记一次 .NET 程序的性能优化实战(3)—— 深入 .NET 源码
记一次 .NET 程序的性能优化实战(3)—— 深入 .NET 源码
前言
前两篇文章 part1 和 part2 基本上理清了 IsSplitter() 运行缓慢的原因 —— 在函数内部使用了带 Compile 选项的正则表达式。
但是没想到在 IsSplitter() 内部使用不带 Compiled 选项的正则表达式,整个程序运行起来非常快,跟静态函数版本的运行速度不相上下。又有了如下疑问:
- 为什么使用不带
Compiled选项实例化的Regex速度会这么快? - 为什么把
Regex变量从局部改成全局变量后运行速度有了极大提升?除了避免重复实例化,还有哪些提升? - 为什么
PerfView收集到的采样数据,大部分发生在MatchCollections.Count内部,极少发生在Regex的构造函数内部?(使用带Compiled选项的正则表达式的时候) Regex.IsMatch()是如何使用缓存的?- 直接实例化的
Regex对象会使用正则表达式引擎内部的缓存吗? - 正则表达式引擎内部根据什么缓存的?
- 什么时候会生成动态方法?生成的动态方法是在哪里调用的?
本文会继续使用 Perfview 抓取一些关键数据进行分析,有些疑问需要到 .NET 源码中寻找答案。在查看代码的过程中,发现有些逻辑单纯看源码不太容易理解,于是又调试跟踪了 .NET 中正则表达式相关源码。由于篇幅原因,本篇不会介绍如何下载 .NET 源码,如何调试 .NET 源码的方法。但是会单独写一篇简单的介绍文章 。
解惑
-
为什么使用不带
Compiled选项实例化的Regex速度会这么快?还是使用
PerfView采集性能数据并分析,如下图: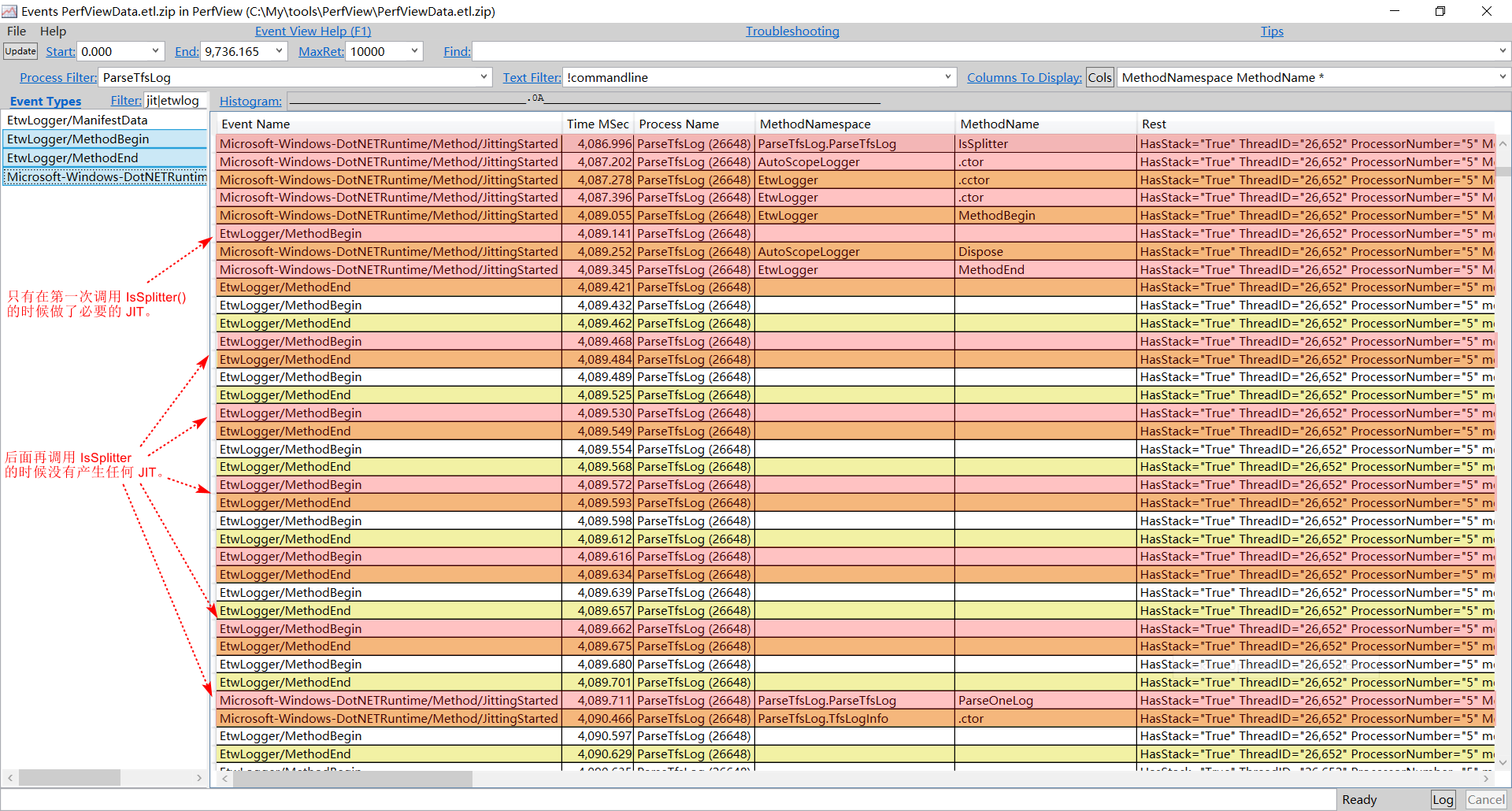
可以发现,
IsSplitter()函数只在第一次被调用时发生了一次JIT,后续调用耗时不到0.1ms(图中最后一次调用耗时:4090.629-4090.597 = 0.032ms)。使用带
Compiled选项实例化的Regex的IsSplitter()函数,如下图: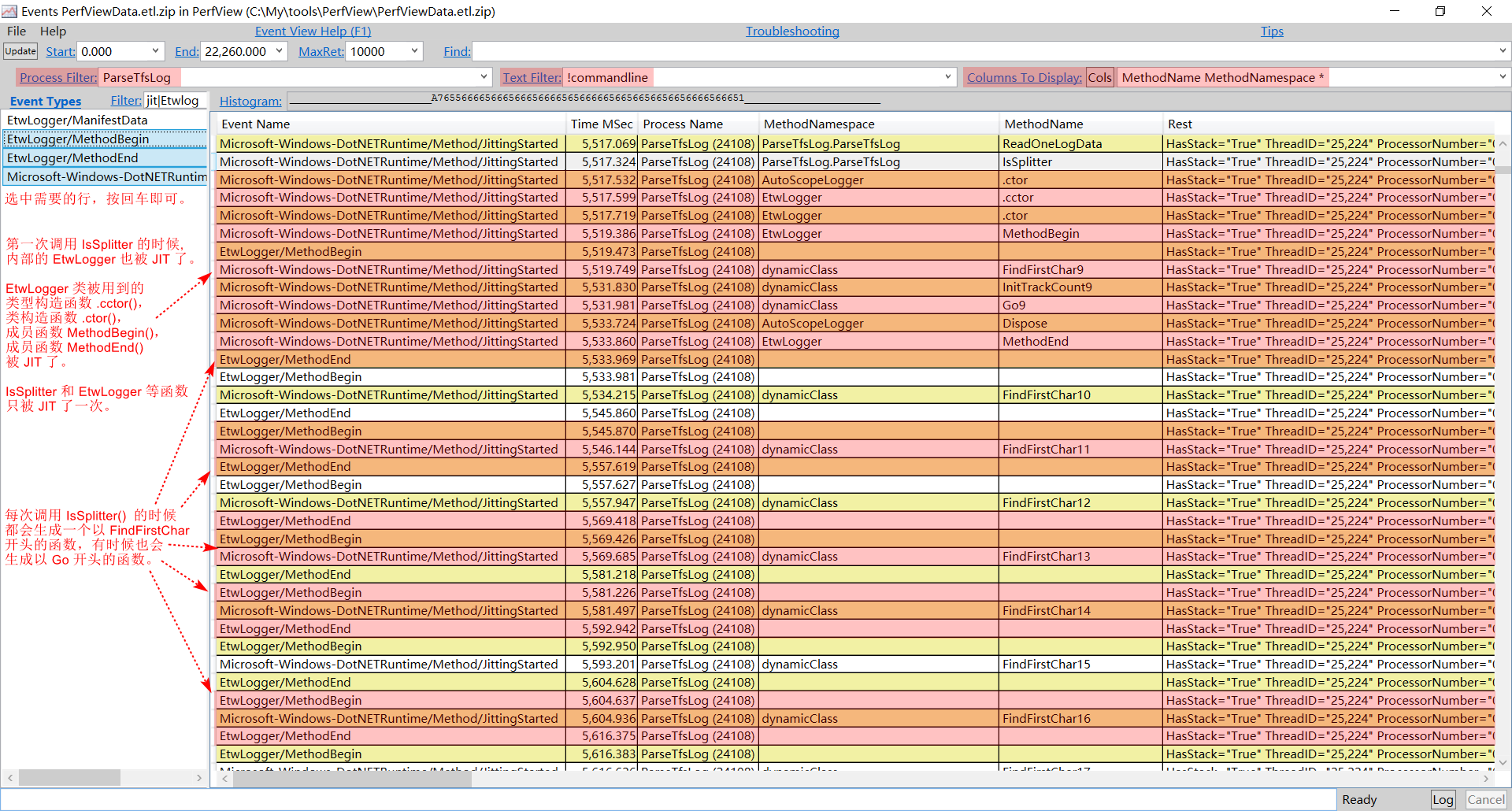
每次调用大概要消耗
11ms(5616.375 - 5604.637 = 11.738 ms)。至于为什么不带
Compiled选项的正则表达式在调用过程中没有多余的JIT,与疑问7一起到源码中找答案。 -
为什么把
Regex变量从局部改成全局变量后运行速度有了极大提升?除了避免重复实例化,还有哪些提升?修改代码,把局部变量改成全局变量,编译。再次使用
PerfView采集性能数据并分析,如下图: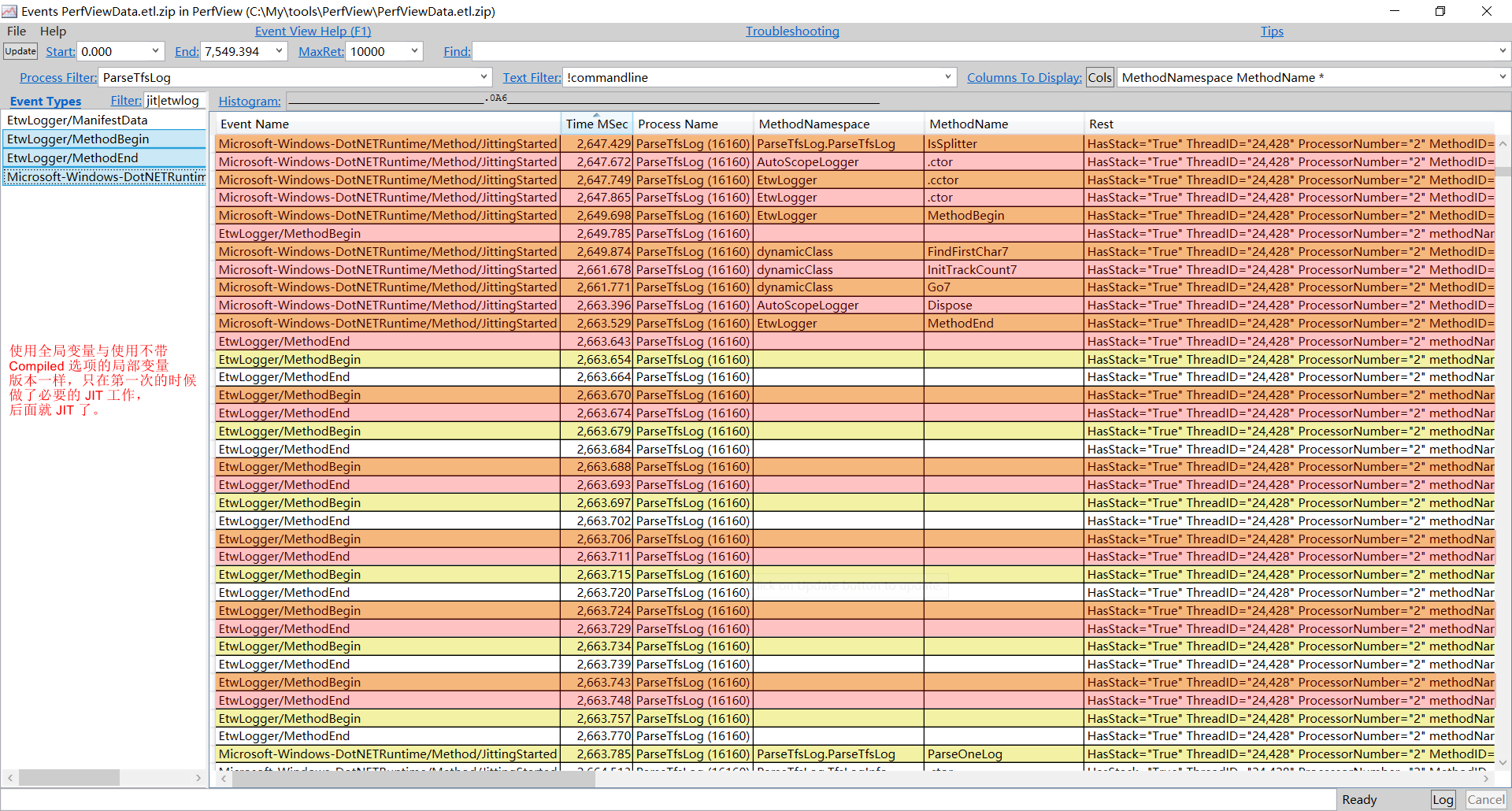
可以发现与使用不带
Compiled选项的局部变量版本一样,只发生了一次JIT。所以把局部变量改成全局变量后,除了避免了重复实例化的开销(很小),更重要的是避免了多余的JIT操作。 -
为什么
PerfView收集到的采样数据,大部分发生在MatchCollections.Count内部,极少发生在Regex的构造函数内部?(使用带Compiled选项的正则表达式的时候)Regex构造函数只被JIT了一次,后面的调用都是在执行原生代码,执行速度非常快。而MatchCollections.Count每次执行的时候都需要执行JIT(每次都需要10ms以 上),所以大部分数据在MatchCollections.Count内部,是非常合理的。 -
