Mybatis笔记二
mybatis第二天 高级映射 查询缓存 和spring整合
课程复习:

mybatis是什么? mybatis是一人持久层框架,mybatis是一个不完全的ORM框架。sql语句需要程序员自己去编写,但是mybatis也有映射(输入参数映射、输出结果映射)。 mybatis入门门槛不高,学习成本低,让程序员把精力放在sql语句上,对sql语句优化非常方便,适用与需求变化较多项目,比如互联网项目。 mybatis框架执行过程: 1、配置mybatis的配置文件,SqlMapConfig.xml(名称不固定) 2、通过配置文件,加载mybatis运行环境,创建SqlSessionFactory会话工厂 SqlSessionFactory在实际使用时按单例方式。 3、通过SqlSessionFactory创建SqlSession SqlSession是一个面向用户接口(提供操作数据库方法),实现对象是线程不安全的,建议sqlSession应用场合在方法体内。 4、调用sqlSession的方法去操作数据。 如果需要提交事务,需要执行SqlSession的commit()方法。 5、释放资源,关闭SqlSession mybatis开发dao的方法: 1、原始dao 的方法 需要程序员编写dao接口和实现类 需要在dao实现类中注入一个SqlSessionFactory工厂。 2、mapper代理开发方法(建议使用) 只需要程序员编写mapper接口(就是dao接口) 程序员在编写mapper.xml(映射文件)和mapper.java需要遵循一个开发规范: 1、mapper.xml中namespace就是mapper.java的类全路径。 2、mapper.xml中statement的id和mapper.java中方法名一致。 3、mapper.xml中statement的parameterType指定输入参数的类型和mapper.java的方法输入 参数类型一致。 4、mapper.xml中statement的resultType指定输出结果的类型和mapper.java的方法返回值类型一致。 SqlMapConfig.xml配置文件:可以配置properties属性、别名、mapper加载。。。 输入映射: parameterType:指定输入参数类型可以简单类型、pojo、hashmap。。 对于综合查询,建议parameterType使用包装的pojo,有利于系统 扩展。 输出映射: resultType: 查询到的列名和resultType指定的pojo的属性名一致,才能映射成功。 reusltMap: 可以通过resultMap 完成一些高级映射。 如果查询到的列名和映射的pojo的属性名不一致时,通过resultMap设置列名和属性名之间的对应关系(映射关系)。可以完成映射。 高级映射: 将关联查询的列映射到一个pojo属性中。(一对一) 将关联查询的列映射到一个List<pojo>中。(一对多) 动态sql:(重点) if判断(掌握) where foreach sql片段(掌握)
课程安排:

对订单商品数据模型进行分析。
高级映射:(了解)
实现一对一查询、一对多、多对多查询。
延迟加载
查询缓存
一级缓存
二级缓存(了解mybatis二级缓存使用场景)
mybatis和spirng整合(掌握)
逆向工程(会用)
订单商品数据模型

1.1 数据模型分析思路
1、每张表记录的数据内容
分模块对每张表记录的内容进行熟悉,相当 于你学习系统 需求(功能)的过程。
2、每张表重要的字段设置
非空字段、外键字段
3、数据库级别表与表之间的关系
外键关系
4、表与表之间的业务关系
在分析表与表之间的业务关系时一定要建立 在某个业务意义基础上去分析。
1.2 数据模型分析
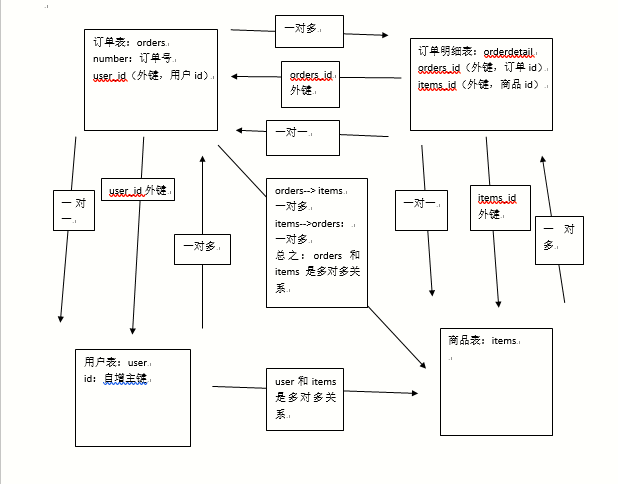
用户表user:
记录了购买商品的用户信息
订单表:orders
记录了用户所创建的订单(购买商品的订单)
订单明细表:orderdetail:
记录了订单的详细信息即购买商品的信息
商品表:items
记录了商品信息
表与表之间的业务关系:
在分析表与表之间的业务关系时需要建立 在某个业务意义基础上去分析。
先分析数据级别之间有关系的表之间的业务关系:
usre和orders:
user---->orders:一个用户可以创建多个订单,一对多
orders--->user:一个订单只由一个用户创建,一对一
orders和orderdetail:
orders---》orderdetail:一个订单可以包括 多个订单明细,因为一个订单可以购买多个商品,每个商品的购买信息在orderdetail记录,一对多关系
orderdetail--> orders:一个订单明细只能包括在一个订单中,一对一
orderdetail和itesm:
orderdetail---》itesms:一个订单明细只对应一个商品信息,一对一
items--> orderdetail:一个商品可以包括在多个订单明细 ,一对多
再分析数据库级别没有关系的表之间是否有业务关系:
orders和items:
orders和items之间可以通过orderdetail表建立 关系。
一对一查询
2.1 需求
查询订单信息,关联查询创建订单的用户信息
2.2 resultType
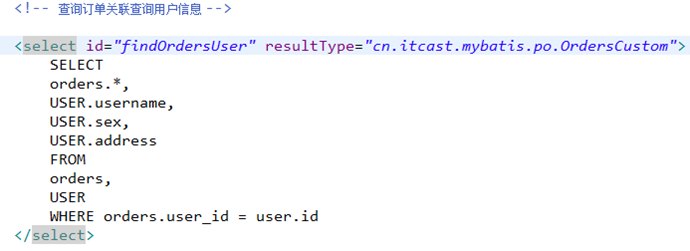
2.2.1 sql语句
确定查询的主表:订单表
确定查询的关联表:用户表
关联查询使用内链接?还是外链接?
由于orders表中有一个外键(user_id),通过外键关联查询用户表只能查询出一条记录,可以使用内链接。
SELECT
orders.*,
USER.username,
USER.sex,
USER.address
FROM
orders,
USER
WHERE orders.user_id = user.id
2.2.2 创建pojo
将上边sql查询的结果映射到pojo中,pojo中必须包括所有查询列名。
原始的Orders.java不能映射全部字段,需要新创建的pojo。
创建 一个pojo继承包括查询字段较多的po类。

2.2.3 mapper.xml
2.2.4 mapper.java
2.3 resultMap
2.3.1 sql语句
同resultType实现的sql
2.3.2 使用resultMap映射的思路
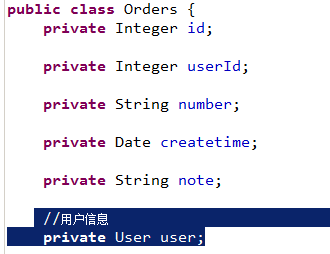
使用resultMap将查询结果中的订单信息映射到Orders对象中,在orders类中添加User属性,将关联查询出来的用户信息映射到orders对象中的user属性中。
2.3.3 需要Orders类中添加user属性
2.3.4 mapper.xml
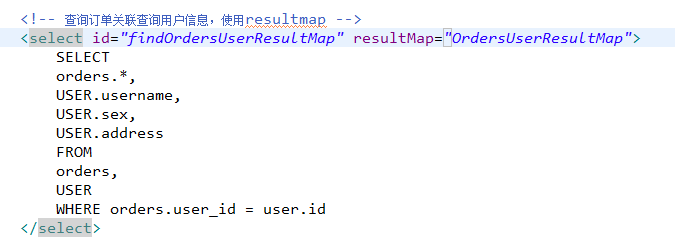
2.3.4.1 定义resultMap

