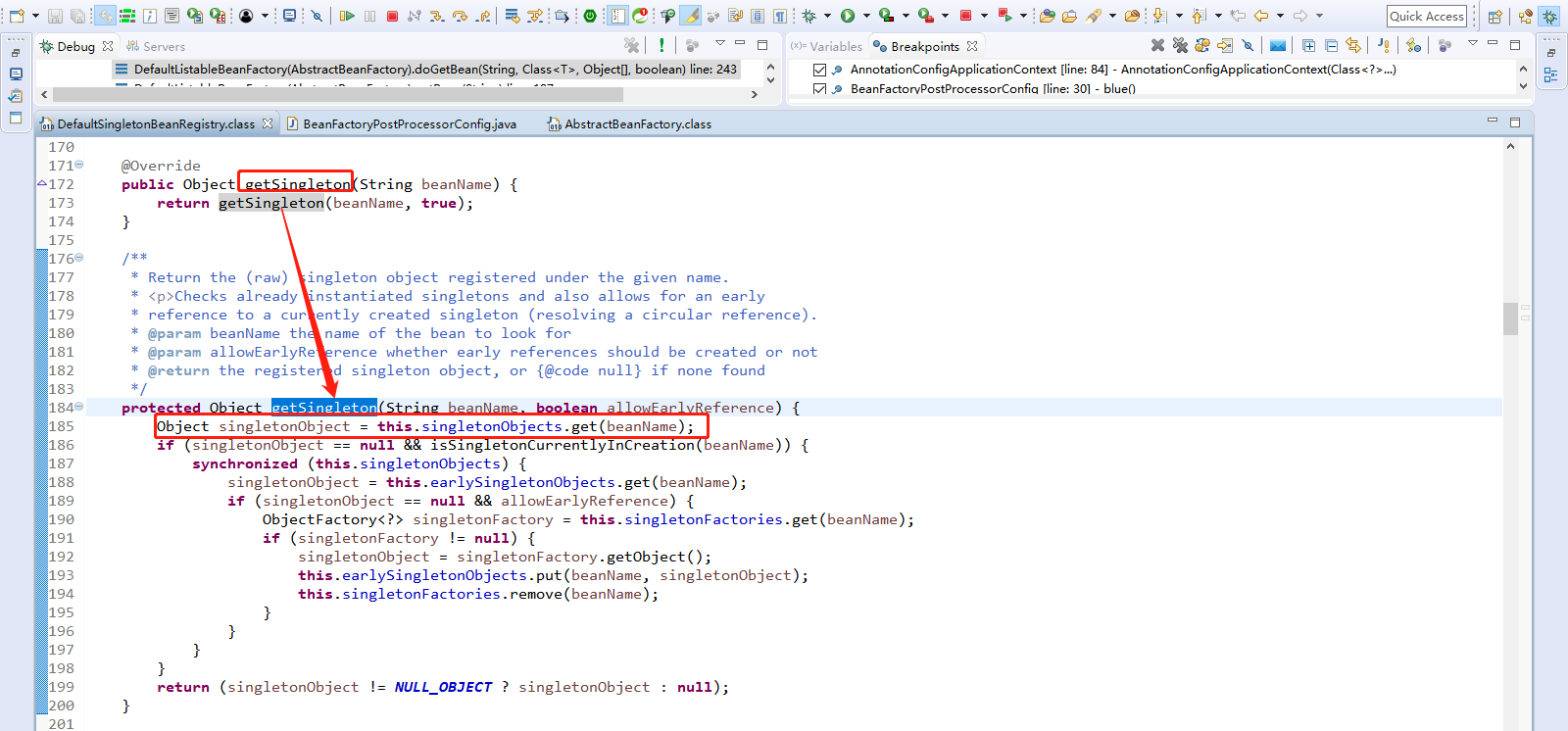
Step Over(F6)下一步,直到走到sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, new ObjectFactory<Object>()。

此时将断点打到return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
点击Resume(F8)放行到此处,然后点击Step Into(F5)进入createBean(beanName, mbd, args);方法。
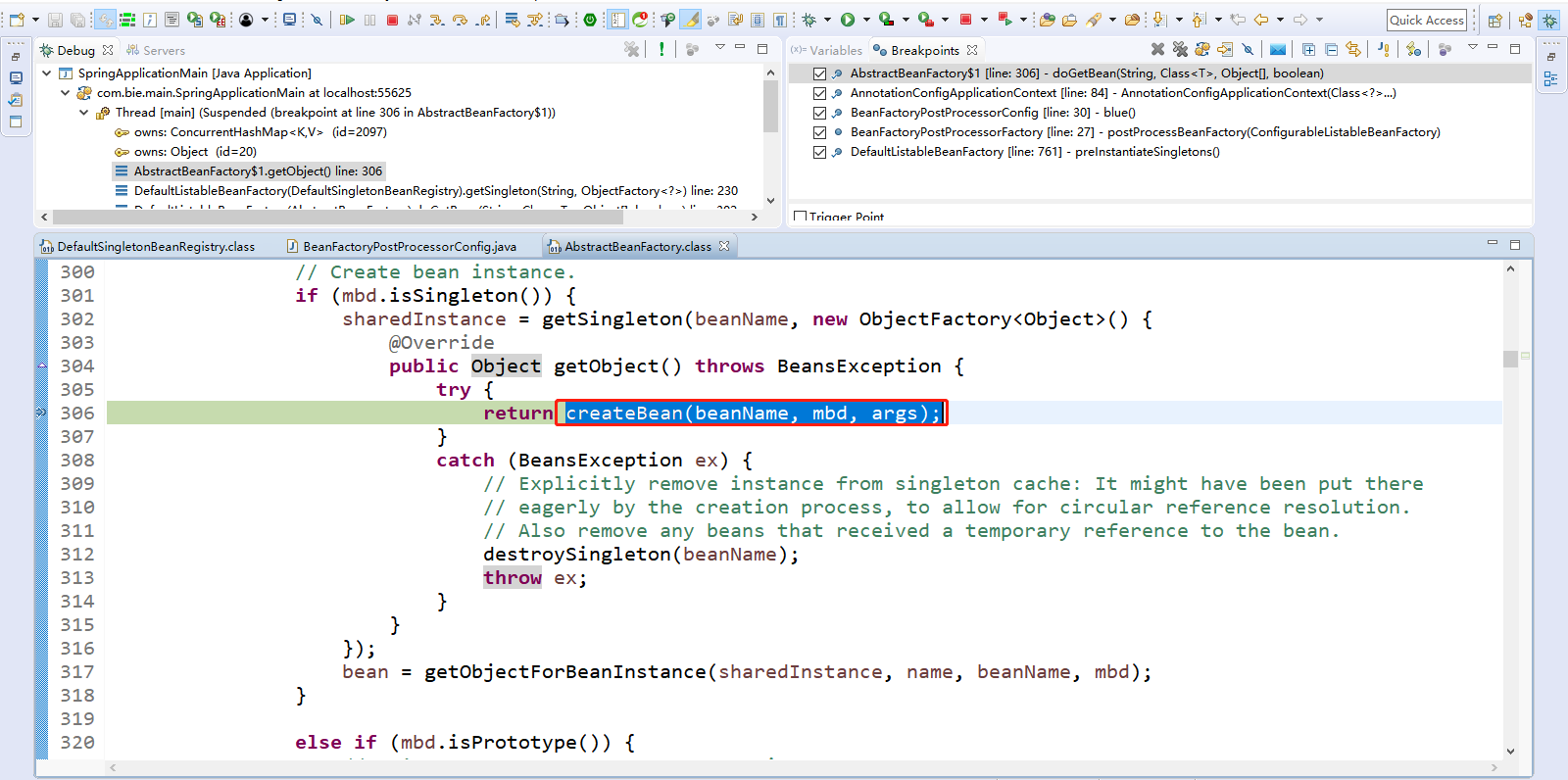
点击Step Into(F5)进入createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
1 @Override 2 protected Object createBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, Object[] args) throws BeanCreationException { 3 // 打印日志信息 4 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 5 logger.debug("Creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'"); 6 } 7 // 将参数mbd赋值给RootBeanDefinition类型的mbdToUse 8 RootBeanDefinition mbdToUse = mbd; 9 10 // Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point, and 11 // clone the bean definition in case of a dynamically resolved Class 12 // which cannot be stored in the shared merged bean definition. 13 // 解析Bean的类型。我们要创建的bean的类型。 14 Class<?> resolvedClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName); 15 // 如果获取到的resolvedClass类型不为空,创建RootBeanDefinition 16 if (resolvedClass != null && !mbd.hasBeanClass() && mbd.getBeanClassName() != null) { 17 mbdToUse = new RootBeanDefinition(mbd); 18 mbdToUse.setBeanClass(resolvedClass); 19 } 20 21 // Prepare method overrides. 22 try { 23 // 24 mbdToUse.prepareMethodOverrides(); 25 } 26 catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) { 27 throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), 28 beanName, "Validation of method overrides failed", ex); 29 } 30 31 try { 32 // Give BeanPostProcessors a chance to return a proxy instead of the target bean instance. 33 // 让BeanPostProcessors先提前拦截代理对象。即提前执行InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor这种类型的后置处理器。 34 // 切记,此时触发InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor这种类型的后置处理器。 35 Object bean = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse); 36 if (bean != null) { 37 return bean; 38 } 39 } 40 catch (Throwable ex) { 41 throw new BeanCreationException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName, 42 "BeanPostProcessor before instantiation of bean failed", ex); 43 } 44 45 // 如果前面的InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor没有返回代理对象。 46 // 执行创建bean方法。 47 Object beanInstance = doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args); 48 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 49 logger.debug("Finished creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'"); 50 } 51 return beanInstance; 52 }
