知识总结
- 数据结构是指相互之间具有(存在)一定联系(关系)的数据元素的集合。
- 使用数据结构的三个原因是:效率、抽象和重用性。
- 数据结构的主要运算包括:
- 建立(Create)一个数据结构
- 消除(Destroy)一个数据结构
- 从一个数据结构中删除(Delete)一个数据元素
- 把一个数据元素插入(Insert)到一个数据结构中
- 对一个数据结构进行访问(Access)
- 对一个数据结构(中的数据元素)进行修改(Modify)
- 对一个数据结构进行排序(Sort)
- 对一个数据结构进行查找(Search)
- ...
- 链表
- LinkedList链表:创建对象以链表结构存储数据
- 创建空链表:
LinkedList<String> mylist = new LinkedList<String>();
- 使用
add(E obj)方法依次增加节点
- 使用
get(int index)方法遍历链表
- 排序与查找
- 升序排序:
public static sort(List<E> list)
- 折半法查找:
int binarySearch(List<T> list,T key,CompareTo<T> c)
- 树集:TreeSet创建对象,在使用add方法增加结点
- 树映射:TreeMap<K,V>对象
- 使用 Comparator
public int compare(java.lang.Object o1, java.lang.Object o2) 如果 o1 和 o2相等,compare返回0;如果o1小于o2,它返回一个负整数;如果o1大于o2,返回一个正整数。- 有类的源代码,针对某一成员变量排序,让类实现Comparable接口,调用
Collection.sort(List)。
- 没有类的源代码,或者多种排序,新建一个类,实现Comparator接口 调用
Collection.sort(List, Compatator)。
- 创建一个 List:
List myList = new ArrayList();
- 将list中的元素按升序排序:
public static sort(List<E>list)
- 链表中插入数据:
list.add("xx");
课堂测试补做
- 数据结构-排序:针对下面的Student类,使用Comparator编程完成以下功能:
- 在测试类StudentTest中新建学生列表,包括自己和学号前后各两名学生,共5名学生,给出运行结果(排序前,排序后)
- 对这5名同学分别用学号和总成绩进行增序排序,提交两个Comparator的代码
- 产品代码
import java.util.*;
class StudentTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Student> list = new LinkedList<>();
list.add(new Student(20165328,"段俊伟","male",20,89,67,89));
list.add(new Student(20165329,"何佳伟","male",20,79,66,45));
list.add(new Student(20165330,"张羽昕","female",20,69,81,78));
list.add(new Student(20165331,"胡麟","male",20,69,56,76));
list.add(new Student(20165332,"延亿卓","male",20,62,80,83));
SortByTotal_score sortBytotal_score = new SortByTotal_score();
Collections.sort(list, sortBytotal_score);
SortByID sortByID = new SortByID();
Collections.sort(list, sortByID);
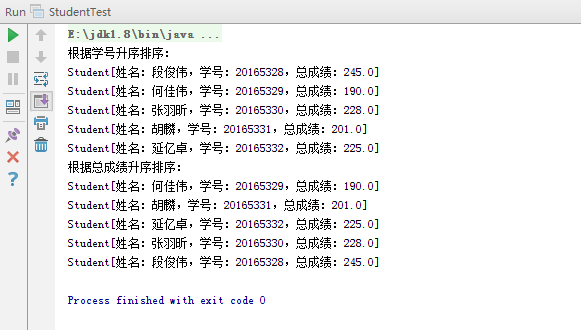
System.out.println("根据学号升序排序:");
for (Student student : list) {
System.out.println(student);
}
Collections.sort(list, sortBytotal_score);
System.out.println("根据总成绩升序排序:");
for (Student student : list) {
System.out.println(student);
}
}
}
class Student {
private int id;//表示学号
private String name;//表示姓名
private int age;//表示年龄
private String sex;
private double computer_score;//表示计算机课程的成绩
private double english_score;//表示英语课的成绩
private double maths_score;//表示数学课的成绩
private double total_score;// 表示总成绩
private double ave_score; //表示平均成绩
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student[姓名:"+name+",学号:"+id+",总成绩:"+total_score+"]";
}
public Student(int id, String name, String sex, int age,double computer_score,
