遗传算法Java实现以及TSP问题遗传算法求解
在以前的文章(简单遗传算法MATLAB实现)中已经介绍过,遗传算法是一种基于达尔文生物进化论的启发式算法,它的核心思想就是优胜劣汰,适应性好的个体将在生存竞争中获得更大的生存机会,而适应差的将更有可能在竞争中失败,从而遭到淘汰。
1. 生物进化
图1用了一个非常形象的实例,来表现进化机制对生物繁衍的作用。
图1 眼睛的进化(摘自http://blog.csdn.net/zzwu/article/details/561588)
可以设想,曾有一个时期动物就根本没有眼睛。那时,动物在它们的环境中航行完全是靠嗅觉和触觉来躲避掠食它们的动物。他们也相当擅长于这样做,因为他们靠这样已经历了成千上万个世代。在那个时候,鼻子大和手脚长的男性是受女孩子们欢迎的。然而,突然有一天,当两个动物配对时,一个基因突变发生在为皮肤细胞提供的蓝图上。这一突变使其后代在他们的头上发育出了一个具有相当光敏效应的细胞,使其后代能足够识别周围环境是亮的还是暗的。这样就给他带来了一个微小的优点,因为,如果一种食肉动物,比如一只鹰,来到了某个范围以内,则它将阻挡了光线,这时,该动物就会感觉得到,就可迅速跑到隐蔽的地方去躲藏起来。另外,这种皮肤细胞还能指示现在是晚上或白天,或告诉他现在是在地面之上或地面之下,这些信息在捕食和吸取营养时都能为它提供方便。你能看到这一新型皮肤细胞将使这一动物与群体中其余的动物相比,具备了稍多的优点,从而更容易获得异性的青睐,因此也就有更多的生存和繁殖的机会。过了一段时间,由于进化机制的作用,许多动物的染色体中都会出现具有光敏皮肤细胞的基因。现在,如果你再作一些外推,想象这一光敏细胞基因得到了进一步的有利突变,则你能看到,经过许多许多世代后,光敏细胞经过分化形成为一个区域;这个区域不断变大,产生出一些更为确定的特征,例如形成一个晶体,或产生能区别颜色的视觉细胞;还可以想象,一个突变使某个动物由一个光敏区域改变为两个光敏区域,由此就使那个动物有了立体视觉。立体视觉对一个生物体来说是一个巨大的进步,因为这能精确告诉他目标离开他有多远。当然,你也可以把会对眼睛产生不利影响的突变装入同样那些基因。但这里重要的一点是,这样生长出来的后代将不会和已具备改进型眼睛的堂表亲戚们那样取得成功,它们最终将会灭绝。只有成功的基因才会得到继承。观察自然界中存在的任何特征就能发现,它们的进化都是利用无数微小的突变发展而来的,且它们都是对拥有者有利。
人类的发展就是进化的一个极为成功的案例。人类从猿猴发展而来(虽然有些生物学家对此并不认同),经过了不能直立行走->可以直立行走->制造工具->创做语言->协同工作->组建社会->……->,这些都是进化的作用。
2. 遗传算法
遗传算法的概念最早是由Bagley J.D 于1967年提出的。后来Michigan大学的J.H.Holland教授于1975年开始对遗传算法(Genetic Algorithm, GA)的机理进行系统化的研究。遗传算法是对达尔文生物进化理论的简单模拟,其遵循“适者生存”、“优胜略汰”的原理。遗传算法模拟一个人工种群的进化过程,并且通过选择、杂交以及变异等机制,种群经过若干代以后,总是达到最优(或近最优)的状态。
自从遗传算法被提出以来,其得到了广泛的应用,特别是在函数优化、生产调度、模式识别、神经网络、自适应控制等领域,遗传算法更是发挥了重大的作用,大大提高了问题求解的效率。遗传算法也是当前“软计算”领域的重要研究课题。
模式(Schema)理论是对遗传算法数学机理的深入解释。所谓一个模式指的是包含了符号*的字符串,例如一个二进制字符串1**000000*1就可以表达一个模式,*可以是0或者1,所以该模式可以匹配23 = 6个不同的二进制字符串实例。
模式理论可以用公式1解释。
模式定理:
在遗传算子选择、交叉以及变异的作用下,具有阶数低、长度短、平均适应度高于种群平均适应度的模式在子代中将以指数级增长。
还有两个定义:
例如:
0*******1**的阶为2,定义距为7.
