YARN源码学习(六)-----JobHistory中的job信息获取与分析
前言
继续延续上一篇文章的主题,2个字,监控,分布式系统要想做到足够大,足够强,足够稳定,首先需要做好的就是其中的监控.现在开源的分布式系统很多,YARN就是其中一种,比较值得庆幸的一点是,Yarn已经在Ganglia做了很多指标的监控分析.比如namenode rpc请求数,datanode写入字节数,读字节数,jvm相关的gc次数等等.但是看似这些指标非常的完美,其实不然,为什么这么说呢,因为粒度太粗,比如说下面这个场景,我想分析集群中特点节点机器上哪个task异常,导致拖垮整个集群的运作效率.这个时候,显然分析Ganglia上的粗粒度监控指标就不能解决这样的场景问题了吧.不过还好,Yarn提供了这样的额外服务,叫做JobHistory,他也是一项独立的服务.
什么是JobHistory
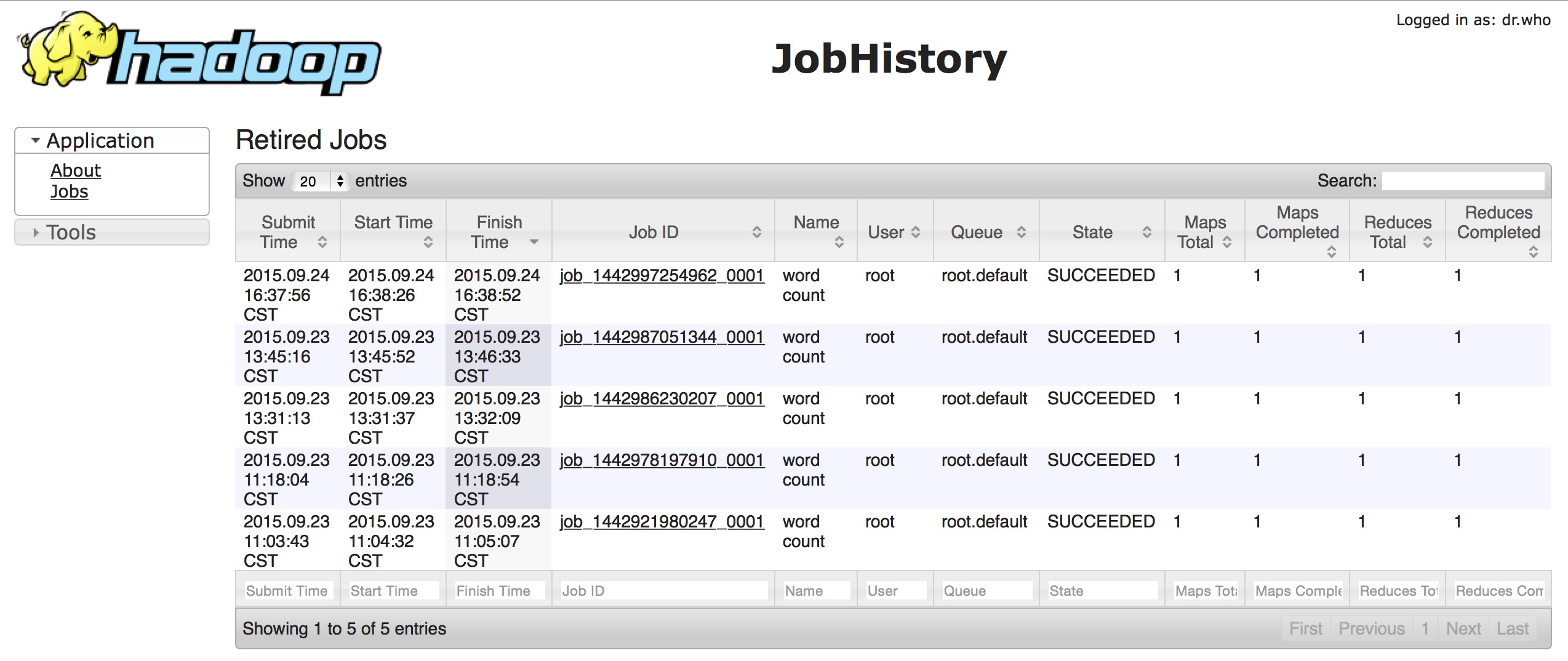
什么是JobHistory,jobHistory翻译成中文就是作业历史,就是作业历史记录.就是保存了集群运行过的历史Job信息数据.下面是一张此服务的Web UI视图:
