BeanFactory和FactoryBean
BeanFactory
BeanFactory是一个工厂,提供了OC容器最基本的形式,给具体的IOC容器的实现提供了规范,其实现类有DefaultListableBeanFactory、XmlBeanFactory、ApplicationContext等


/* * Copyright 2002-2019 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.beans.factory; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.core.ResolvableType; import org.springframework.lang.Nullable; /** * The root interface for accessing a Spring bean container. * This is the basic client view of a bean container; * further interfaces such as {@link ListableBeanFactory} and * {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableBeanFactory} * are available for specific purposes. * * <p>This interface is implemented by objects that hold a number of bean definitions, * each uniquely identified by a String name. Depending on the bean definition, * the factory will return either an independent instance of a contained object * (the Prototype design pattern), or a single shared instance (a superior * alternative to the Singleton design pattern, in which the instance is a * singleton in the scope of the factory). Which type of instance will be returned * depends on the bean factory configuration: the API is the same. Since Spring * 2.0, further scopes are available depending on the concrete application * context (e.g. "request" and "session" scopes in a web environment). * * <p>The point of this approach is that the BeanFactory is a central registry * of application components, and centralizes configuration of application * components (no more do individual objects need to read properties files, * for example). See chapters 4 and 11 of "Expert One-on-One J2EE Design and * Development" for a discussion of the benefits of this approach. * * <p>Note that it is generally better to rely on Dependency Injection * ("push" configuration) to configure application objects through setters * or constructors, rather than use any form of "pull" configuration like a * BeanFactory lookup. Spring's Dependency Injection functionality is * implemented using this BeanFactory interface and its subinterfaces. * * <p>Normally a BeanFactory will load bean definitions stored in a configuration * source (such as an XML document), and use the {@code org.springframework.beans} * package to configure the beans. However, an implementation could simply return * Java objects it creates as necessary directly in Java code. There are no * constraints on how the definitions could be stored: LDAP, RDBMS, XML, * properties file, etc. Implementations are encouraged to support references * amongst beans (Dependency Injection). * * <p>In contrast to the methods in {@link ListableBeanFactory}, all of the * operations in this interface will also check parent factories if this is a * {@link HierarchicalBeanFactory}. If a bean is not found in this factory instance, * the immediate parent factory will be asked. Beans in this factory instance * are supposed to override beans of the same name in any parent factory. * * <p>Bean factory implementations should support the standard bean lifecycle interfaces * as far as possible. The full set of initialization methods and their standard order is: * <ol> * <li>BeanNameAware's {@code setBeanName} * <li>BeanClassLoaderAware's {@code setBeanClassLoader} * <li>BeanFactoryAware's {@code setBeanFactory} * <li>EnvironmentAware's {@code setEnvironment} * <li>EmbeddedValueResolverAware's {@code setEmbeddedValueResolver} * <li>ResourceLoaderAware's {@code setResourceLoader} * (only applicable when running in an application context) * <li>ApplicationEventPublisherAware's {@code setApplicationEventPublisher} * (only applicable when running in an application context) * <li>MessageSourceAware's {@code setMessageSource} * (only applicable when running in an application context) * <li>ApplicationContextAware's {@code setApplicationContext} * (only applicable when running in an application context) * <li>ServletContextAware's {@code setServletContext} * (only applicable when running in a web application context) * <li>{@code postProcessBeforeInitialization} methods of BeanPostProcessors * <li>InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet} * <li>a custom init-method definition * <li>{@code postProcessAfterInitialization} methods of BeanPostProcessors * </ol> * * <p>On shutdown of a bean factory, the following lifecycle methods apply: * <ol> * <li>{@code postProcessBeforeDestruction} methods of DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessors * <li>DisposableBean's {@code destroy} * <li>a custom destroy-method definition * </ol> * * @author Rod Johnson * @author Juergen Hoeller * @author Chris Beams * @since 13 April 2001 * @see BeanNameAware#setBeanName * @see BeanClassLoaderAware#setBeanClassLoader * @see BeanFactoryAware#setBeanFactory * @see org.springframework.context.ResourceLoaderAware#setResourceLoader * @see org.springframework.context.ApplicationEventPublisherAware#setApplicationEventPublisher * @see org.springframework.context.MessageSourceAware#setMessageSource * @see org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware#setApplicationContext * @see org.springframework.web.context.ServletContextAware#setServletContext * @see org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInitialization * @see InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet * @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition#getInitMethodName * @see org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInitialization * @see DisposableBean#destroy * @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition#getDestroyMethodName */ public interface BeanFactory { /** * Used to dereference a {@link FactoryBean} instance and distinguish it from * beans <i>created</i> by the FactoryBean. For example, if the bean named * {@code myJndiObject} is a FactoryBean, getting {@code &myJndiObject} * will return the factory, not the instance returned by the factory. */ String FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX = "&"; /** * Return an instance, which may be shared or independent, of the specified bean. * <p>This method allows a Spring BeanFactory to be used as a replacement for the * Singleton or Prototype design pattern. Callers may retain references to * returned objects in the case of Singleton beans. * <p>Translates aliases back to the corresponding canonical bean name. * Will ask the parent factory if the bean cannot be found in this factory instance. * @param name the name of the bean to retrieve * @return an instance of the bean * @throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException if there is no bean with the specified name * @throws BeansException if the bean could not be obtained */ Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException; /** * Return an instance, which may be shared or independent, of the specified bean. * <p>Behaves the same as {@link #getBean(String)}, but provides a measure of type * safety by throwing a BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException if the bean is not of the * required type. This means that ClassCastException can't be thrown on casting * the result correctly, as can happen with {@link #getBean(String)}. * <p>Translates aliases back to the corresponding canonical bean name. * Will ask the parent factory if the bean cannot be found in this factory instance. * @param name the name of the bean to retrieve * @param requiredType type the bean must match; can be an interface or superclass * @return an instance of the bean * @throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException if there is no such bean definition * @throws BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException if the bean is not of the required type * @throws BeansException if the bean could not be created */ <T> T getBean(String name, Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException; /** * Return an instance, which may be shared or independent, of the specified bean. * <p>Allows for specifying explicit constructor arguments / factory method arguments, * overriding the specified default arguments (if any) in the bean definition. * @param name the name of the bean to retrieve * @param args arguments to use when creating a bean instance using explicit arguments * (only applied when creating a new instance as opposed to retrieving an existing one) * @return an instance of the bean * @throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException if there is no such bean definition * @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException if arguments have been given but * the affected bean isn't a prototype * @throws BeansException if the bean could not be created * @since 2.5 */ Object getBean(String name, Object... args) throws BeansException; /** * Return the bean instance that uniquely matches the given object type, if any. * <p>This method goes into {@link ListableBeanFactory} by-type lookup territory * but may also be translated into a conventional by-name lookup based on the name * of the given type. For more extensive retrieval operations across sets of beans, * use {@link ListableBeanFactory} and/or {@link BeanFactoryUtils}. * @param requiredType type the bean must match; can be an interface or superclass * @return an instance of the single bean matching the required type * @throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException if no bean of the given type was found * @throws NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException if more than one bean of the given type was found * @throws BeansException if the bean could not be created * @since 3.0 * @see ListableBeanFactory */ <T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException; /** * Return an instance, which may be shared or independent, of the specified bean. * <p>Allows for specifying explicit constructor arguments / factory method arguments, * overriding the specified default arguments (if any) in the bean definition. * <p>This method goes into {@link ListableBeanFactory} by-type lookup territory * but may also be translated into a conventional by-name lookup based on the name * of the given type. For more extensive retrieval operations across sets of beans, * use {@link ListableBeanFactory} and/or {@link BeanFactoryUtils}. * @param requiredType type the bean must match; can be an interface or superclass * @param args arguments to use when creating a bean instance using explicit arguments * (only applied when creating a new instance as opposed to retrieving an existing one) * @return an instance of the bean * @throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException if there is no such bean definition * @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException if arguments have been given but * the affected bean isn't a prototype * @throws BeansException if the bean could not be created * @since 4.1 */ <T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType, Object... args) throws BeansException; /** * Return a provider for the specified bean, allowing for lazy on-demand retrieval * of instances, including availability and uniqueness options. * @param requiredType type the bean must match; can be an interface or superclass * @return a corresponding provider handle * @since 5.1 * @see #getBeanProvider(ResolvableType) */ <T> ObjectProvider<T> getBeanProvider(Class<T> requiredType); /** * Return a provider for the specified bean, allowing for lazy on-demand retrieval * of instances, including availability and uniqueness options. * @param requiredType type the bean must match; can be a generic type declaration. * Note that collection types are not supported here, in contrast to reflective * injection points. For programmatically retrieving a list of beans matching a * specific type, specify the actual bean type as an argument here and subsequently * use {@link ObjectProvider#orderedStream()} or its lazy streaming/iteration options. * @return a corresponding provider handle * @since 5.1 * @see ObjectProvider#iterator() * @see ObjectProvider#stream() * @see ObjectProvider#orderedStream() */ <T> ObjectProvider<T> getBeanProvider(ResolvableType requiredType); /** * Does this bean factory contain a bean definition or externally registered singleton * instance with the given name? * <p>If the given name is an alias, it will be translated back to the corresponding * canonical bean name. * <p>If this factory is hierarchical, will ask any parent factory if the bean cannot * be found in this factory instance. * <p>If a bean definition or singleton instance matching the given name is found, * this method will return {@code true} whether the named bean definition is concrete * or abstract, lazy or eager, in scope or not. Therefore, note that a {@code true} * return value from this method does not necessarily