倒排索引构建算法BSBI和SPIMI
参考文献:
http://www.cnblogs.com/fly1988happy/archive/2012/04/01/2429000.html
http://blog.csdn.net/v_july_v/article/details/7109500
我的数据挖掘算法:https://github.com/linyiqun/DataMiningAlgorithm
我的算法库:https://github.com/linyiqun/lyq-algorithms-lib
算法介绍
在信息搜索领域,构建索引一直是是一种非常有效的方式,但是当搜索引擎面对的是海量数据的时候,你如果要从茫茫人海的数据中去找出数据,显然这不是一个很好的办法。于是倒排索引这个概念就被提了出来。再说倒排索引概念之前,先要理解一下,一般的索引检索信息的方式。比如原始的数据源假设都是以文档的形式被分开,文档1拥有一段内容,文档2也富含一段内容,文档3同样如此。然后给定一个关键词,要搜索出与此关键词相关的文档,自然而然我们联想到的办法就是一个个文档的内容去比较,判断是否含有此关键词,如果含有则返回这个文档的索引地址,如果不是接着用后面的文档去比,这就有点类似于字符串的匹配类似。很显然,当数据量非常巨大的时候,这种方式并不适用。原来的这种方式可以理解为是索引-->关键词,而倒排索引的形式则是关键词--->索引位置,也就是说,给出一个关键词信息,我能立马根据倒排索引的信息得出他的位置。当然,这里说的是倒排索引最后要达到的效果,至于是用什么方式实现,就不止一种了,本文所述的就是其中比较出名的BSBI和SPIMI算法。
算法的原理
这里首先给出一个具体的实例来了解一般的构造过程,先避开具体的实现方式,给定下面一组词句。
Doc1:Mike spoken English Frequently at home.And he can write English every day.
Doc2::Mike plays football very well.
首先我们必须知道,我们需要的是一些关键的信息,诸如一些修饰词等等都需要省略,动词的时态变化等都需要还原,如果代词指的是同个人也能够省略,于是上面的句子可以简化成
Doc1:Mike spoken English home.write English.
Doc2:Mike play football.
下面进行索引的倒排构建,因为Mike出现在文档1和文档2 中,所以Mike:{1, 2}后面的词的构造同样的道理。最后的关系就会构成词对应于索引位置的映射关系。理解了这个过程之后呢,可以介绍一下本文主要要说的BSBI(基于磁盘的外部排序构建索引)和SPIMI(内存单遍扫描构建索引)算法了,一般来说,后者比前者常用。
BSBI
此算法的主要步骤如下:
1、将文档中的词进行id的映射,这里可以用hash的方法去构造
2、将文档分割成大小相等的部分。
3、将每部分按照词ID对上文档ID的方式进行排序
4、将每部分排序好后的结果进行合并,最后写出到磁盘中。
5、然后递归的执行,直到文档内容全部完成这一系列操作。
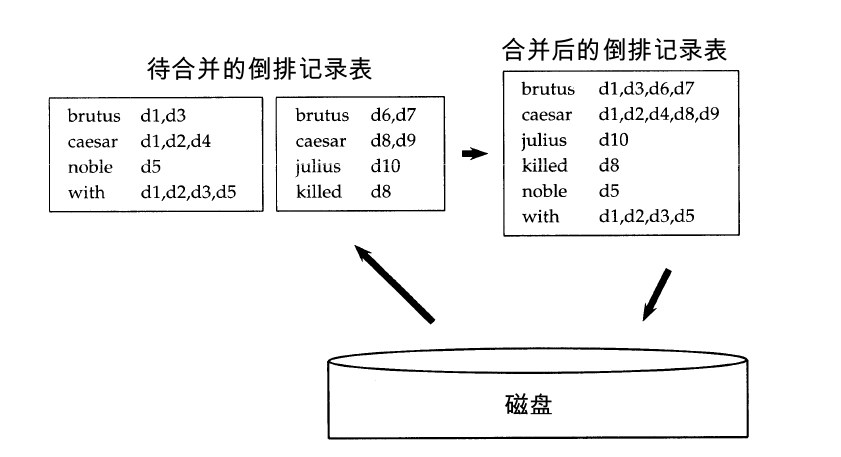
这里有一张示意图:
在算法的过程中会用到读缓冲区和写缓冲区,至于期间的大小多少如何配置都是看个人的,我在后面的代码实现中也有进行设置。至于其中的排序算法的选择,一般建议使用效果比较好的快速排序算法,但是我在后面为了方便,直接用了自己更熟悉的冒泡排序算法,这个也看个人。
SPIMI
接下来说说SPIMI算法,就是内存单遍扫描算法,这个算法与上面的算法一上来就有直接不同的特点就是他无须做id的转换,还是采用了词对索引的直接关联。还有1个比较大的特点是他不经过排序,直接按照先后顺序构建索引,算法的主要步骤如下:
1、对每个块构造一个独立的倒排索引。
2、最后将所有独立的倒排索引进行合并就OK了。
本人为了方便就把这个算法的实现简洁化了,直接在内存中完成所有的构建工作。望读者稍加注意。SPIMI相对比较的简单,这里就不给出截图了。
算法的代码实现
首先是文档的输入数据,采用了2个一样的文档,我也是实在想不出有更好的测试数据了
doc1.txt:
Mike studyed English hardly yesterday
He got the 100 at the last exam
He thinks English is very interestingdoc2.txt:
Mike studyed English hardly yesterday
He got the 100 at the last exam
He thinks English is very interesting
package InvertedIndex;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
/**
* 文档预处理工具类
*
* @author lyq
*
*/
public class PreTreatTool {
// 一些无具体意义的过滤词
public static String[] FILTER_WORDS = new String[] { "at", "At", "The",
"the", "is", "very" };
// 批量文档的文件地址
private ArrayList<String> docFilePaths;
// 输出的有效词的存放路径
private ArrayList<String> effectWordPaths;
public PreTreatTool(ArrayList<String> docFilePaths) {
this.docFilePaths = docFilePaths;
}
/**
* 获取文档有效词文件路径
*
* @return
*/
public ArrayList<String> getEFWPaths() {
return this.effectWordPaths;
}
/**
* 从文件中读取数据
*
* @param filePath
* 单个文件
*/
private ArrayList<String> readDataFile(String filePath) {
File file = new File(filePath);
ArrayList<String[]> dataArray = new ArrayList<String[]>();
ArrayList<String> words = new ArrayList<>();
