Dart学习笔记
一、数据类型
1. 字符串 和 数字 互转
// String 转为 int var one = int.parse('1'); assert(one == 1); // String 转为 double var onePointOne = double.parse('1.1'); assert(onePointOne == 1.1); // int 转为 String String oneAsString = 1.toString(); assert(oneAsString == '1'); // double 转为 String String piAsString = 3.14159.toStringAsFixed(2); assert(piAsString == '3.14');
2.字符串
关键字String用于表示字符串文字,字符串值嵌入单引号或双引号中。因此可以使用单引号或双引号来创建字符串:
var s1 = 'Single quotes work well for string literals.'; var s2 = "Double quotes work just as well."; var s3 = 'It\'s easy to escape the string delimiter.'; var s4 = "It's even easier to use the other delimiter.";
可以使用${expression}将表达式的值放在字符串中:
var s = 'string interpolation'; assert('Dart has $s, which is very handy.' == 'Dart has string interpolation, ' + 'which is very handy.'); assert('That deserves all caps. ' + '${s.toUpperCase()} is very handy!' == 'That deserves all caps. ' + 'STRING INTERPOLATION is very handy!');
使用带有单引号或双引号的三引号创建多行字符串:
var s1 = ''' You can create multi-line strings like this one. '''; var s2 = """This is also a multi-line string.""";
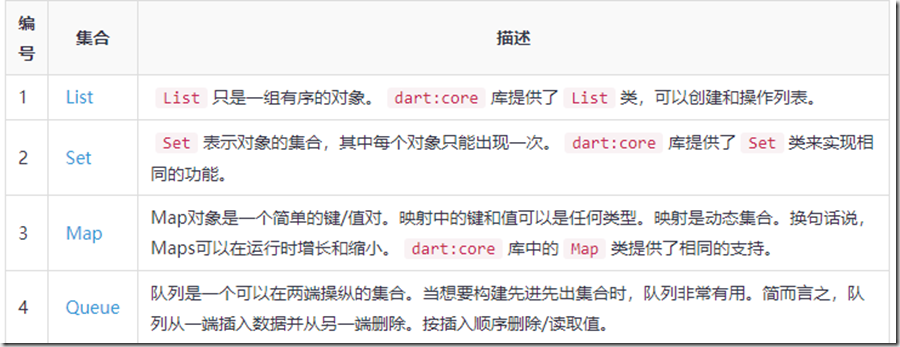
3.列表类型
声明固定长度列表的语法如下 -
var list_name = new List(initial_size)
上面的语法创建了指定大小的列表。列表不能在运行时增长或缩小。任何调整列表大小的尝试都将导致异常。
可增长列表的长度可以在运行时更改。声明和初始化可增长列表的语法如下所示,看起来像JavaScript数组文字
var list = [1, 2, 3];
列表使用从0开始的索引,其中0是第一个元素的索引,list.length-1是最后一个元素的索引。
要创建一个编译时常量的列表,请在列表文字之前添加const:
var constantList = const [1, 2, 3]; // constantList[1] = 1; // Uncommenting this causes an error.
Dart 2.3引入了扩展运算符(...)和空值感知扩展运算符(...?),它提供了一种将多个元素插入集合的简洁方法。
例如,使用扩展运算符(...)将列表的所有元素插入另一个列表:
var list = [1, 2, 3]; var list2 = [0, ...list]; assert(list2.length == 4);
Dart 2.3还引入了if和collection的集合,使用它在条件(if)和重复(for)构建集合。
var nav = [ 'Home', 'Furniture', 'Plants', if (promoActive) 'Outlet' ]; var listOfInts = [1, 2, 3]; var listOfStrings = [ '#0', for (var i in listOfInts) '#$i' ]; assert(listOfStrings[1] == '#1');
4.集合
要创建一个空集合,请使用前面带有类型参数的{},或者将{}赋给类型为Set的变量:
var halogens = {'yiibai.com', 'chlorine', 'bromine', 'iodine', 'astatine'}; var names = <String>{}; Set<String> names = {}; // This works, too. //var names = {}; // Creates a map, not a set.