indicate that {@link #getBean} * will be able to obtain an instance for the same name. * @param name the name of the bean to query * @return whether a bean with the given name is present */ boolean containsBean(String name); /** * Is this bean a shared singleton? That is, will {@link #getBean} always * return the same instance? * <p>Note: This method returning {@code false} does not clearly indicate * independent instances. It indicates non-singleton instances, which may correspond * to a scoped bean as well. Use the {@link #isPrototype} operation to explicitly * check for independent instances. * <p>Translates aliases back to the corresponding canonical bean name. * Will ask the parent factory if the bean cannot be found in this factory instance. * @param name the name of the bean to query * @return whether this bean corresponds to a singleton instance * @throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException if there is no bean with the given name * @see #getBean * @see #isPrototype */ boolean isSingleton(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException; /** * Is this bean a prototype? That is, will {@link #getBean} always return * independent instances? * <p>Note: This method returning {@code false} does not clearly indicate * a singleton object. It indicates non-independent instances, which may correspond * to a scoped bean as well. Use the {@link #isSingleton} operation to explicitly * check for a shared singleton instance. * <p>Translates aliases back to the corresponding canonical bean name. * Will ask the parent factory if the bean cannot be found in this factory instance. * @param name the name of the bean to query * @return whether this bean will always deliver independent instances * @throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException if there is no bean with the given name * @since 2.0.3 * @see #getBean * @see #isSingleton */ boolean isPrototype(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException; /** * Check whether the bean with the given name matches the specified type. * More specifically, check whether a {@link #getBean} call for the given name * would return an object that is assignable to the specified target type. * <p>Translates aliases back to the corresponding canonical bean name. * Will ask the parent factory if the bean cannot be found in this factory instance. * @param name the name of the bean to query * @param typeToMatch the type to match against (as a {@code ResolvableType}) * @return {@code true} if the bean type matches, * {@code false} if it doesn't match or cannot be determined yet * @throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException if there is no bean with the given name * @since 4.2 * @see #getBean * @see #getType */ boolean isTypeMatch(String name, ResolvableType typeToMatch) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException; /** * Check whether the bean with the given name matches the specified type. * More specifically, check whether a {@link #getBean} call for the given name * would return an object that is assignable to the specified target type. * <p>Translates aliases back to the corresponding canonical bean name. * Will ask the parent factory if the bean cannot be found in this factory instance. * @param name the name of the bean to query * @param typeToMatch the type to match against (as a {@code Class}) * @return {@code true} if the bean type matches, * {@code false} if it doesn't match or cannot be determined yet * @throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException if there is no bean with the given name * @since 2.0.1 * @see #getBean * @see #getType */ boolean isTypeMatch(String name, Class<?> typeToMatch) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException; /** * Determine the type of the bean with the given name. More specifically, * determine the type of object that {@link #getBean} would return for the given name. * <p>For a {@link FactoryBean}, return the type of object that the FactoryBean creates, * as exposed by {@link FactoryBean#getObjectType()}. This may lead to the initialization * of a previously uninitialized {@code FactoryBean} (see {@link #getType(String, boolean)}). * <p>Translates aliases back to the corresponding canonical bean name. * Will ask the parent factory if the bean cannot be found in this factory instance. * @param name the name of the bean to query * @return the type of the bean, or {@code null} if not determinable * @throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException if there is no bean with the given name * @since 1.1.2 * @see #getBean * @see #isTypeMatch */ @Nullable Class<?