try {
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
String str;
String[] tempArray;
while ((str = in.readLine()) != null) {
tempArray = str.split(" ");
dataArray.add(tempArray);
}
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.getStackTrace();
}
// 将每行词做拆分加入到总列表容器中
for (String[] array : dataArray) {
for (String word : array) {
words.add(word);
}
}
return words;
}
/**
* 对文档内容词汇进行预处理
*/
public void preTreatWords() {
String baseOutputPath = "";
int endPos = 0;
ArrayList<String> tempWords = null;
effectWordPaths = new ArrayList<>();
for (String filePath : docFilePaths) {
tempWords = readDataFile(filePath);
filterWords(tempWords, true);
// 重新组装出新的输出路径
endPos = filePath.lastIndexOf(".");
baseOutputPath = filePath.substring(0, endPos);
writeOutOperation(tempWords, baseOutputPath + "-efword.txt");
effectWordPaths.add(baseOutputPath + "-efword.txt");
}
}
/**
*
* 对文档中的词语进行过滤操作
*
* @param words
* 待处理文档词语
* @param canRepeated
* 有效词是否可以重复
*/
private void filterWords(ArrayList<String> words, boolean canRepeated) {
boolean isFilterWord;
// 做形容词匹配
Pattern adjPattern;
// 做动词时态的匹配
Pattern formerPattern;
// 数字匹配
Pattern numberPattern;
Matcher adjMatcher;
Matcher formerMatcher;
Matcher numberMatcher;
ArrayList<String> deleteWords = new ArrayList<>();
adjPattern = Pattern.compile(".*(ly$|ful$|ing$)");
formerPattern = Pattern.compile(".*ed$");
numberPattern = Pattern.compile("[0-9]+(.[0-9]+)?");
String w;
for (int i = 0; i < words.size(); i++) {
w = words.get(i);
isFilterWord = false;
for (String fw : FILTER_WORDS) {
if (fw.equals(w)) {
deleteWords.add(w);
isFilterWord = true;
break;
}
}
if (isFilterWord) {
continue;
}
adjMatcher = adjPattern.matcher(w);
formerMatcher = formerPattern.matcher(w);
numberMatcher = numberPattern.matcher(w);
// 将词语统一小写字母化
w = w.toLowerCase();
// 如果是形容词,副词形式的或是纯数字的词,则进行过滤
if (adjMatcher.matches() || numberMatcher.matches()) {
deleteWords.add(w);
} else if (formerMatcher.matches()) {
// 如果是ed结尾表明是动词的在时态方面的变化,进行变化,转为原有动词的形式,截去最末尾2个额外添加的后缀词
w = w.substring(0, w.length() - 2);
}
words.set(i, w);
}
// 进行无效词的过滤
words.removeAll(deleteWords);
deleteWords.clear();
String s1;
String s2;
// 进行词语的去重
for (int i = 0; i < words.size() - 1; i++) {
s1 = words.get(i);
for (int j = i + 1; j < words.size(); j++) {
s2 = words.get(j);
// 找到存在相同的词了,就挑出循环
if (s1.equals(s2)) {
deleteWords.add(s1);
break;
}
}
}
// 删除多余重复的词语
words.removeAll(deleteWords);
words.addAll(deleteWords);
}
/**
* 将数据写出到磁盘文件操作,如果文件已经存在,则在文件尾部进行内容追加
*
* @param buffer
* 当前写缓冲中的数据
* @param filePath
* 输出地址
*/
private void writeOutOperation(ArrayList<String> buffer, String filePath) {
StringBuilder strBuilder = new StringBuilder();
// 将缓冲中的数据组成字符写入到文件中
for (String word : buffer) {
strBuilder.append(word);
strBuilder.append("\n");
}
try {
File file = new File(filePath);
