python11文件读写模块


将文件的打开和关闭,交给上下文管理工具with去实现。
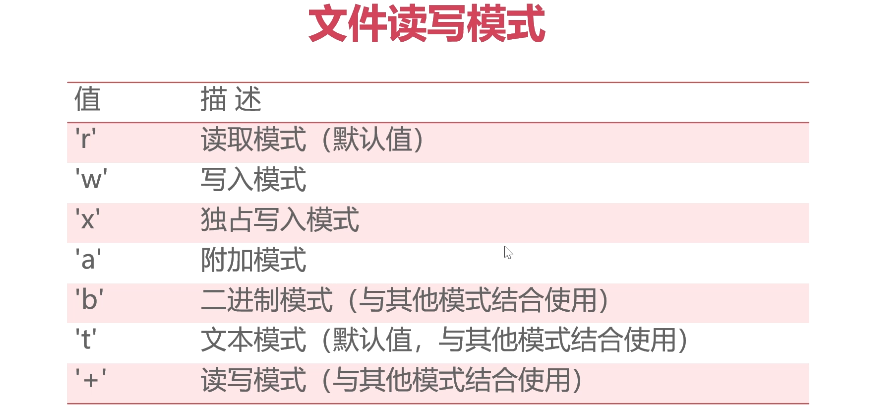
def read_file(): """ 读取文件 :return: """ file_path1 = 'D:\\PycharmProjects\\p1\\text.txt' file_path2 = 'D:/PycharmProjects/p1/text.txt' #普通读取 f = open(file_path1,encoding='utf-8') #rest = f.read() ############################### #读取指定的内容 ###他不会从头开始读取,而是延续上一次读取的位置进行读取 rest = f.read(10) print(rest) print("@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@") rest = f.read(20) print(rest) print("@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@") rest = f.read() print(rest) ############################## f.close() if __name__ == "__main__": read_file() jieguo : 【发文说明】 博客园 @@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@ 是面向开发者的知识分享社区,不允许发布任 @@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@ 何推广、广告、政治方面的内容。 博客园首页(即网站首页)只能发布原创的、高质量的、能让读者从中学到东西的内容。 如果博文质量不符合首页要求,会被工作人员移出首页,望理解。如有疑问,请联系contact@cnblogs.com。
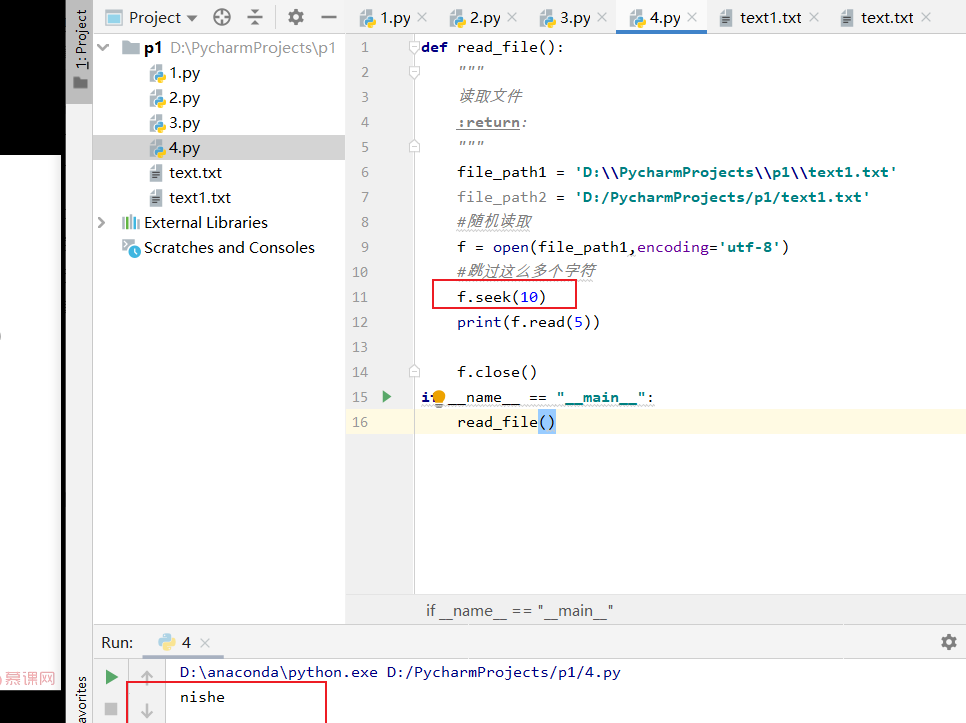
def read_file(): """ 读取文件 :return: """ file_path1 = 'D:\\PycharmProjects\\p1\\text1.txt' file_path2 = 'D:/PycharmProjects/p1/text1.txt' #随机读取 f = open(file_path1,encoding='utf-8') #跳过这么多个字符 #f.seek(10) #print(f.read(5)) #rest = f.readline() # print(rest) #print(f.readline())#接着上一次读取继续读取 # print(f.readline()) #读取所有的行,返回列表: rest = f.readlines() print(rest) f.close() if __name__ == "__main__": read_file() jeiguo : ['Process finished with exit code 0\n', 'finished with exit code\n', '\n', 'finished with exit\n', '\n', 'finished with exit code\n']
import random from datetime import datetime def w_f(): """ 写入文件 :return: """ file_name = 'D:/PycharmProjects/p1/text1.txt' f = open(file_name,'w') f.write("quanzhiqiang") f.write("\n") f.write("QQQQ") f.close() def w_m_f(): file_name = "D:/PycharmProjects/p1/text1.txt" with open(file_name,"w",encoding='utf-8') as f: l = ["11111","2222222","3333"] f.writelines(l) def w_u_l(): rest = "用户:{}-访问时间:{}\n".format(random.randint(1000,9999),datetime.now()) file_name = "write_user_log.txt" with open(file_name,"a",encoding="utf-8") as f: f.writelines(rest) def read_and_write(): """ 先读再写入 :return: """ file_name = "read_and_write.txt" with open(file_name,"r+",encoding="utf-8") as f: read_rest = f.read() #如果里面没用1,写入一行数据aaa #如果有,写入bbb if "1" in read_rest: f.write("bbb") else: f.write("aaa") if __name__ == "__main__": read_and_write()
文件的备份:
import os class FileBackup(object): """ 文本的备份 """ def __init__(self,src,dist): """ 构造方法 :param src: 需要备份的文件目录 :param dist: 备份到的目录 """ self.src = src self.dist = dist def read_files(self): """ 读取src的所有文件 :return: """ ls = os.listdir(self.src) print(ls) for l in ls: self.back_file(l) def back_file(self,filename): """ 备份 :param filename: 文件/文件夹的名称 :return: """ #判断dist是否存在,不存在就创建这个目录 if not os.path.exists(self.dist): os.makedirs(self.dist) print("文件夹不存在,已经创建") #拼接文件的完整路径 full_src_path = os.path.join(self.src,filename) full_dist_path = os.path.join(self.dist, filename) #判断文件是否为我们备份的文件 if os.path.isfile(full_src_path) and os.path.splitext(full_src_path)[-1].lower() == ".txt": print(full_src_path) #读取文件内容 with open(full_dist_path,"w",encoding="utf-8") as f_dist: print(">>开始备份 {}".format(filename)) with open(full_src_path,"r",encoding="utf-8") as f_src: while True: rest = f_src.read(100) if not rest: break f_dist.write(rest) f_dist.flush() #把读取的内容写入新的文件 else: print("不存在") if __name__ == "__main__": """ 这样子写通用性不高 src_path = 'D:\\PycharmProjects\\p1\\src' dist_path = 'D:\\PycharmProjects\\p1\\dist' """ base_path = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)) src_path = os.path.join(base_path,"src") dist_path = os.path.join(base_path,"dist") print(base_path) bak = FileBackup(src_path,dist_path) bak.read_files()