Regex.IsMatch()是如何使用缓存的?Regex.IsMatch()有很多重载版本,最后都会调用下面的版本:static bool IsMatch(String input, String pattern, RegexOptions options, TimeSpan matchTimeout) { return new Regex(pattern, options, matchTimeout, true).IsMatch(input); }该函数会在内部构造一个临时的
Regex对象,并且构造函数的最后一个参数useCaChe的值是true,表示使用缓存。
疑问5 和 疑问6 的答案在 Regex 的构造函数中,先看看 Regex 的构造函数。
Regex 构造函数
Regex 有很多个构造函数,列举如下:
public Regex(String pattern)
: this(pattern, RegexOptions.None, DefaultMatchTimeout, false) {}
public Regex(String pattern, RegexOptions options)
: this(pattern, options, DefaultMatchTimeout, false) {}
Regex(String pattern, RegexOptions options, TimeSpan matchTimeout)
: this(pattern, options, matchTimeout, false) {}注意: 以上构造函数的最后一个参数都是
false,表示不使用缓存。
这些构造函数最后都会调用下面的私有构造函数(代码有所精简调整):
private Regex(String pattern, RegexOptions options, TimeSpan matchTimeout, bool useCache)
{
string cultureKey = null;
if ((options & RegexOptions.CultureInvariant) != 0)
cultureKey = CultureInfo.InvariantCulture.ToString(); // "English (United States)"
else
cultureKey = CultureInfo.CurrentCulture.ToString();
// 构造缓存用到的 key,包含 options,culture 和 pattern
String key = ((int) options).ToString(NumberFormatInfo.InvariantInfo) + ":" + cultureKey + ":" + pattern;
CachedCodeEntry cached = LookupCachedAndUpdate(key);
this.pattern = pattern;
this.roptions = options;
if (cached == null) {
// 如果没找到缓存就生成类型为 RegexCodes 的 code,包含了字节码等信息
RegexTree tree = RegexParser.Parse(pattern, roptions);