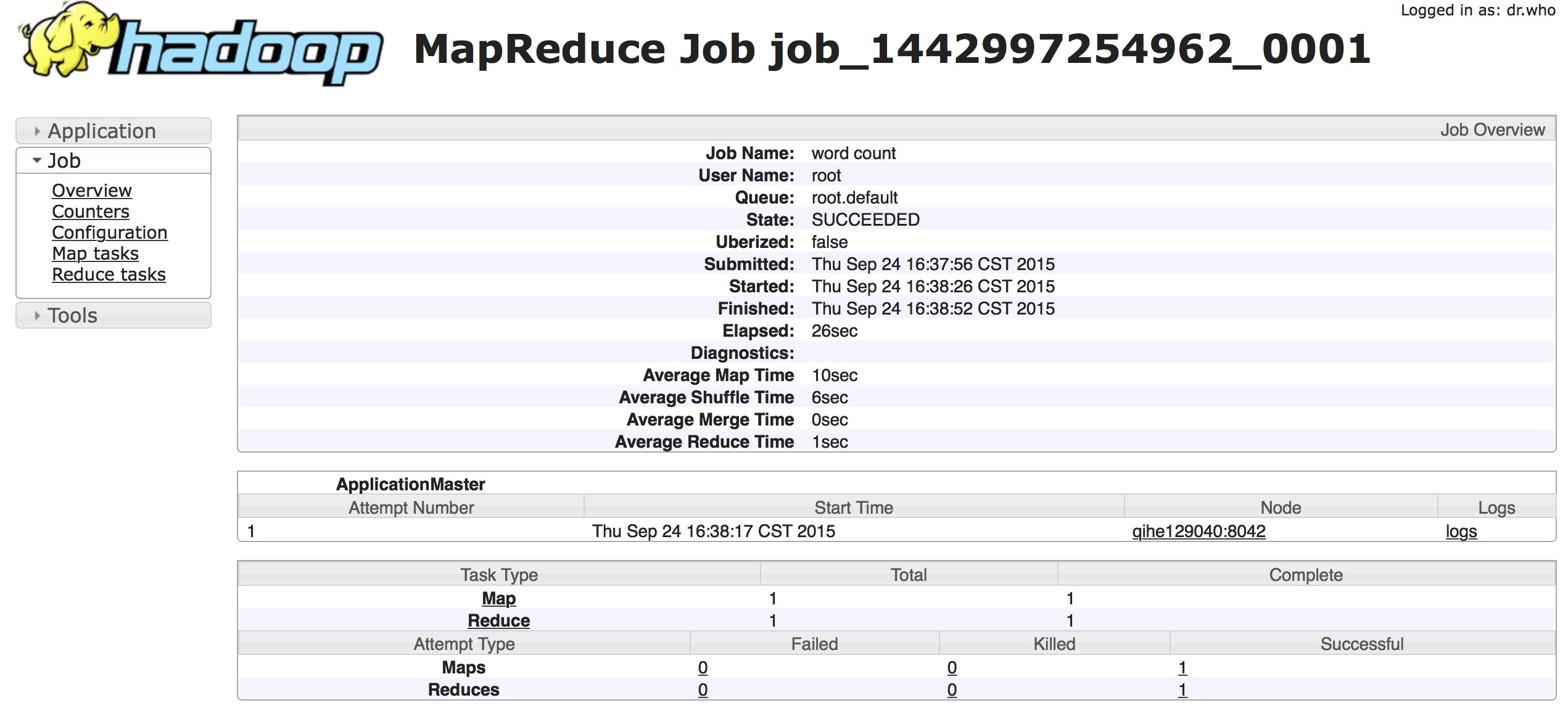
可以很清楚的看到了上面执行过的job记录.因为是我测试是跑的几个word-count程序,所以信息比较少.当然每个job记录的链接还能往里继续点,里面保存了更加详细的task的运行信息,包括map数,reduce数,开始结束时间等等,如下图
JobHistory上所展示的数据是非常多的,但是唯一感到不足的是,JobHistory的展示效果太过单一,每个Job的数据结果都是独立展现的,并没有一个汇总的页面,不便于比较分析.所以一个比较大胆的想法就诞生了,我们是不是可以拿到Job的信息记录,存入自己的db,然后自己做分析呢.OK,想法固然不错,但是还是得从源码中进行分析,首先要明白这些数据到底存在哪.
JobHistory作业数据存储
下面来描述一下我是如何分析发现JobHistory作业数据的存储源的.首先定位到JobHistory这个大类.
/**
* Loads and manages the Job history cache.
