Android Okhttp3的使用与运行流程
基本使用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | fun okhttp3Demo() { val client: OkHttpClient = OkHttpClient.Builder().build()//创建OkHttpClient val r: Request = Request.Builder().url("").build()//创建Request请求 val call:okhttp3.Call = client.newCall(r)//创建一个Call //添加回调并且添加到等待缓存 call.enqueue(object : okhttp3.Callback { override fun onFailure(call: okhttp3.Call, e: IOException) { } override fun onResponse(call: okhttp3.Call, response: okhttp3.Response) { } }) //call.execute()//直接加入运行缓存 } |
运行过程图
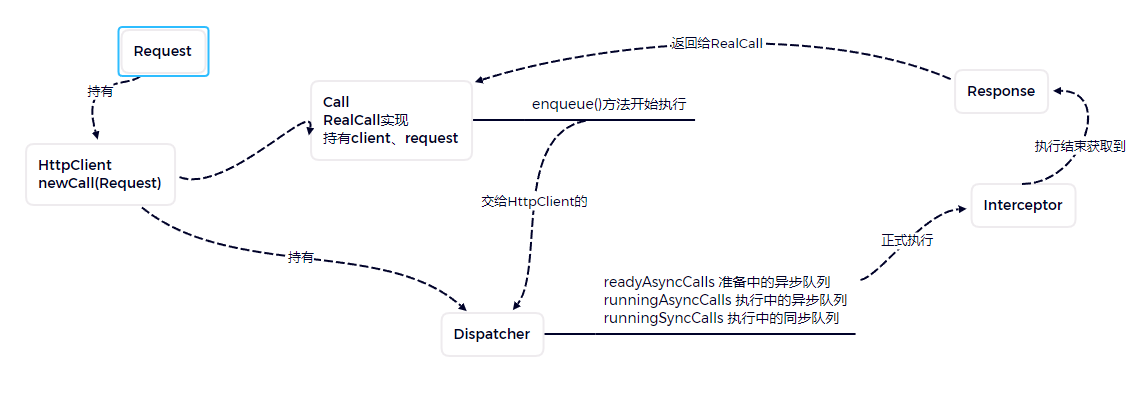
Call接口的实现类RealCall
HttpClient调用newCall(r:Request)方法 创建Call的实现类RealCall
1 2 3 | @Override public Call newCall(Request request) { return RealCall.newRealCall(this, request, false /* for web socket */);} |
跳转到RealCall的newRealCall方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 | static RealCall newRealCall(OkHttpClient client, Request originalRequest, boolean forWebSocket) { // Safely publish the Call instance to the EventListener. RealCall call = new RealCall(client, originalRequest, forWebSocket); call.eventListener = client.eventListenerFactory().create(call); return call; } |
找到RealCall的enqueue()方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | @Override public void enqueue(Callback responseCallback) { synchronized (this) { if (executed) throw new IllegalStateException("Already Executed"); executed = true; } captureCallStackTrace(); eventListener.callStart(this); //调用了HttpClient的Dispatcher的enqueue方法 此时创建了一个Runable的实现类 AsyncCall client.dispatcher().enqueue(new RealCall.AsyncCall(responseCallback));} |
先看AsyncCall 实现了NamedRunnable接口 NamedRunnable实现了Runnable 其run方法调用了AsyncCall的execute()方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | public abstract class NamedRunnable implements Runnable { protected final String name; public NamedRunnable(String format, Object... args) { this.name = Util.format(format, args); } @Override public final void run() { String oldName = Thread.currentThread().getName(); Thread.currentThread().setName(name); try { execute(); } finally { Thread.currentThread().setName(oldName); } } protected abstract void execute();} |
进入AsyncCall方法的execute()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 | @Override protected void execute() { try{ //...other //添加interceptors拦截器 责任链 Response response = getResponseWithInterceptorChain(); //...other } finally { client.dispatcher().finished(this); } } Response getResponseWithInterceptorChain() throws IOException { // Build a full stack of interceptors. List<Interceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<>(); interceptors.addAll(client.interceptors()); interceptors.add(retryAndFollowUpInterceptor); interceptors.add(new BridgeInterceptor(client.cookieJar())); interceptors.add(new CacheInterceptor(client.internalCache())); interceptors.add(new ConnectInterceptor(client)); if (!forWebSocket) { interceptors.addAll(client.networkInterceptors()); } interceptors.add(new CallServerInterceptor(forWebSocket)); Interceptor.Chain chain = new RealInterceptorChain(interceptors, null, null, null, 0, originalRequest, this, eventListener, client.connectTimeoutMillis(), client.readTimeoutMillis(), client.writeTimeoutMillis()); return chain.proceed(originalRequest); } |
RealInterceptorChain实现拦截器功能 分别调用拦截器的proceed()方法执行网络请求返回Response
Dispatcher
Call看完接着进入HttpClient的Dispatcher的enqueue方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 | //准备中的异步队列 private final Deque<RealCall.AsyncCall> readyAsyncCalls = new ArrayDeque<>(); //执行中的异步队列 private final Deque<RealCall.AsyncCall> runningAsyncCalls = new ArrayDeque<>(); //执行中的同步队列 private final Deque<RealCall> runningSyncCalls = new ArrayDeque<>(); void enqueue(RealCall.AsyncCall call) { synchronized (this) { readyAsyncCalls.add(call); } //处理和执行线程 promoteAndExecute(); } private boolean promoteAndExecute() { assert (!Thread.holdsLock(this)); List<RealCall.AsyncCall> executableCalls = new ArrayList<>(); boolean isRunning; synchronized (this) {//将线程进行缓存处理 for (Iterator<RealCall.AsyncCall> i = readyAsyncCalls.iterator(); i.hasNext(); ) { //从readyAsyncCalls中取出可执行线程并添加到runningAsyncCalls中 并执行线程 RealCall.AsyncCall asyncCall = i.next(); if (runningAsyncCalls.size() >= maxRequests) break; // Max capacity. if (runningCallsForHost(asyncCall) >= maxRequestsPerHost) continue; // Host max capacity. i.remove(); executableCalls.add(asyncCall); runningAsyncCalls.add(asyncCall); } isRunning = runningCallsCount() > 0; } for (int i = 0, size = executableCalls.size(); i < size; i++) { RealCall.AsyncCall asyncCall = executableCalls.get(i); //调用RealCall的executeOn方法 其内部执行 executorService.execute(this);线程池启动线程 asyncCall.executeOn(executorService()); } return isRunning; } |
关于Dispatcher内部的线程池--线程池另外写一个随笔
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | public synchronized ExecutorService executorService() { if (executorService == null) { //创建一个线程池 executorService = new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(), Util.threadFactory("OkHttp Dispatcher", false)); } return executorService; } |
分类:
Android 源码学习
标签:
Android




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 全程不用写代码,我用AI程序员写了一个飞机大战
· DeepSeek 开源周回顾「GitHub 热点速览」
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· MongoDB 8.0这个新功能碉堡了,比商业数据库还牛
· .NET10 - 预览版1新功能体验(一)