code = RegexWriter.Write(tree);
// 如果指定了 useCache 参数就缓存起来,下次就能在缓存中找到了
if (useCache)
cached = CacheCode(key);
} else {
// 如果找到了缓存就使用缓存中的信息
code = cached._code;
factory = cached._factory;
runnerref = cached._runnerref;
}
// 如果指定了 Compiled 选项,并且 factory 是空(没使用缓存,或者缓存中的 _factory 是空)
if (UseOptionC() && factory == null) {
// 根据 code 和 roptions 生成 factory
factory = Compile(code, roptions);
// 需要缓存就缓存起来
if (useCache && cached != null)
cached.AddCompiled(factory);
}
}注意: 带
bool useCache标记的构造函数是私有的,也就是说不能直接使用此构造函数实例化Regex。
首先会根据 option + culture + pattern 到缓存中查找。如果没找到缓存就生成类型为 RegexCodes 的 code(包含了字节码等信息),如果找到了缓存就使用缓存中的信息。 如果指定了 Compiled 选项(UseOptionC() 会返回 true),并且 factory 是空(没使用缓存或者缓存中的 _factory 是空),就会执行 Compile() 函数,并把返回值保存到 factory 成员中。
至此,可以回答第 5 6 两个疑问了。
-
直接实例化的
Regex对象会使用正则表达式引擎内部的缓存吗?会优先根据
option + culture + pattern到缓存中查找,但是否更新缓存是由最后一个参数useCache决定的,与是否指定Compiled选项无关。 -
正则表达式引擎内部根据什么缓存的?
根据
option + culture + pattern缓存。
疑问7 与由 疑问1 引申出来的 JIT 问题是一个问题。之所以会 JIT,是因为有需要 JIT 的代码,如果不断有新的动态方法产生出来并执行,那么就需要不断地 JIT。由于此问题涉及到的代码量比较大,逻辑比较复杂,需要深入 .NET 源码进行查看。为了更好的理解整个过程,我简单梳理了 IsSpitter() 函数中涉及到的关键类以及类之间的关系,整理成下图,供参考。
流程 & 类关系梳理

看完上图后,可以继续看剩下的 JIT 问题了。因为大多数 JIT 都出现在 MatchCollection.Count 中,可以由此切入。
MatchCollection.Count
实现代码如下:
public int Count {
get {
if (_done)
return _matches.Count;
GetMatch(infinite);
return _matches.Count;
}
}Count 会调用 GetMatch() 函数,而 GetMatch() 函数会不断调用 _regex.Run() 函数。
_regex 是哪来的呢?在构造 MatchCollection 实例时传过来的。