*/
public class JobHistory extends AbstractService implements HistoryContext {
private static final Log LOG = LogFactory.getLog(JobHistory.class);
public static final Pattern CONF_FILENAME_REGEX = Pattern.compile("("
+ JobID.JOBID_REGEX + ")_conf.xml(?:\\.[0-9]+\\.old)?");
public static final String OLD_SUFFIX = ".old";
// Time interval for the move thread.
private long moveThreadInterval;
private Configuration conf;
private ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor scheduledExecutor = null;
//注意下面这2个类的名称,显然与存储信息相关
private HistoryStorage storage = null;
private HistoryFileManager hsManager = null;
ScheduledFuture<?> futureHistoryCleaner = null;
...从这里就可以看出来,JobHistory也是一项服务.关注到上面的倒数3行有与存储相关的类,我们可以重点关注这2个变量.然后扫描JobHistory的内部方法,你应该会发现有下面这样的方法
@Override
public Map<JobId, Job> getAllJobs() {
return storage.getAllPartialJobs();
}@Override
protected void serviceInit(Configuration conf) throws Exception {
LOG.info("JobHistory Init");
.....
hsManager = createHistoryFileManager();
hsManager.init(conf);
try {
hsManager.initExisting();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new YarnRuntimeException("Failed to intialize existing directories", e);
}
storage = createHistoryStorage();
if (storage instanceof Service) {
((Service) storage).init(conf);
}
storage.setHistoryFileManager(hsManager);
super.serviceInit(conf);
}protected HistoryStorage createHistoryStorage() {
return ReflectionUtils.newInstance(conf.getClass(
JHAdminConfig.MR_HISTORY_STORAGE, CachedHistoryStorage.class,
HistoryStorage.class), conf);
}@Override
public Map<JobId, Job> getAllPartialJobs() {
LOG.debug("Called getAllPartialJobs()");
SortedMap<JobId, Job> result = new TreeMap<JobId, Job>();
try {
for (HistoryFileInfo mi : hsManager.getAllFileInfo()) {
if (mi != null) {
JobId id = mi.getJobId();
result.put(id, new PartialJob(mi.getJobIndexInfo(), id));
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
LOG.warn("Error trying to scan for all FileInfos", e);
throw new YarnRuntimeException(e);
}
return result;
}public Collection<HistoryFileInfo> getAllFileInfo() throws IOException {
scanIntermediateDirectory();
return jobListCache.values();
} /**
* Populates index data structures. Should only be called at initialization
* times.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
void initExisting() throws IOException {
LOG.info("Initializing Existing Jobs...");
List<FileStatus> timestampedDirList = findTimestampedDirectories();
// Sort first just so insertion is in a consistent order
Collections.sort(timestampedDirList);
for (FileStatus fs : timestampedDirList) {
// TODO Could verify the correct format for these directories.
addDirectoryToSerialNumberIndex(fs.getPath());
}
for (int i= timestampedDirList.size() - 1;
i >= 0 && !jobListCache.isFull(); i--) {
FileStatus fs = timestampedDirList.get(i);
addDirectoryToJobListCache(fs.getPath());
}
}/**
* Finds all history directories with a timestamp component by scanning the
* filesystem. Used when the JobHistory server is started.
*
* @return list of history directories
*/
protected List<FileStatus> findTimestampedDirectories() throws IOException {
List<FileStatus> fsList = JobHistoryUtils.localGlobber(doneDirFc,
doneDirPrefixPath, DONE_BEFORE_SERIAL_TAIL);
return fsList;
}/**
* Gets the configured directory prefix for Done history files.