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream(file));
ps.print(strBuilder.toString());// 往文件里写入字符串
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
package InvertedIndex;
import java.util.ArrayList;
/**
* 文档类
* @author lyq
*
*/
public class Document {
//文档的唯一标识
int docId;
//文档的文件地址
String filePath;
//文档中的有效词
ArrayList<String> effectWords;
public Document(ArrayList<String> effectWords, String filePath){
this.effectWords = effectWords;
this.filePath = filePath;
}
public Document(ArrayList<String> effectWords, String filePath, int docId){
this(effectWords, filePath);
this.docId = docId;
}
}
package InvertedIndex;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* BSBI基于磁盘的外部排序算法
*
* @author lyq
*
*/
public class BSBITool {
// 文档唯一标识ID
public static int DOC_ID = 0;
// 读缓冲区的大小
private int readBufferSize;
// 写缓冲区的大小
private int writeBufferSize;
// 读入的文档的有效词文件地址
private ArrayList<String> effectiveWordFiles;
// 倒排索引输出文件地址
private String outputFilePath;
// 读缓冲 1
private String[][] readBuffer1;
// 读缓冲2
private String[][] readBuffer2;
// 写缓冲区
private String[][] writeBuffer;
// 有效词与hashcode的映射
private Map<String, String> code2word;
public BSBITool(ArrayList<String> effectiveWordFiles, int readBufferSize,
int writeBufferSize) {
this.effectiveWordFiles = effectiveWordFiles;
this.readBufferSize = readBufferSize;
this.writeBufferSize = writeBufferSize;
initBuffers();
}
/**
* 初始化缓冲区的设置
*/
private void initBuffers() {
readBuffer1 = new String[readBufferSize][2];
readBuffer2 = new String[readBufferSize][2];
writeBuffer = new String[writeBufferSize][2];
}
/**
* 从文件中读取有效词并进行编码替换
*
* @param filePath
* 返回文档
*/
private Document readEffectWords(String filePath) {
long hashcode = 0;
String w;
Document document;
code2word = new HashMap<String, String>();
ArrayList<String> words;
words = readDataFile(filePath);
for (int i = 0; i < words.size(); i++) {
w = words.get(i);
hashcode = BKDRHash(w);
hashcode = hashcode % 10000;
// 将有效词的hashcode取模值作为对应的代表
code2word.put(hashcode + "", w);
w = hashcode + "";
words.set(i, w);
}
document = new Document(words, filePath, DOC_ID);
DOC_ID++;
return document;
}
/**
* 将字符做哈希值的转换
*
* @param str
* 待转换字符
* @return
*/
private long BKDRHash(String str) {
int seed = 31; /* 31 131 1313 13131 131313 etc.. */
long hash = 0;
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
hash = (hash * seed) + (str.charAt(i));
}
return hash;
}
/**
* 根据输入的有效词输出倒排索引文件
*/
public void outputInvertedFiles() {
int index = 0;
String baseFilePath = "";
outputFilePath = "";
Document doc;
ArrayList<String> tempPaths;
ArrayList<String[]> invertedData1;
ArrayList<String[]> invertedData2;
tempPaths = new ArrayList<>();
for (String filePath : effectiveWordFiles) {
doc = readEffectWords(filePath);
writeOutFile(doc);
index = doc.filePath.lastIndexOf(".");
baseFilePath = doc.filePath.substring(0, index);