MatchCollection 是由 Regex.Matches() 实例化的,代码如下(去掉了判空逻辑):
public MatchCollection Matches(String input, int startat) {
return new MatchCollection(this, input, 0, input.Length, startat);
}该函数会实例化一个 MatchCollection 对象,并把当前 Regex 实例作为第一个参数传给 MatchCollection 的构造函数。该参数会被保存到 MatchCollection 实例的 _regex 成员中。
接下来继续查看 Regex.Run 函数的实现。
Regex.Run()
具体实现代码如下(代码有精简):
internal Match Run(bool quick, int prevlen, String input, int beginning, int length, int startat) {
Match match;
// 使用缓存的时候,可能从缓存中拿到一个有效的 runner,其它情况下都是 null。
RegexRunner runner = (RegexRunner)runnerref.Get();
// 不使用缓存的时候 runner是 null
if (runner == null) {
// 如果 factory 不为空就通过 factory 创建一个 runner。
// 使用了 Compiled 标志创建的 Regex 实例的 factory 不为空
if (factory != null)
runner = factory.CreateInstance();
else
runner = new RegexInterpreter(code, UseOptionInvariant() ? CultureInfo.InvariantCulture : CultureInfo.CurrentCulture);
}
try {
// 调用 RegexRunner.Scan 扫描匹配项。
match = runner.Scan(this, input, beginning, beginning + length, startat, prevlen, quick, internalMatchTimeout);
} finally {
runnerref.Release(runner);
}
return match;
}逻辑还是非常清晰的,先找到或者创建(通过 factory.CreateInstance() 或者直接 new)一个类型为 RegexRunner 实例 runner,然后调用 runner->Scan() 进行匹配。
对于使用 Compiled 选项创建的 Regex,其 factory 成员变量会在 Regex 构造函数中赋值,对应的语句是 factory = Compile(code, roptions); ,类型是 CompiledRegexRunnerFactory。
我们先来看看 CompiledRegexRunnerFactory.CreateInstance() 的实现。
CompiledRegexRunnerFactory.CreateInstance()
代码如下:
protected internal override RegexRunner CreateInstance() {