<!-- 订单查询关联用户的resultMap 将整个查询的结果映射到cn.itcast.mybatis.po.Orders中 --> <resultMap type="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.Orders" id="OrdersUserResultMap"> <!-- 配置映射的订单信息 --> <!-- id:指定查询列中的唯 一标识,订单信息的中的唯 一标识,如果有多个列组成唯一标识,配置多个id column:订单信息的唯 一标识 列 property:订单信息的唯 一标识 列所映射到Orders中哪个属性 --> <id column="id" property="id"/> <result column="user_id" property="userId"/> <result column="number" property="number"/> <result column="createtime" property="createtime"/> <result column="note" property=note/> <!-- 配置映射的关联的用户信息 --> <!-- association:用于映射关联查询单个对象的信息 property:要将关联查询的用户信息映射到Orders中哪个属性 --> <association property="user" javaType="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.User"> <!-- id:关联查询用户的唯 一标识 column:指定唯 一标识用户信息的列 javaType:映射到user的哪个属性 --> <id column="user_id" property="id"/> <result column="username" property="username"/> <result column="sex" property="sex"/> <result column="address" property="address"/> </association> </resultMap>
2.3.4.2 statement定义
2.3.5 mapper.java
2.4 resultType和resultMap实现一对一查询小结
实现一对一查询:
resultType:使用resultType实现较为简单,如果pojo中没有包括查询出来的列名,需要增加列名对应的属性,即可完成映射。
如果没有查询结果的特殊要求建议使用resultType。
resultMap:需要单独定义resultMap,实现有点麻烦,如果对查询结果有特殊的要求,使用resultMap可以完成将关联查询映射pojo的属性中。
resultMap可以实现延迟加载,resultType无法实现延迟加载。
一对多查询
注意:
1.在使用resultmap配置多表连接查询的时候,注意唯一标示这这条记录的字段名不得重复,重复则使用别名
3.1 需求
查询订单及订单明细的信息。
3.2 sql语句
确定主查询表:订单表
确定关联查询表:订单明细表
在一对一查询基础上添加订单明细表关联即可。
SELECT
orders.*,
USER.username,
USER.sex,
USER.address,
orderdetail.id orderdetail_id,
orderdetail.items_id,
orderdetail.items_num,
orderdetail.orders_id
FROM
orders,
USER,
orderdetail
WHERE orders.user_id = user.id AND orderdetail.orders_id=orders.id
3.3 分析
使用resultType将上边的 查询结果映射到pojo中,订单信息的就是重复。
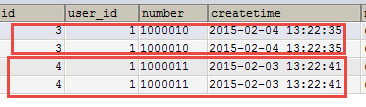
要求:
对orders映射不能出现重复记录。
在orders.java类中添加List<orderDetail> orderDetails属性。
最终会将订单信息映射到orders中,订单所对应的订单明细映射到orders中的orderDetails属性中。
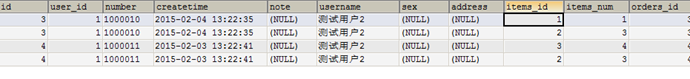
映射成的orders记录数为两条(orders信息不重复)
每个orders中的orderDetails属性存储了该 订单所对应的订单明细。
3.4 在orders中添加list订单明细属性

3.5 mapper.xml
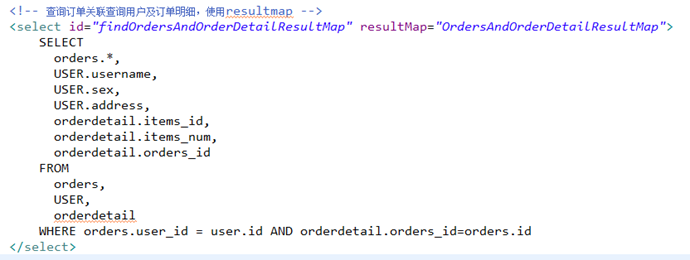
3.6 resultMap定义

<!-- 订单及订单明细的resultMap 使用extends继承,不用在中配置订单信息和用户信息的映射 --> <resultMap type="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.Orders" id="OrdersAndOrderDetailResultMap" extends="OrdersUserResultMap"> <!-- 订单信息 --> <!-- 用户信息 --> <!-- 使用extends继承,不用在中配置订单信息和用户信息的映射 --> <!-- 订单明细信息 一个订单关联查询出了多条明细,要使用collection进行映射 collection:对关联查询到多条记录映射到集合对象中 property:将关联查询到多条记录映射到cn.itcast.mybatis.po.Orders哪个属性 ofType:指定映射到list集合属性中pojo的类型 --> <collection property="orderdetails" ofType="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.Orderdetail"> <!-- id:订单明细唯 一标识 property:要将订单明细的唯 一标识 映射到cn.itcast.mybatis.po.Orderdetail的哪个属性 --> <id column="orderdetail_id" property="id"/> <result column="items_id" property="itemsId"/> <result column="items_num" property="itemsNum"/> <result column="orders_id" property="ordersId"/> </collection> </resultMap>
3.7 mapper.java

3.8 小结
mybatis使用resultMap的collection对关联查询的多条记录映射到一个list集合属性中。
使用resultType实现:
将订单明细映射到orders中的orderdetails中,需要自己处理,使用双重循环遍历,去掉重复记录,将订单明细放在orderdetails中。
多对多查询
4.1 需求
查询用户及用户购买商品信息。
4.2 sql语句
查询主表是:用户表
关联表:由于用户和商品没有直接关联,通过订单和订单明细进行关联,所以关联表:
orders、orderdetail、items
SELECT
orders.*,
USER.username,
USER.sex,
USER.address,
orderdetail.id orderdetail_id,
orderdetail.items_id,
orderdetail.items_num,
orderdetail.orders_id,
items.name items_name,
items.detail items_detail,
items.price items_price
FROM
orders,
USER,
orderdetail,
items
WHERE orders.user_id = user.id AND orderdetail.orders_id=orders.id AND orderdetail.items_id = items.id
4.3 映射思路
将用户信息映射到user中。
在user类中添加订单列表属性List<Orders> orderslist,将用户创建的订单映射到orderslist
在Orders中添加订单明细列表属性List<OrderDetail>orderdetials,将订单的明细映射到orderdetials
在OrderDetail中添加Items属性,将订单明细所对应的商品映射到Items
4.4 mapper.xml
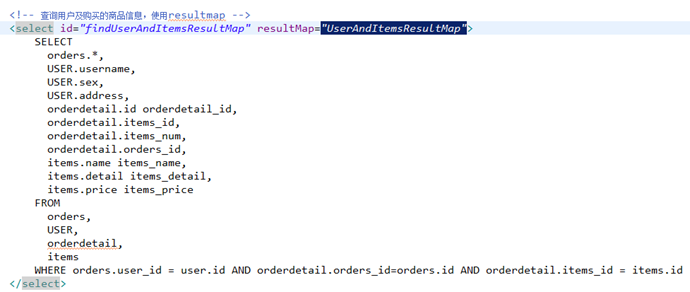
4.5 resultMap定义