double english_score,double maths_score) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
this.age = age;
this.computer_score = computer_score;
this.english_score = english_score;
this.maths_score = maths_score;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}//获得当前对象的学号,
public double getComputer_score() {
return computer_score;
}//获得当前对象的计算机课程成绩,
public double getMaths_score() {
return maths_score;
}//获得当前对象的数学课程成绩,
public double getEnglish_score() {
return english_score;
}//获得当前对象的英语课程成绩,
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}// 设置当前对象的id值,
public void setComputer_score(double computer_score) {
this.computer_score = computer_score;
}//设置当前对象的Computer_score值,
public void setEnglish_score(double english_score) {
this.english_score = english_score;
}//设置当前对象的English_score值,
public void setMaths_score(double maths_score) {
this.maths_score = maths_score;
}//设置当前对象的Maths_score值,
public double getTotalScore() {
total_score=computer_score + maths_score + english_score;
return total_score;
}// 计算Computer_score, Maths_score 和English_score 三门课的总成绩。
public double getAveScore() {
return getTotalScore() / 3;
}// 计算Computer_score, Maths_score 和English_score 三门课的平均成绩。
}
class SortByID implements Comparator<Student> {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
return o1.getId() - o2.getId();
}
}
class SortByTotal_score implements Comparator<Student> {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
return (int)( o1.getTotalScore() - o2.getTotalScore());
}
}
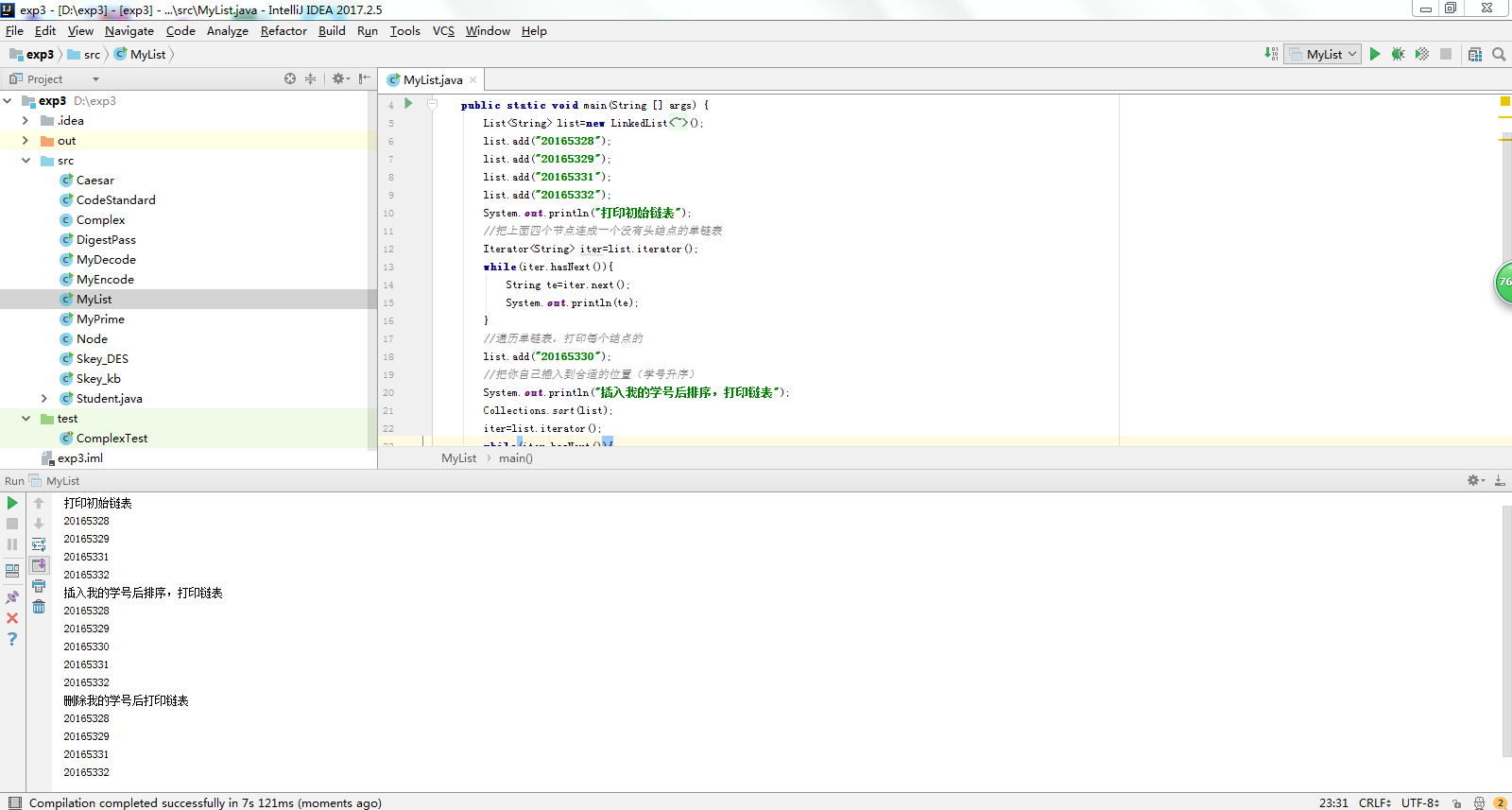
- 运行结果截图
- 数据结构-单链表:补充MyList.java的内容,提交运行结果截图(全屏)
import java.util.*;
import java.util.*;
public class MyList {
public static void main(String [] args) {
List<String> list=new LinkedList<String>();
list.add("20165328");
list.add("20165329");
list.add("20165331");
list.add("20165332");
System.out.println("打印初始链表");
//把上面四个节点连成一个没有头结点的单链表
Iterator<String> iter=list.iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()){
String te=iter.next();
System.out.println(te);
}
//遍历单链表,打印每个结点的
list.add("20165330");
//把你自己插入到合适的位置(学号升序)
System.out.println("插入我的学号后排序,打印链表");
Collections.sort(list);
iter=list.iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()){
String te=iter.next();
System.out.println(te);
}
//遍历单链表,打印每个结点的
list.remove("20165330");
//从链表中删除自己
System.out.println("删除我的学号后打印链表");
iter=list.iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()){
String te=iter.next();
System.out.println(te);
}
//遍历单链表,打印每个结点的
}
}
- 运行结果截图
教材习题
第十五章