在基本遗传算法(或者简单遗传算法)中,有三个基本的遗传操作(operator),即选择操作(Selection)、交叉操作(Crossover)以及变异操作(Mutation)。关于这些操作详细的过程请参见简单遗传算法MATLAB实现。
3. TSP问题遗传算法实现
关于TSP问题的定义,在上一篇(蚁群算法Java实现以及TSP问题蚁群算法求解)中已有详细的说明和定义,在此不予重述。
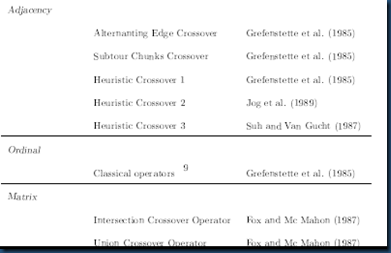
用遗传算法求解TSP问题,最困难的是要解决三个方面的问题,即编码,交叉操作以及变异操作。从文献中发现这些问题主要有一下几种解决方法,见表1
表1 主要的编码方式,交叉操作以及变异操作
3.1 编码
TSP问题编码一般有五种种不同的方式:
- 基于二进制的编码
- 基于矩阵的编码
- 基于邻接的编码
- 基于索引(Ordinary)的编码
- 基于路径的编码
基于二进制的编码是一种传统的编码方式,但是这种方式的编码,在经过遗传操作以后很难保证后代还是一个可行解,还需要另外的修正操作;基于矩阵的编码、邻接的编码以及索引的编码均比较复杂,并且需要占用大量的内存,应用的不是很广泛;目前最普遍用的编码方式就是基于路径的编码方式,因为它最直观最容易理解,操作起来也比较方便。以下将主要介绍基于路径的编码方式以及相关的遗传操作。
例如:
一个TSP问题,有六个城市{1,2,3,4,5,6},那么用基于路径的编码(1 3 5 4 6 2)就可以表示为一个个体。
3.2 交叉操作
下面主要介绍几种常见的交叉操作的方式。
3.2.1 部分匹配法(Partially Matching Crossover, PMX)
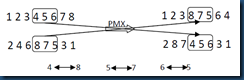
以两个父代个体为例:(1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8)和(2 4 6 8 7 5 3 1),随机选择两个交叉的点,假如第一个点为位置4,第二个交叉点为位置6,那么在两个点之间的位置将进行交叉,其它的位置进行复制或者用相匹配的数进行替换。在此实例中,第一个父代个体中4 5 6被选中,第二个父代个体中,8 7 5被选中。那么4 与8,5与7,6与5相匹配。匹配过程和如图2所示。
图2 PMX交叉操作
首先将4 5 6与8 7 5分别加入到子代2和子代1中相应的位置,然后将其他位置上的数字直接复制到相应的后代中,如果该数字已经在该子代中已经存在,则用相应的匹配法则进行替换,例如子代1中将7复制进去的时候,发现7已经存在在子代中,通过查找相应的匹配法则,发现,7与5匹配,然后复制5,又发现5也已经存在在该子代中,在此查找匹配法则,发现5与6匹配,将6复制,6不存在在该子代中,所以可以将6复制进去,如此反复,知道子代中城市的数目达到定义的长度,该子代创建完成。
3.2.2 循环交叉法(Cycle Crossover, CX)
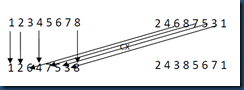
依旧以两个父代个体为例:(1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8)和(2 4 6 8 7 5 3 1),在构造子代的过程中,首先从父代1中选取第一个元素,然后查找父代2中对应位置的元素在在父代1中的位置,将这个位置对应的元素假如到子代1中,如此过程反复,直到找到一个元素对应的父代2元素等于起始元素,次循环结束,然后将剩余未填充的位置用父代2相应的位置的元素进行填充,这样就可以完成子代1的创建。子代2创建方法类似。CX操作过程如图2所示。
图3 CX操作
首先选择父代1中的第一个元素1,将它加入到子代1中,然后检查父代2中对应位置,该位置元素为2,在父代1中查找该元素,该元素在父代1中的位置为2, 将2加入到子代1的第二个位置,再次检查父代2中第二个位置的元素,它为4,然后查找它在父代1中的位置为4,将4加入到子代1的第四个位置,然后将其加入到子代1中对应的位置4,在检查父代2中该位置的元素,它为8,查找到它在父代1中的位置为8,然后将其加入到子代1中位置8,再次查找父代2中位置8的元素,它为1,等于起始选择的元素,循环结束,然后将子代1中3,5,6,7元素为空的位置,用父代2对应位置的元素进行填充,这些元素为6,7,5,3,所以得到的子代1为(1 2 5 4 7 5 3 8)。同样的方法,得到子代2为(2 4 3 8 5 6 7 1)。