如下所示:
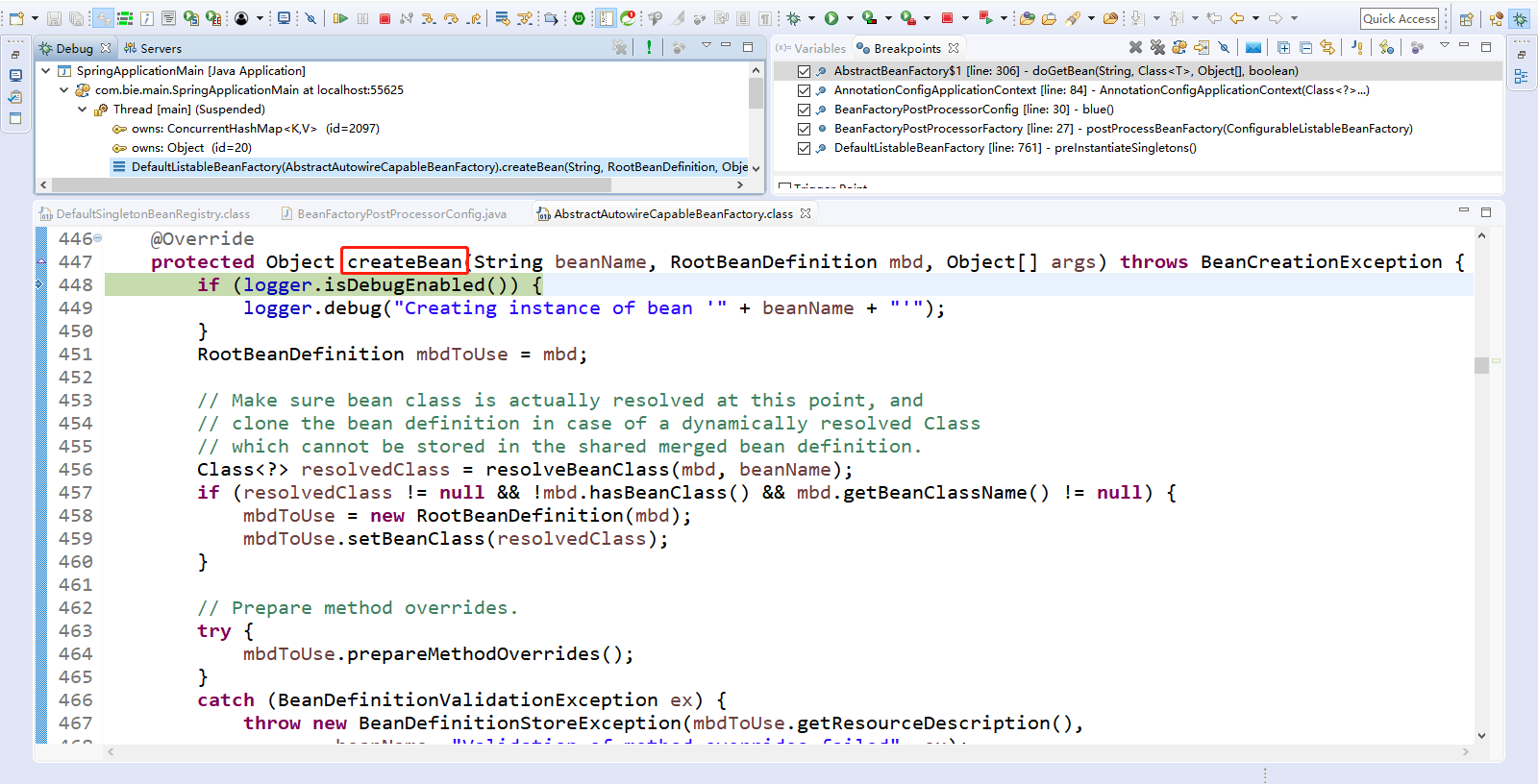
Step Over(F6)下一步,直到走到Object bean = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse);
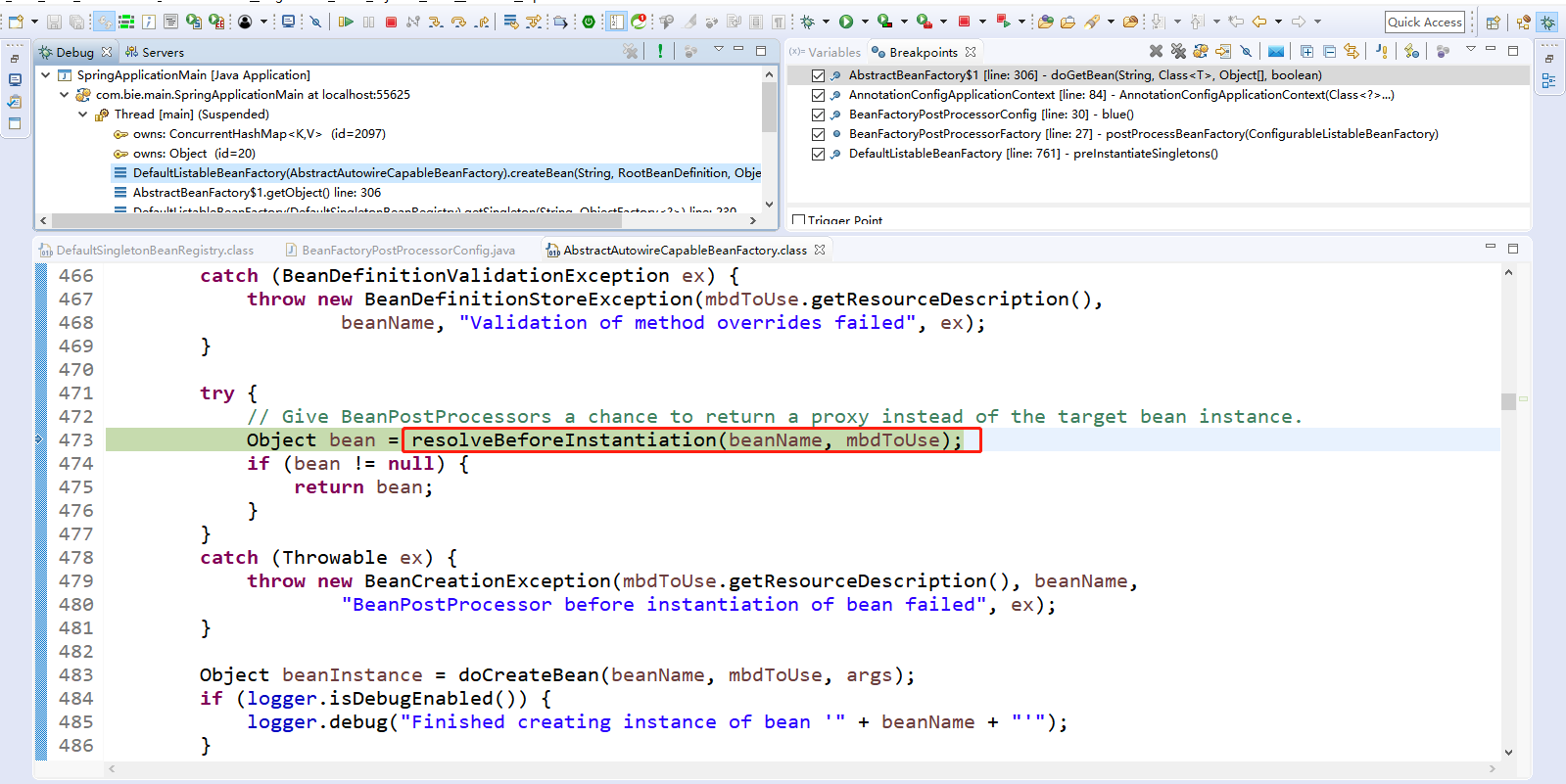
点击Step Into(F5)进入resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse);
提前执行InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor这种类型的后置处理器。
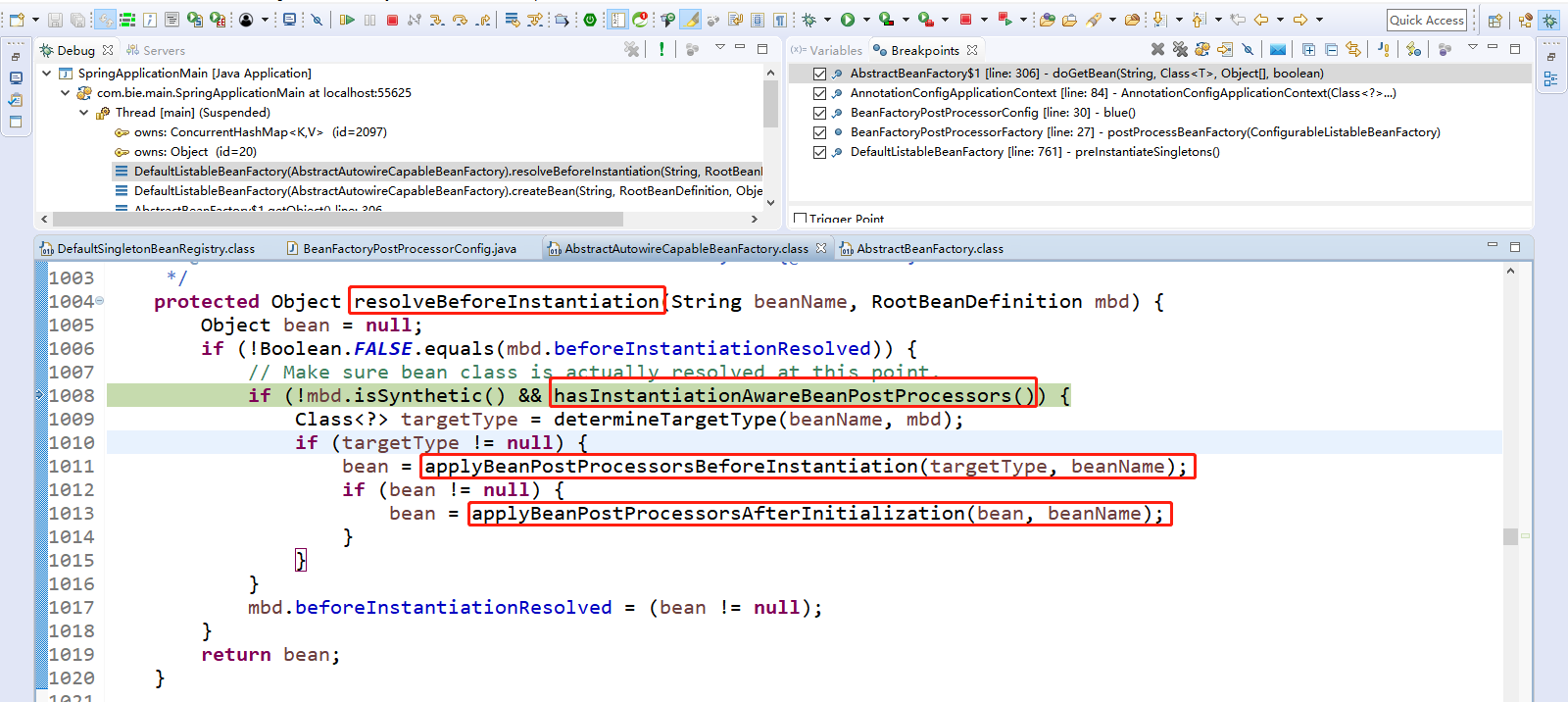
Step Over(F6)下一步,直到走到applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation(targetType, beanName);
触发applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation(targetType, beanName);方法,如果触发的该方法有返回对象,触发applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(bean, beanName);方法。
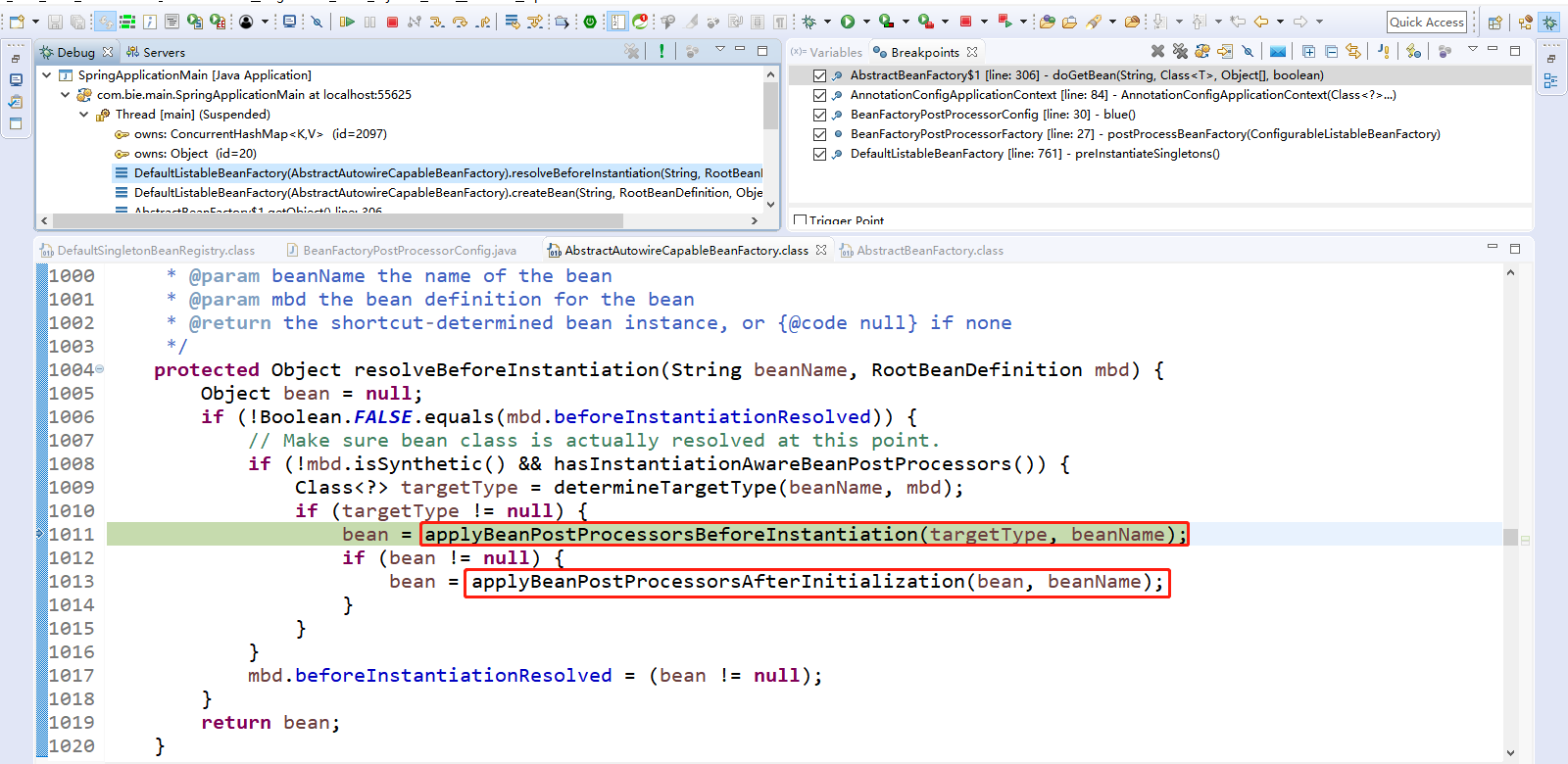
然后点击Step Into(F5)进入applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation(targetType, beanName);
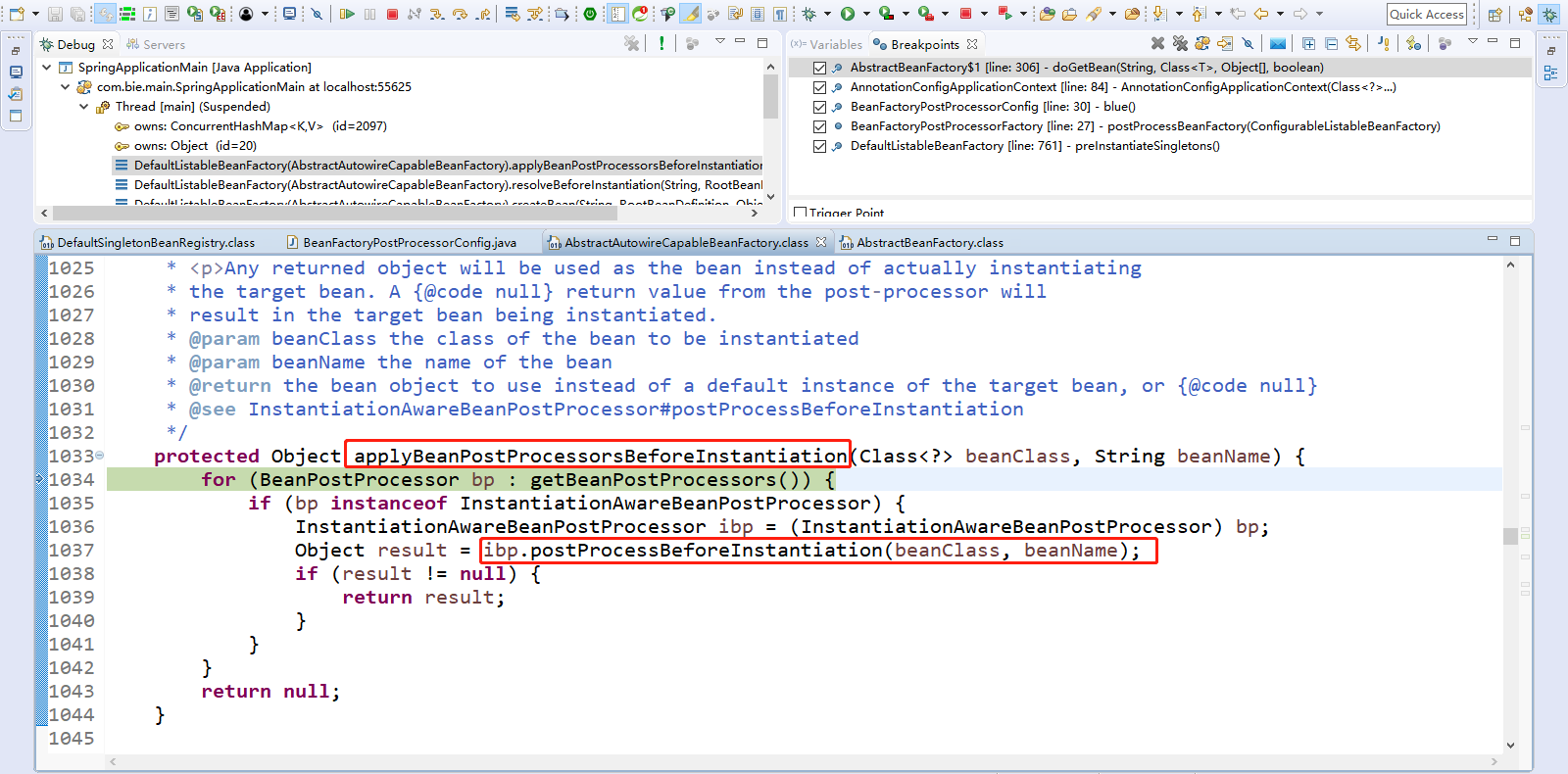
Step Over(F6)下一步,直到走到Object bean = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse);即刚才点击Step Into(F5)的起始点。
继续Step Over(F6)下一步,直到走到doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args);
1 protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final Object[] args) 2 throws BeanCreationException { 3 4 // Instantiate the bean. 5 // 创建bean的包装类型变量。 6 BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null; 7 // 如果mbd是单实例的。 8 if (mbd.isSingleton()) { 9 // 先从缓存中移除已有的beanName的实例。 10 instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName); 11 } 12 // 如果instanceWrapper是null的。 13 if (instanceWrapper == null) { 14 // 第一步、创建Bean实例。执行完此步,bean实例就已经创建成功的。 15 instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args); 16 } 17 final Object bean = (instanceWrapper != null ? instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance() : null); 18 Class<?> beanType = (instanceWrapper != null ? instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass() : null); 19 mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType; 20 21 // Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition. 22 // bean实例创建完毕以后,允许后置处理器修改bean的定义。 23 // 第二步、调用此种MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor类型的后置处理器的postProcessMergedBeanDefinition方法。 