CompiledRegexRunner runner = new CompiledRegexRunner();
new ReflectionPermission(PermissionState.Unrestricted).Assert();
// 设置关键的动态函数,这三个函数是在 `RegexLWCGCompiler`
// 类的 `FactoryInstanceFromCode()` 中生成的。
runner.SetDelegates(
(NoParamDelegate) goMethod.CreateDelegate(typeof(NoParamDelegate)),
(FindFirstCharDelegate) findFirstCharMethod.CreateDelegate(typeof(FindFirstCharDelegate)),
(NoParamDelegate) initTrackCountMethod.CreateDelegate(typeof(NoParamDelegate))
);
return runner;
}该函数返回的是 CompiledRegexRunner 类型的 runner。在返回之前会先调用 runner.SetDelegates 为对应的关键函数(Go, FindFirstChar, InitTrackCount)赋值。参数中的 goMethod, findFirstCharMethod, initTrackCountMethod 是在哪里赋值的呢?在 Regex.Compile() 函数中赋值的。
Regex.Compile()
Regex.Compile() 会直接转调 RegexCompiler 的静态函数 Compile(),相关代码如下(有调整):
internal static RegexRunnerFactory Compile(RegexCode code, RegexOptions options) {
RegexLWCGCompiler c = new RegexLWCGCompiler();
return c.FactoryInstanceFromCode(code, options);
}该函数直接调用了 RegexLWCGCompiler 类的 FactoryInstanceFromCode() 成员函数。相关代码如下(有删减):
internal RegexRunnerFactory FactoryInstanceFromCode(RegexCode code, RegexOptions options) {
// 获取唯一标识符,也就是FindFirstChar后面的数字
int regexnum = Interlocked.Increment(ref _regexCount);
string regexnumString = regexnum.ToString(CultureInfo.InvariantCulture);
// 生成动态函数Go
DynamicMethod goMethod = DefineDynamicMethod("Go" + regexnumString, null, typeof(CompiledRegexRunner));
GenerateGo();
// 生成动态函数FindFirstChar
