springboot-mybatis整合多数据源的两种方法
简介
随着并发量的不断增加,显然单个数据库已经承受不了高并发带来的压力。一个项目使用多个数据库(无论是主从复制- - 读写分离还是分布式数据库结构)的重要性变得越来越明显。传统项目中(个人对传统项目的理解就是所有的业务模块都在一个tomcat中完成,多个相同的tomcat集群也可认为是传统项目)整合多数据源有两种方法:分包和AOP。
版本
springboot:1.5.9.RELEASE
mariadb:5.7
一、分包方式实现
1、在application.properties中配置两个数据库
## test1 database spring.datasource.test1.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3307/multipledatasource1?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false spring.datasource.test1.username=root spring.datasource.test1.password=root spring.datasource.test1.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver ##下面的四行配置相应的连接池参数,定是去检查连接的有效性,定时清理无效的连接 spring.datasource.primary.validation-query=SELECT 1 spring.datasource.primary.test-on-borrow=false spring.datasource.primary.test-while-idle=true spring.datasource.primary.time-between-eviction-runs-millis=18800 ## test2 database spring.datasource.test2.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3307/multipledatasource2?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false spring.datasource.test2.username=root spring.datasource.test2.password=root spring.datasource.test2.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver ##下面的四行配置相应的连接池参数,定是去检查连接的有效性,定时清理无效的连接 spring.datasource.primary.validation-query=SELECT 1 spring.datasource.primary.test-on-borrow=false spring.datasource.primary.test-while-idle=true spring.datasource.primary.time-between-eviction-runs-millis=18800
Note:如果不增加定时清理无效连接配置超过8小时会连接异常
No operations allowed after connection closed
之所以会出现这个异常,是因为MySQL5.0以后针对超长时间DB连接做了一个处理,那就是如果一个DB连接在无任何操作情况下过了8个小时后(Mysql 服务器默认的“wait_timeout”是8小时),Mysql会自动把这个连接关闭。这就是问题的所在,在连接池中的connections如果空闲超过8小时,mysql将其断开,而连接池自己并不知道该connection已经失效,如果这时有 Client请求connection,连接池将该失效的Connection提供给Client,将会造成上面的异常。
所以配置datasource时需要配置相应的连接池参数,定是去检查连接的有效性,定时清理无效的连接。
2、建立连个数据源的配置文件
第一个配置文件:
//表示这个类为一个配置类 @Configuration // 配置mybatis的接口类放的地方 @MapperScan(basePackages = "com.mzd.multipledatasources.mapper.test01", sqlSessionFactoryRef = "test1SqlSessionFactory") public class DataSourceConfig1 { // 将这个对象放入Spring容器中 @Bean(name = "test1DataSource") // 表示这个数据源是默认数据源 @Primary // 读取application.properties中的配置参数映射成为一个对象 // prefix表示参数的前缀 @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.test1") public DataSource getDateSource1() { return DataSourceBuilder.create().build(); } @Bean(name = "test1SqlSessionFactory") // 表示这个数据源是默认数据源 @Primary // @Qualifier表示查找Spring容器中名字为test1DataSource的对象 public SqlSessionFactory test1SqlSessionFactory(@Qualifier("test1DataSource") DataSource datasource) throws Exception { SqlSessionFactoryBean bean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean(); bean.setDataSource(datasource); bean.setMapperLocations( // 设置mybatis的xml所在位置 new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources("classpath*:mapping/test01/*.xml")); return bean.getObject(); } @Bean("test1SqlSessionTemplate") // 表示这个数据源是默认数据源 @Primary public SqlSessionTemplate test1sqlsessiontemplate( @Qualifier("test1SqlSessionFactory") SqlSessionFactory sessionfactory) { return new SqlSessionTemplate(sessionfactory); } }
第二个配置文件:
@Configuration @MapperScan(basePackages = "com.mzd.multipledatasources.mapper.test02", sqlSessionFactoryRef = "test2SqlSessionFactory") public class DataSourceConfig2 { @Bean(name = "test2DataSource") @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.test2") public DataSource getDateSource2() { return DataSourceBuilder.create().build(); } @Bean(name = "test2SqlSessionFactory") public SqlSessionFactory test2SqlSessionFactory(@Qualifier("test2DataSource") DataSource datasource) throws Exception { SqlSessionFactoryBean bean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean(); bean.setDataSource(datasource); bean.setMapperLocations( new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources("classpath*:mapping/test02/*.xml")); return bean.getObject(); } @Bean("test2SqlSessionTemplate") public SqlSessionTemplate test2sqlsessiontemplate( @Qualifier("test2SqlSessionFactory") SqlSessionFactory sessionfactory) { return new SqlSessionTemplate(sessionfactory); } }
注意:
1、@Primary这个注解必须要加,因为不加的话spring将分不清楚那个为主数据源(默认数据源)
2、mapper的接口、xml形式以及dao层都需要两个分开,目录如图:
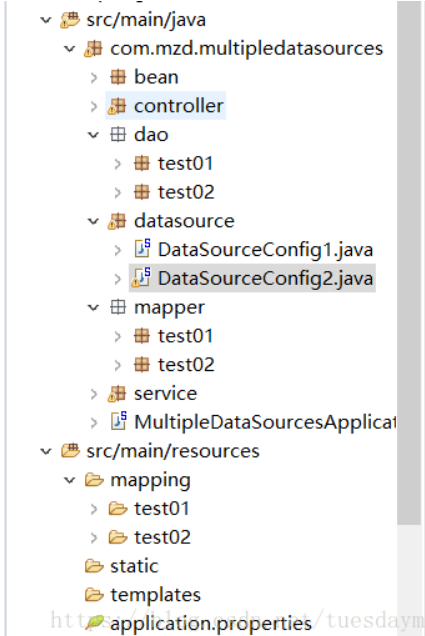
3、bean.setMapperLocations(new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources(“XXXX”));mapper的xml形式文件位置必须要配置,不然将报错:no statement (这种错误也可能是mapper的xml中,namespace与项目的路径不一致导致的,具体看情况吧,注意一下就行,问题不大的)
4、在service层中根据不同的业务注入不同的dao层。
5、如果是主从复制- -读写分离:比如test01中负责增删改,test02中负责查询。但是需要注意的是负责增删改的数据库必须是主库(master)
6、如果是分布式结构的话,不同模块操作各自的数据库就好,test01包下全是test01业务,test02全是test02业务,但是如果test01中掺杂着test02的编辑操作,这时候将会产生事务问题:即test01中的事务是没法控制test02的事务的,这个问题在之后的博客中会解决。
二、AOP实现
简介: 用这种方式实现多数据源的前提必须要清楚两个知识点:AOP原理和AbstractRoutingDataSource抽象类。
1、AOP:这个东西。。。不切当的说就是相当于拦截器,只要满足要求的都会被拦截过来,然后进行一些列的操作。具体需要自己去体会。。。
2、AbstractRoutingDataSource:这个类是实现多数据源的关键,他的作用就是动态切换数据源,实质:有多少个数据源就存多少个数据源在targetDataSources(是AbstractRoutingDataSource的一个map类型的属性,其中value为每个数据源,key表示每个数据源的名字)这个属性中,然后根据determineCurrentLookupKey()这个方法获取当前数据源在map中的key值,然后determineTargetDataSource()方法中动态获取当前数据源,如果当前数据源不存并且默认数据源也不存在就抛出异常。
public abstract class AbstractRoutingDataSource extends AbstractDataSource implements InitializingBean { //多数据源map集合 private Map<Object, Object> targetDataSources; //默认数据源 private Object defaultTargetDataSource; //其实就是targetDataSources,后面的afterPropertiesSet()方法会将targetDataSources赋值给resolvedDataSources private Map<Object, DataSource> resolvedDataSources; private DataSource resolvedDefaultDataSource; public void setTargetDataSources(Map<Object, Object> targetDataSources) { this.targetDataSources = targetDataSources; } protected DataSource determineTargetDataSource() { Assert.notNull(this.resolvedDataSources, "DataSource router not initialized"); Object lookupKey = this.determineCurrentLookupKey(); DataSource dataSource = (DataSource)this.resolvedDataSources.get(lookupKey); if (dataSource == null && (this.lenientFallback || lookupKey == null)) { dataSource = this.resolvedDefaultDataSource; } if (dataSource == null) { throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot determine target DataSource for lookup key [" + lookupKey + "]"); } else { return dataSource; } } protected abstract Object determineCurrentLookupKey(); }
具体实现:
1、定义一个动态数据源:继承AbstractRoutingDataSource 抽象类,并重写determineCurrentLookupKey()方法