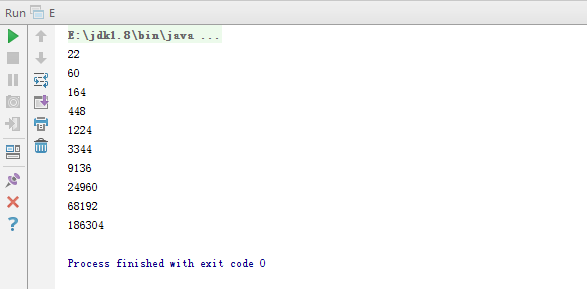
- 使用堆栈结构输出an的若干项,其中an=2an-1+2an-2,a1=3,a2=8。
import java.util.*;
public class E {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Stack<Integer> stack=new Stack<Integer>();
stack.push(new Integer(8));
stack.push(new Integer(3));
int k=1;
while(k<=10) {
for(int i=1;i<=2;i++) {
Integer F1=stack.pop();
int f1=F1.intValue();
Integer F2=stack.pop();
int f2=F2.intValue();
Integer temp=new Integer(f1*2+f2*2);
System.out.println(""+temp.toString());
stack.push(temp);
stack.push(F2);
k++;
}
}
}
}
- 运行截图
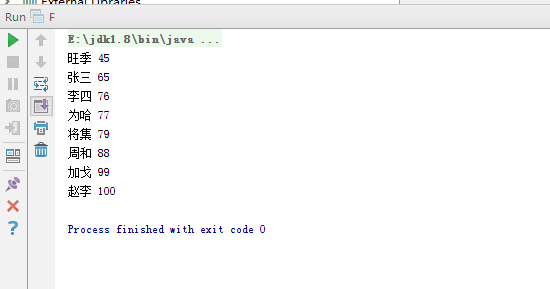
- 编写一个程序,将链表中的学生英语成绩单存放到一个树集中,使得按成绩自动排序,并输出排序结果。
import java.util.*;
class student implements Comparable {
int english=0;
String name;
student(int english,String name) {
this.name=name;
this.english=english;
}
public int compareTo(Object b) {
student st=(student)b;
return (this.english-st.english);
}
}
public class F {
public static void main(String args[]) {
List<student> list=new LinkedList<student>();
int score []={65,76,45,99,77,88,100,79};
String name[]={"张三","李四","旺季","加戈","为哈","周和","赵李","将集"};
for(int i=0;i<score.length;i++){
list.add(new student(score[i],name[i]));
}
Iterator<student> iter=list.iterator();
TreeSet<student> mytree=new TreeSet<student>();
while(iter.hasNext()){
student stu=iter.next();
mytree.add(stu);
}
Iterator<student> te=mytree.iterator();
while(te.hasNext()) {
student stu=te.next();
System.out.println(""+stu.name+" "+stu.english);
}
}
}
- 运行截图
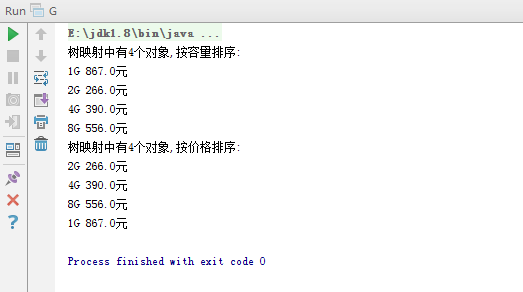
- 有10个U盘,有两个重要的属性:价格和容量。
- 编写一个应用程序,使用TreeMap<K,V>类,分别按照价格和容量排序输出10个U盘的详细信息。
- 代码
import java.util.*;
class UDiscKey implements Comparable {
double key=0;
UDiscKey(double d) {
key=d;
}
public int compareTo(Object b) {
UDiscKey disc=(UDiscKey)b;
if((this.key-disc.key)==0)
return -1;
else
return (int)((this.key-disc.key)*1000);
}
}
class UDisc{
int amount;
double price;
UDisc(int m,double e) {
amount=m;
price=e;
}
}
public class G {
public static void main(String args[ ]) {
TreeMap<UDiscKey,UDisc> treemap= new TreeMap<UDiscKey,UDisc>();
int amount[]={1,2,4,8,16};
double price[]={867,266,390,556};
UDisc UDisc[]=new UDisc[4];
for(int k=0;k<UDisc.length;k++) {
UDisc[k]=new UDisc(amount[k],price[k]);
}
UDiscKey key[]=new UDiscKey[4] ;
for(int k=0;k<key.length;k++) {
key[k]=new UDiscKey(UDisc[k].amount);//按容量排列
}
for(int k=0;k<UDisc.length;k++) {
treemap.put(key[k],UDisc[k]);
}
int number=treemap.size();
System.out.println("树映射中有"+number+"个对象,按容量排序:");
Collection<UDisc> collection=treemap.values();