<!-- 查询用户及购买的商品 --> <resultMap type="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.User" id="UserAndItemsResultMap"> <!-- 用户信息 --> <id column="user_id" property="id"/> <result column="username" property="username"/> <result column="sex" property="sex"/> <result column="address" property="address"/> <!-- 订单信息 一个用户对应多个订单,使用collection映射 --> <collection property="ordersList" ofType="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.Orders"> <id column="id" property="id"/> <result column="user_id" property="userId"/> <result column="number" property="number"/> <result column="createtime" property="createtime"/> <result column="note" property="note"/> <!-- 订单明细 一个订单包括 多个明细 --> <collection property="orderdetails" ofType="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.Orderdetail"> <id column="orderdetail_id" property="id"/> <result column="items_id" property="itemsId"/> <result column="items_num" property="itemsNum"/> <result column="orders_id" property="ordersId"/> <!-- 商品信息 一个订单明细对应一个商品 --> <association property="items" javaType="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.Items"> <id column="items_id" property="id"/> <result column="items_name" property="name"/> <result column="items_detail" property="detail"/> <result column="items_price" property="price"/> </association> </collection> </collection> </resultMap>
4.6 mapper.java

4.7 多对多查询总结
将查询用户购买的商品信息明细清单,(用户名、用户地址、购买商品名称、购买商品时间、购买商品数量)
针对上边的需求就使用resultType将查询到的记录映射到一个扩展的pojo中,很简单实现明细清单的功能。
一对多是多对多的特例,如下需求:
查询用户购买的商品信息,用户和商品的关系是多对多关系。
需求1:
查询字段:用户账号、用户名称、用户性别、商品名称、商品价格(最常见)
企业开发中常见明细列表,用户购买商品明细列表,
使用resultType将上边查询列映射到pojo输出。
需求2:
查询字段:用户账号、用户名称、购买商品数量、商品明细(鼠标移上显示明细)
使用resultMap将用户购买的商品明细列表映射到user对象中。
总结:
使用resultMap是针对那些对查询结果映射有特殊要求的功能,,比如特殊要求映射成list中包括 多个list。
resultMap总结
resultType:
作用:
将查询结果按照sql列名pojo属性名一致性映射到pojo中。
场合:
常见一些明细记录的展示,比如用户购买商品明细,将关联查询信息全部展示在页面时,此时可直接使用resultType将每一条记录映射到pojo中,在前端页面遍历list(list中是pojo)即可。
resultMap:
使用association和collection完成一对一和一对多高级映射(对结果有特殊的映射要求)。
association:
作用:
将关联查询信息映射到一个pojo对象中。
场合:
为了方便查询关联信息可以使用association将关联订单信息映射为用户对象的pojo属性中,比如:查询订单及关联用户信息。
使用resultType无法将查询结果映射到pojo对象的pojo属性中,根据对结果集查询遍历的需要选择使用resultType还是resultMap。
collection:
作用:
将关联查询信息映射到一个list集合中。
场合:
为了方便查询遍历关联信息可以使用collection将关联信息映射到list集合中,比如:查询用户权限范围模块及模块下的菜单,可使用collection将模块映射到模块list中,将菜单列表映射到模块对象的菜单list属性中,这样的作的目的也是方便对查询结果集进行遍历查询。
如果使用resultType无法将查询结果映射到list集合中。
延迟加载
6.1 什么是延迟加载
resultMap可以实现高级映射(使用association、collection实现一对一及一对多映射),association、collection具备延迟加载功能。
需求:
如果查询订单并且关联查询用户信息。如果先查询订单信息即可满足要求,当我们需要查询用户信息时再查询用户信息。把对用户信息的按需去查询就是延迟加载。
延迟加载:先从单表查询、需要时再从关联表去关联查询,大大提高 数据库性能,因为查询单表要比关联查询多张表速度要快。
6.2 使用association实现延迟加载
6.2.1 需求
查询订单并且关联查询用户信息
6.2.2 mapper.xml

需要定义两个mapper的方法对应的statement。
1、只查询订单信息
SELECT * FROM orders
在查询订单的statement中使用association去延迟加载(执行)下边的satatement(关联查询用户信息)
2、关联查询用户信息
通过上边查询到的订单信息中user_id去关联查询用户信息
使用UserMapper.xml中的findUserById

上边先去执行findOrdersUserLazyLoading,当需要去查询用户的时候再去执行findUserById,通过resultMap的定义将延迟加载执行配置起来。
6.2.3 延迟加载resultMap
使用association中的select指定延迟加载去执行的statement的id。

<!-- 延迟加载的resultMap --> <resultMap type="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.Orders" id="OrdersUserLazyLoadingResultMap"> <!--对订单信息进行映射配置 --> <id column="id" property="id"/> <result column="user_id" property="userId"/> <result column="number" property="number"/> <result column="createtime" property="createtime"/> <result column="note" property="note"/> <!-- 实现对用户信息进行延迟加载 select:指定延迟加载需要执行的statement的id(是根据user_id查询用户信息的statement) 要使用userMapper.xml中findUserById完成根据用户id(user_id)用户信息的查询,如果findUserById不在本mapper中需要前边加namespace column:订单信息中关联用户信息查询的列,是user_id 关联查询的sql理解为: SELECT orders.*, (SELECT username FROM USER WHERE orders.user_id = user.id)username, (SELECT sex FROM USER WHERE orders.user_id = user.id)sex FROM orders --> <association property="user" javaType="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.User" select="cn.itcast.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper.findUserById" column="user_id"> <!-- 实现对用户信息进行延迟加载 --> </association> </resultMap>
6.2.4 mapper.java
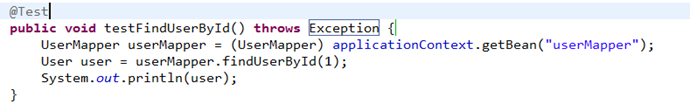
6.2.5 测试
6.2.5.1 测试思路:
1、执行上边mapper方法(findOrdersUserLazyLoading),内部去调用cn.itcast.mybatis.mapper.OrdersMapperCustom中的findOrdersUserLazyLoading只查询orders信息(单表)。
2、在程序中去遍历上一步骤查询出的List<Orders>,当我们调用Orders中的getUser方法时,开始进行延迟加载。
3、延迟加载,去调用UserMapper.xml中findUserbyId这个方法获取用户信息。
6.2.5.2 延迟加载配置
mybatis默认没有开启延迟加载,需要在SqlMapConfig.xml中setting配置。
在mybatis核心配置文件中配置:
lazyLoadingEnabled、aggressiveLazyLoading
|
设置项 |
描述 |
允许值 |
默认值 |
|
lazyLoadingEnabled |
全局性设置懒加载。如果设为‘false’,则所有相关联的都会被初始化加载。 |
true | false |
false |
|
aggressiveLazyLoading |
当设置为‘true’的时候,懒加载的对象可能被任何懒属性全部加载。否则,每个属性都按需加载。 |
true | false |
true |
在SqlMapConfig.xml中配置:

6.2.5.3 测试代码
6.2.6 延迟加载思考
不使用mybatis提供的association及collection中的延迟加载功能,如何实现延迟加载??
实现方法如下:
定义两个mapper方法:
1、查询订单列表
2、根据用户id查询用户信息
实现思路:
先去查询第一个mapper方法,获取订单信息列表
在程序中(service),按需去调用第二个mapper方法去查询用户信息。
总之:
使用延迟加载方法,先去查询简单的sql(最好单表,也可以关联查询),再去按需要加载关联查询的其它信息。
查询缓存
7.1 什么是查询缓存
mybatis提供查询缓存,用于减轻数据压力,提高数据库性能。
mybaits提供一级缓存,和二级缓存。
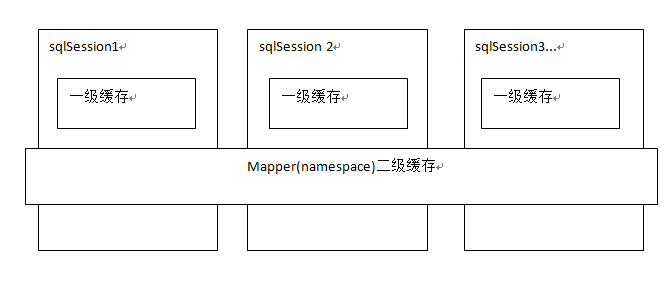
一级缓存是SqlSession级别的缓存。在操作数据库时需要构造 sqlSession对象,在对象中有一个数据结构(HashMap)用于存储缓存数据。不同的sqlSession之间的缓存数据区域(HashMap)是互相不影响的。
二级缓存是mapper级别的缓存,多个SqlSession去操作同一个Mapper的sql语句,多个SqlSession可以共用二级缓存,二级缓存是跨SqlSession的。
为什么要用缓存?
如果缓存中有数据就不用从数据库中获取,大大提高系统性能。
7.2 一级缓存
7.2.1 一级缓存工作原理
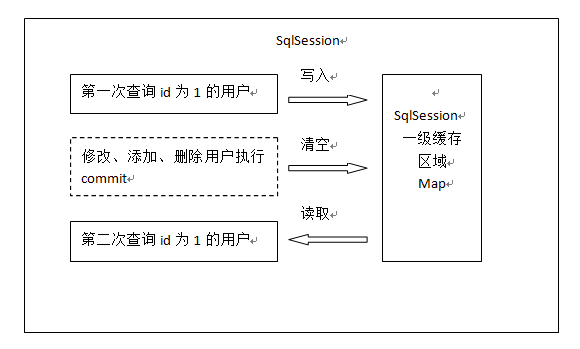
第一次发起查询用户id为1的用户信息,先去找缓存中是否有id为1的用户信息,如果没有,从数据库查询用户信息。
得到用户信息,将用户信息存储到一级缓存中。
如果sqlSession去执行commit操作(执行插入、更新、删除),清空SqlSession中的一级缓存,这样做的目的为了让缓存中存储的是最新的信息,避免脏读。
第二次发起查询用户id为1的用户信息,先去找缓存中是否有id为1的用户信息,缓存中有,直接从缓存中获取用户信息。
7.2.2 一级缓存测试
mybatis默认支持一级缓存,不需要在配置文件去配置。
按照上边一级缓存原理步骤去测试。

@Test public void testCache1() throws Exception{ SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();//创建代理对象 UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class); //下边查询使用一个SqlSession //第一次发起请求,查询id为1的用户 User user1 = userMapper.findUserById(1); System.out.println(user1); // 如果sqlSession去执行commit操作(执行插入、更新、删除),清空SqlSession中的一级缓存,这样做的目的为了让缓存中存储的是最新的信息,避免脏读。 //更新user1的信息 user1.setUsername("测试用户22"); userMapper.updateUser(user1); //执行commit操作去清空缓存 sqlSession.commit(); //第二次发起请求,查询id为1的用户 User user2 = userMapper.findUserById(1); System.out.println(user2); sqlSession.close(); }
7.2.3 一级缓存应用
正式开发,是将mybatis和spring进行整合开发,事务控制在service中。
一个service方法中包括 很多mapper方法调用。
service{ //开始执行时,开启事务,创建SqlSession对象 //第一次调用mapper的方法findUserById(1) //第二次调用mapper的方法findUserById(1),从一级缓存中取数据 //方法结束,sqlSession关闭 }
如果是执行两次service调用查询相同 的用户信息,不走一级缓存,因为session方法结束,sqlSession就关闭,一级缓存就清空。
7.3 二级缓存
7.3.1 原理
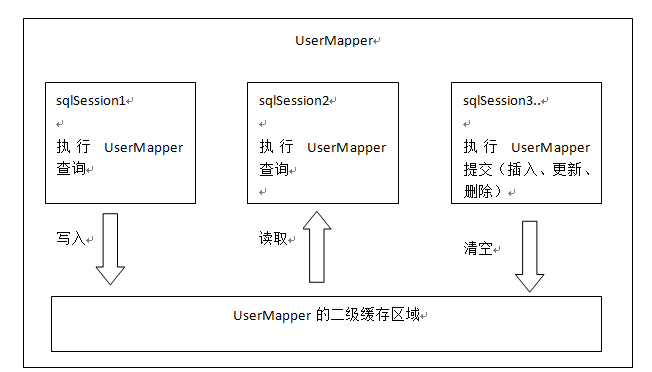
首先开启mybatis的二级缓存。
sqlSession1去查询用户id为1的用户信息,查询到用户信息会将查询数据存储到二级缓存中。
如果SqlSession3去执行相同 mapper下sql,执行commit提交,清空该 mapper下的二级缓存区域的数据。
sqlSession2去查询用户id为1的用户信息,去缓存中找是否存在数据,如果存在直接从缓存中取出数据。
二级缓存与一级缓存区别,二级缓存的范围更大,多个sqlSession可以共享一个UserMapper的二级缓存区域。
UserMapper有一个二级缓存区域(按namespace分) ,其它mapper也有自己的二级缓存区域(按namespace分)。
每一个namespace的mapper都有一个二缓存区域,两个mapper的namespace如果相同,这两个mapper执行sql查询到数据将存在相同 的二级缓存区域中。
7.3.2 开启二级缓存
mybaits的二级缓存是mapper范围级别,除了在SqlMapConfig.xml设置二级缓存的总开关,还要在具体的mapper.xml中开启二级缓存。
在核心配置文件SqlMapConfig.xml中加入
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
|
描述 |
允许值 |
默认值 |
|
|
cacheEnabled |
对在此配置文件下的所有cache 进行全局性开/关设置。 |
true false |
true |
在UserMapper.xml中开启二缓存,UserMapper.xml下的sql执行完成会存储到它的缓存区域(HashMap)。
7.3.3 调用pojo类实现序列化接口
为了将缓存数据取出执行反序列化操作,因为二级缓存数据存储介质多种多样,不一样在内存。
7.3.4 测试方法

// 二级缓存测试 @Test public void testCache2() throws Exception { SqlSession sqlSession1 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); SqlSession sqlSession2 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); SqlSession sqlSession3 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); // 创建代理对象 UserMapper userMapper1 = sqlSession1.getMapper(UserMapper.class); // 第一次发起请求,查询id为1的用户 User user1 = userMapper1.findUserById(1); System.out.println(user1); //这里执行关闭操作,将sqlsession中的数据写到二级缓存区域 sqlSession1.close(); //使用sqlSession3执行commit()操作 UserMapper userMapper3 = sqlSession3.getMapper(UserMapper.class); User user = userMapper3.findUserById(1); user.setUsername("张明明"); userMapper3.updateUser(user); //执行提交,清空UserMapper下边的二级缓存 sqlSession3.commit(); sqlSession3.close(); UserMapper userMapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(UserMapper.class); // 第二次发起请求,查询id为1的用户 User user2 = userMapper2.findUserById(1); System.out.println(user2); sqlSession2.close(); }
7.3.5 useCache配置
在statement中设置useCache=false可以禁用当前select语句的二级缓存,即每次查询都会发出sql去查询,默认情况是true,即该sql使用二级缓存。
<select id="findOrderListResultMap" resultMap="ordersUserMap" useCache="false">
总结:针对每次查询都需要最新的数据sql,要设置成useCache=false,禁用二级缓存。
7.3.6 刷新缓存(就是清空缓存)
在mapper的同一个namespace中,如果有其它insert、update、delete操作数据后需要刷新缓存,如果不执行刷新缓存会出现脏读。
设置statement配置中的flushCache="true" 属性,默认情况下为true即刷新缓存,如果改成false则不会刷新。使用缓存时如果手动修改数据库表中的查询数据会出现脏读。
如下:
<insert id="insertUser" parameterType="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.User" flushCache="true">
总结:一般下执行完commit操作都需要刷新缓存,flushCache=true表示刷新缓存,这样可以避免数据库脏读。
7.4 mybatis整合ehcache
ehcache是一个分布式缓存框架。
7.4.1 分布缓存
我们系统为了提高系统并发,性能、一般对系统进行分布式部署(集群部署方式)