public class DynamicDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource { @Override protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() { DataSourceType.DataBaseType dataBaseType = DataSourceType.getDataBaseType(); return dataBaseType; } }
2、创建一个切换数据源类型的类
public class DataSourceType { public enum DataBaseType { TEST01, TEST02 } // 使用ThreadLocal保证线程安全 private static final ThreadLocal<DataBaseType> TYPE = new ThreadLocal<DataBaseType>(); // 往当前线程里设置数据源类型 public static void setDataBaseType(DataBaseType dataBaseType) { if (dataBaseType == null) { throw new NullPointerException(); } System.err.println("[将当前数据源改为]:" + dataBaseType); TYPE.set(dataBaseType); } // 获取数据源类型 public static DataBaseType getDataBaseType() { DataBaseType dataBaseType = TYPE.get() == null ? DataBaseType.TEST01 : TYPE.get(); System.err.println("[获取当前数据源的类型为]:" + dataBaseType); return dataBaseType; } // 清空数据类型 public static void clearDataBaseType() { TYPE.remove(); } }
3、定义多个数据源:怎么定义就不多说了,和方法一是一样的,主要是将定义好的多个数据源放在动态数据源中。
@Configuration @MapperScan(basePackages = "com.mzd.multipledatasources.mapper", sqlSessionFactoryRef = "SqlSessionFactory") public class DataSourceConfig { @Primary @Bean(name = "test1DataSource") @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.test1") public DataSource getDateSource1() { return DataSourceBuilder.create().build(); } @Bean(name = "test2DataSource") @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.test2") public DataSource getDateSource2() { return DataSourceBuilder.create().build(); } @Bean(name = "dynamicDataSource") public DynamicDataSource DataSource(@Qualifier("test1DataSource") DataSource test1DataSource, @Qualifier("test2DataSource") DataSource test2DataSource) { Map<Object, Object> targetDataSource = new HashMap<>(); targetDataSource.put(DataSourceType.DataBaseType.TEST01, test1DataSource); targetDataSource.put(DataSourceType.DataBaseType.TEST02, test2DataSource); DynamicDataSource dataSource = new DynamicDataSource(); dataSource.setTargetDataSources(targetDataSource); dataSource.setDefaultTargetDataSource(test1DataSource); return dataSource; } @Bean(name = "SqlSessionFactory") public SqlSessionFactory test1SqlSessionFactory(@Qualifier("dynamicDataSource") DataSource dynamicDataSource) throws Exception { SqlSessionFactoryBean bean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean(); bean.setDataSource(dynamicDataSource); bean.setMapperLocations( new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources("classpath*:mapping/*.xml")); return bean.getObject(); } }
4、定义AOP:就是不同业务切换不同数据库的入口。
@Aspect @Component public class DataSourceAop { @Before("execution(* com.mzd.multipledatasources.service..*.test01*(..))") public void setDataSource2test01() { System.err.println("test01业务"); DataSourceType.setDataBaseType(DataBaseType.TEST01); } @Before("execution(* com.mzd.multipledatasources.service..*.test02*(..))") public void setDataSource2test02() { System.err.println("test02业务"); DataSourceType.setDataBaseType(DataBaseType.TEST02); } }
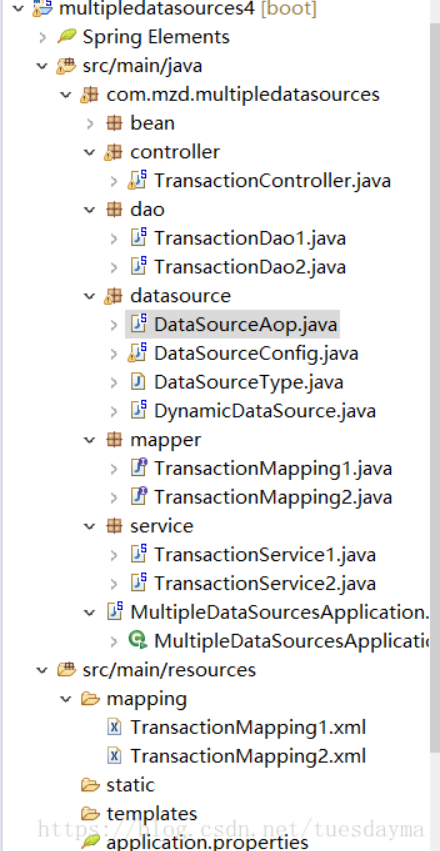
整体目录如图:
参考文章:https://blog.csdn.net/tuesdayma/article/details/81081666


