Spring 使用 JPA
导GAV先:
<dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.12</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <!-- Spring --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-core</artifactId> <version>5.0.5.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <!-- hibernate start --> <!-- spring data jpa --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.data</groupId> <artifactId>spring-data-jpa</artifactId> <version>2.5.0</version> </dependency> <!-- hibernate --> <dependency> <groupId>org.hibernate</groupId> <artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId> <version>5.4.0.Final</version> </dependency> <!-- MySql --> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>5.1.38</version> </dependency> <!-- log日志 --> <dependency> <groupId>log4j</groupId> <artifactId>log4j</artifactId> <version>1.2.17</version> </dependency>
然后创建JPA的配置文件xml :
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <persistence xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence/persistence_2_0.xsd" version="2.0"> <!--配置持久化单元 name:持久化单元名称 transaction-type:事务类型 RESOURCE_LOCAL:本地事务管理 JTA:分布式事务管理 --> <persistence-unit name="myJpa" transaction-type="RESOURCE_LOCAL"> <!--配置JPA规范的服务提供商 --> <provider>org.hibernate.jpa.HibernatePersistenceProvider</provider> <properties> <!-- 数据库驱动 --> <property name="javax.persistence.jdbc.driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" /> <!-- 数据库地址 --> <property name="javax.persistence.jdbc.url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jpa" /> <!-- 数据库用户名 --> <property name="javax.persistence.jdbc.user" value="root" /> <!-- 数据库密码 --> <property name="javax.persistence.jdbc.password" value="root" /> <!--jpa提供者的可选配置:我们的JPA规范的提供者为hibernate,所以jpa的核心配置中兼容hibernate的配 --> <property name="hibernate.show_sql" value="true" /> <property name="hibernate.format_sql" value="true" /> <property name="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto" value="create" /> </properties> </persistence-unit> </persistence>
因为实际提供者是 hibernate 所以这里也配了一下 hibernate的配置。
这么文件名字一定要是 persistence.xml 而且 一定要放在 resource 下面的 META-INF 文件夹下 不然会找不到报错!!!
第三步:创建对应的 Bena ,并且 把Bean中的字段映射到 数据库表中:
package com.sze.jpa.bean; import javax.persistence.*; /** *@Entity 声明实体类 * @Table 配置实体类和表的映射关系 name是映射表名字 */ @Entity @Table(name = "cst_customer") /** * @Id 主键 * @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) 设置自增长 * @Column 映射表字段名 */ public class Customer { @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) @Column(name = "cust_id") private Long custId; //ID @Column(name = "cust_name") private String custName; //名字 @Column(name = "cust_source") private String custSource; //来源 @Column(name = "cust_industry") private String custIndustry; //所属行业 @Column(name = "cust_level") private String custLevel; //级别 @Column(name = "cust_address") private String custAddress; //地址 @Column(name = "cust_phone") private String custPhone; //联系方式 public Customer() { } public Customer(Long custId, String