3.2.3 次序交叉法1(Order Crossover, OX1)
还以两个相同的父代个体为例:(1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8)和(2 4 6 8 7 5 3 1),随机选择两个交叉的点,假如第一个点为位置3,第二个交叉点为位置5,那么在两个点之间的位置将进行交叉。然后从第二个交叉点开始,将原来相应的父代按照顺序进行填充,如果选择的元素已经存在在该子代中,跳过该元素,选择下一个元素,这种过程反复进行,知道所有的城市都被选择一次。在此实例中,第一个父代个体中3 4 5被选中,第二个父代个体中,6 8 7被选中。匹配过程和如图4所示。
图4 OX1操作
首先,将选择的位串进行替换,即3 4 5换到子代2中,6 8 7换到子代1中。现在从第二个交叉点开始,将父代1中的基因插入到子代1中, 所以,1 插入到第六个位置,2 插入到第七个位置,3插入到第八个位置,第二个交叉点后面已经填充满,将剩下的插入到第一个插入点前面的位置,所以4插入到第一个位置,5插入到第二个位置。这样,子代1构建完成。同样地方法,可以构建子代2.当遇到子代中已经存在的基因,就跳到下一个。
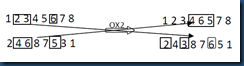
3.2.4 次序交叉法2(Order Crossover, OX2)
还以两个相同的父代个体为例:(1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8)和(2 4 6 8 7 5 3 1),随机选择几个交叉的点,假如第一个点为位置2,第二个交叉点为位置是3,第三个为位置6。首先找到父代2中相应位置的基因在父代1中位置,然后将其用父代2中选择的位置的基因进行替换插入到子代1中相应的位置中。然后将其它的位置用OX1相似的方法进行填充。这样就可以得到子代1.同样,替换角色,可以得到子代2。具体的操作过程如图5所示。
图5 OX2操作
首先找到父代2中第,2,3以及第六个位置的基因,它们为4,6和5,这三个基因在父代1中的位置为4,5和6,将它们替换成4,6,5,加入到子代1中相应的位置,然后将父代1中的基因按照顺序插入到子代1中,如果该基因已经存在在位串中,则跳过该基因,继续下一个。这样就可以构建完子代1。子代2也可以以相同的方法构造完成。
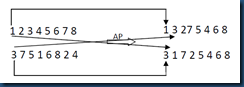
3.2.5 基于位置的交叉法(Position Based Crossover, POS)
还以两个相同的父代个体为例:(1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8)和(2 4 6 8 7 5 3 1),随机选择几个交叉的点,假如第一个点为位置2,第二个交叉点为位置是3,第三个为位置6。将两个父代中这些选择基因按照顺序交换,并且插入到子代1和2中。然后对其它位置的基因,按照顺序插入。具体操作过程如图6所示。
图6 POS操作
首先将2 3 6和4 6 8交换,分别插入到子代2和子代1相应的位置2,4,6中,然后将将父代1和父代2中的基因按照顺序插入到子代1和2中,如果该基因已经存在在位串中,则跳过该基因,继续下一个,知道位串的长度等于定义的长度。
3.2.6 交替位置交叉法(Alternating Position Crossover,APX)
以两个父代个体为例:(1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8)和(3 7 5 1 6 8 2 4),APX是一种简单的交叉操作方法,它是轮流选择父代1和2中的基因,直到子代的长度达到定义的长度为止。具体操作如图7所示。
图7 APX操作
首先选择父代1中的第一个元素1,加入到子代1中,然后选择父代2中的第一个元素3,它不等于1所以也加入到子代1中,然后再选择父代1中的第二个元素2,它也不包含在当前的位串中,所以,也加入进去,然后再选择父代2中的第二个元素,……,直到子代1的长度达到8为止。同样的方法,可以得到子代2.