24 synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) { 25 if (!mbd.postProcessed) { 26 try { 27 // bean实例创建完毕以后调用该方法,如果是MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor这种类型的,循环遍历执行bdp.postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanType, beanName); 28 applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName); 29 } 30 catch (Throwable ex) { 31 throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, 32 "Post-processing of merged bean definition failed", ex); 33 } 34 mbd.postProcessed = true; 35 } 36 } 37 38 // Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references 39 // even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware. 40 boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences && 41 isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)); 42 // 获取到要暴露的单实例的bean组件 43 if (earlySingletonExposure) { 44 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 45 logger.debug("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName + 46 "' to allow for resolving potential circular references"); 47 } 48 // 将这些要暴漏的添加到缓存中 49 addSingletonFactory(beanName, new ObjectFactory<Object>() { 50 @Override 51 public Object getObject() throws BeansException { 52 return getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean); 53 } 54 }); 55 } 56 57 // Initialize the bean instance. 58 Object exposedObject = bean; 59 try { 60 // 为属性赋值的操作。 61 populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper); 62 if (exposedObject != null) { 63 // 如果exposedObject不为空的话。初始化bean操作。点进去研究吧 64 exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd); 65 } 66 } 67 catch (Throwable ex) { 68 if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) { 69 throw (BeanCreationException) ex; 70 } 71 else { 72 throw new BeanCreationException( 73 mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex); 74 } 75 } 76 77 // 获取到要暴露的单实例的bean组件 78 if (earlySingletonExposure) { 79 // 获取到单实例的bean组件。此时单实例bean已经创建完毕,也已经初始化完毕。 80 // 先从缓存中获取,此时beanName已经有值了。 81 Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false); 82 // 此时缓存获取到的earlySingletonReference中如果不为空。 83 if (earlySingletonReference != null) { 84 if (exposedObject == bean) { 85 exposedObject = earlySingletonReference; 86 } 87 else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) { 88 String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName); 89 Set<String> actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<String>(dependentBeans.length); 90 for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) { 91 if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) { 92 actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean); 93 } 94 } 95 if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) { 