writeOutOperation(writeBuffer, baseFilePath + "-temp.txt");
tempPaths.add(baseFilePath + "-temp.txt");
}
outputFilePath = baseFilePath + "-bsbi-inverted.txt";
// 将中间产生的倒排索引数据进行总的合并并输出到一个文件中
for (int i = 1; i < tempPaths.size(); i++) {
if (i == 1) {
invertedData1 = readInvertedFile(tempPaths.get(0));
} else {
invertedData1 = readInvertedFile(outputFilePath);
}
invertedData2 = readInvertedFile(tempPaths.get(i));
mergeInvertedData(invertedData1, invertedData2, false,
outputFilePath);
writeOutOperation(writeBuffer, outputFilePath, false);
}
}
/**
* 将文档的最终的倒排索引结果写出到文件
*
* @param doc
* 待处理文档
*/
private void writeOutFile(Document doc) {
// 在读缓冲区中是否需要再排序
boolean ifSort = true;
int index = 0;
String baseFilePath;
String[] temp;
ArrayList<String> tempWords = (ArrayList<String>) doc.effectWords
.clone();
ArrayList<String[]> invertedData1;
ArrayList<String[]> invertedData2;
invertedData1 = new ArrayList<>();
invertedData2 = new ArrayList<>();
// 将文档的数据平均拆分成2份,用于读入后面的2个缓冲区中
for (int i = 0; i < tempWords.size() / 2; i++) {
temp = new String[2];
temp[0] = tempWords.get(i);
temp[1] = doc.docId + "";
invertedData1.add(temp);
temp = new String[2];
temp[0] = tempWords.get(i + tempWords.size() / 2);
temp[1] = doc.docId + "";
invertedData2.add(temp);
}
// 如果是奇数个,则将最后一个补入
if (tempWords.size() % 2 == 1) {
temp = new String[2];
temp[0] = tempWords.get(tempWords.size() - 1);
temp[1] = doc.docId + "";
invertedData2.add(temp);
}
index = doc.filePath.lastIndexOf(".");
baseFilePath = doc.filePath.substring(0, index);
mergeInvertedData(invertedData1, invertedData2, ifSort, baseFilePath
+ "-temp.txt");
}
/**
* 合并读缓冲区数据写到写缓冲区中,用到了归并排序算法
*
* @param outputPath
* 写缓冲区的写出的路径
*/
private void mergeWordBuffers(String outputPath) {
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
int num1 = 0;
int num2 = 0;
// 写缓冲区下标
int writeIndex = 0;
while (readBuffer1[i][0] != null && readBuffer2[j][0] != null) {
num1 = Integer.parseInt(readBuffer1[i][0]);
num2 = Integer.parseInt(readBuffer2[j][0]);
// 如果缓冲1小,则优先存缓冲1到写缓冲区中
if (num1 < num2) {
writeBuffer[writeIndex][0] = num1 + "";
writeBuffer[writeIndex][1] = readBuffer1[i][1];
i++;
} else if (num2 < num1) {
writeBuffer[writeIndex][0] = num2 + "";
writeBuffer[writeIndex][1] = readBuffer1[j][1];
j++;
} else if (num1 == num2) {
// 如果两个缓冲区中的数字一样,说明是同个有效词,先进行合并再写入
writeBuffer[writeIndex][0] = num1 + "";
writeBuffer[writeIndex][1] = readBuffer1[i][1] + ":"
+ readBuffer2[j][1];
i++;
j++;
}
// 写的指针往后挪一位
writeIndex++;
// 如果写满写缓冲区时,进行写出到文件操作
if (writeIndex >= writeBufferSize) {
writeOutOperation(writeBuffer, outputPath);
writeIndex = 0;
}
}
if (readBuffer1[i][0] == null) {
writeRemainReadBuffer(readBuffer2, j, outputPath);
}
if (readBuffer2[j][0] == null) {
writeRemainReadBuffer(readBuffer1, j, outputPath);
}
}
/**
* 将数据写出到磁盘文件操作,如果文件已经存在,则在文件尾部进行内容追加
*