3.3 变异操作
同样地,下面介绍几种常见的变异操作方法。
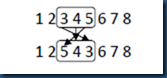
3.3.1 替换变异(Displacement Mutation, DM)
DM先从父代个体中选择一个子位串,然后再随机在剩下的位串中选择一个为止,并插入该子位串,如图8所示。
图8 DM操作
3.3.2 交换变异(Exchange Mutation, EM)
EM是从父代个体中选择两个基因位置,然后互换这两个位置的基因。如图9所示。
图9 EM操作
3.3.3 插入变异(Insertion Mutation, IM)
IM和DM类似,唯一的区别在于它是从父代个体中只选择一个基因,然后随机的插入到剩下的基因串中。如图10所示。
图10 IM操作
3.3.4 简单倒位变异(Simple Inversion Mutation, SIM)
SIM先从父代个体中选择一个基因串,然后将这个基因串中所有的基因倒位放置,如图11所示。
图11 SIM操作
3.3.5 倒位变异(Inversion Mutation, IVM)
IVM在SIM的基础上,随机选择一个插入位置,将这个到位后的基因串在插入到其中。如图12所示。
图12 IVM操作
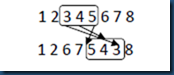
3.3.6 争夺变异(Scramble Mutation, SM)
SM非常简单,先随机从父代个体中选择一个基因串,然后将除了第一个基因外的基因均向前移动一位,将第一个基因移到最后一位。具体操作过程如图13所示。
图13 SM操作
4. TSP问题遗传算法求解以及Java实现
该程序分成两个java类,Chromosome类和GA类。
Chromosome类的实现:
1: import java.util.Random;
2: import java.util.Vector;
3:
4: public class Chromosome implements Cloneable {
5:
6:
7: private int[] tour;
8: private int[][] distance;
9: private int cityNum;
10: private double fitness;
11:
12: public Chromosome(){
13: cityNum = 30;
14: tour = new int[cityNum];
15: distance = new int[cityNum][cityNum];
16: }
17:
18: public Chromosome(int num, int[][] distance){
19: this.cityNum = num;
20: tour = new int[cityNum];
21: this.distance = distance;
22:
23: }
24:
25: public void randomGeneration(){
26: Vector<Integer> allowedCities = new Vector<Integer>();
27: for (int i = 0; i < cityNum; i++) {
28: allowedCities.add(Integer.valueOf(i));
29: }
30:
31: Random r = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis());
32: for (int i = 0; i < cityNum; i++) {
33:
34: int index = r.nextInt(allowedCities.size());
35: int selectedCity = allowedCities.get(index).intValue();
36: tour[i] = selectedCity;
37: allowedCities.remove(index);
38: }
39:
40: }
41:
42: public void print(){
43: for (int i = 0; i < cityNum; i++) {
44: System.out.print(tour[i] + ",");
45: }
46: System.out.println();
47: System.out.println("Its fitness measure is: "+ getFitness());
48: }
49:
50: private double calculatefitness(){
51: /*for (int i = 0; i < cityNum; i++) {
52: for (int j = 0; j < cityNum; j++) {
53: System.out.print(distance[i][j]+"\t");
54: }
55: System.out.println();
56: }*/
57: double fitness = 0.0;
58: int len = 0;
59: for (int i = 0; i < cityNum - 1; i++) {
60: len += distance[this.tour[i]][this.tour[i+1]];
61: }
62: len += distance[0][tour[cityNum-1]];
63: fitness = 1.0/len;
64: return fitness;
65: }
66:
67: public int[] getTour() {
68: return tour;
69: }
70:
71: public void setTour(int[] tour) {
72: this.tour = tour;
73: }
74:
75: public int[][] getDistance() {
76: return distance;
77: }
78:
79: public void setDistance(int[][] distance) {
80: this.distance = distance;
81: }
82:
83: public int getCityNum() {
84: return cityNum;
85: }
86:
87: public void setCityNum(int cityNum) {
88: this.cityNum = cityNum;
89: }
90:
91: public double getFitness() {
92: this.fitness = calculatefitness();
93: return fitness;
94: }
95:
96: public void setFitness(double fitness) {
97: this.fitness = fitness;
98: }
99:
100: @Override
101: protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
102: Chromosome chromosome = (Chromosome) super.clone();
103: chromosome.cityNum = this.cityNum;
104: chromosome.distance = this.distance.clone();
105: chromosome.tour = this.tour.clone();
106: chromosome.fitness = this.fitness;
107: return chromosome;
108: }
109:
110:
111:
112: }
GA类的实现:
1: import java.io.BufferedReader;
2:
3: import java.io.FileInputStream;
4: import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
5: import java.io.FileOutputStream;
6:
7: import java.io.IOException;
8: import java.io.InputStreamReader;
9: import java.util.ArrayList;
10: import java.util.List;
11: import java.util.Random;
12:
13:
14: public class GA {
15:
16: private Chromosome[] chromosomes;
17: private Chromosome[] nextGeneration;
18: private int N;
19: private int cityNum;
20: private double p_c_t;
21: private double p_m_t;
22: private int MAX_GEN;
23: private int bestLength;