96 throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName, 97 "Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" + 98 StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) + 99 "] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " + 100 "wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " + 101 "bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " + 102 "'getBeanNamesOfType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example."); 103 } 104 } 105 } 106 } 107 108 // Register bean as disposable. 109 try { 110 // 注册Bean的销毁方法。销毁方法是在容器关闭以后执行的。看是否实现了DisposableBean销毁接口的方法。 111 registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd); 112 } 113 catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) { 114 throw new BeanCreationException( 115 mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex); 116 } 117 118 // 返回exposedObject 119 return exposedObject; 120 }
如下所示:
然后点击Step Into(F5)进入doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args);
Step Over(F6)下一步,直到走到createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
然后点击Step Into(F5)进入createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);

Step Over(F6)下一步,直到走到instantiateUsingFactoryMethod(beanName, mbd, args);

然后点击Step Into(F5)进入instantiateUsingFactoryMethod(beanName, mbd, args);
此时就是使用构造器进行解析,调用创建bean实例对象。
然后点击Step Into(F5)进入,然后Step Over(F6)下一步,然后点击Step Into(F5)进入,然后Step Over(F6)下一步,直到走到instantiateUsingFactoryMethod(beanName, mbd, explicitArgs);
里面的详细步骤可以研究一下,执行里面的代码最终会调用beanInstance = this.beanFactory.getInstantiationStrategy().instantiate(mbd, beanName, this.beanFactory, factoryBean, factoryMethodToUse, argsToUse);此时就会去创建Bean实例对象。
1 protected BeanWrapper createBeanInstance(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, Object[] args) { 2 // Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point. 3 // 解析我们要创建的bean实例的类型。 4 Class<?> beanClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName); 5 6 // 如果创建的bean类型不为空,等等,就抛出异常 7 if (beanClass != null && !Modifier.isPublic(beanClass.getModifiers()) && !mbd.isNonPublicAccessAllowed()) { 8 throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, 9 "Bean class isn't public, and non-public access not allowed: " + beanClass.getName()); 10 } 11 12 // 获取到工厂方法的名称,如果不为空,返回执行的工厂方法。 13 if (mbd.getFactoryMethodName() != null) { 14 // 里面的代码很多,自己可以去研究一下的。 