* @param buffer
* 当前写缓冲中的数据
* @param filePath
* 输出地址
*/
private void writeOutOperation(String[][] buffer, String filePath) {
String word;
StringBuilder strBuilder = new StringBuilder();
// 将缓冲中的数据组成字符写入到文件中
for (String[] array : buffer) {
if (array[0] == null) {
continue;
}
word = array[0];
strBuilder.append(word);
strBuilder.append(" ");
strBuilder.append(array[1]);
strBuilder.append("\n");
}
try {
File file = new File(filePath);
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream(file));
ps.print(strBuilder.toString());// 往文件里写入字符串
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 将数据写出到磁盘文件操作,如果文件已经存在,则在文件尾部进行内容追加
*
* @param buffer
* 当前写缓冲中的数据
* @param filePath
* 输出地址
* @param isCoded
* 是否以编码的方式输出
*/
private void writeOutOperation(String[][] buffer, String filePath, boolean isCoded) {
String word;
StringBuilder strBuilder = new StringBuilder();
// 将缓冲中的数据组成字符写入到文件中
for (String[] array : buffer) {
if (array[0] == null) {
continue;
}
if(!isCoded){
word = code2word.get(array[0]);
}else{
word = array[0];
}
strBuilder.append(word);
strBuilder.append(" ");
strBuilder.append(array[1]);
strBuilder.append("\n");
}
try {
File file = new File(filePath);
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream(file));
ps.print(strBuilder.toString());// 往文件里写入字符串
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 将剩余的读缓冲区中的数据读入写缓冲区中
*
* @param remainBuffer
* 读缓冲区的剩余缓冲
* @param currentReadPos
* 当前的读取位置
* @param outputPath
* 写缓冲区的写出文件路径
*/
private void writeRemainReadBuffer(String[][] remainBuffer,
int currentReadPos, String outputPath) {
while (remainBuffer[currentReadPos][0] != null
&& currentReadPos < readBufferSize) {
removeRBToWB(remainBuffer[currentReadPos]);
currentReadPos++;
// 如果写满写缓冲区时,进行写出到文件操作
if (writeBuffer[writeBufferSize - 1][0] != null) {
writeOutOperation(writeBuffer, outputPath);
}
}
}
/**
* 将剩余读缓冲区中的数据通过插入排序的方式插入写缓冲区
*
* @param record
*/
private void removeRBToWB(String[] record) {
int insertIndex = 0;
int endIndex = 0;
long num1;
long num2;
long code = Long.parseLong(record[0]);
// 如果写缓冲区目前为空,则直接加入
if (writeBuffer[0][0] == null) {
writeBuffer[0] = record;
return;
}
// 寻找待插入的位置
for (int i = 0; i < writeBufferSize - 1; i++) {
if (writeBuffer[i][0] == null) {
endIndex = i;
break;
}
num1 = Long.parseLong(writeBuffer[i][0]);
if (writeBuffer[i + 1][0] == null) {
if (code > num1) {
endIndex = i + 1;
insertIndex = i + 1;
}
} else {
num2 = Long.parseLong(writeBuffer[i + 1][0]);
if (code > num1 && code < num2) {
insertIndex = i + 1;
}
}
}
// 进行插入操作,相关数据进行位置迁移
for (int i = endIndex; i > insertIndex; i--) {
writeBuffer[i] = writeBuffer[i - 1];
}
writeBuffer[insertIndex] = record;
}
/**
* 将磁盘中的2个倒排索引数据进行合并
*
* @param invertedData1
* 倒排索引为文件数据1
* @param invertedData2
* 倒排索引文件数据2
* @param isSort
* 是否需要对缓冲区中的数据进行排序
* @param outputPath
* 倒排索引输出文件地址
*/