24: private int[] bestTour;
25: private double bestFitness;
26: private double[] averageFitness;
27: private int[][] distance;
28: private String filename;
29:
30: public GA(){
31: N = 100;
32: cityNum = 30;
33: p_c_t = 0.9;
34: p_m_t = 0.1;
35: MAX_GEN = 1000;
36: bestLength = 0;
37: bestTour = new int [cityNum];
38: bestFitness = 0.0;
39: averageFitness = new double[MAX_GEN];
40: chromosomes = new Chromosome[N];
41: distance = new int[cityNum][cityNum];
42:
43: }
44:
45: /**
46: * Constructor of GA class
47: * @param n 种群规模
48: * @param num 城市规模
49: * @param g 运行代数
50: * @param p_c 交叉率
51: * @param p_m 变异率
52: * @param filename 数据文件名
53: */
54: public GA(int n, int num, int g, double p_c, double p_m, String filename){
55: this.N = n;
56: this.cityNum = num;
57: this.MAX_GEN = g;
58: this.p_c_t = p_c;
59: this.p_m_t = p_m;
60: bestTour = new int [cityNum];
61: averageFitness = new double[MAX_GEN];
62: bestFitness = 0.0;
63: chromosomes = new Chromosome[N];
64: nextGeneration = new Chromosome[N];
65: distance = new int[cityNum][cityNum];
66: this.filename = filename;
67: }
68:
69: public void solve() throws IOException{
70: System.out.println("---------------------Start initilization---------------------");
71: init();
72: System.out.println("---------------------End initilization---------------------");
73: System.out.println("---------------------Start evolution---------------------");
74: for (int i = 0; i < MAX_GEN; i++) {
75: System.out.println("-----------Start generation "+ i+"----------");
76: evolve(i);
77: System.out.println("-----------End generation "+ i+"----------");
78: }
79: System.out.println("---------------------End evolution---------------------");
80: printOptimal();
81: outputResults();
82:
83: }
84: /**
85: * 初始化GA
86: * @throws IOException
87: */
88: @SuppressWarnings("resource")
89: private void init() throws IOException{
90: //读取数据文件
91: int[] x;
92: int[] y;
93: String strbuff;
94: BufferedReader data = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(filename)));
95:
96: distance = new int[cityNum][cityNum];
97: x = new int[cityNum];
98: y = new int[cityNum];
99: for (int i = 0; i < cityNum; i++) {
100: strbuff = data.readLine();
101: String[] strcol = strbuff.split("");
102: x[i] = Double.valueOf(strcol[1]).intValue();
103: y[i] = Double.valueOf(strcol[2]).intValue();
104: }
105: //计算距离矩阵 ,针对具体问题,距离计算方法也不一样,此处用的是att48作为案例,它有48个城市,距离计算方法为伪欧氏距离,最优值为10628
106: for (int i = 0; i < cityNum - 1; i++) {
107: distance[i][i] = 0; //对角线为0
108: for (int j = i + 1; j < cityNum; j++) {
109: double rij = Math.sqrt((x[i] - x[j]) * (x[i] - x[j])+ (y[i] - y[j]) * (y[i] - y[j]));
110: int tij = (int) Math.round(rij);
111: //if (tij < rij) {
112: distance[i][j] = tij;
113: distance[j][i] = distance[i][j];
114: /*}else {
115: distance[i][j] = tij;
116: distance[j][i] = distance[i][j];
117: }*/
118: }
119: }
120: distance[cityNum - 1][cityNum - 1] = 0;
121:
122:
123:
124: for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
125: Chromosome chromosome = new Chromosome(cityNum, distance);
126: chromosome.randomGeneration();
127: chromosomes[i] = chromosome;
128: chromosome.print();
129: }
130: }
131:
132: private void evolve(int g){
133: double[] selectionP = new double[N];//选择概率
134: double sum = 0.0;
135: double tmp = 0.0;
136:
137: for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
138: sum += chromosomes[i].getFitness();
139: if (chromosomes[i].getFitness() > bestFitness) {
140: bestFitness = chromosomes[i].getFitness();
141: bestLength = (int) (1.0/bestFitness);
142: for (int j = 0; j < cityNum; j++) {
143: bestTour[j] = chromosomes[i].getTour()[j];
144: }
145:
146: }
147: }
148: averageFitness[g] = sum/N;
149:
150: System.out.println("The average fitness in "+g+ " generation is: "+averageFitness[g]+ ", and the best fitness is: "+bestFitness);
151: for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
152: tmp += chromosomes[i].getFitness()/sum;
153: selectionP[i] = tmp;
154: }
