PAT.1066 Root of AVL Tree(平衡树模板题)
1066 Root of AVL Tree (25分)
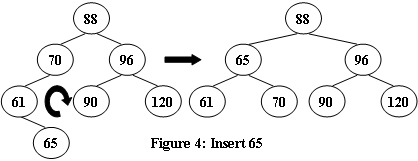
An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. In an AVL tree, the heights of the two child subtrees of any node differ by at most one; if at any time they differ by more than one, rebalancing is done to restore this property. Figures 1-4 illustrate the rotation rules.
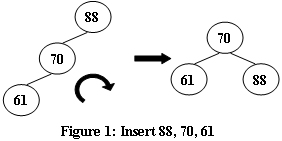
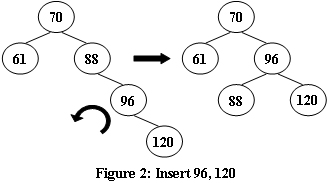
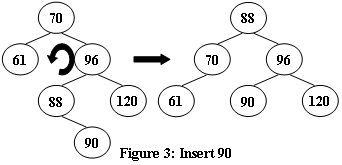
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤) which is the total number of keys to be inserted. Then N distinct integer keys are given in the next line. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the root of the resulting AVL tree in one line.
Sample Input 1:
5
88 70 61 96 120
Sample Output 1:
70
Sample Input 2:
7
88 70 61 96 120 90 65
Sample Output 2:
88
平衡树模板题。
口诀:
先插入,后旋转。
插入记得更新高度。
旋转儿子父亲交换。
儿子的儿子也要管。
直线型儿子父亲交换。
S型先旋S下部变为直然后再旋直。
1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <cstring> 3 #include <cmath> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 struct Tree { 7 int data, high; 8 Tree *l, *r; 9 } *root; 10 11 int max(int a, int b) { 12 return a > b ? a : b; 13 } 14 15 typedef Tree * ptree; 16 17 int get_high(ptree root) { 18 if(root == NULL) return 0; 19 else return root -> high; 20 } 21 22 void update_high(ptree root) { 23 root -> high = max(get_high(root -> l), get_high(root -> r)) + 1; 24 } 25 26 int balance_factor(ptree root) { 27 return get_high(root -> l) - get_high(root -> r); 28 } 29 30 void left_rotary(ptree &root) { 31 ptree temp = root -> r; 32 root -> r = temp -> l; 33 temp -> l = root; 34 update_high(root); 35 update_high(temp); 36 root = temp; 37 } 38 39 //右旋:root做root的左儿子的右儿子,那么如果root的左儿子原本就有右儿子,需要把他变为root的左儿子。然后再将root变为他的左儿子的右儿子,记得更新这两颗子树的高度,还要将这两颗子树的 40 //根节点变为root的左儿子 41 42 void right_rotary(ptree &root) { 43 ptree temp = root -> l; 44 root -> l = temp -> r; 45 temp -> r = root; 46 update_high(root); 47 update_high(temp); 48 root = temp; 49 } 50 51 void avl_insert(ptree &root, int num) { 52 if(root == NULL) {//叶子节点,设定叶子节点高度为1 53 root = new Tree; 54 root -> data = num; 55 root -> high = 1; 56 root -> l = root -> r = NULL; 57 } else { 58 if(num < root -> data) { 59 avl_insert(root -> l, num); 60 update_high(root);//在root的子树中插入新元素需要重新调整这个树的高度 61 if(balance_factor(root) == 2) {//在root的子树中插入新元素后需要检查树是否平衡 62 if(balance_factor(root -> l) == 1) {//如果root的左子树高度为1,则说明需要右旋 63 right_rotary(root); 64 } else if(balance_factor(root -> l) == -1) {//如果root的左子树比右子树低,则需要先左旋再右旋 65 left_rotary(root -> l); 66 right_rotary(root); 67 } 68 } 69 } else { 70 avl_insert(root -> r, num); 71 update_high(root); 72 if(balance_factor(root) == -2) {//如果是插入到root的右子树的话,那么root的右子树比左子树高2才需要调整 73 if(balance_factor(root -> r) == -1) { 74 left_rotary(root); 75 } else if(balance_factor(root -> r) == 1) { 76 right_rotary(root -> r); 77 left_rotary(root); 78 } 79 } 80 } 81 } 82 } 83 84 int main() { 85 int n, num; 86 scanf("%d", &n); 87 while(n --) { 88 scanf("%d", &num); 89 avl_insert(root, num); 90 } 91 printf("%d\n", root -> data); 92 return 0; 93 }
时间并不会因为你的迷茫和迟疑而停留,就在你看这篇文章的同时,不知道有多少人在冥思苦想,在为算法废寝忘食,不知道有多少人在狂热地拍着代码,不知道又有多少提交一遍又一遍地刷新着OJ的status页面……
没有谁生来就是神牛,而千里之行,始于足下!