private void mergeInvertedData(ArrayList<String[]> invertedData1,
ArrayList<String[]> invertedData2, boolean ifSort, String outputPath) {
int rIndex1 = 0;
int rIndex2 = 0;
// 重新初始化缓冲区
initBuffers();
while (invertedData1.size() > 0 && invertedData2.size() > 0) {
readBuffer1[rIndex1][0] = invertedData1.get(0)[0];
readBuffer1[rIndex1][1] = invertedData1.get(0)[1];
readBuffer2[rIndex2][0] = invertedData2.get(0)[0];
readBuffer2[rIndex2][1] = invertedData2.get(0)[1];
invertedData1.remove(0);
invertedData2.remove(0);
rIndex1++;
rIndex2++;
if (rIndex1 == readBufferSize) {
if (ifSort) {
wordBufferSort(readBuffer1);
wordBufferSort(readBuffer2);
}
mergeWordBuffers(outputPath);
initBuffers();
}
}
if (ifSort) {
wordBufferSort(readBuffer1);
wordBufferSort(readBuffer2);
}
mergeWordBuffers(outputPath);
readBuffer1 = new String[readBufferSize][2];
readBuffer2 = new String[readBufferSize][2];
if (invertedData1.size() == 0 && invertedData2.size() > 0) {
readRemainDataToRB(invertedData2, outputPath);
} else if (invertedData1.size() > 0 && invertedData2.size() == 0) {
readRemainDataToRB(invertedData1, outputPath);
}
}
/**
* 剩余的有效词数据读入读缓冲区
*
* @param remainData
* 剩余数据
* @param outputPath
* 输出文件路径
*/
private void readRemainDataToRB(ArrayList<String[]> remainData,
String outputPath) {
int rIndex = 0;
while (remainData.size() > 0) {
readBuffer1[rIndex][0] = remainData.get(0)[0];
readBuffer1[rIndex][1] = remainData.get(0)[1];
remainData.remove(0);
rIndex++;
// 读缓冲 区写满,进行写入到写缓冲区中
if (readBuffer1[readBufferSize - 1][0] != null) {
wordBufferSort(readBuffer1);
writeRemainReadBuffer(readBuffer1, 0, outputPath);
initBuffers();
}
}
wordBufferSort(readBuffer1);
writeRemainReadBuffer(readBuffer1, 0, outputPath);
}
/**
* 缓冲区数据进行排序
*
* @param buffer
* 缓冲空间
*/
private void wordBufferSort(String[][] buffer) {
String[] temp;
int k = 0;
long num1 = 0;
long num2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < buffer.length - 1; i++) {
// 缓冲区可能没填满
if (buffer[i][0] == null) {
continue;
}
k = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < buffer.length; j++) {
// 缓冲区可能没填满
if (buffer[j][0] == null) {
continue;
}
// 获取2个缓冲区小块的起始编号值
num1 = Long.parseLong(buffer[k][0]);
num2 = Long.parseLong(buffer[j][0]);
if (num2 < num1) {
k = j;
}
}
if (k != i) {
temp = buffer[k];
buffer[k] = buffer[i];
buffer[i] = temp;
}
}
}
/**
* 从文件中读取倒排索引数据
*
* @param filePath
* 单个文件
*/
private ArrayList<String[]> readInvertedFile(String filePath) {
File file = new File(filePath);
ArrayList<String[]> dataArray = new ArrayList<String[]>();
try {
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
String str;
String[] tempArray;
while ((str = in.readLine()) != null) {
tempArray = str.split(" ");
dataArray.add(tempArray);
}
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.getStackTrace();
}
return dataArray;
}
/**
* 从文件中读取数据
*