155: Random random = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis());
156: for (int i = 0; i < N; i = i+2) {
157:
158: Chromosome[] children = new Chromosome[2];
159: //轮盘赌选择两个染色体
160: //System.out.println("---------start selection-----------");
161: //System.out.println();
162: for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++) {
163:
164: int selectedCity=0;
165: for (int k = 0; k < N - 1; k++) {
166: double p = random.nextDouble();
167: if (p > selectionP[k] && p <= selectionP[k+1]) {
168: selectedCity = k;
169: }
170: if (k==0 && random.nextDouble() <= selectionP[k]) {
171: selectedCity = 0;
172: }
173: }
174: try {
175: children[j] = (Chromosome) chromosomes[selectedCity].clone();
176:
177: //children[j].print();
178: //System.out.println();
179: } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
180: // TODO Auto-generated catch block
181: e.printStackTrace();
182: }
183: }
184:
185: //交叉操作(OX1)
186:
187: //System.out.println("----------Start crossover----------");
188: //System.out.println();
189: //Random random = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis());
190: if (random.nextDouble() < p_c_t) {
191: //System.out.println("crossover");
192: //random = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis());
193: //定义两个cut点
194: int cutPoint1 = -1;
195: int cutPoint2 = -1;
196: int r1 = random.nextInt(cityNum);
197: if (r1 > 0 && r1 < cityNum -1) {
198: cutPoint1 = r1;
199: //random = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis());
200: int r2 = random.nextInt(cityNum - r1);
201: if (r2 == 0) {
202: cutPoint2 = r1 + 1;
203: }else if(r2 > 0){
204: cutPoint2 = r1 + r2;
205: }
206:
207: }
208: if (cutPoint1 > 0 && cutPoint2 > 0) {
209: //System.out.println("Cut point1 is: "+cutPoint1 +", and cut point2 is: "+cutPoint2);
210: int [] tour1 = new int[cityNum];
211: int [] tour2 = new int[cityNum];
212: if (cutPoint2 == cityNum - 1) {
213: for (int j = 0; j < cityNum; j++) {
214: tour1[j] = children[0].getTour()[j];
215: tour2[j] = children[1].getTour()[j];
216: }
217: }else {
218:
219: //int n = 1;
220: for (int j = 0; j < cityNum; j++) {
221: if (j < cutPoint1) {
222: tour1[j] = children[0].getTour()[j];
223: tour2[j] = children[1].getTour()[j];
224: }else if (j >= cutPoint1 && j < cutPoint1+cityNum-cutPoint2-1) {
225: tour1[j] = children[0].getTour()[j+cutPoint2-cutPoint1+1];
226: tour2[j] = children[1].getTour()[j+cutPoint2-cutPoint1+1];
227: }else {
228: tour1[j] = children[0].getTour()[j-cityNum+cutPoint2+1];
229: tour2[j] = children[1].getTour()[j-cityNum+cutPoint2+1];
230: }
231:
232: }
233: }
234: /*System.out.println("The two tours are: ");
235: for (int j = 0; j < cityNum; j++) {
236: System.out.print(tour1[j] +"\t");
237: }
238: System.out.println();
239: for (int j = 0; j < cityNum; j++) {
240: System.out.print(tour2[j] +"\t");
241: }
242: System.out.println();*/
243:
244: for (int j = 0; j < cityNum; j++) {
245: if (j < cutPoint1 || j > cutPoint2) {
246:
247: children[0].getTour()[j] = -1;
248: children[1].getTour()[j] = -1;
249: }else {
250: int tmp1 = children[0].getTour()[j];
251: children[0].getTour()[j] = children[1].getTour()[j];
252: children[1].getTour()[j] = tmp1;
253: }
254: }
255: /*for (int j = 0; j < cityNum; j++) {
256: System.out.print(children[0].getTour()[j]+"\t");
257: }
258: System.out.println();
259: for (int j = 0; j < cityNum; j++) {
260: System.out.print(children[1].getTour()[j]+"\t");
261: }
262: System.out.println();*/
263: if (cutPoint2 == cityNum - 1) {
264: int position = 0;
265: for (int j = 0; j < cutPoint1; j++) {
266: for (int m = position; m < cityNum; m++) {
267: boolean flag = true;
268: for (int n = 0; n < cityNum; n++) {
269: if (tour1[m] == children[0].getTour()[n]) {
270: flag = false;
271: break;
272: }
273: }
274: if (flag) {
275:
276: children[0].getTour()[j] = tour1[m];
277: position = m + 1;
278: break;
279: }
280: }
281: }
282: position = 0;
283: for (int j = 0; j < cutPoint1; j++) {