DynamicMethod firstCharMethod = DefineDynamicMethod("FindFirstChar" + regexnumString, typeof(bool), typeof(CompiledRegexRunner));
GenerateFindFirstChar();
// 生成动态函数InitTrackCount
DynamicMethod trackCountMethod = DefineDynamicMethod("InitTrackCount" + regexnumString, null, typeof(CompiledRegexRunner));
GenerateInitTrackCount();
return new CompiledRegexRunnerFactory(goMethod, firstCharMethod, trackCountMethod);
}该函数非常清晰易懂,但却是非常关键的一个函数,会生成三个动态函数(也就是通过 PerfView 采集到的 FindFirstCharXXX,GoXXX,InitTrackCountXXX),最后会构造一个类型为 CompiledRegexRunnerFactory 的实例,并把生成的动态函数作为参数传递给 CompiledRegexRunnerFactory 的构造函数。
至此,已经找到生成动态函数的地方了。动态函数是什么时候被调用的呢?在 runner.Scan() 函数中被调用的。
RegexRunner.Scan()
关键代码如下(做了大量删减):
Match Scan(Regex regex, String text, int textbeg, int textend, int textstart, int prevlen, bool quick, TimeSpan timeout) {
for (; ; ) {
if (FindFirstChar()) {
Go();
if (runmatch._matchcount [0] > 0)
return TidyMatch(quick);
}
}
} 可以看到,Scan() 函数内部会调用 FindFirstChar() 和 Go(),而且只有当 FindFirstChar() 返回 true 的时候,才会调用 Go()。这两个函数是虚函数,具体的子类会重写。对于 Compiled 类型的正则表达式,对应的 runner 类型是 CompiledRegexRunner。这三个关键的函数实现如下:
internal sealed class CompiledRegexRunner : RegexRunner {
NoParamDelegate goMethod;
FindFirstCharDelegate findFirstCharMethod;
NoParamDelegate initTrackCountMethod;
protected override void Go() {
goMethod(this);
}
protected override bool FindFirstChar() {
return findFirstCharMethod(this);
}
protected override void InitTrackCount() {
initTrackCountMethod(this);
}
}现在可以回答疑问7 及疑问1 引申出来的 JIT 问题了。
-
什么时候会生成动态方法?生成的动态方法是在哪里调用的?