* @param filePath
* 单个文件
*/
private ArrayList<String> readDataFile(String filePath) {
File file = new File(filePath);
ArrayList<String[]> dataArray = new ArrayList<String[]>();
ArrayList<String> words = new ArrayList<>();
try {
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
String str;
String[] tempArray;
while ((str = in.readLine()) != null) {
tempArray = str.split(" ");
dataArray.add(tempArray);
}
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.getStackTrace();
}
// 将每行词做拆分加入到总列表容器中
for (String[] array : dataArray) {
for (String word : array) {
if (!word.equals("")) {
words.add(word);
}
}
}
return words;
}
}
package InvertedIndex;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
/**
* SPIMI内存式单边扫描构建算法
* @author lyq
*
*/
public class SPIMITool {
//倒排索引输出文件地址
private String outputFilePath;
// 读入的文档的有效词文件地址
private ArrayList<String> effectiveWordFiles;
// 内存缓冲区,不够还能够在增加空间
private ArrayList<String[]> buffers;
public SPIMITool(ArrayList<String> effectiveWordFiles){
this.effectiveWordFiles = effectiveWordFiles;
}
/**
* 从文件中读取数据
*
* @param filePath
* 单个文件
*/
private ArrayList<String> readDataFile(String filePath) {
File file = new File(filePath);
ArrayList<String[]> dataArray = new ArrayList<String[]>();
ArrayList<String> words = new ArrayList<>();
try {
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
String str;
String[] tempArray;
while ((str = in.readLine()) != null) {
tempArray = str.split(" ");
dataArray.add(tempArray);
}
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.getStackTrace();
}
// 将每行词做拆分加入到总列表容器中
for (String[] array : dataArray) {
for (String word : array) {
words.add(word);
}
}
return words;
}
/**
* 根据已有的文档数据进行倒排索引文件的构建
* @param docs
* 文档集合
*/
private void writeInvertedIndex(ArrayList<Document> docs){
ArrayList<String> datas;
String[] recordData;
buffers = new ArrayList<>();
for(Document tempDoc: docs){
datas = tempDoc.effectWords;
for(String word: datas){
recordData = new String[2];
recordData[0] = word;
recordData[1] = tempDoc.docId + "";
addRecordToBuffer(recordData);
}
}
//最后将数据写出到磁盘中
writeOutOperation(buffers, outputFilePath);
}
/**
* 将新读入的数据记录读入到内存缓冲中,如果存在则加入到倒排记录表中
* @param insertedData
* 待插入的数据
*/
private void addRecordToBuffer(String[] insertedData){
boolean isContained = false;
String wordName;
wordName = insertedData[0];
for(String[] array: buffers){
if(array[0].equals(wordName)){
isContained = true;
//添加倒排索引记录,以:隔开
array[1] += ":" + insertedData[1];
break;
}
}
//如果没有包含,则说明是新的数据,直接添加
if(!isContained){
buffers.add(insertedData);
}
}
/**
* 将数据写出到磁盘文件操作,如果文件已经存在,则在文件尾部进行内容追加
* @param buffer
* 当前写缓冲中的数据
* @param filePath
* 输出地址
*/
private void writeOutOperation(ArrayList<String[]> buffer, String filePath) {
StringBuilder strBuilder = new StringBuilder();
//将缓冲中的数据组成字符写入到文件中
for(String[] array: buffer){
strBuilder.append(array[0]);
