5. SpringBoot 导入配置 @PropertySource 、 @ImportResource 、@Bean 注解
@PropertySource 、 @ImportResource 、@Bean 三个注解讲解:
@PropertySource
之前4-1、4-2、4-3 做实验的时候 ,把配置数据都写在了SpringBoot的根配置文件上,是全局的,那这样肯定是不行的,如果写很多个yml文件或properties文件也会很乱,也可能会重复。
@PropertySource:加载指定的配置文件;
新建一个s1.properties 文件

person.last-name=BiHu person.age=18 person.boss=false person.birth=2025/10/10 person.maps.k1=value1 person.maps.k2=value2 person.lists=v1,v2,v3,v4 person.dog.name=小勾勾 person.dog.age=2
然后JavaBean中指定用某个配置文件:

package com.bihu.Bean; import org.hibernate.validator.constraints.Email; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties; import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.util.Date; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; @PropertySource("classpath:s1.properties") //这个类 指定用这个配置文件【classpath 这个不多说了】 @Component @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person") public class JavaBean { private String lastName; private Integer age; private Boolean boss; private Date birth; private Map<String,Object> maps; private List<Object> lists; private Dog dog; @Override public String toString() { return "Person{" + "lastName='" + lastName + '\'' + ", age=" + age + ", boss=" + boss + ", birth=" + birth + ", maps=" + maps + ", lists=" + lists + ", dog=" + dog + '}'; } public String getLastName() { return lastName; } public void setLastName(String lastName) { this.lastName = lastName; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } public Boolean getBoss() { return boss; } public void setBoss(Boolean boss) { this.boss = boss; } public Date getBirth() { return birth; } public void setBirth(Date birth) { this.birth = birth; } public Map<String, Object> getMaps() { return maps; } public void setMaps(Map<String, Object> maps) { this.maps = maps; } public List<Object> getLists() { return lists; } public void setLists(List<Object> lists) { this.lists = lists; } public Dog getDog() { return dog; } public void setDog(Dog dog) { this.dog = dog; } }
可以看到 里面指定了用 classpath 目录下的s1.properties [classpath 是什么 自己去百度]
注意事项: 如果你SpringBoot 配置 也有一样的 Person 数据,那么因为权限大范围大 所以无论是否指定配置文件 都用SpringBoot的,但一般不会那样做。一般SpringBoot配置文件都是配SpringBoot自己。
有了这个注解 除了SpringBoot配置文件,其他的配置文件你都不用担心 "名字" 冲突。

就算s1 和 s2 一样的配置都是 Person 都不怕,因为指定了用s1。
完整写法: @PropertySource(value = {"classpath:xxx.properties"})
@ImportResource:
@ImportResource:导入Spring的配置文件,让配置文件里面的内容生效;
因为 Spring Boot里面没有Spring的配置文件,我们自己编写的配置文件,也不能自动识别; 想让Spring的配置文件生效,加载进来 就在主配置类上用这个注解,相当于导入了Spring配置文件xml
主配置类其实就是那个入口函数。
测试: 新建一个Spring配置文件 => 在主配置类 Application.java 使用@ImportResource注解 => 用SpringBoot单元测试 测试配置文件是否存在Bean:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- 创建Bean s1 --> <bean id="s1" class="com.bihu.Bean.JavaBean"></bean> </beans>
主配置类 Application.java:

package com.bihu; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ImportResource; @ImportResource(locations = {"classpath:SpringApplication.xml"}) //导入Spring配置文件,可以导入多个【注意属性是locations】 @SpringBootApplication public class Application { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args); } }
Test.java :测试类:

package com.bihu; import com.bihu.Bean.JavaBean; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner; @RunWith(SpringRunner.class) @SpringBootTest public class ApplicationTests { //测试Bean @Autowired ApplicationContext ioc; @Test public void contextLoads() { //如果主配置类未导入@ImportResource注解,那么会显示false System.out.println(ioc.containsBean("s1")); //查看Spring配置文件是否存在Bean : s1 } }
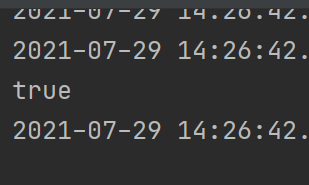
运行可以发现 是teue,所以说 ,Spring配置可以导入多个,但如果不用@ImportSource 相当于没有,其次注意不是Value属性 是 locations 属性!
我们都是SpringBoot 了 ,怎么可能还用那种?退化? 我们要用全注解方式:
SpringBoot推荐给容器中添加组件的方式;推荐使用全注解的方式
配置文件 = 配置类 所以我们用配置类!
1、@Configuration : 指明一个类是 配置类,用来替代Spring配置文件。
2、使用@Bean给容器中添加组件
其中:配置类中方法名相当于组件默认ID,返回的值会添加到容器中。
新建一个配置类:

package com.bihu.config; import com.bihu.Contorller.HelloController; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration //指明当前类是 配置类,用来替代Spring配置文件 public class MyAppConfig { @Bean //将方法的返回值添加到容器中;容器中这个组件默认的id就是方法名 public HelloController helloController(){ System.out.println("注解@Bean生效 组件返回值将被加入到容器 默认id为:helloController"); return new HelloController(); } }
然后在测试文件测试 看下 helloController 组件是否被加入到容器:

package com.bihu; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner; @RunWith(SpringRunner.class) @SpringBootTest public class ApplicationTests { @Autowired ApplicationContext ioc; @Test public void contextLoads() { System.out.println(ioc.containsBean("helloController")); } }
运行结果:
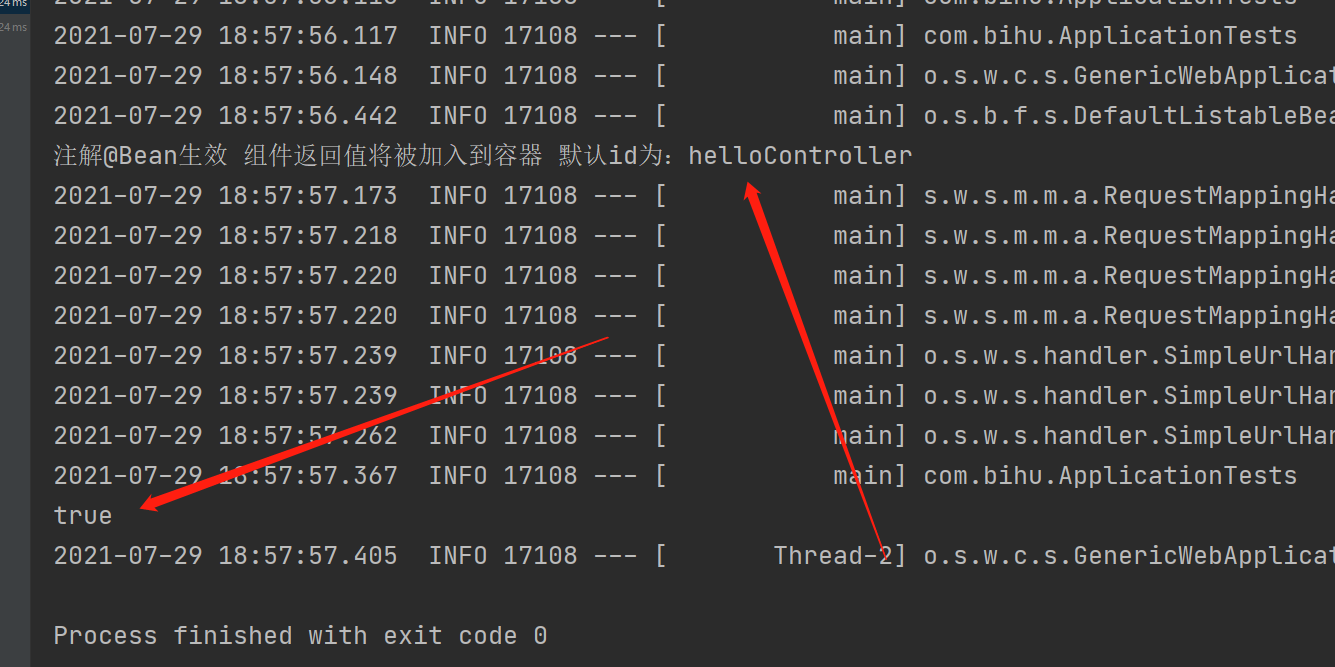
所以我们用配置类就好了 他制动会执行加入的。。。其他的你也要懂。
本文来自博客园,作者:咸瑜,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/bi-hu/p/15076609.html