使用add()或addAll()方法将项添加到现有集合:
var elements = <String>{}; elements.add('fluorine'); elements.addAll(halogens);
使用.length来获取集合中的项目数量:
var elements = <String>{}; elements.add('fluorine'); elements.addAll(halogens); assert(elements.length == 5);
要创建一个编译时常量的集合,请在set文字之前添加const:
final constantSet = const { 'fluorine', 'chlorine', 'bromine', 'iodine', 'astatine', }; // constantSet.add('helium'); // Uncommenting this causes an error.
5.映射
通常映射是关联键和值的对象。键和值都可以是任何类型的对象。每个键只出现一次,但可以多次使用相同的值。
var gifts = { // Key: Value 'first': 'partridge', 'second': 'turtledoves', 'fifth': 'golden rings' }; var nobleGases = { 2: 'helium', 10: 'neon', 18: 'argon', };
或者:
var gifts = Map(); gifts['first'] = 'partridge'; gifts['second'] = 'turtledoves'; gifts['fifth'] = 'golden rings'; var nobleGases = Map(); nobleGases[2] = 'helium'; nobleGases[10] = 'neon'; nobleGases[18] = 'argon';
像在JavaScript中一样,将新的键值对添加到现有映射:
var gifts = {'first': 'partridge'}; assert(gifts['first'] == 'partridge');
以与在JavaScript中相同的方式从映射中检索值:
var gifts = {'first': 'partridge'}; assert(gifts['first'] == 'partridge');
如果查找不在映射中的键,则将返回null:
var gifts = {'first': 'partridge'}; assert(gifts['fifth'] == null);
使用.length来获取映射中键值对的数量:
var gifts = {'first': 'partridge'}; gifts['fourth'] = 'calling birds'; assert(gifts.length == 2);
要创建一个编译时常量的映射,请在map文字之前添加const关键字:
final constantMap = const { 2: 'helium', 10: 'neon', 18: 'argon', }; // constantMap[2] = 'Helium'; // Uncommenting this causes an error.
6.符文
在Dart中,符文是字符串的UTF-32代码点。
Unicode为世界上所有书写系统中使用的每个字母,数字和符号定义唯一的数值。由于Dart字符串是UTF-16代码单元的序列,因此在字符串中表示32位Unicode值需要特殊语法。
String类有几个属性可用于提取符文信息。codeUnitAt和codeUnit属性返回16位代码单元。使用runes属性获取字符串的符文。
以下示例说明了符文,16位代码单元和32位代码点之间的关系。
print(clapping.codeUnits); print(clapping.runes.toList()); Runes input = new Runes( '\u2665 \u{1f605} \u{1f60e} \u{1f47b} \u{1f596} \u{1f44d}'); print(new String.fromCharCodes
(这个地方代码有点问题,应该是说 fromCharCodes 函数有这个作用)
7.符号(Symbol)
Symbol对象表示Dart程序中声明的运算符或标识符。可能永远不需要使用符号,但它们对于按名称引用标识符的API非常有用,因为缩小会更改标识符名称而不会更改标识符符号。
要获取标识符的符号,请使用符号文字,它只是#后跟标识符:
#radix
#bar
符号文字是编译时常量。
符号看起来是用在 对第三方库引用的时候,可以直接根据函数的字符串名称来实现调用函数,正常写代码似乎不会遇上,没想到什么情况会用上这个特性。具体使用参考:https://www.yiibai.com/dart/dart_programming_symbol.html
二、变量
默认值
未初始化的变量的初始值为null。即使是具有数字类型的变量的初始值也是null,因为数字与Dart中的其他变量一样,它们都是对象。
dynamic 关键字
声明没有未指定静态类型的变量则会隐式声明为 dynamic 。也可以使用dynamic关键字代替var关键字声明变量。
final和Const
final和const关键字用于声明常量。在Dart中不能修改使用final或const关键字声明变量的值。这些关键字可以与变量的数据类型一起使用,也可以与var关键字一起使用。