不使用分布缓存,缓存的数据在各各服务单独存储,不方便系统 开发。所以要使用分布式缓存对缓存数据进行集中管理。
mybatis无法实现分布式缓存,需要和其它分布式缓存框架进行整合。
7.4.2 整合方法(掌握)
mybatis提供了一个cache接口,如果要实现自己的缓存逻辑,实现cache接口开发即可。
mybatis和ehcache整合,mybatis和ehcache整合包中提供了一个cache接口的实现类。

mybatis默认实现cache类是:

7.4.3 加入ehcache包
7.4.4 整合ehcache
配置mapper中cache中的type为ehcache对cache接口的实现类型。

7.4.5 加入ehcache的配置文件
在classpath下配置ehcache.xml

7.5 二级应用场景
对于访问多的查询请求且用户对查询结果实时性要求不高,此时可采用mybatis二级缓存技术降低数据库访问量,提高访问速度,业务场景比如:耗时较高的统计分析sql、电话账单查询sql等。
实现方法如下:通过设置刷新间隔时间,由mybatis每隔一段时间自动清空缓存,根据数据变化频率设置缓存刷新间隔flushInterval,比如设置为30分钟、60分钟、24小时等,根据需求而定。
7.6 二级缓存局限性
mybatis二级缓存对细粒度的数据级别的缓存实现不好,比如如下需求:对商品信息进行缓存,由于商品信息查询访问量大,但是要求用户每次都能查询最新的商品信息,此时如果使用mybatis的二级缓存就无法实现当一个商品变化时只刷新该商品的缓存信息而不刷新其它商品的信息,因为mybaits的二级缓存区域以mapper为单位划分,当一个商品信息变化会将所有商品信息的缓存数据全部清空。解决此类问题需要在业务层根据需求对数据有针对性缓存。
spring和mybatis整合
8.1 整合思路
需要spring通过单例方式管理SqlSessionFactory。
spring和mybatis整合生成代理对象,使用SqlSessionFactory创建SqlSession。(spring和mybatis整合自动完成)
持久层的mapper都需要由spring进行管理。
8.2 整合环境
创建一个新的java工程(接近实际开发的工程结构)
jar包:
mybatis3.2.7的jar包
spring3.2.0的jar包
mybatis和spring的整合包:早期ibatis和spring整合是由spring官方提供,mybatis和spring整合由mybatis提供。

全部jar包

8.3 sqlSessionFactory
在applicationContext.xml配置sqlSessionFactory和数据源
sqlSessionFactory在mybatis和spring的整合包下。

<!-- 加载配置文件 --> <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties" /> <!-- 数据源,使用dbcp --> <bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource" destroy-method="close"> <property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}" /> <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" /> <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" /> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" /> <property name="maxActive" value="10" /> <property name="maxIdle" value="5" /> </bean> <!-- sqlSessinFactory --> <bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean"> <!-- 加载mybatis的配置文件 --> <property name="configLocation" value="mybatis/SqlMapConfig.xml" /> <!-- 数据源 --> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" /> </bean>
8.4 原始dao开发(和spring整合后)
8.4.1 User.xml

在SqlMapconfig.xml中加载User.xml

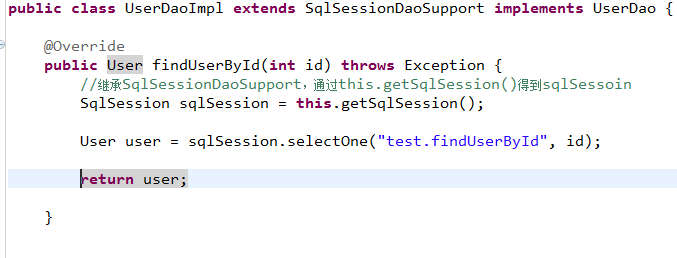
8.4.2 dao(实现类继承SqlSessionDaoSupport)
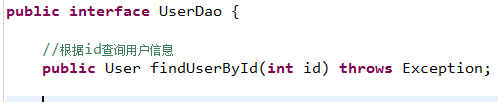
dao接口实现类需要注入SqlSessoinFactory,通过spring进行注入。
这里spring声明配置方式,配置dao的bean:
让UserDaoImpl实现类继承SqlSessionDaoSupport
8.4.3 配置dao
在applicationContext.xml中配置dao。

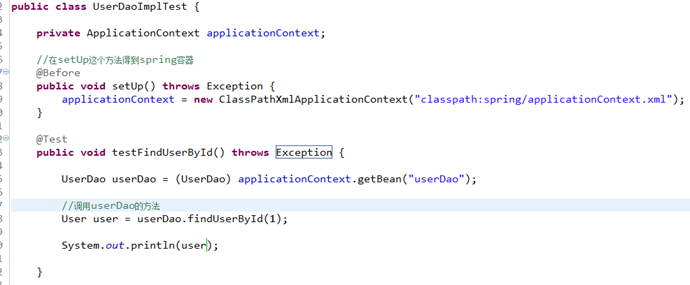
8.4.4 测试程序
8.5 mapper代理开发
8.5.1 mapper.xml和mapper.java
8.5.2 通过MapperFactoryBean创建代理对象

此方法问题:
需要针对每个mapper进行配置,麻烦。
8.5.3 通过MapperScannerConfigurer进行mapper扫描(建议使用)

8.5.4 测试代码
逆向工程
9.1 什么是逆向工程
mybaits需要程序员自己编写sql语句,mybatis官方提供逆向工程 可以针对单表自动生成mybatis执行所需要的代码(mapper.java,mapper.xml、po..)
企业实际开发中,常用的逆向工程方式:
由于数据库的表生成java代码。
9.2 下载逆向工程
9.3 使用方法(会用)
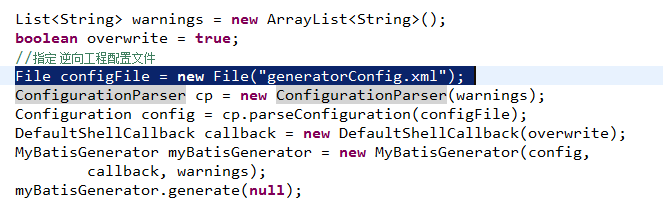
9.3.1 运行逆向工程