15 return instantiateUsingFactoryMethod(beanName, mbd, args); 16 } 17 18 // Shortcut when re-creating the same bean... 19 boolean resolved = false; 20 boolean autowireNecessary = false; 21 if (args == null) { 22 synchronized (mbd.constructorArgumentLock) { 23 if (mbd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod != null) { 24 resolved = true; 25 autowireNecessary = mbd.constructorArgumentsResolved; 26 } 27 } 28 } 29 if (resolved) { 30 if (autowireNecessary) { 31 return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, null, null); 32 } 33 else { 34 return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd); 35 } 36 } 37 38 // Need to determine the constructor... 39 Constructor<?>[] ctors = determineConstructorsFromBeanPostProcessors(beanClass, beanName); 40 if (ctors != null || 41 mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR || 42 mbd.hasConstructorArgumentValues() || !ObjectUtils.isEmpty(args)) { 43 return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, ctors, args); 44 } 45 46 // No special handling: simply use no-arg constructor. 47 return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd); 48 }
如下所示:
然后Step Over(F6)下一步,直到走到return new Blue();可以看到执行到了创建bean实例的步骤。

此时,利用工厂方法或者对象的构造器创建出Bean实例。然后Step Over(F6)下一步。直到下一步到instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
Step Over(F6)下一步,直到走到populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
初始化bean实例的操作,populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper); 方法的调用作用是给bean赋值。

点击Step Into(F5)进入populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
1 protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw) { 2 // 获取到所有要赋值属性的值。 3 PropertyValues pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues(); 4 5 // 如果包装的bean为空,就抛出异常了 6 if (bw == null) { 7 if (!pvs.isEmpty()) { 8 throw new BeanCreationException( 9 mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Cannot apply property values to null instance"); 10 } 11 else { 12 // Skip property population phase for null instance. 13 return; 14 } 15 } 16 17 // Give any InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors the opportunity to modify the 18 // state of the bean before properties are set. This can be used, for example, 19 // to support styles of field injection. 20 // 定义变量,方便下面处理这种类型的InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor后置处理器使用。 21 boolean continueWithPropertyPopulation = true; 22 23 // 赋值之前先遍历了这种类型的InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor后置处理器。 