const关键字用于表示编译时常量。使用const关键字声明的变量是隐式final。
final关键字语法:
final variable_name // 或者 final data_type variable_name
示例:
void main() { final val1 = 12; print(val1); // 输出:12 }
const关键字语法:
const variable_name // 或者 const data_type variable_name
示例:
void main() { const pi = 3.14; const area = pi*12*12; print("The output is ${area}"); // 输出: 452.15999999999997 }
注 - 只有const变量可用于计算编译时常量。编译时常量是常量,其值将在编译时确定。
三、枚举
enum Status { none, running, stopped, paused }
四、函数
1.要指定可选的位置参数,请使用方括号[]
如:
void main() { test_param(123); } test_param(n1,[s1]) { print(n1); print(s1); }
以上代码输出:
123
null
2.可选的命名参数
与位置参数不同,必须在传递值时指定参数名称。花括号{}可用于指定可选的命名参数。
如:
void main() { test_param(123); test_param(123,s1:'hello'); test_param(123,s2:'hello',s1:'world'); } test_param(n1,{s1,s2}) { print(n1); print(s1); }
带有默认值的可选参数:
void main() { test_param(123); } void test_param(n1,{s1:12}) { print(n1); print(s1); }
3.Lambda函数
语法
[return_type]function_name(parameters)=>expression;
如:
void main() { printMsg(); print(test()); } printMsg()=> print("hello"); int test()=>123; // returning function
执行结果:
hello 123
五、接口
Dart没有声明接口的语法。类声明本身就是Dart中的接口。
类应该使用implements关键字来使用接口。实现类必须提供已实现接口的所有功能的具体实现。换句话说,类必须重新定义它希望实现的接口中的每个函数。
void main() { Calculator c = new Calculator(); print("The gross total : ${c.ret_tot()}"); print("Discount :${c.ret_dis()}"); } class Calculate_Total { int ret_tot() {} } class Calculate_Discount { int ret_dis() {} } class Calculator implements Calculate_Total,Calculate_Discount { int ret_tot() { return 1000; } int ret_dis() { return 50; } }
六、类
命名构造函数
Dart提供了命名构造函数,以使类定义多个构造函数。命名构造函数的语法如下所示:
class_name.constructor_name(param_list)
示例:
void main() { Car c1 = new Car.namedConst('EA888'); Car c2 = new Car(); } class Car { Car() { print("Non-parameterized constructor invoked"); } Car.namedConst(String engine) { print("The engine is : ${engine}"); } }
类继承和方法重写:
void main() { Child c = new Child(); c.m1(12); } class Parent { void m1(int a){ print("value of a ${a}");} } class Child extends Parent { @override void m1(int b) { print("value of b ${b}"); } }
super关键字
void main() { Child c = new Child(); c.m1(12); } class Parent { String msg = "message variable from the parent class"; void m1(int a){ print("value of a ${a}");} } class Child extends Parent { @override void m1(int b) { print("value of b ${b}"); super.m1(13); print("${super.msg}") ; } }
七、对象
级联运算符(..)