建议使用java程序方式,不依赖开发工具。
9.3.2 生成代码配置文件

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE generatorConfiguration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD MyBatis Generator Configuration 1.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-generator-config_1_0.dtd"> <generatorConfiguration> <context id="testTables" targetRuntime="MyBatis3"> <commentGenerator> <!-- 是否去除自动生成的注释 true:是 : false:否 --> <property name="suppressAllComments" value="true" /> </commentGenerator> <!--数据库连接的信息:驱动类、连接地址、用户名、密码 --> <jdbcConnection driverClass="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" connectionURL="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis" userId="root" password="mysql"> </jdbcConnection> <!-- <jdbcConnection driverClass="oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver" connectionURL="jdbc:oracle:thin:@127.0.0.1:1521:yycg" userId="yycg" password="yycg"> </jdbcConnection> --> <!-- 默认false,把JDBC DECIMAL 和 NUMERIC 类型解析为 Integer,为 true时把JDBC DECIMAL 和 NUMERIC 类型解析为java.math.BigDecimal --> <javaTypeResolver> <property name="forceBigDecimals" value="false" /> </javaTypeResolver> <!-- targetProject:生成PO类的位置 --> <javaModelGenerator targetPackage="cn.itcast.ssm.po" targetProject=".\src"> <!-- enableSubPackages:是否让schema作为包的后缀 --> <property name="enableSubPackages" value="false" /> <!-- 从数据库返回的值被清理前后的空格 --> <property name="trimStrings" value="true" /> </javaModelGenerator> <!-- targetProject:mapper映射文件生成的位置 --> <sqlMapGenerator targetPackage="cn.itcast.ssm.mapper" targetProject=".\src"> <!-- enableSubPackages:是否让schema作为包的后缀 --> <property name="enableSubPackages" value="false" /> </sqlMapGenerator> <!-- targetPackage:mapper接口生成的位置 --> <javaClientGenerator type="XMLMAPPER" targetPackage="cn.itcast.ssm.mapper" targetProject=".\src"> <!-- enableSubPackages:是否让schema作为包的后缀 --> <property name="enableSubPackages" value="false" /> </javaClientGenerator> <!-- 指定数据库表 --> <table tableName="items"></table> <table tableName="orders"></table> <table tableName="orderdetail"></table> <table tableName="user"></table> </context> </generatorConfiguration>
9.3.3 执行生成程序
生成后的代码:
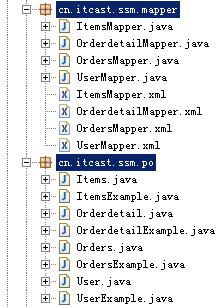
9.3.4 使用生成的代码
需要将生成工程中所生成的代码拷贝到自己的工程中。
测试ItemsMapper中的方法

//自定义条件查询 @Test public void testSelectByExample() { ItemsExample itemsExample = new ItemsExample(); //通过criteria构造查询条件 ItemsExample.Criteria criteria = itemsExample.createCriteria(); criteria.andNameEqualTo("笔记本3"); //可能返回多条记录 List<Items> list = itemsMapper.selectByExample(itemsExample); System.out.println(list); } //根据主键查询 @Test public void testSelectByPrimaryKey() { Items items = itemsMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(1); System.out.println(items); } //插入 @Test public void testInsert() { //构造 items对象 Items items = new Items(); items.setName("手机"); items.setPrice(999f); itemsMapper.insert(items); } //更新数据 @Test public void testUpdateByPrimaryKey() { //对所有字段进行更新,需要先查询出来再更新 Items items = itemsMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(1); items.setName("水杯"); itemsMapper.updateByPrimaryKey(items); //如果传入字段不空为才更新,在批量更新中使用此方法,不需要先查询再更新 //itemsMapper.updateByPrimaryKeySelective(record); }
逆向生成的映射文件用法:
案例:

package com.mikey.bean; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class EmployeeExample { protected String orderByClause;//排序 protected boolean distinct;//消除重复 protected List<Criteria> oredCriteria;//or条件多个Criteria进行循环操作 public EmployeeExample() { oredCriteria = new ArrayList<Criteria>(); }//主类构造方法 public void setOrderByClause(String orderByClause) { this.orderByClause = orderByClause; }//设置排序条件 public String getOrderByClause() { return orderByClause; }//获取排序条件 public void setDistinct(boolean distinct) { this.distinct = distinct; }//设置是否消除重复 public boolean isDistinct() { return distinct; }//获取是否消除重复 public List<Criteria> getOredCriteria() { return oredCriteria; }//获取所有or规则 public void or(Criteria criteria) { oredCriteria.add(criteria); }//添加criteria操作 public Criteria or() { Criteria criteria = createCriteriaInternal(); oredCriteria.add(criteria); return criteria; } public Criteria createCriteria() { Criteria criteria = createCriteriaInternal(); if (oredCriteria.size() == 0) { oredCriteria.add(criteria); } return criteria; }//创建criteria protected Criteria createCriteriaInternal() { Criteria criteria = new Criteria(); return criteria; } public void clear() { oredCriteria.clear(); orderByClause = null; distinct = false; }//清除本criteria规则 protected abstract static class GeneratedCriteria { protected List<Criterion> criteria;//and连接条件 protected GeneratedCriteria() { super(); criteria = new ArrayList<Criterion>(); } public boolean isValid() { return criteria.size() > 0; } public List<Criterion> getAllCriteria() { return criteria; } public List<Criterion> getCriteria() { return criteria; } protected void addCriterion(String condition) { if (condition == null) { throw new RuntimeException("Value for condition cannot be null"); } criteria.add(new Criterion(condition)); } protected void addCriterion(String condition, Object value, String property) { if (value == null) { throw new RuntimeException("Value for " + property + " cannot be null"); } criteria.add(new Criterion(condition, value)); } protected void addCriterion(String condition, Object value1, Object value2, String property) { if (value1 == null || value2 == null) { throw new RuntimeException("Between values for " + property + " cannot be null"); } criteria.add(new Criterion(condition, value1, value2)); } public Criteria andEmpIdIsNull() { addCriterion("emp_id is null"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andEmpIdIsNotNull() { addCriterion("emp_id is not null"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andEmpIdEqualTo(Integer value) { addCriterion("emp_id =", value, "empId"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andEmpIdNotEqualTo(Integer value) { addCriterion("emp_id <>", value, "empId"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andEmpIdGreaterThan(Integer value) { addCriterion("emp_id >", value, "empId"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andEmpIdGreaterThanOrEqualTo(Integer value) { addCriterion("emp_id >=", value, "empId"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andEmpIdLessThan(Integer value) { addCriterion("emp_id <", value, "empId"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andEmpIdLessThanOrEqualTo(Integer value) { addCriterion("emp_id <=", value, "empId"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andEmpIdIn(List<Integer> values) { addCriterion("emp_id in", values, "empId"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andEmpIdNotIn(List<Integer> values) { addCriterion("emp_id not in", values, "empId"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andEmpIdBetween(Integer value1, Integer value2) { addCriterion("emp_id between", value1, value2, "empId"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andEmpIdNotBetween(Integer value1, Integer value2) { addCriterion("emp_id not between", value1, value2, "empId"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andEmpNameIsNull() { addCriterion("emp_name is null"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andEmpNameIsNotNull() { addCriterion("emp_name is not null"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andEmpNameEqualTo(String value) { addCriterion("emp_name =", value, "empName"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andEmpNameNotEqualTo(String value) { addCriterion("emp_name <>", value, "empName"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andEmpNameGreaterThan(String value) { addCriterion("emp_name >", value, "empName"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andEmpNameGreaterThanOrEqualTo(String value) { addCriterion("emp_name >=", value, "empName"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andEmpNameLessThan(String value) { addCriterion("emp_name <", value, "empName"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andEmpNameLessThanOrEqualTo(String value) { addCriterion("emp_name <=", value, "empName"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andEmpNameLike(String value) { addCriterion("emp_name like", value, "empName"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andEmpNameNotLike(String value) { addCriterion("emp_name not like", value, "empName"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andEmpNameIn(List<String> values) { addCriterion("emp_name in", values, "empName"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andEmpNameNotIn(List<String> values) { addCriterion("emp_name not in", values, "empName"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andEmpNameBetween(String value1, String value2) { addCriterion("emp_name between", value1, value2, "empName"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andEmpNameNotBetween(String value1, String value2) { addCriterion("emp_name not between", value1, value2, "empName"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andGenderIsNull() { addCriterion("gender is null"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andGenderIsNotNull() { addCriterion("gender is not null"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andGenderEqualTo(String value) { addCriterion("gender =", value, "gender"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andGenderNotEqualTo(String value) { addCriterion("gender <>", value, "gender"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andGenderGreaterThan(String value) { addCriterion("gender >", value, "gender"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andGenderGreaterThanOrEqualTo(String value) { addCriterion("gender >=", value, "gender"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andGenderLessThan(String value) { addCriterion("gender <", value, "gender"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andGenderLessThanOrEqualTo(String value) { addCriterion("gender <=", value, "gender"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andGenderLike(String value) { addCriterion("gender like", value, "gender"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andGenderNotLike(String value) { addCriterion("gender not like", value, "gender"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andGenderIn(List<String> values) { addCriterion("gender in", values, "gender"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andGenderNotIn(List<String> values) { addCriterion("gender not in", values, "gender"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andGenderBetween(String value1, String value2) { addCriterion("gender between", value1, value2, "gender"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andGenderNotBetween(String value1, String value2) { addCriterion("gender not between", value1, value2, "gender"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andEmailIsNull() { addCriterion("email is null"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andEmailIsNotNull() { addCriterion("email is not null"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andEmailEqualTo(String value) { addCriterion("email =", value, "email"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andEmailNotEqualTo(String value) { addCriterion("email <>", value, "email"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andEmailGreaterThan(String value) { addCriterion("email >", value, "email"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andEmailGreaterThanOrEqualTo(String value) { addCriterion("email >=", value, "email"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andEmailLessThan(String value) { addCriterion("email <", value, "email"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andEmailLessThanOrEqualTo(String value) { addCriterion("email <=", value, "email"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andEmailLike(String value) { addCriterion("email like", value, "email"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andEmailNotLike(String value) { addCriterion("email not like", value, "email"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andEmailIn(List<String> values) { addCriterion("email in", values, "email"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andEmailNotIn(List<String> values) { addCriterion("email not in", values, "email"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andEmailBetween(String value1, String value2) { addCriterion("email between", value1, value2, "email"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andEmailNotBetween(String value1, String value2) { addCriterion("email not between", value1, value2, "email"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andDIdIsNull() { addCriterion("d_id is null"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andDIdIsNotNull() { addCriterion("d_id is not null"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andDIdEqualTo(Integer value) { addCriterion("d_id =", value, "dId"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andDIdNotEqualTo(Integer value) { addCriterion("d_id <>", value, "dId"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andDIdGreaterThan(Integer value) { addCriterion("d_id >", value, "dId"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andDIdGreaterThanOrEqualTo(Integer value) { addCriterion("d_id >=", value, "dId"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andDIdLessThan(Integer value) { addCriterion("d_id <", value, "dId"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andDIdLessThanOrEqualTo(Integer value) { addCriterion("d_id <=", value, "dId"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andDIdIn(List<Integer> values) { addCriterion("d_id in", values, "dId"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andDIdNotIn(List<Integer> values) { addCriterion("d_id not in", values, "dId"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andDIdBetween(Integer value1, Integer value2) { addCriterion("d_id between", value1, value2, "dId"); return (Criteria) this; } public Criteria andDIdNotBetween(Integer value1, Integer value2) { addCriterion("d_id not between", value1, value2, "dId"); return (Criteria) this; } } /** * oredCriteria * Example内有一个成员叫oredCriteria,是Criteria的集合,就想其名字所预示的一样, * 这个集合中的Criteria是由OR连接的,是逻辑或关系。oredCriteria就是ORed Criteria */ public static class Criteria extends GeneratedCriteria { protected Criteria() { super(); } } /** * Criteria包含一个Criterion的集合,每一个Criteria对象内包含的Criterion之间是由AND连接的,是逻辑与的关系。 */ public static class Criterion { private String condition; private Object value; private Object secondValue; private boolean noValue; private boolean singleValue; private boolean betweenValue; private boolean listValue; private String typeHandler; public String getCondition() { return condition; } public Object getValue() { return value; } public Object getSecondValue() { return secondValue; } public boolean isNoValue() { return noValue; } public boolean isSingleValue() { return singleValue; } public boolean isBetweenValue() { return betweenValue; } public boolean isListValue() { return listValue; } public String getTypeHandler() { return typeHandler; } protected Criterion(String condition) { super(); this.condition = condition; this.typeHandler = null; this.noValue = true; } protected Criterion(String condition, Object value, String typeHandler) { super(); this.condition = condition; this.value = value; this.typeHandler = typeHandler; if (value instanceof List<?>) { this.listValue = true; } else { this.singleValue = true; } } protected Criterion(String condition, Object value) { this(condition, value, null); } protected Criterion(String condition, Object value, Object secondValue, String typeHandler) { super(); this.condition = condition; this.value = value; this.secondValue = secondValue; this.typeHandler = typeHandler; this.betweenValue = true; } protected Criterion(String condition, Object value, Object secondValue) { this(condition, value, secondValue, null); } } }