24 if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) { 25 // 遍历所有的后置处理器 26 for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) { 27 // 如果后置处理器是这个类型InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor的后置处理器 28 if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) { 29 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp; 30 // 执行这些后置处理器的这个方法postProcessAfterInstantiation()。 31 if (!ibp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) { 32 continueWithPropertyPopulation = false; 33 break; 34 } 35 } 36 } 37 } 38 39 // 如果定义的变量continueWithPropertyPopulation为false。直接返回。 40 if (!continueWithPropertyPopulation) { 41 return; 42 } 43 44 if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME || 45 mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) { 46 MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues(pvs); 47 48 // Add property values based on autowire by name if applicable. 49 if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME) { 50 autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs); 51 } 52 53 // Add property values based on autowire by type if applicable. 54 if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) { 55 autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs); 56 } 57 58 pvs = newPvs; 59 } 60 61 boolean hasInstAwareBpps = hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors(); 62 boolean needsDepCheck = (mbd.getDependencyCheck() != RootBeanDefinition.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE); 63 64 if (hasInstAwareBpps || needsDepCheck) { 65 PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching); 66 if (hasInstAwareBpps) { 67 // 循环遍历,获取到所有的后置处理器 68 for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) { 69 // 如果是InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor这种类型的后置处理器。 70 if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) { 71 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp; 72 // 执行InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor后置处理器的postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);这个方法。 73 pvs = ibp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName); 74 if (pvs == null) { 75 return; 76 } 77 } 78 } 79 } 80 if (needsDepCheck) { 81 checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs); 82 } 83 } 84 85 // 应用Bean属性的值,此时才是为属性利用setter方法进行赋值操作的。利用反射调用setter方法,可以点进去研究一下的。 86 applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs); 87 }
如下所示:

Step Over(F6)下一步,直到走到populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