> getType(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException; /** * Determine the type of the bean with the given name. More specifically, * determine the type of object that {@link #getBean} would return for the given name. * <p>For a {@link FactoryBean}, return the type of object that the FactoryBean creates, * as exposed by {@link FactoryBean#getObjectType()}. Depending on the * {@code allowFactoryBeanInit} flag, this may lead to the initialization of a previously * uninitialized {@code FactoryBean} if no early type information is available. * <p>Translates aliases back to the corresponding canonical bean name. * Will ask the parent factory if the bean cannot be found in this factory instance. * @param name the name of the bean to query * @param allowFactoryBeanInit whether a {@code FactoryBean} may get initialized * just for the purpose of determining its object type * @return the type of the bean, or {@code null} if not determinable * @throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException if there is no bean with the given name * @since 5.2 * @see #getBean * @see #isTypeMatch */ @Nullable Class<?> getType(String name, boolean allowFactoryBeanInit) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException; /** * Return the aliases for the given bean name, if any. * All of those aliases point to the same bean when used in a {@link #getBean} call. * <p>If the given name is an alias, the corresponding original bean name * and other aliases (if any) will be returned, with the original bean name * being the first element in the array. * <p>Will ask the parent factory if the bean cannot be found in this factory instance. * @param name the bean name to check for aliases * @return the aliases, or an empty array if none * @see #getBean */ String[] getAliases(String name); }
FactoryBean
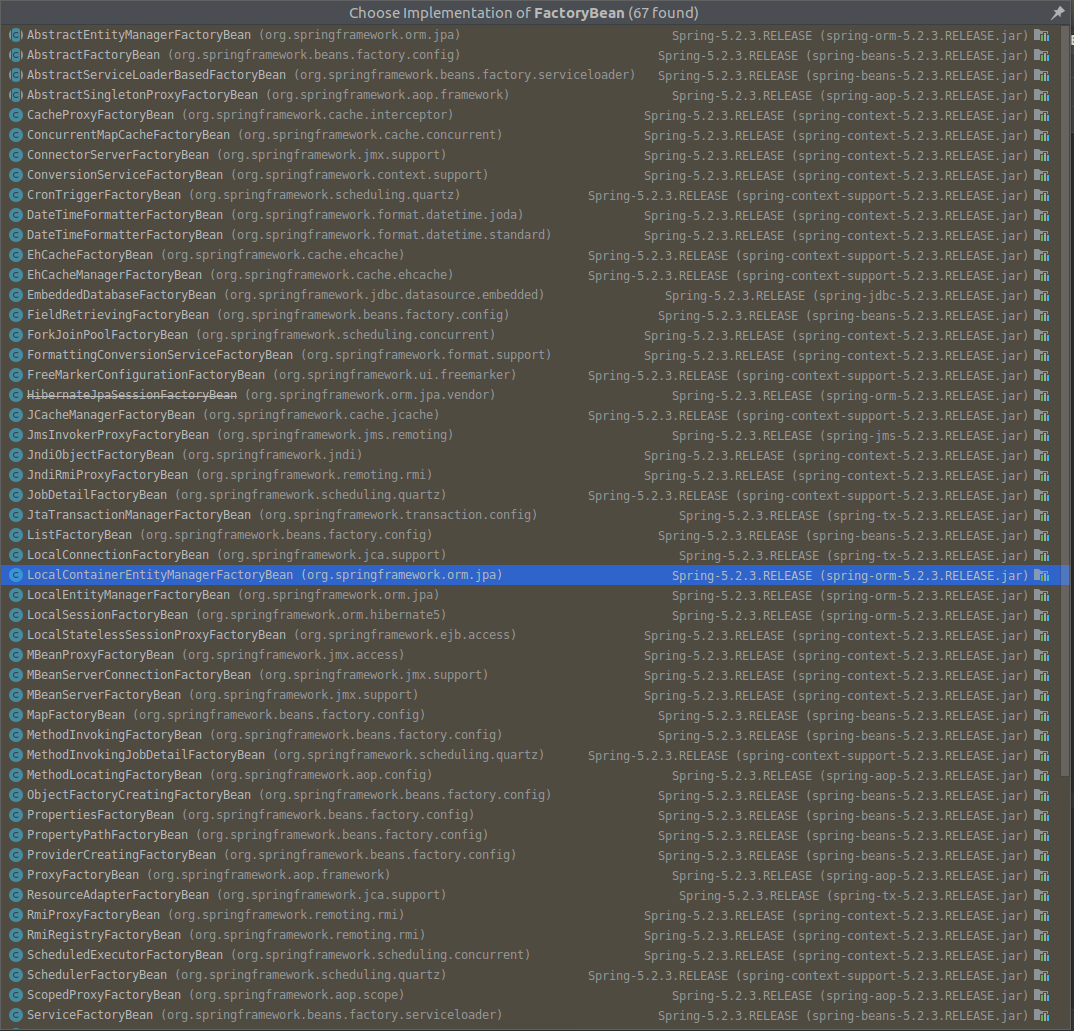
FactoryBean是一个bean,为IOC容器中Bean的实现提供了更加灵活的方式,FactoryBean在IOC容器的基础上给Bean的实现加上了一个简单工厂模式和装饰模式,我们可以在getObject()方法中灵活配置。其实在Spring源码中有很多FactoryBean的实现类.
要想获取FactoryBean的实现类,就要getBean(&BeanName),在BeanName之前加上&。
实现类

/* * Copyright 2002-2019 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.beans.factory; import org.springframework.lang.Nullable; /** * Interface to be implemented by objects used within a {@link BeanFactory} which * are themselves factories for individual objects. If a bean implements this * interface, it is used as a factory for an object to expose, not directly as a * bean instance that will be exposed itself. * * <p><b>NB: A bean that implements this interface cannot be used as a normal bean.</b> * A FactoryBean is defined in a bean style, but the object exposed for bean * references ({@link #getObject()}) is always the object that it creates. * * <p>FactoryBeans can support singletons and prototypes, and can either create * objects lazily on demand or eagerly on startup. The {@link SmartFactoryBean} * interface allows for exposing more fine-grained behavioral metadata. * * <p>This interface is heavily used within the framework itself, for example for * the AOP {@link org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean} or the * {@link org.springframework.jndi.JndiObjectFactoryBean}. It can be used for * custom components as well; however, this is only common for infrastructure code. * * <p><b>{@code FactoryBean} is a programmatic contract. Implementations are not * supposed to rely on annotation-driven injection or other reflective facilities.