Spring加载properties文件的两种方式
在项目中如果有些参数经常需要修改,或者后期可能需要修改,那我们最好把这些参数放到properties文件中,源代码中读取properties里面的配置,这样后期只需要改动properties文件即可,不需要修改源代码,这样更加方便。在spring中也可以这么做,而且Spring有两种加载properties文件的方式:基于xml方式和基于注解方式。下面分别讨论下这两种方式。
一、通过xml方式加载properties文件
我们以Spring实例化dataSource为例,我们一般会在beans.xml文件中进行如下配置:
<!-- com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource类在c3p0-0.9.5.1.jar包的com.mchange.v2.c3p0包中 --> <bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource"> <property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" /> <property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/shop" /> <property name="user" value="root" /> <property name="password" value="root" /> </bean>
现在如果我们要改变dataSource,我们就得修改这些源代码,但是我们如果使用properties文件的话,只需要修改那里面的即可,就不管源代码的东西了。那么如何做呢?
Spring中有个<context:property-placeholder location=""/>标签,可以用来加载properties配置文件,location是配置文件的路径,我们现在在工程目录的src下新建一个conn.properties文件,里面写上上面dataSource的配置:
dataSource=com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource
driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbcUrl=jdbc\:mysql\://localhost\:3306/shop
user=root
password=root
现在只需要在beans.xml中做如下修改即可:
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:conn.properties"/><!-- 加载配置文件 --> <!-- com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource类在c3p0-0.9.5.1.jar包的com.mchange.v2.c3p0包中 --> <bean id="dataSource" class="${dataSource}"> <!-- 这些配置Spring在启动时会去conn.properties中找 --> <property name="driverClass" value="${driverClass}" /> <property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbcUrl}" /> <property name="user" value="${user}" /> <property name="password" value="${password}" /> </bean>
<context:property-placeholder location=""/>标签也可以用下面的<bean>标签来代替,<bean>标签我们更加熟悉,可读性更强:
<!-- 与上面的配置等价,下面的更容易理解 --> <bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer"> <property name="locations"> <!-- PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer类中有个locations属性,接收的是一个数组,即我们可以在下面配好多个properties文件 --> <array> <value>classpath:conn.properties</value> </array> </property> </bean>
虽然看起来没有上面的<context:property-placeholder location=""/>简洁,但是更加清晰,建议使用后面的这种。但是这个只限于xml的方式,即在beans.xml中用${key}获取配置文件中的值value。
二、通过注解方式加载properties文件
还有一种就是通过注解的方式,在Java代码中使用@Value注解来加载配置文件中的值。
我们来看一个例子:假如我们要在程序中获取某个文件的绝对路径,我们很自然会想到不能在程序中写死,那么我们也可以卸载properties文件中。还是在src目录下新建一个public.properties文件,假设里面写了一条记录:
filePath=E\:\\web\\apache-tomcat-8.0.26\\webapps\\E_shop\\image
如果想在java代码中通过注解来获取这个filePath的话,首先得在beans.xml文件中配置一下注解的方式:
<!-- 第二种方式是使用注解的方式注入,主要用在java代码中使用注解注入properties文件中相应的value值 --> <bean id="prop" class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertiesFactoryBean"> <property name="locations"><!-- 这里是PropertiesFactoryBean类,它也有个locations属性,也是接收一个数组,跟上面一样 <array> <value>classpath:public.properties</value> </array> </property> </bean>
现在我们可以在java代码中使用注解来获取filePath的值了:
@Component("fileUpload")
public class FileUploadUtil implements FileUpload {
private String filePath;
@Value("#{prop.filePath}")
//@Value表示去beans.xml文件中找id="prop"的bean,它是通过注解的方式读取properties配置文件的,然后去相应的配置文件中读取key=filePath的对应的value值
public void setFilePath(String filePath) {
System.out.println(filePath);
this.filePath = filePath;
}
注意要有set方法才能被注入进来,注解写在set方法上即可。在setFilePath方法中通过控制台打印filePath是为了在启动tomcat的时候,观察控制台有没有输出来,如果有,说明Spring在启动时,已经将filePath给加载好了,我们看一下控制台的启动信息:
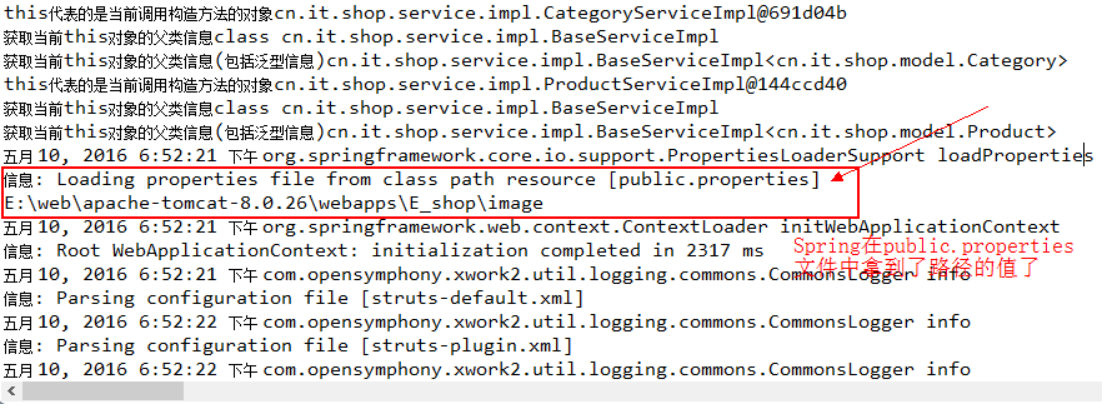
以上就是Spring加载properties配置文件的两种方式。实际上,上面基于xml方式中的PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer类和这里基于注解方式的PropertiesFactoryBean类都是继承PropertiesLoaderSupport,都是用来加载properties配置文件的。
三、Spring用代码来读取properties文件
重写PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer
public class PropertyPlaceholder extends PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer { private static Map<String,String> propertyMap; @Override protected void processProperties(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactoryToProcess, Properties props) throws BeansException { super.processProperties(beanFactoryToProcess, props); propertyMap = new HashMap<String, String>(); for (Object key : props.keySet()) { String keyStr = key.toString(); String value = props.getProperty(keyStr); propertyMap.put(keyStr, value); } } //static method for accessing context properties public static Object getProperty(String name) { return propertyMap.get(name); } }
在配置文件中,用上面的类,代替PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer
<bean id="propertyConfigurer" class="com.gyoung.mybatis.util.PropertyPlaceholder"> <property name="location"> <value>classpath:config.properties</value> </property> </bean>
这样在代码中就可以直接用编程方式获取:
PropertyPlaceholder.getProperty("sql.name");
如果是多个配置文件,配置locations属性:
<bean id="propertyConfigurer" class="com.gyoung.mybatis.util.PropertyPlaceholder"> <property name="ignoreResourceNotFound" value="true"/> <property name="locations"> <list> <value>file:./jdbc.properties</value> <value>file:./module.config.properties</value> <value>classpath:jdbc.properties</value> <value>classpath*:*.config.properties</value> </list> </property> </bean>
参考文章:
https://www.cnblogs.com/shanheyongmu/p/5806872.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/Gyoung/p/5507063.html