strBuilder.append(" ");
strBuilder.append(array[1]);
strBuilder.append("\n");
}
try {
File file = new File(filePath);
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream(file));
ps.println(strBuilder.toString());// 往文件里写入字符串
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 构造倒排索引文件
*/
public void createInvertedIndexFile(){
int docId = 1;
String baseFilePath;
String fileName;
String p;
int index1 = 0;
int index2 = 0;
Document tempDoc;
ArrayList<String> words;
ArrayList<Document> docs;
outputFilePath = "spimi";
docs = new ArrayList<>();
p = effectiveWordFiles.get(0);
//提取文件名称
index1 = p.lastIndexOf("\\");
baseFilePath = p.substring(0, index1+1);
outputFilePath = baseFilePath + "spimi";
for(String path: effectiveWordFiles){
//获取文档有效词
words = readDataFile(path);
tempDoc = new Document(words, path, docId);
docId++;
docs.add(tempDoc);
//提取文件名称
index1 = path.lastIndexOf("\\");
index2 = path.lastIndexOf(".");
fileName = path.substring(index1+1, index2);
outputFilePath += "-" + fileName;
}
outputFilePath += ".txt";
//根据文档数据进行倒排索引文件的创建
writeInvertedIndex(docs);
}
}
package InvertedIndex;
import java.util.ArrayList;
/**
* 倒排索引测试类
* @author lyq
*
*/
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args){
//读写缓冲区的大小
int readBufferSize;
int writeBufferSize;
String baseFilePath;
PreTreatTool preTool;
//BSBI基于磁盘的外部排序算法
BSBITool bTool;
//SPIMI内存式单边扫描构建算法
SPIMITool sTool;
//有效词文件路径
ArrayList<String> efwFilePaths;
ArrayList<String> docFilePaths;
readBufferSize = 10;
writeBufferSize = 20;
baseFilePath = "C:\\Users\\lyq\\Desktop\\icon\\";
docFilePaths = new ArrayList<>();
docFilePaths.add(baseFilePath + "doc1.txt");
docFilePaths.add(baseFilePath + "doc2.txt");
//文档预处理工具类
preTool = new PreTreatTool(docFilePaths);
preTool.preTreatWords();
//预处理完获取有效词文件路径
efwFilePaths = preTool.getEFWPaths();
bTool = new BSBITool(efwFilePaths, readBufferSize, writeBufferSize);
bTool.outputInvertedFiles();
sTool = new SPIMITool(efwFilePaths);
sTool.createInvertedIndexFile();
}
}
为了模拟出真实性,算法的输出都是以文件的形式。
首先是预处理类处理之后的有效词文件doc1-efword.txt和doc2-efword.txt:
mike
study
yesterday
got
last
exam
thinks
english
he
下面是BSBI算法生成的中间文件,就是映射成编码的文件,也许你看了这些数值真实表示的是什么词语:
1426 0
1542 0
2540 0
3056 0
3325 0
4326 0
4897 0
6329 0
7327 0
1426 1
1542 1
2540 1
3056 1
3325 1
4326 1
4897 1
6329 1
7327 1
yesterday 0:1
mike 0:1
got 0:1
english 0:1
he 0:1
last 0:1
thinks 0:1
study 0:1
exam 0:1
mike 1:2
study 1:2
yesterday 1:2
got 1:2
last 1:2
exam 1:2
thinks 1:2
english 1:2
he 1:2
算法小结
我在实现算法的过程中无疑低估了此算法的难度,尤其是BSBI的实现,因为中间读写缓冲区在做数据操作的时候,各种情况需要判断,诸如写缓冲区满了的时候要刷出到磁盘上,读缓冲区满的时候要通过归并排序移入读缓冲区中,这里面的判断实在过多,加上之前早期没有想到这个问题,导致算法可读性不是很好,就索性把缓冲区设大,先走通这个流程,所以这个算法大家还是以理解为主,就不要拿来实际运用了,同样对于SPIMI算法一样的道理,算法实现在这里帮助大家更好的理解吧,还有很多不足的地方。还有1点是文档内容预处理的时候,我只是象征性的进行过滤,真实的信息过滤实现复杂程度远远超过我所写的,这里包括了修饰词,时态词的变化,副词等等,这些有时还需要语义挖掘的一些知识来解决,大家意会即可。