springboot默认提供的ThreadPoolTaskExecutor
1、了解与使用
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor是springboot提供的默认线程池 。也就是说如果没有自定义线程池,那么会自动装配这个默认的。
In the absence of an Executor bean in the context, Spring Boot auto-configures a ThreadPoolTaskExecutor with sensible defaults that can be automatically associated to asynchronous task execution (@EnableAsync) and Spring MVC asynchronous request processing.
在springboot当中,根据 官方文档的说明,如果没有配置线程池的话,springboot会自动配置一个ThreadPoolTaskExecutor 线程池到bean当中,我们只需要按照他的方式调用就可以了!!
PS:
ThreadPoolExecutor:这个是JAVA自己实现的线程池执行类,基本上创建线程池都是通过这个类进行的创建!
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor :这个是springboot基于ThreadPoolExecutor实现的一个线程池执行类。
这是默认提供的几个配置参数看一下
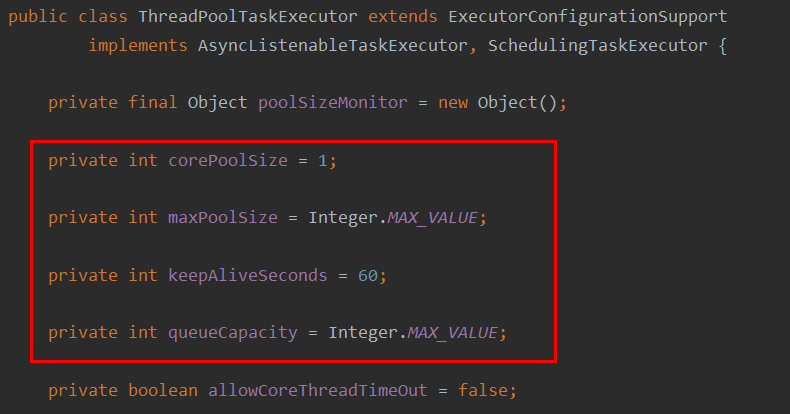
拒绝策略默认是超出后抛出RejectedExecutionException异常并直接丢弃。
可通过配置文件修改默认配置
# 核心线程数 spring.task.execution.pool.core-size=8 # 最大线程数 spring.task.execution.pool.max-size=16 # 空闲线程存活时间 spring.task.execution.pool.keep-alive=60s # 是否允许核心线程超时 spring.task.execution.pool.allow-core-thread-timeout=true # 线程队列数量 spring.task.execution.pool.queue-capacity=100 # 线程关闭等待 spring.task.execution.shutdown.await-termination=false spring.task.execution.shutdown.await-termination-period= # 线程名称前缀 spring.task.execution.thread-name-prefix=task-
package com.xiaotong.cleandata.config; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor; /** * 自定义线程池配置 * @date 2021年2月21日14:28:26 * @author Lvshiyang */ @Configuration @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.task.execution") public class ThreadPoolConfiguration { @Value("${pool.core-size}") private int corePoolSize; @Value("${pool.max-size}") private int maxPoolSize; @Value("${pool.queue-capacity}") private int queueCapacity; @Value("${pool.keep-alive}") private int keepAliveSeconds; @Value("${thread-name-prefix}") private String threadNamePrefix; @Bean(name = "threadPoolTaskExecutor") public ThreadPoolTaskExecutor threadPoolTaskExecutor() { ThreadPoolTaskExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor(); pool.setCorePoolSize(corePoolSize);//核心线程池数 pool.setMaxPoolSize(maxPoolSize); // 最大线程数 pool.setQueueCapacity(queueCapacity);//队列容量,当核心线程数达到最大时,新任务会放在队列中排队等待执行 pool.setKeepAliveSeconds(keepAliveSeconds);//线程空闲时间 pool.setAllowCoreThreadTimeOut(false);//核心线程会一直存活,即使没有任务需要执行。(默认false)时,核心线程会超时关闭 pool.setThreadNamePrefix(threadNamePrefix);//线程前缀名称 //默认:AbortPolicy 丢弃任务,抛运行时异常 //CallerRunsPolicy由调用线程处理该任务 pool.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
return pool;
}
}
使用方式:
@Resource(name="threadPoolTaskExecutor") ThreadPoolTaskExecutor threadPoolTaskExecutor; threadPoolTaskExecutor.execute(() -> { //业务代码 });
如果想知道什么时候执行完可搭配CountDownLatch,主线程countDownLatch.await()等待即可。也可以使用待返回参数的Fulture.get()处理。