在指定了
Compiled标志的Regex的构造函数内部会调用RegexCompiler.Compile()函数,Compile()函数又会调用RegexLWCGCompiler.FactoryInstanceFromCode(),FactoryInstanceFromCode()函数内部会分别调用GenerateFindFirstChar(),GenerateGo(),GenerateInitTrackCount()生成对应的动态方法。在执行
MatchCollection.Count的时候,会调用MatchCollection.GetMatch()函数,GetMatch()函数会调用对应RegexRunner的Scan()函数。Scan()函数会调用RegexRunner.FindFirstChar(),而CompiledRegexRunner类型中的FindFirstChar()函数调用的是设置好的动态函数。
Compiled 与 非 Compiled 对比
1. 构造函数
**带 Compiled 选项的 Regex **
useCache 传递的是 false,表示不使用缓存。因为指定了 RegexOptions.Compiled 选项, Regex 的构造函数内部会调用 RegexCompiler.Compile() 函数,Compile() 函数又会调用 RegexLWCGCompiler.FactoryInstanceFromCode(),FactoryInstanceFromCode() 函数内部会分别调用 GenerateFindFirstChar(), GenerateGo(), GenerateInitTrackCount() 生成对应的动态方法,然后返回 CompiledRegexRunnerFactory 类型的实例。如下图:

**不带 Compiled 选项的 Regex **
构造函数与 Compiled 的基本一致,useCache 传递的也是 false,不使用缓存。因为 UseOptionC() 返回的是 false,所以不会执行 Compile() 函数。所以 factory 成员变量是 null。
这里就不贴图了。
2. matches.Count
**带 Compiled 选项的 Regex **

MatchCollection.Count 内部会调用 GetMatch() 函数,GetMatch() 函数会调用对应 RegexRunner 的 Scan() 函数(这里的 runner 类型是 CompiledRegexRunner)。Scan() 内部会调用 FindFirstChar() 函数,而 CompiledRegexRunner 类型的 FindFirstChar() 函数内部调用的是设置好的动态方法。
**不带 Compiled 选项的 Regex **

与带 Compiled 版本的调用栈基本一致,不一样的是这里 runner 的类型是 RegexInterpreter,该类型的 FindFirstChar() 函数调用的代码不是动态生成的。
3. runner 赋值
当 runner 是 null 的时候,需要根据情况获取对应的 runner。
**带 Compiled 选项的 Regex **
factory 成员在 Regex 构造函数里通过 Compile() 赋过值,runner 会通过下图 1306 行的 factory.CreateInstance() 赋值。
**不带 Compiled 选项的 Regex **
factory 成员没有被赋过值,因此是空的,runner 会通过下图 1308 行的 new RegexInterpreter() 赋值。

总结
- 不要在循环内部创建编译型的正则表达式(带
Compiled选项),会频繁导致JIT的发生进而影响效率。 Regex.IsMatch()也会创建 Regex 实例,但是最后一个参数bUseCache是true,表示使用缓存。Regex构造函数的最后一个参数bUseCache是true的时候才会更新缓存。- 正则表达式引擎内部会根据
option + culture + pattern查找缓存。








【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构