</b> * {@link #getObjectType()} {@link #getObject()} invocations may arrive early in * the bootstrap process, even ahead of any post-processor setup. If you need access * other beans, implement {@link BeanFactoryAware} and obtain them programmatically. * * <p>Finally, FactoryBean objects participate in the containing BeanFactory's * synchronization of bean creation. There is usually no need for internal * synchronization other than for purposes of lazy initialization within the * FactoryBean itself (or the like). * * @author Rod Johnson * @author Juergen Hoeller * @since 08.03.2003 * @param <T> the bean type * @see org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory * @see org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean * @see org.springframework.jndi.JndiObjectFactoryBean */ public interface FactoryBean<T> { /** * The name of an attribute that can be * {@link org.springframework.core.AttributeAccessor#setAttribute set} on a * {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition} so that * factory beans can signal their object type when it can't be deduced from * the factory bean class. * @since 5.2 */ String OBJECT_TYPE_ATTRIBUTE = "factoryBeanObjectType"; /** * Return an instance (possibly shared or independent) of the object * managed by this factory. * <p>As with a {@link BeanFactory}, this allows support for both the * Singleton and Prototype design pattern. * <p>If this FactoryBean is not fully initialized yet at the time of * the call (for example because it is involved in a circular reference), * throw a corresponding {@link FactoryBeanNotInitializedException}. * <p>As of Spring 2.0, FactoryBeans are allowed to return {@code null} * objects. The factory will consider this as normal value to be used; it * will not throw a FactoryBeanNotInitializedException in this case anymore. * FactoryBean implementations are encouraged to throw * FactoryBeanNotInitializedException themselves now, as appropriate. * @return an instance of the bean (can be {@code null}) * @throws Exception in case of creation errors * @see FactoryBeanNotInitializedException */ @Nullable T getObject() throws Exception; /** * Return the type of object that this FactoryBean creates, * or {@code null} if not known in advance. * <p>This allows one to check for specific types of beans without * instantiating objects, for example on autowiring. * <p>In the case of implementations that are creating a singleton object, * this method should try to avoid singleton creation as far as possible; * it should rather estimate the type in advance. * For prototypes, returning a meaningful type here is advisable too. * <p>This method can be called <i>before</i> this FactoryBean has * been fully initialized. It must not rely on state created during * initialization; of course, it can still use such state if available. * <p><b>NOTE:</b> Autowiring will simply ignore FactoryBeans that return * {@code null} here. Therefore it is highly recommended to implement * this method properly, using the current state of the FactoryBean. * @return the type of object that this FactoryBean creates, * or {@code null} if not known at the time of the call * @see ListableBeanFactory#getBeansOfType */ @Nullable Class<?> getObjectType(); /** * Is the object managed by this factory a singleton? That is, * will {@link #getObject()} always return the same object * (a reference that can be cached)? * <p><b>NOTE:</b> If a FactoryBean indicates to hold a singleton object, * the object returned from {@code getObject()} might get cached * by the owning BeanFactory. Hence, do not return {@code true} * unless the FactoryBean always exposes the same reference. * <p>The singleton status of the FactoryBean itself will generally * be provided by the owning BeanFactory; usually, it has to be * defined as singleton there. * <p><b>NOTE:</b> This method returning {@code false} does not * necessarily indicate that returned objects are independent instances. * An implementation of the extended {@link SmartFactoryBean} interface * may explicitly indicate independent instances through its * {@link SmartFactoryBean#isPrototype()} method. Plain {@link FactoryBean} * implementations which do not implement this extended interface are * simply assumed to always return independent instances if the * {@code isSingleton()} implementation returns {@code false}. * <p>The default implementation returns {@code true}, since a * {@code FactoryBean} typically manages a singleton instance. * @return whether the exposed object is a singleton * @see #getObject() * @see SmartFactoryBean#isPrototype() */ default boolean isSingleton() { return true; } }
你都这么优秀了,不打算关注我一下嘛

合群是堕落的开始 优秀的开始是孤行