2、深入springboot默认的线程池
根据官方文档的说明,Spring Boot auto-configures a ThreadPoolTaskExecutor 。最终找到springboot的线程池自动装配类:TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration
@Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public TaskExecutorBuilder taskExecutorBuilder(TaskExecutionProperties properties, ObjectProvider<TaskExecutorCustomizer> taskExecutorCustomizers, ObjectProvider<TaskDecorator> taskDecorator) { Pool pool = properties.getPool(); TaskExecutorBuilder builder = new TaskExecutorBuilder(); builder = builder.queueCapacity(pool.getQueueCapacity()); builder = builder.corePoolSize(pool.getCoreSize()); builder = builder.maxPoolSize(pool.getMaxSize()); builder = builder.allowCoreThreadTimeOut(pool.isAllowCoreThreadTimeout()); builder = builder.keepAlive(pool.getKeepAlive()); Shutdown shutdown = properties.getShutdown(); builder = builder.awaitTermination(shutdown.isAwaitTermination()); builder = builder.awaitTerminationPeriod(shutdown.getAwaitTerminationPeriod()); builder = builder.threadNamePrefix(properties.getThreadNamePrefix()); Stream var10001 = taskExecutorCustomizers.orderedStream(); var10001.getClass(); builder = builder.customizers(var10001::iterator); builder = builder.taskDecorator((TaskDecorator)taskDecorator.getIfUnique()); return builder; }
同时在ThreadPoolTaskExecutor源码当中可以看到线程池的初始化方式是直接调用的ThreadPoolExecutor进行的初始化。
protected ExecutorService initializeExecutor(ThreadFactory threadFactory, RejectedExecutionHandler rejectedExecutionHandler) { BlockingQueue<Runnable> queue = this.createQueue(this.queueCapacity); ThreadPoolExecutor executor; if (this.taskDecorator != null) { executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(this.corePoolSize, this.maxPoolSize, (long)this.keepAliveSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS, queue, threadFactory, rejectedExecutionHandler) { public void execute(Runnable command) { Runnable decorated = ThreadPoolTaskExecutor.this.taskDecorator.decorate(command); if (decorated != command) { ThreadPoolTaskExecutor.this.decoratedTaskMap.put(decorated, command); } super.execute(decorated); } }; } else { executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(this.corePoolSize, this.maxPoolSize, (long)this.keepAliveSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS, queue, threadFactory, rejectedExecutionHandler); } if (this.allowCoreThreadTimeOut) { executor.allowCoreThreadTimeOut(true); } this.threadPoolExecutor = executor; return executor; }
同时会发现默认的线程池拒绝策略是: AbortPolicy 直接抛出异常!!!
private RejectedExecutionHandler rejectedExecutionHandler = new AbortPolicy();
3、使用自定义的线程池
在默认配置信息里面是没有线程池的拒绝策略设置的方法的,如果需要更换拒绝策略就需要自定义线程池,并且如果项目当中需要多个自定义的线程池,又要如何进行管理呢?