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.mikey.mapper.EmployeeMapper">
<resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="com.mikey.bean.Employee">
<id column="emp_id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="empId" />
<result column="emp_name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="empName" />
<result column="gender" jdbcType="CHAR" property="gender" />
<result column="email" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="email" />
<result column="d_id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="dId" />
</resultMap>
<sql id="Example_Where_Clause">
<where>
<foreach collection="oredCriteria" item="criteria" separator="or">
<if test="criteria.valid">
<trim prefix="(" prefixOverrides="and" suffix=")">
<foreach collection="criteria.criteria" item="criterion">
<choose>
<when test="criterion.noValue">
and ${criterion.condition}
</when>
<when test="criterion.singleValue">
and ${criterion.condition} #{criterion.value}
</when>
<when test="criterion.betweenValue">
and ${criterion.condition} #{criterion.value} and #{criterion.secondValue}
</when>
<when test="criterion.listValue">
and ${criterion.condition}
<foreach close=")" collection="criterion.value" item="listItem" open="(" separator=",">
#{listItem}
</foreach>
</when>
</choose>
</foreach>
</trim>
</if>
</foreach>
</where>
</sql>
<sql id="Update_By_Example_Where_Clause">
<where>
<foreach collection="example.oredCriteria" item="criteria" separator="or">
<if test="criteria.valid">
<trim prefix="(" prefixOverrides="and" suffix=")">
<foreach collection="criteria.criteria" item="criterion">
<choose>
<when test="criterion.noValue">
and ${criterion.condition}
</when>
<when test="criterion.singleValue">
and ${criterion.condition} #{criterion.value}
</when>
<when test="criterion.betweenValue">
and ${criterion.condition} #{criterion.value} and #{criterion.secondValue}
</when>
<when test="criterion.listValue">
and ${criterion.condition}
<foreach close=")" collection="criterion.value" item="listItem" open="(" separator=",">
#{listItem}
</foreach>
</when>
</choose>
</foreach>
</trim>
</if>
</foreach>
</where>
</sql>
<sql id="Base_Column_List">
emp_id, emp_name, gender, email, d_id
</sql>
<select id="selectByExample" parameterType="com.mikey.bean.EmployeeExample" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
select
<if test="distinct">
distinct
</if>
<include refid="Base_Column_List" />
from tbl_emp
<if test="_parameter != null">
<include refid="Example_Where_Clause" />
</if>
<if test="orderByClause != null">
order by ${orderByClause}
</if>
</select>
<select id="selectByPrimaryKey" parameterType="java.lang.Integer" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
select
<include refid="Base_Column_List" />
from tbl_emp
where emp_id = #{empId,jdbcType=INTEGER}
</select>
<delete id="deleteByPrimaryKey" parameterType="java.lang.Integer">
delete from tbl_emp
where emp_id = #{empId,jdbcType=INTEGER}
</delete>
<delete id="deleteByExample" parameterType="com.mikey.bean.EmployeeExample">
delete from tbl_emp
<if test="_parameter != null">
<include refid="Example_Where_Clause" />
</if>
</delete>
<insert id="insert" parameterType="com.mikey.bean.Employee">
insert into tbl_emp (emp_id, emp_name, gender,
email, d_id)
values (#{empId,jdbcType=INTEGER}, #{empName,jdbcType=VARCHAR}, #{gender,jdbcType=CHAR},
#{email,jdbcType=VARCHAR}, #{dId,jdbcType=INTEGER})
</insert>
<insert id="insertSelective" parameterType="com.mikey.bean.Employee">
insert into tbl_emp
<trim prefix="(" suffix=")" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="empId != null">
emp_id,
</if>
<if test="empName != null">
emp_name,
</if>
<if test="gender != null">
gender,
</if>
<if test="email != null">
email,
</if>
<if test="dId != null">
d_id,
</if>
</trim>
<trim prefix="values (" suffix=")" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="empId != null">
#{empId,jdbcType=INTEGER},
</if>
<if test="empName != null">
#{empName,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="gender != null">
#{gender,jdbcType=CHAR},
</if>
<if test="email != null">
#{email,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="dId != null">
#{dId,jdbcType=INTEGER},
</if>
</trim>
</insert>
<select id="countByExample" parameterType="com.mikey.bean.EmployeeExample" resultType="java.lang.Long">
select count(*) from tbl_emp
<if test="_parameter != null">
<include refid="Example_Where_Clause" />
</if>
</select>
<update id="updateByExampleSelective" parameterType="map">
update tbl_emp
<set>
<if test="record.empId != null">
emp_id = #{record.empId,jdbcType=INTEGER},
</if>
<if test="record.empName != null">
emp_name = #{record.empName,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="record.gender != null">
gender = #{record.gender,jdbcType=CHAR},
</if>
<if test="record.email != null">
email = #{record.email,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="record.dId != null">
d_id = #{record.dId,jdbcType=INTEGER},
</if>
</set>
<if test="_parameter != null">
<include refid="Update_By_Example_Where_Clause" />
</if>
</update>
<update id="updateByExample" parameterType="map">
update tbl_emp
set emp_id = #{record.empId,jdbcType=INTEGER},
emp_name = #{record.empName,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
gender = #{record.gender,jdbcType=CHAR},
email = #{record.email,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
d_id = #{record.dId,jdbcType=INTEGER}
<if test="_parameter != null">
<include refid="Update_By_Example_Where_Clause" />
</if>
</update>
<update id="updateByPrimaryKeySelective" parameterType="com.mikey.bean.Employee">
update tbl_emp
<set>
<if test="empName != null">
emp_name = #{empName,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="gender != null">
gender = #{gender,jdbcType=CHAR},
</if>
<if test="email != null">
email = #{email,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="dId != null">
d_id = #{dId,jdbcType=INTEGER},
</if>
</set>
where emp_id = #{empId,jdbcType=INTEGER}
</update>
<update id="updateByPrimaryKey" parameterType="com.mikey.bean.Employee">
update tbl_emp
set emp_name = #{empName,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
gender = #{gender,jdbcType=CHAR},
email = #{email,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
d_id = #{dId,jdbcType=INTEGER}
where emp_id = #{empId,jdbcType=INTEGER}
</update>
<sql id="Withdept_Column_List">emp_id, emp_name, gender, email, d_id,dept_id,dept_name</sql>
<!--List<Employee> selectByExampleWithDept(EmployeeExample employeeExample);-->
<select id="selectByExampleWithDept" resultMap="WithDeptResultMap">
SELECT
<if test="distinct">
distinct
</if>
<include refid="WithDept_Column_List" />
from tbl_emp left join tnl_dept t on tbl_emp.d_id = t.dept_id
<if test="_parameter != null">
<include refid="Example_Where_Clause" />
</if>
<if test="orderByClause != null">
order by ${orderByClause}
</if>
</select>
<!--Employee selectByPrimaryKeyWithDept(Integer empId);-->
<resultMap id="WithDeptResultMap" type="com.mikey.bean.Employee">
<id column="emp_id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="empId" />
<result column="emp_name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="empName" />
<result column="gender" jdbcType="CHAR" property="gender" />
<result column="email" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="email" />
<result column="d_id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="dId" />
<association property="department" javaType="com.mikey.bean.Department">
<id column="dept_id" property="deptId"/>
<result column="dept_name" property="deptName"/>
</association>
</resultMap>
<sql id="WithDept_Column_List">
tbl_emp.emp_id, tbl_emp.emp_name, tbl_emp.gender, tbl_emp.email, tbl_emp.d_id,t.dept_id,t.dept_name
</sql>
<select id="selectByPrimaryKeyWithDept" resultMap="WithDeptResultMap">
select
<include refid="Withdept_Column_List" />
from tbl_emp left join tnl_dept t on tbl_emp.d_id = t.dept_id
where emp_id = #{empId,jdbcType=INTEGER}
</select>
</mapper>
测试

package com.mikey.Test; import com.mikey.bean.EmployeeExample; import com.mikey.mapper.EmployeeMapper; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; /** * @author Mikey * @Title: * @Description: * @date 2018/11/1 19:10 * @Version 1.0 */ @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration(locations={"classpath:spring/applicationContext.xml"}) public class EmpServiceTest { @Autowired private EmployeeMapper employeeMapper; @Test public void Test(){ /** * 1.创建实例对象EmployeeExample */ EmployeeExample employeeExample=new EmployeeExample(); /** * 2-1.如果查询条件是and就创建critical对象 */ EmployeeExample.Criteria criteria = employeeExample.createCriteria(); // criteria.andDIdIsNull();//select emp_id, emp_name, gender, email, d_id from tbl_emp WHERE ( d_id is null ) // criteria.andDIdGreaterThanOrEqualTo(1);//select emp_id, emp_name, gender, email, d_id from tbl_emp WHERE ( d_id >= ? ) criteria.andDIdLessThanOrEqualTo(10); criteria.andEmpNameEqualTo("aa"); /** * 2-2.如果查询条件是or就直接使用创建好的实例对象调用or()方法在调用对应的条件方法 */ employeeExample.or().andDIdIsNull(); employeeExample.or().andDIdLessThan(10);//select emp_id, emp_name, gender, email, d_id from tbl_emp WHERE ( d_id is null ) or( d_id < ? ) /** * 3.执行查询 * 4.如果有需要,可以自定义(改造)mapper文件 * 5.上面的查询and和or支持多个添加 */ employeeMapper.selectByExample(employeeExample); } }
逆向无法生成主键查询方法:
解决方法:改用5.1版本以下的mysql包