* @param conf the configuration object
* @return the done history directory
*/
public static String getConfiguredHistoryServerDoneDirPrefix(
Configuration conf) {
String doneDirPrefix = conf.get(JHAdminConfig.MR_HISTORY_DONE_DIR);
if (doneDirPrefix == null) {
doneDirPrefix = conf.get(MRJobConfig.MR_AM_STAGING_DIR,
MRJobConfig.DEFAULT_MR_AM_STAGING_DIR)
+ "/history/done";
}
return ensurePathInDefaultFileSystem(doneDirPrefix, conf);
}<property>
<name>mapreduce.jobhistory.done-dir</name>
<value>${yarn.app.mapreduce.am.staging-dir}/history/done</value>
<source>mapred-default.xml</source>
</property><property>
<name>yarn.app.mapreduce.am.staging-dir</name>
<value>/tmp/hadoop-yarn/staging</value>
<source>mapred-default.xml</source>
</property>因此我找到我的配置最终地址为/tmp/hadoop-yarn/staging/history/done,然后马上用hadoop fs -ls 目标目录观察一下保存job信息的文件,
bin/hadoop fs -ls /tmp/hadoop-yarn/staging/history/done/2015/09/23drwxrwx--- - root supergroup 0 2015-09-23 13:47 /tmp/hadoop-yarn/staging/history/done/2015/09/23/000000不过这还是目录,继续ls命令
Found 8 items
-rwxrwx--- 1 root supergroup 33711 2015-09-23 11:05 /tmp/hadoop-yarn/staging/history/done/2015/09/23/000000/job_1442921980247_0001-1442977423178-root-word+count-1442977507137-1-1-SUCCEEDED-root.default-1442977472789.jhist
-rwxrwx--- 1 root supergroup 115932 2015-09-23 11:05 /tmp/hadoop-yarn/staging/history/done/2015/09/23/000000/job_1442921980247_0001_conf.xml
-rwxrwx--- 1 root supergroup 33707 2015-09-23 11:18 /tmp/hadoop-yarn/staging/history/done/2015/09/23/000000/job_1442978197910_0001-1442978284737-root-word+count-1442978334462-1-1-SUCCEEDED-root.default-1442978306980.jhist
-rwxrwx--- 1 root supergroup 115933 2015-09-23 11:18 /tmp/hadoop-yarn/staging/history/done/2015/09/23/000000/job_1442978197910_0001_conf.xml
-rwxrwx--- 1 root supergroup 33703 2015-09-23 13:32 /tmp/hadoop-yarn/staging/history/done/2015/09/23/000000/job_1442986230207_0001-1442986273588-root-word+count-1442986329305-1-1-SUCCEEDED-root.default-1442986297304.jhist
-rwxrwx--- 1 root supergroup 115933 2015-09-23 13:32 /tmp/hadoop-yarn/staging/history/done/2015/09/23/000000/job_1442986230207_0001_conf.xml
-rwxrwx--- 1 root supergroup 33720 2015-09-23 13:46 /tmp/hadoop-yarn/staging/history/done/2015/09/23/000000/job_1442987051344_0001-1442987116527-root-word+count-1442987193624-1-1-SUCCEEDED-root.default-1442987152826.jhist
-rwxrwx--- 1 root supergroup 115933 2015-09-23 13:46 /tmp/hadoop-yarn/staging/history/done/2015/09/23/000000/job_1442987051344_0001_conf.xml{"type":"JOB_FINISHED","event":{"org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.jobhistory.JobFinished":{"jobid":"job_1442921980247_0001","finishTime":1442977507137,"finishedMaps":1,"finishedReduces":1,"failedMaps":0,"failedReduces":0,"totalCounters":{"name":"TOTAL_COUNTERS","groups":[{"name":"org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.FileSystemCounter","displayName":"File System Counters","counts":[{"name":"FILE_BYTES_READ","displayName":"FILE: Number of bytes read","value":10992}JobHistory文件信息获取
OK,上一步骤了解了存储文件的存储位置后,我们面临的问题就是如何取出来,最好转化为对象的形式进行值的获取.非常幸运的是在HistoryFileManager中,恰好有对HistoryFileInfo到Job的转换方法
/**
* Parse a job from the JobHistoryFile, if the underlying file is not going
* to be deleted.
*
* @return the Job or null if the underlying file was deleted.
* @throws IOException
* if there is an error trying to read the file.