自定义Configuration
第一步:创建一个ThreadPoolConfig 先只配置一个线程池,并设置拒绝策略为CallerRunsPolicy
@Configuration public class ThreadPoolConfig { @Bean("taskExecutor") public Executor taskExecutor() { ThreadPoolTaskExecutor taskExecutor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor(); //设置线程池参数信息 taskExecutor.setCorePoolSize(10); taskExecutor.setMaxPoolSize(50); taskExecutor.setQueueCapacity(200); taskExecutor.setKeepAliveSeconds(60); taskExecutor.setThreadNamePrefix("myExecutor--"); taskExecutor.setWaitForTasksToCompleteOnShutdown(true); //线程池中任务等待时间,超过等待时间直接销毁 taskExecutor.setAwaitTerminationSeconds(60); //修改拒绝策略为使用当前线程执行 taskExecutor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy()); //初始化线程池 taskExecutor.initialize(); return taskExecutor; } }
4、配置多个自定义线程池
/** * @author shf * @date 2022-03-14 11:46 */ @Configuration public class ThreadPoolConfig { /** * 核心线程数 默认的核心线程数为1 */ private static final int CORE_POOL_SIZE = 2; /** * 最大线程数 默认的最大线程数是Integer.MAX_VALUE */ private static final int MAX_POOL_SIZE = 20; /** * 缓冲队列数 默认的缓冲队列数是Integer.MAX_VALUE */ private static final int QUEUE_CAPACITY = 50; /** * 允许线程空闲时间 默认的线程空闲时间为60秒 */ private static final int KEEP_ALIVE_SECONDS = 30; @Bean("destroyResource") public AsyncTaskExecutor destroyImGroupTaskExecutor() { return getAsyncTaskExecutor("del-resource-td-", MAX_POOL_SIZE, QUEUE_CAPACITY); } @Bean("statisticsData") public AsyncTaskExecutor statisticsDataExecutor() { return getAsyncTaskExecutor("save-data-td-", MAX_POOL_SIZE, QUEUE_CAPACITY); } @Bean("commonTaskExecutor") public AsyncTaskExecutor get() { return getAsyncTaskExecutor("common-ex-td-", MAX_POOL_SIZE, QUEUE_CAPACITY); } private AsyncTaskExecutor getAsyncTaskExecutor(String threadNamePrefix , int MAX_POOL_SIZE, int QUEUE_CAPACITY) { ThreadPoolTaskExecutor taskExecutor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor(); taskExecutor.setCorePoolSize(CORE_POOL_SIZE); taskExecutor.setMaxPoolSize(MAX_POOL_SIZE); taskExecutor.setQueueCapacity(QUEUE_CAPACITY); taskExecutor.setKeepAliveSeconds(KEEP_ALIVE_SECONDS); taskExecutor.setThreadNamePrefix(threadNamePrefix); taskExecutor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy()); return taskExecutor; } }
使用:
@Autowired ThreadPoolTaskExecutor commonTaskExecutor; //会去匹配 @Bean("commonTaskExecutor") 这个线程池
如果是使用的@Async注解,只需要在注解里面指定bean的名称就可以切换到对应的线程池去了。如下所示:
@Async("commonTaskExecutor")
public void hello(String name){
logger.info("异步线程启动 started."+name);
}
5、使用异步注解@Async注意事项
总结@Async可能失效的原因
1.@SpringBootApplication启动类当中没有添加@EnableAsync注解。
2.异步方法使用注解@Async的返回值只能为void或者Future。
3.没有走Spring的代理类。因为@Transactional和@Async注解的实现都是基于Spring的AOP,而AOP的实现是基于动态代理模式实现的。那么注解失效的原因就很明显了,有可能因为调用方法的是对象本身而不是代理对象,因为没有经过Spring容器管理。
解决方法:
这里具体说一下第三种情况的解决方法。
1、注解的方法必须是public方法。
2、注解的方法不要定义为static
3、方法一定要从另一个类中调用,也就是从类的外部调用,类的内部调用是无效的。
4、如果需要从类的内部调用,需要先获取其代理类。
参考文章:
https://blog.csdn.net/ycf921244819/article/details/106108904





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 探究高空视频全景AR技术的实现原理
· 理解Rust引用及其生命周期标识(上)
· 物流快递公司核心技术能力-地址解析分单基础技术分享
· .NET 10首个预览版发布:重大改进与新特性概览!
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 单线程的Redis速度为什么快?
· Pantheons:用 TypeScript 打造主流大模型对话的一站式集成库
2018-07-09 数据库事务的四大特性以及事务的隔离级别
2018-07-09 订单系统中并发问题和锁机制的探讨