284: for (int m = position; m < cityNum; m++) {
285: boolean flag = true;
286: for (int n = 0; n < cityNum; n++) {
287: if (tour2[m] == children[1].getTour()[n]) {
288: flag = false;
289: break;
290: }
291: }
292: if (flag) {
293: children[1].getTour()[j] = tour2[m];
294: position = m + 1;
295: break;
296: }
297: }
298: }
299:
300: }else {
301:
302: int position = 0;
303: for (int j = cutPoint2 + 1; j < cityNum; j++) {
304: for (int m = position; m < cityNum; m++) {
305: boolean flag = true;
306: for (int n = 0; n < cityNum; n++) {
307: if (tour1[m] == children[0].getTour()[n]) {
308: flag = false;
309: break;
310: }
311: }
312: if (flag) {
313: children[0].getTour()[j] = tour1[m];
314: position = m+1;
315: break;
316: }
317: }
318: }
319: for (int j = 0; j < cutPoint1; j++) {
320: for (int m = position; m < cityNum; m++) {
321: boolean flag = true;
322: for (int n = 0; n < cityNum; n++) {
323: if (tour1[m] == children[0].getTour()[n]) {
324: flag = false;
325: break;
326: }
327: }
328: if (flag) {
329: children[0].getTour()[j] = tour1[m];
330: position = m+1;
331: break;
332: }
333: }
334: }
335:
336:
337: position = 0;
338: for (int j = cutPoint2 + 1; j < cityNum; j++) {
339: for (int m = position; m < cityNum; m++) {
340: boolean flag = true;
341: for (int n = 0; n < cityNum; n++) {
342: if (tour2[m] == children[1].getTour()[n]) {
343: flag = false;
344: break;
345: }
346: }
347: if (flag) {
348: children[1].getTour()[j] = tour2[m];
349: position = m+1;
350: break;
351: }
352: }
353: }
354: for (int j = 0; j < cutPoint1; j++) {
355: for (int m = position; m < cityNum; m++) {
356: boolean flag = true;
357: for (int n = 0; n < cityNum; n++) {
358: if (tour2[m] == children[1].getTour()[n]) {
359: flag = false;
360: break;
361: }
362: }
363: if (flag) {
364: children[1].getTour()[j] = tour2[m];
365: position = m+1;
366: break;
367: }
368: }
369: }
370: }
371:
372:
373:
374: }
375: }
376: //children[0].print();
377: //children[1].print();
378:
379:
380: //变异操作(DM)
381:
382: //System.out.println("---------Start mutation------");
383: //System.out.println();
384: //random = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis());
385: if (random.nextDouble() < p_m_t) {
386: //System.out.println("mutation");
387: for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++) {
388: //random = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis());
389: //定义两个cut点
390: int cutPoint1 = -1;
391: int cutPoint2 = -1;
392: int r1 = random.nextInt(cityNum);
393: if (r1 > 0 && r1 < cityNum -1) {
394: cutPoint1 = r1;
395: //random = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis());
396: int r2 = random.nextInt(cityNum - r1);
397: if (r2 == 0) {
398: cutPoint2 = r1 + 1;
399: }else if(r2 > 0){
400: cutPoint2 = r1 + r2;
401: }
402:
403: }
404:
405:
406: if (cutPoint1 > 0 && cutPoint2 > 0) {
407: List<Integer> tour = new ArrayList<Integer>();
408: //System.out.println("Cut point1 is "+cutPoint1+", and cut point2 is "+cutPoint2);
409: if (cutPoint2 == cityNum - 1) {
410: for (int k = 0; k < cutPoint1; k++) {
411: tour.add(Integer.valueOf(children[j].getTour()[k]));
412: }
413: }else {
414: for (int k = 0; k < cityNum; k++) {
415: if (k < cutPoint1 || k > cutPoint2) {
416: tour.add(Integer.valueOf(children[j].getTour()[k]));
417: }
418: }
419: }
420: //random = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis());
421: int position = random.nextInt(tour.size());
422:
423: if (position == 0) {
424:
425: for (int k = cutPoint2; k >= cutPoint1; k--) {
426: tour.add(0, Integer.valueOf(children[j].getTour()[k]));
427: }
428:
429: }else if (position == tour.size()-1) {
430:
431: for (int k = cutPoint1; k <= cutPoint2; k++) {
432: tour.add(Integer.valueOf(children[j].getTour()[k]));
433: }
434:
435: } else {
436:
437: for (int k = cutPoint1; k <= cutPoint2; k++) {
438: tour.add(position, Integer.valueOf(children[j].getTour()[k]));
439: }
440:
441: }
442:
443:
444: for (int k = 0; k < cityNum; k++) {