class Student { void test_method() { print("This is a test method"); } void test_method1() { print("This is a test method1"); } } void main() { new Student() ..test_method() ..test_method1(); }
八、集合
迭代集合
dart:core库的Iterator类可以进行集合遍历。每个集合都有一个迭代器属性。此属性返回指向集合中对象的迭代器
import 'dart:collection'; void main() { Queue numQ = new Queue(); numQ.addAll([11,22,33]); Iterator i= numQ.iterator; while(i.moveNext()) { print(i.current); } }
九、异常
自定义异常
语法:
class Custom_exception_Name implements Exception { // can contain constructors, variables and methods }
示例:
class AmtException implements Exception { String errMsg() => 'Amount should be greater than zero'; } void main() { try { withdraw_amt(-1); } catch(e) { print(e.errMsg()); } finally { print('Ending requested operation.....'); } } void withdraw_amt(int amt) { if (amt <= 0) { throw new AmtException(); } }
十、typedef
typedef可用于指定希望特定函数匹配的函数签名。函数签名由函数的参数(包括其类型)定义。返回类型不是函数签名的一部分
示例:
typedef ManyOperation(int firstNo, int secondNo); //function signature int Add(int firstNo, int second) { print("Add result is ${firstNo + second}"); return firstNo + second; } Subtract(int firstNo, int second) { print("Subtract result is ${firstNo - second}"); } Divide(int firstNo, int second) { print("Divide result is ${firstNo / second}"); } Calculator(int a, int b, ManyOperation oper) { print("Inside calculator"); oper(a, b); } void main() { ManyOperation oper = Add; oper(10, 20); print(oper(10, 20)); oper = Subtract; oper(30, 20); oper = Divide; oper(50, 5); Calculator(5, 5, Add); Calculator(5, 5, Subtract); Calculator(5, 5, Divide); }
十一、库
常用库
Dart脚本可以使用下划线(_)为标识符添加前缀,以将其组件标记为私有。如:
library loggerlib; void _log(msg) { print("Log method called in loggerlib msg:$msg"); }
_log函数为 私有函数,外部无法调用。
如果导入两个具有冲突标识符的库,则可以为一个或两个库指定前缀。使用as关键字指定前缀,如:
import 'loggerlib.dart'; import 'webloggerlib.dart' as web; // prefix avoids function name clashes void main(){ log("hello from loggerlib"); web.log("hello from webloggerlib"); }
十二、异步
创建 contact.txt文件如下:
1, One
2, Two
3, Three
4, Four
异步读取:
import "dart:async"; import "dart:io"; void main(){ File file = new File( Directory.current.path+"\\data\\contact.txt"); Future<String> f = file.readAsString(); // returns a futrue, this is Async method f.then((data)=>print(data)); // once file is read , call back method is invoked print("End of main"); // this get printed first, showing fileReading is non blocking or async }
程序运行结果:
End of main
1, One
2, Two
3, Three
4, Four
当脚本继续读取文件时,首先执行“main of main"。Future类是dart:async的一部分,用于在异步任务完成后获取计算结果。然后,此Future值用于在计算完成后执行某些操作。
当读取操作完成,执行控制就在then()内传送。这是因为读取操作可能需要更多时间,因此不希望阻止程序的其他部分。
十三、并发
并发是同时执行多个指令序列。它涉及同时执行多个任务。Dart使用Isolates作为并行工作的工具。dart:isolate包是Dart的解决方案,用于获取单线程Dart代码并允许应用程序更多地使用可用的硬件。
隔离(Isolates)顾名思义,是运行代码的独立单元。在它们之间发送数据的唯一方法是传递消息,就像在客户端和服务器之间传递消息的方式一样。隔离有助于程序利用多核微处理器开箱即用。
示例:
import 'dart:isolate'; void foo(var message){ print('execution from foo ... the message is :${message}'); } void main(){ Isolate.spawn(foo,'Hello!!'); Isolate.spawn(foo,'Greetings!!'); Isolate.spawn(foo,'Welcome!!'); print('execution from main1'); print('execution from main2'); print('execution from main3'); }
这两个函数(foo和main)可能不一定每次都以相同的顺序运行。无法保证foo何时执行以及何时执行main()。每次运行时输出都不同。
输出1:
execution from main1
execution from main2
execution from main3
execution from foo ... the message is :Hello!!
输出2:
execution from main1
execution from main2
execution from main3
execution from foo ... the message is :Welcome!!
execution from foo ... the message is :Hello!!
execution from foo ... the message is :Greetings!!
隔离与线程的不同之处在于隔离区有自己的内存。没有办法在隔离区之间共享变量 - 隔离区之间通信的唯一方法是通过消息传递。
十四、Dart HTML DOM
Dart提供了dart:html库来操作DOM中的对象和元素。基于控制台的应用程序无法使用dart:html库。要在Web应用程序中使用HTML库,请导入dart:html。
(个人看法,这其实就是一个html解析库)
参考网址:https://www.yiibai.com/dart/dart_programming_symbol.html