Step Over(F6)下一步,直到走到initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);然后点击Step Into(F5)进入initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
1 // 这里面其实之前也写过了。 2 protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd) { 3 if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) { 4 AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() { 5 @Override 6 public Object run() { 7 invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean); 8 return null; 9 } 10 }, getAccessControlContext()); 11 } 12 else { 13 // 第一步、 14 // 执行实现了xxxAware接口的方法。调用就是判断是否是实现了Aware接口、BeanNameAware接口、BeanClassLoaderAware接口、BeanFactoryAware接口。 15 // 执行Aware接口的方法。 16 invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean); 17 } 18 19 Object wrappedBean = bean; 20 if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) { 21 // 第二步、 22 // 执行所有的BeanPostProcessor后置处理器,调用BeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization方法。 23 // 执行后置处理器初始化之前的方法。 24 wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName); 25 } 26 27 try { 28 // 第三步 29 // 执行初始化方法。有很多方法执行初始化的方法,如实现了InitializingBean接口的、@Bean注解的initMethod属性等等。 30 // 自己可以点进去研究一下执行流程。里面首先判断是否是InitializingBean接口的实现,执行接口规定的初始化。然后再判断是否自定义初始化方法。 31 invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd); 32 } 33 catch (Throwable ex) { 34 throw new BeanCreationException( 35 (mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null), 36 beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex); 37 } 38 39 if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) { 40 // 第四步、 41 // 执行后置处理器初始化之后的方法。 42 // BeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization()方法。 43 wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName); 44 } 45 // 返回包装的bean组件。 46 return wrappedBean; 47 }
如下所示:
Step Over(F6)下一步,直到走到exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
Step Over(F6)下一步,直到走到Object beanInstance = doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args);此时bean已经创建成功了。
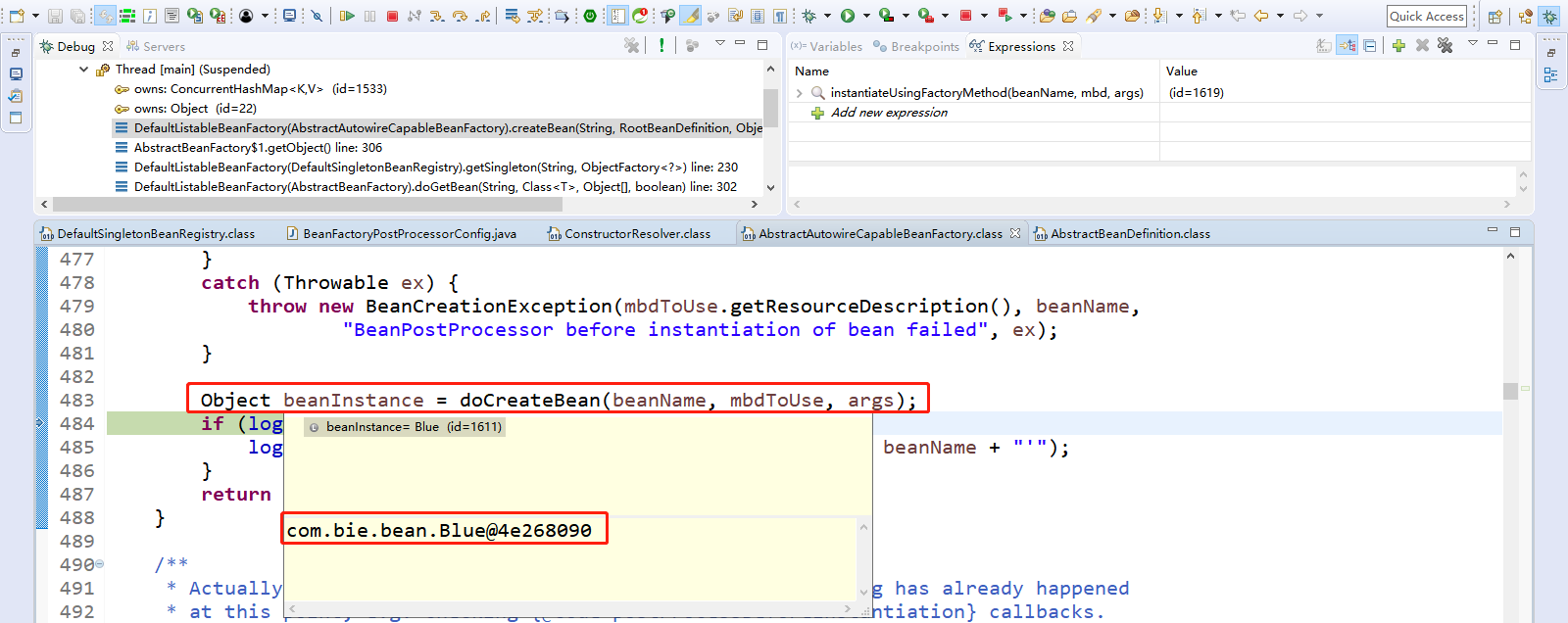
Step Over(F6)下一步,直到走到return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
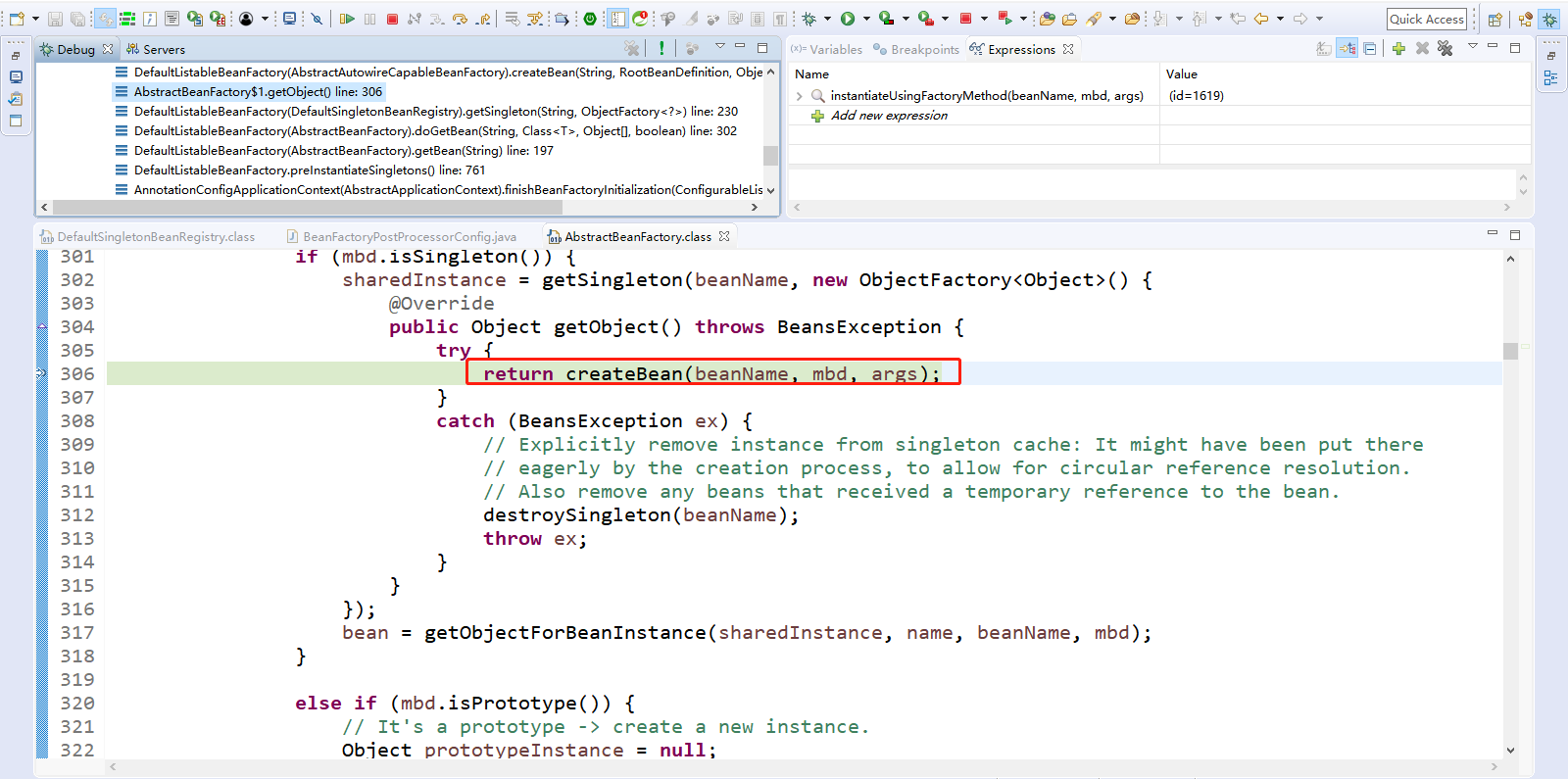
Step Over(F6)下一步,直到走到singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
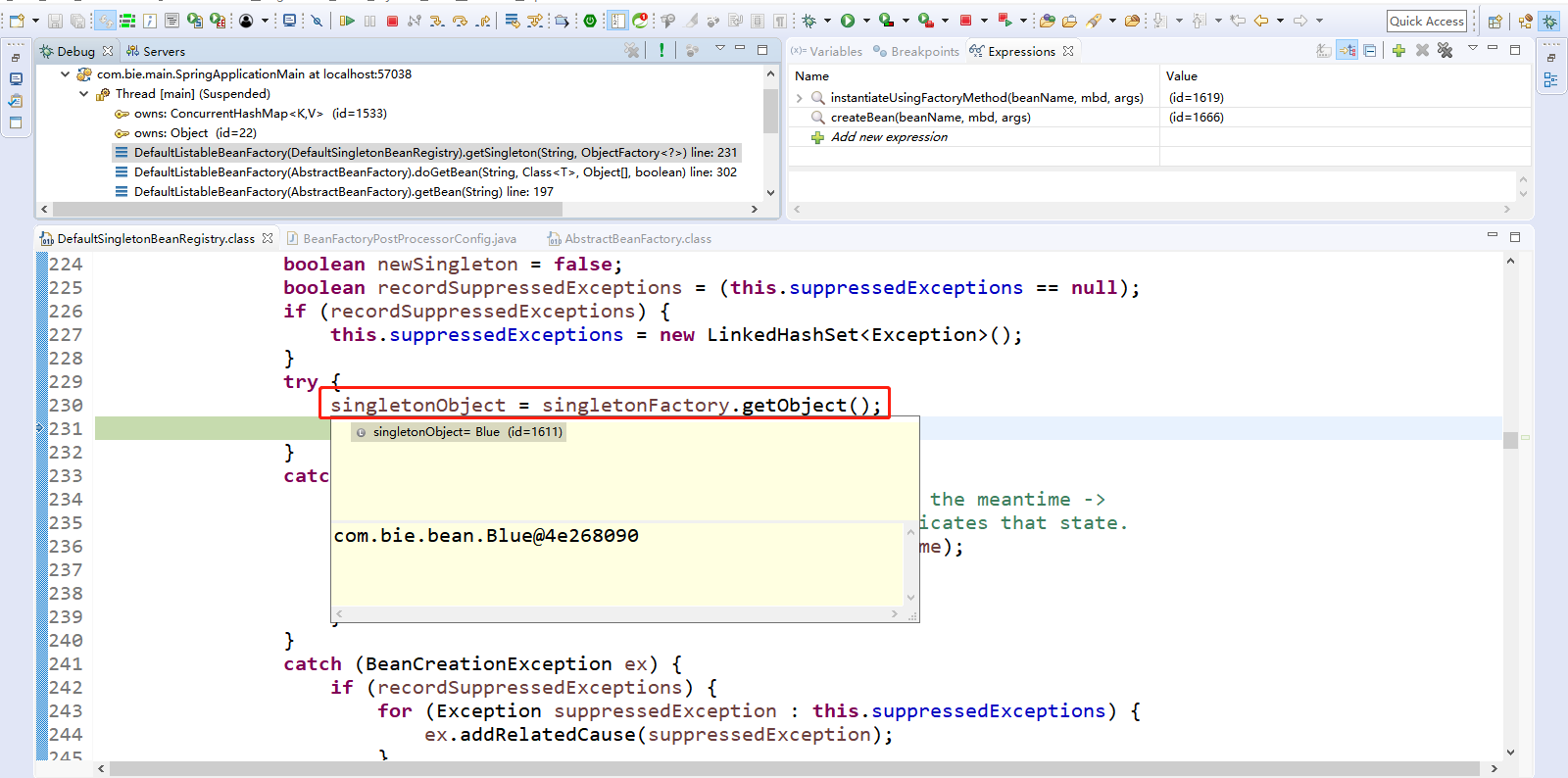
由于是匿名内部类,getSingleton(beanName, new ObjectFactory<Object>()匿名内部类,调用的是DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.getSingleton()方法,调用此方法,最后将单实例bean添加到缓存中。注意这一点吧,不然很迷。

Step Over(F6)下一步,直到走到sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, new ObjectFactory<Object>()。