445: children[j].getTour()[k] = tour.get(k).intValue();
446:
447: }
448: //System.out.println();
449: }
450:
451:
452: }
453: }
454:
455:
456: //children[0].print();
457: //children[1].print();
458:
459:
460: nextGeneration[i] = children[0];
461: nextGeneration[i+1] = children[1];
462:
463: }
464:
465: for (int k = 0; k < N; k++) {
466: try {
467: chromosomes[k] = (Chromosome) nextGeneration[k].clone();
468:
469: } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
470: // TODO Auto-generated catch block
471: e.printStackTrace();
472: }
473: }
474: /*System.out.println("Next generation is:");
475: for (int k = 0; k < N; k++) {
476: chromosomes[k].print();
477: }*/
478: }
479:
480: private void printOptimal(){
481: System.out.println("The best fitness is: " + bestFitness);
482: System.out.println("The best tour length is: " + bestLength);
483: System.out.println("The best tour is: ");
484: for (int i = 0; i < cityNum; i++) {
485: System.out.print(bestTour[i] + ",");
486: }
487: System.out.println();
488: }
489:
490: private void outputResults(){
491: String filename = "C://result.txt";
492: /*File file = new File(filename);
493: if (!file.exists()) {
494: try {
495: file.createNewFile();
496: } catch (IOException e) {
497: // TODO Auto-generated catch block
498: e.printStackTrace();
499: }
500: }
501: */
502: try {
503: @SuppressWarnings("resource")
504: FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(filename);
505: for (int i = 0; i < averageFitness.length; i++) {
506: String line = String.valueOf(averageFitness[i]) + "\r\n";
507:
508: outputStream.write(line.getBytes());
509:
510: }
511:
512: } catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
513: // TODO Auto-generated catch block
514: e.printStackTrace();
515: }catch (IOException e) {
516: // TODO Auto-generated catch block
517: e.printStackTrace();
518: }
519:
520:
521: }
522: public Chromosome[] getChromosomes() {
523: return chromosomes;
524: }
525: public void setChromosomes(Chromosome[] chromosomes) {
526: this.chromosomes = chromosomes;
527: }
528: public int getCityNum() {
529: return cityNum;
530: }
531: public void setCityNum(int cityNum) {
532: this.cityNum = cityNum;
533: }
534: public double getP_c_t() {
535: return p_c_t;
536: }
537: public void setP_c_t(double p_c_t) {
538: this.p_c_t = p_c_t;
539: }
540: public double getP_m_t() {
541: return p_m_t;
542: }
543: public void setP_m_t(double p_m_t) {
544: this.p_m_t = p_m_t;
545: }
546: public int getMAX_GEN() {
547: return MAX_GEN;
548: }
549: public void setMAX_GEN(int mAX_GEN) {
550: MAX_GEN = mAX_GEN;
551: }
552: public int getBestLength() {
553: return bestLength;
554: }
555: public void setBestLength(int bestLength) {
556: this.bestLength = bestLength;
557: }
558: public int[] getBestTour() {
559: return bestTour;
560: }
561: public void setBestTour(int[] bestTour) {
562: this.bestTour = bestTour;
563: }
564: public double[] getAverageFitness() {
565: return averageFitness;
566: }
567: public void setAverageFitness(double[] averageFitness) {
568: this.averageFitness = averageFitness;
569: }
570: public int getN() {
571: return N;
572: }
573:
574:
575: public void setN(int n) {
576: N = n;
577: }
578:
579:
580: public int[][] getDistance() {
581: return distance;
582: }
583:
584: public void setDistance(int[][] distance) {
585: this.distance = distance;
586: }
587:
588: /**
589: * @param args
590: * @throws IOException
591: */
592: public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
593: GA ga = new GA(2, 52, 1, 0.95, 0.75, "c://data.txt");
594: ga.solve();
595: }
596:
597:
598: }
599:
5. 总结
TSP问题是一类NP hard问题,用传统的方法非常难以获得最优解,特别是当问题规模很大时,最优解基本上不可能能得到。这时候,基于启发式的算法就可以发挥其作用,虽然它并不能保证可以获得最优解,但是可以以较快的速度得对近最优解。此文和前一篇类似,都是用启发式算法(蚁群算法和遗传算法)求解TSP问题,并且可以获得比较好的结果。但是程序的参数以及效率需要进一步的测试和研究,才能得到最佳的参数设置。
作者:Alex Yu
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/biaoyu/
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。










【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步