*/
public synchronized Job loadJob() throws IOException {
return new CompletedJob(conf, jobIndexInfo.getJobId(), historyFile,
false, jobIndexInfo.getUser(), this, aclsMgr);
}package org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.v2.hs.tool;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileContext;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileStatus;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.PathFilter;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.RemoteIterator;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.UnsupportedFileSystemException;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.v2.api.records.TaskId;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.v2.app.job.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.v2.app.job.Task;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.v2.hs.tool.HistoryFileInfo;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.v2.jobhistory.FileNameIndexUtils;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.v2.jobhistory.JobHistoryUtils;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.v2.jobhistory.JobIndexInfo;
import com.google.common.annotations.VisibleForTesting;
public class HSTool {
private static String DONE_BEFORE_SERIAL_TAIL = JobHistoryUtils
.doneSubdirsBeforeSerialTail();
String jobHistoryPath;
Path doneDirPrefixPath;
FileContext doneDirFc;
ArrayList<HistoryFileInfo> historyFileInfos;
public HSTool(String jobHistoryPath) {
this.jobHistoryPath = jobHistoryPath;
this.historyFileInfos = new ArrayList<HistoryFileInfo>();
}
public void getHistoryData() {
String doneDirPrefix = jobHistoryPath;
List<FileStatus> fileStatus;
try {
doneDirPrefixPath = FileContext.getFileContext(new Configuration())
.makeQualified(new Path(doneDirPrefix));
doneDirFc = FileContext.getFileContext(doneDirPrefixPath.toUri());
doneDirFc.setUMask(JobHistoryUtils.HISTORY_DONE_DIR_UMASK);
} catch (UnsupportedFileSystemException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
fileStatus = null;
try {
fileStatus = findTimestampedDirectories();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (fileStatus == null) {
System.out.println("fileStatus is null");
} else {
System.out.println("dir fileStatus size is " + fileStatus.size());
for (FileStatus fs : fileStatus) {
System.out.println("child path name is "
+ fs.getPath().getName());
try {
addDirectoryToJobListCache(fs.getPath());
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
System.out.println("history fileInfo size is "
+ this.historyFileInfos.size());
for (HistoryFileInfo hfi : this.historyFileInfos) {
System.out.println("file jobId is " + hfi.getJobId());
parseCompleteJob(hfi, true);
}
}
/**
* Finds all history directories with a timestamp component by scanning the
* filesystem. Used when the JobHistory server is started.
*
* @return list of history directories
*/
private List<FileStatus> findTimestampedDirectories() throws IOException {
List<FileStatus> fsList = JobHistoryUtils.localGlobber(doneDirFc,
doneDirPrefixPath, DONE_BEFORE_SERIAL_TAIL);
return fsList;
}
private void addDirectoryToJobListCache(Path path) throws IOException {
List<FileStatus> historyFileList = scanDirectoryForHistoryFiles(path,
doneDirFc);
for (FileStatus fs : historyFileList) {
JobIndexInfo jobIndexInfo = FileNameIndexUtils.getIndexInfo(fs
.getPath().getName());
String confFileName = JobHistoryUtils
.getIntermediateConfFileName(jobIndexInfo.getJobId());
String summaryFileName = JobHistoryUtils
.getIntermediateSummaryFileName(jobIndexInfo.getJobId());
HistoryFileInfo fileInfo = new HistoryFileInfo(fs.getPath(),
new Path(fs.getPath().getParent(), confFileName), new Path(
fs.getPath().getParent(), summaryFileName),
jobIndexInfo, true);
historyFileInfos.add(fileInfo);
}
}
protected List<FileStatus> scanDirectoryForHistoryFiles(Path path,
FileContext fc) throws IOException {
return scanDirectory(path, fc, JobHistoryUtils.getHistoryFileFilter());
}
@VisibleForTesting
protected static List<FileStatus> scanDirectory(Path path, FileContext fc,
PathFilter pathFilter) throws IOException {
path = fc.makeQualified(path);
List<FileStatus> jhStatusList = new ArrayList<FileStatus>();
try {
RemoteIterator<FileStatus> fileStatusIter = fc.listStatus(path);
while (fileStatusIter.hasNext()) {
FileStatus fileStatus = fileStatusIter.next();
Path filePath = fileStatus.getPath();
if (fileStatus.isFile() && pathFilter.accept(filePath)) {
jhStatusList.add(fileStatus);
}
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException fe) {
System.out.println("Error while scanning directory " + path);
}
return jhStatusList;
}
private void parseCompleteJob(HistoryFileInfo hfi, boolean loadTask) {
Job job;
Task task;
Map<TaskId, Task> taskInfos;
job = null;
try {
job = hfi.loadJob(loadTask);
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("job info : job user is" + job.getUserName()
+ ", map num is " + job.getTotalMaps() + ", job name is "
+ job.getName() + ", start time is "
+ job.getReport().getStartTime() + ", finish time is "
+ job.getReport().getFinishTime());
taskInfos = job.getTasks();
System.out.println("job task total num is " + taskInfos.size());
for (Map.Entry<TaskId, Task> entry : taskInfos.entrySet()) {
task = entry.getValue();
System.out.println("task id is " + task.getID()
+ "task start time is " + task.getReport().getStartTime());
}
}
}有了这把利器,相信会帮助大家更精准的发现Yarn集群中的问题.
全部代码的分析请点击链接https://github.com/linyiqun/yarn-jobhistory-crawler,后续将会继续更新YARN其他方面的代码分析。
参考源代码
Apach-hadoop-2.7.1(hadoop-mapreduce-client-hs)