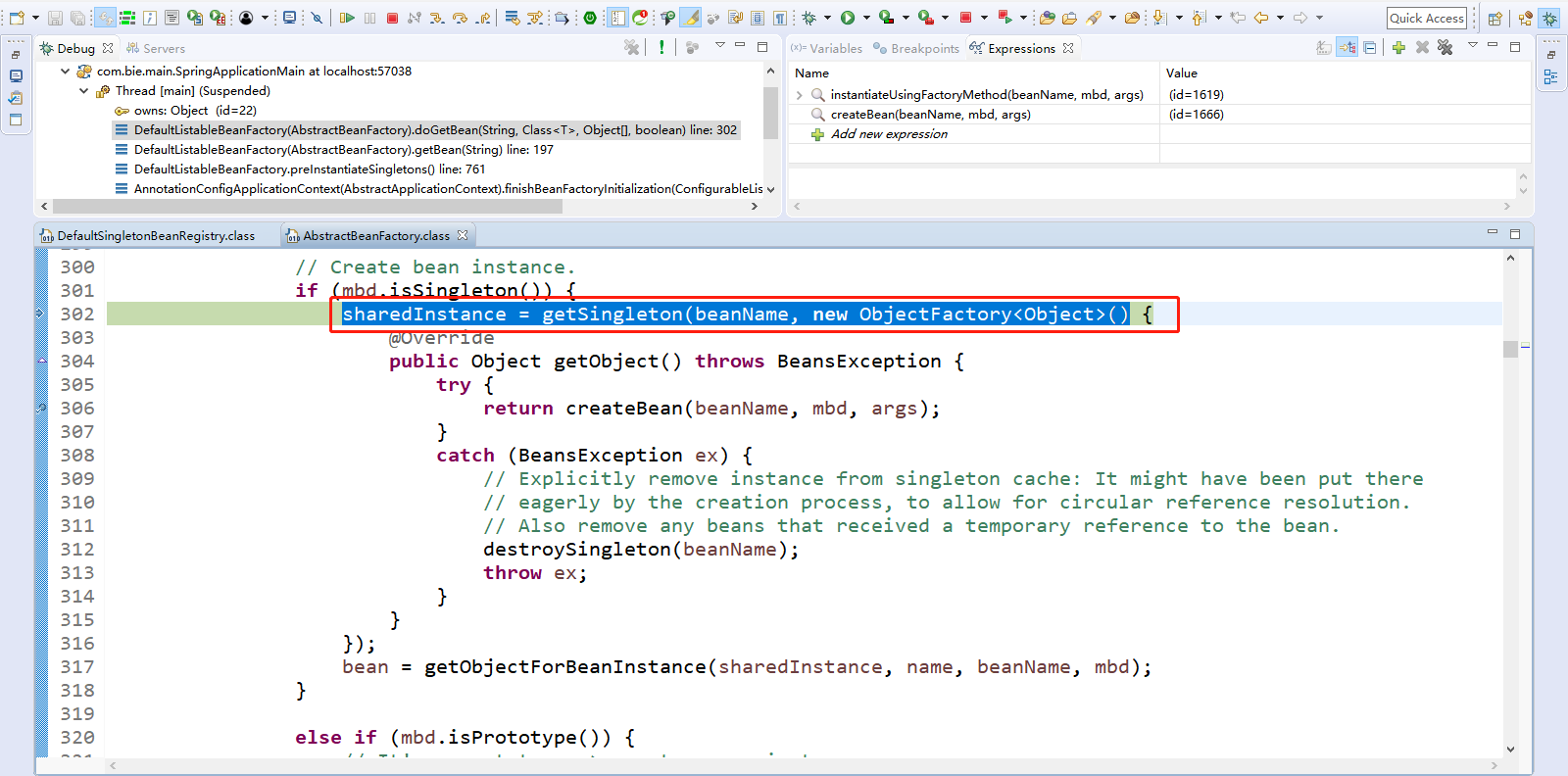
Step Over(F6)下一步,直到走到return doGetBean(name, null, null, false);

Step Over(F6)下一步,直到走到getBean(beanName);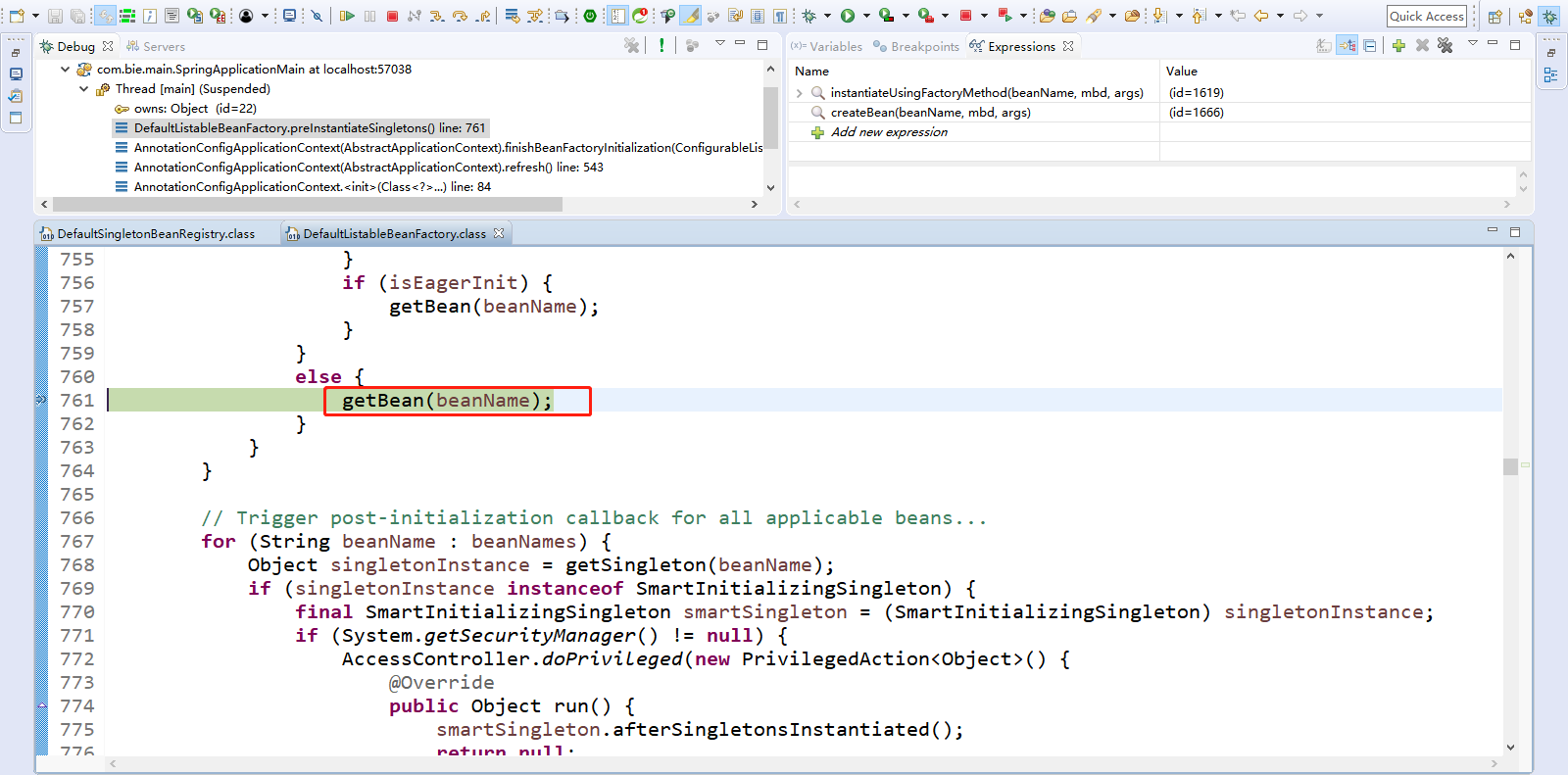
IOC容器就是这些MAP,很多的MAP里面保存了单实例Bean,环境信息等等。所有的这些MAP构成了IOC容器,容器里面保存所有组件,从容器中获取组件就是从Map中取出对应的值。
此时,所有的bean就已经创建完毕了,使用循环遍历创建所有的bean实例。Step Over(F6)下一步,直到走到Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName);获取到所有的bean对象。
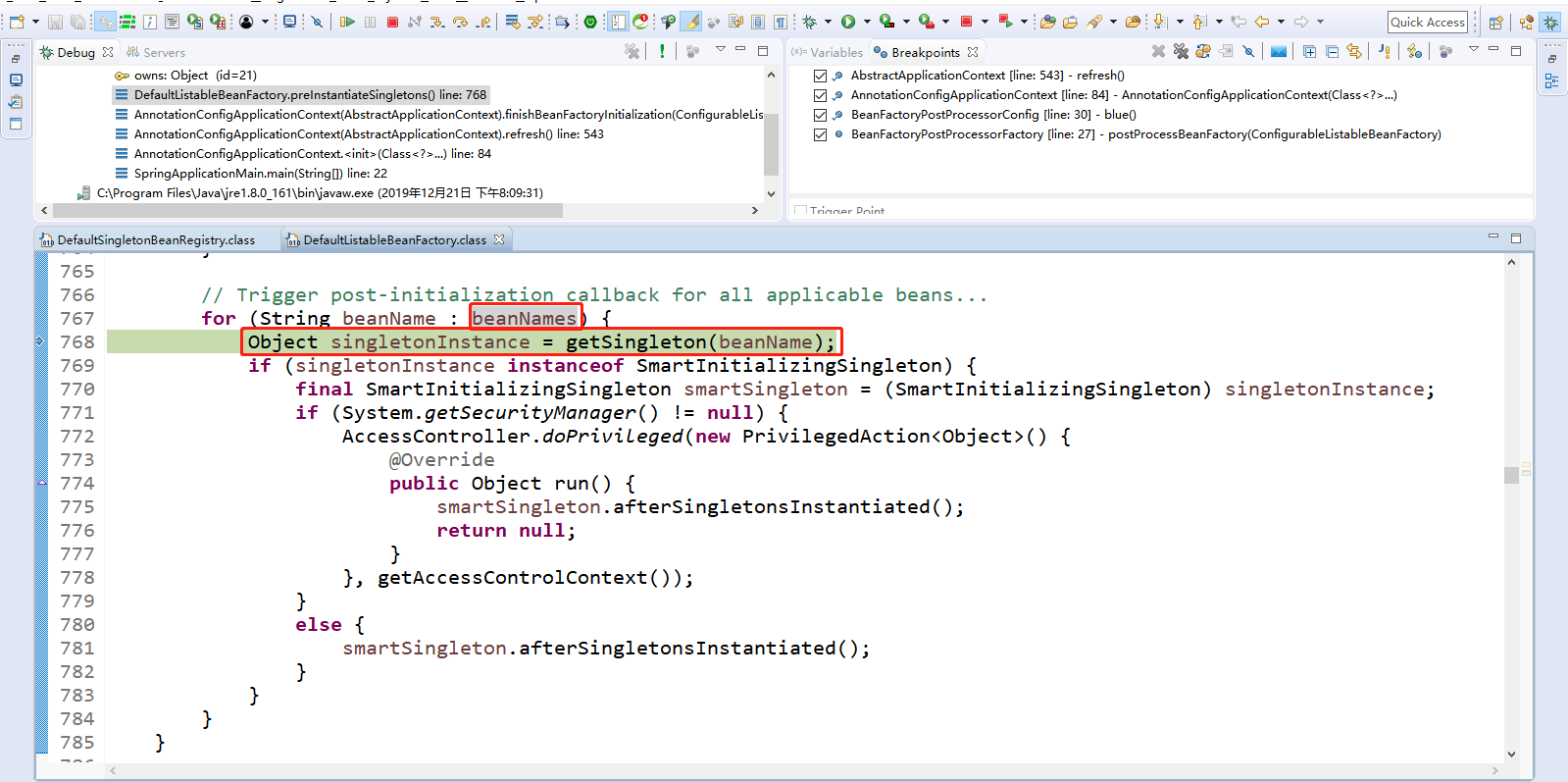
Step Over(F6)下一步,直到走到beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();
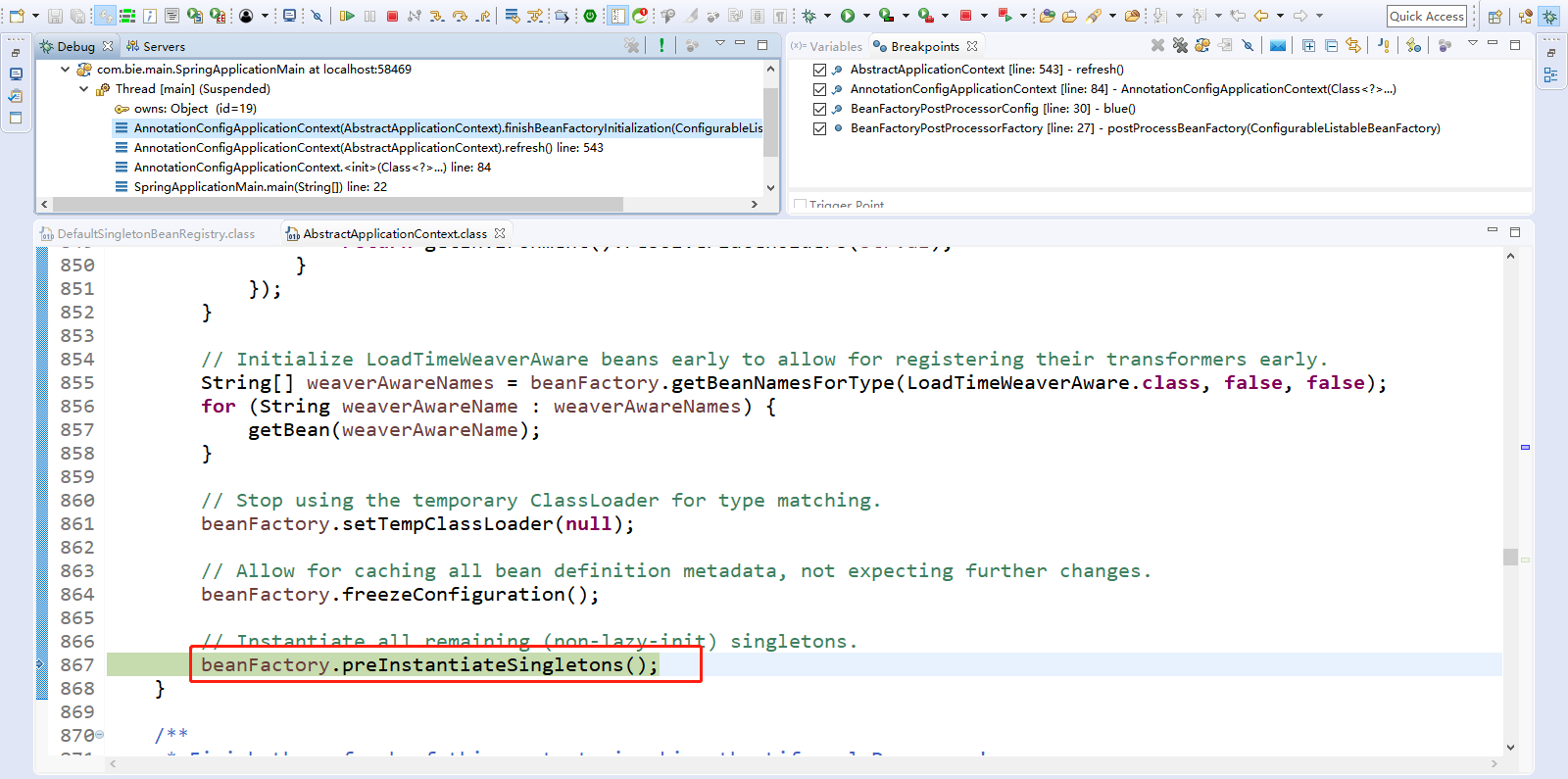
12、Step Over(F6)下一步,直到走到finishRefresh();

然后点击Step Into(F5)进入finishRefresh()方法。
1 protected void finishRefresh() { 2 // Initialize lifecycle processor for this context. 3 // 初始化和生命周期相关的后置处理器。自己可以点进去研究一下的。 4 // 允许我们自己定义LifecycleProcessor的实现类。在BeanFactory容器的生命周期期间来进行一些回调操作onRefresh()、onClose()。 5 // 默认从容器中找是否有LifecycleProcessor类型的组件,如果没有使用默认的生命周期组件new DefaultLifecycleProcessor();。 6 initLifecycleProcessor(); 7 8 // Propagate refresh to lifecycle processor first. 9 // 获取到生命周期处理器回调onRefresh()方法。监听BeanFactory生命周期的。 10 getLifecycleProcessor().onRefresh(); 11 12 // Publish the final event. 13 // 给容器发布一个事件,叫容器刷新完成事件。发布容器刷新完成事件。 14 publishEvent(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this)); 15 16 // Participate in LiveBeansView MBean, if active. 17 // 暴露一些MBean 18 LiveBeansView.registerApplicationContext(this); 19 }
如下所示:

至此,嗯,头蒙眼花。
1 Spring源码理解点。 2 第一点、Spring容器在启动的时候,先会保存所有注册进来的Bean的定义信息。切记,Bean的定义,不是创建Bean对象的哦。未来,BeanFactory按照bean的定义创建bean的信息。 3 有两种方式定义bean的定义信息。 4 第一种,使用xml注册bean的定义信息。 5 第二种,使用注解注册bean的定义信息。如@Component、@Service、@Controller、@Repository、@Bean,都是给容器中注册bean的定义信息。 6 第二点、Spring容器会在合适的时机创建这些Bean。 7 合适的时机主要有两个,如下所示: 8 第一个,当使用到这个bean的时候,会利用getBean方法创建该bean,创建成功以后保存到容器中。 9 第二个,统一创建剩下所有bean的时候。finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);如果单实例bean,还没有创建的时候,此时会进行创建。 10 第三点、后置处理器,每一个bean创建完成以后,都会使用各种后置处理器进行处理,来增强bean的功能。 11 比如AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor,处理自动注入的。 12 AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator,来做aop功能的,给bean创建代理对象。 13 第四点、Spring的事件驱动模型。 14 比如,ApplicationListener,做事件监听的。 15 ApplicationEventMulticaster事件的派发。
作者:别先生
博客园:https://www.cnblogs.com/biehongli/
如果您想及时得到个人撰写文章以及著作的消息推送,可以扫描上方二维码,关注个人公众号哦。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 分享 3 个 .NET 开源的文件压缩处理库,助力快速实现文件压缩解压功能!
· Ollama——大语言模型本地部署的极速利器
· DeepSeek如何颠覆传统软件测试?测试工程师会被淘汰吗?
2018-12-29 Mysql的性能优化