custName, String custSource, String custIndustry, String custLevel, String custAddress, String custPhone) { this.custId = custId; this.custName = custName; this.custSource = custSource; this.custIndustry = custIndustry; this.custLevel = custLevel; this.custAddress = custAddress; this.custPhone = custPhone; } public Long getCustId() { return custId; } public void setCustId(Long custId) { this.custId = custId; } public String getCustName() { return custName; } public void setCustName(String custName) { this.custName = custName; } public String getCustSource() { return custSource; } public void setCustSource(String custSource) { this.custSource = custSource; } public String getCustIndustry() { return custIndustry; } public void setCustIndustry(String custIndustry) { this.custIndustry = custIndustry; } public String getCustLevel() { return custLevel; } public void setCustLevel(String custLevel) { this.custLevel = custLevel; } public String getCustAddress() { return custAddress; } public void setCustAddress(String custAddress) { this.custAddress = custAddress; } public String getCustPhone() { return custPhone; } public void setCustPhone(String custPhone) { this.custPhone = custPhone; } @Override public String toString() { return "Customer{" + "custId=" + custId + ", custName='" + custName + '\'' + ", custSource='" + custSource + '\'' + ", custIndustry='" + custIndustry + '\'' + ", custLevel='" + custLevel + '\'' + ", custAddress='" + custAddress + '\'' + ", custPhone='" + custPhone + '\'' + '}'; } }
【注解一定得是JPA的规范提供的注解一定要导入javax.persistence下的 包】里面的注解也有解释,认真看看即可。下面是常用的注解:
@Entity
作用:指定当前类是实体类。
@Table
作用:指定实体类和表之间的对应关系。
属性:
name:指定数据库表的名称
@Id
作用:指定当前字段是主键。
@GeneratedValue
作用:指定主键的生成方式。。
属性:
strategy :指定主键生成策略。
@Column
作用:指定实体类属性和数据库表之间的对应关系
属性:
name:指定数据库表的列名称。
unique:是否唯一
nullable:是否可以为空
inserttable:是否可以插入
updateable:是否可以更新
columnDefinition: 定义建表时创建此列的DDL
secondaryTable: 从表名。如果此列不建在主表上(默认建在主表),该属性定义该列所在从表的名字搭建开发环境[重点]
下面我们做一个插入一条数据测试:
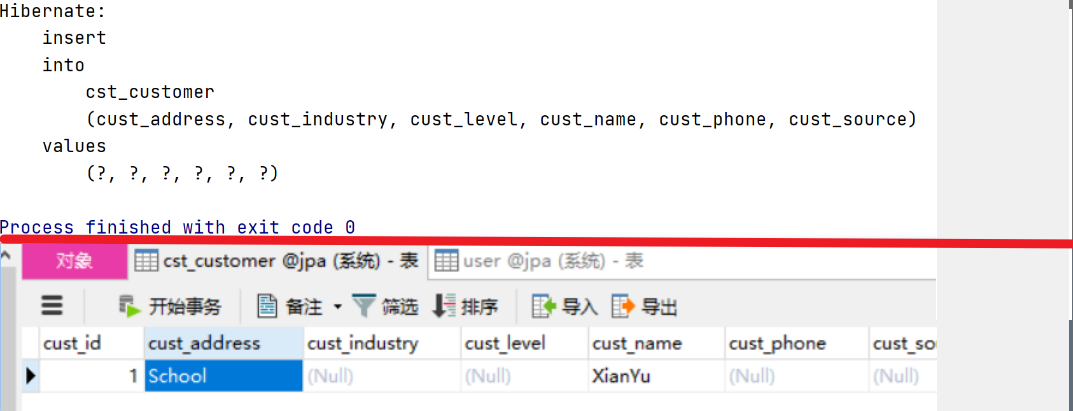
package com.sze.jpa; import com.sze.jpa.bean.Customer; import org.junit.Test; import javax.persistence.EntityManager; import javax.persistence.EntityManagerFactory; import javax.persistence.EntityTransaction; import javax.persistence.Persistence; public class TestJpa { @Test public void testSave(){ //实体管理类工厂,借助Persistence的静态方法获取 其中传递的参数为持久化单元名称,需要jpa配置文件中指定 EntityManagerFactory factory = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("myJpa"); //创建实体管理类 EntityManager entityManager = factory.createEntityManager(); //获取事务对象 EntityTransaction transaction = entityManager.getTransaction(); //开启事务 transaction.begin(); //创建一个对象 Customer customer = new Customer(); customer.setCustName("XianYu"); customer.setCustAddress("School"); //保存操作(插入) entityManager.persist(customer); //提交事务 transaction.commit(); //释放资源 entityManager.close(); factory.close(); } }
这只是简单使用JPA的实例
结果:
本文来自博客园,作者:咸瑜,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/bi-hu/p/15503112.html