Iterator<UDisc> iter=collection.iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
UDisc disc=iter.next();
System.out.println(""+disc.amount+"G "+disc.price+"元");
}
treemap.clear();
for(int k=0;k<key.length;k++) {
key[k]=new UDiscKey(UDisc[k].price);//按价格排列
}
for(int k=0;k<UDisc.length;k++) {
treemap.put(key[k],UDisc[k]);
}
number=treemap.size();
System.out.println("树映射中有"+number+"个对象,按价格排序:");
collection=treemap.values();
iter=collection.iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
UDisc disc=iter.next();
System.out.println(""+disc.amount+"G "+disc.price+"元");
}
}
}
- 运行截图
代码分析
码云链接
Example15_1
- 代码主要声明了一个泛型类Cone,泛型的目的在于建立具有安全类型的数据结构,使用Cone类计算体积,并定义Rect类计算矩形的面积,Circle类计算圆的面积,这两种类都重写了Object类中的同String方法,最后在主类中输入值调用泛型类进行计算。
Example15_2
- 遍历链表方法:迭代器遍历和`get(int index)方法
Iterator<String> iter=list.iterator():创建迭代器iteriter.hasNext():判断链表中下一个结点是否还存在结点iter.next():判断列表中下一个结点是否是空结点,如果不是,获取下一个结点long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis():以毫秒为单位计算遍历完链表后的时间
Example15_3
- 代码通过
LinkedList mylist=new LinkedList()创建链表对象,使用add(Object obj)方法依次添加结点
LinkedList mylist = new LinkedList();//创建链表对象
mylist.add("你"); //链表中的第一个节点
mylist.add("好"); //链表中的第二个节点
Example15_4
- 代码实现了链表中的排序和查找,通过Comparable接口,实现`int compareTo(Object b)来规定对象的大小关系。
public int compareTo(Object b) { //两个Student对象相等当且仅当二者的height值相等
Student st=(Student)b;
return (this.height-st.height);
}
Collections.sort(list):提供用于排序和查找的方法
Example15_5
- 代码实现Collections类的对链表数据随机排列以及旋转链表数据的方法
list.add(new Integer(i)):添加结点Collections.shuffle(list):重新随机排列Collections.rotate(list, 1):旋转链表,向右旋转一次
Example15_6
- 代码实现数据结构中的堆栈,遍历采用“后进先出”
- 创建堆栈对象:Stack
- 压栈操作:public E push(E item);
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();//建立一个堆栈对象
stack.push(new Integer(1));//压栈,第一项为1
stack.push(new Integer(1));//压栈,第二项为1
- 弹栈操作:public E pop();
- 判断堆栈是否还有数据:public boolean empty();
- 获取堆栈顶端的数据,但不删除该数据:public int search(Object data);
Integer F1 = stack.pop();//取出栈顶对象
int f1 = F1.intValue();//得到对象的int值
Integer F2 = stack.pop();//取出栈顶对象
int f2 = F2.intValue();//得到对象的int值
Example15_7
- 代码体现散列映射的意义,利用GUI程序查询英语单词,用WordPolice类使用Scanner解析word.txt中的单词,然后将英文单词/汉语对应键/值存储到散列映射中供用户查询。
Example15_8
- 代码实现用树集存放数据等信息
TreeSet<Student> mytree = new TreeSet<Student>():创建树集对象- 利用add方法为树集添加结点
mytree.add(st2);
mytree.add(st3);
mytree.add(st4);
Example15_9
- 代码使用树映射进行排序,利用TreeMap<K,V>类实现Map<K,V>接口
TreeMap<StudentKey, Student> treemap = new TreeMap<StudentKey, Student>()
- 使用
public V put(K key,V value)方法添加结点
treemap.put(key[k], student[k]);//向树映射中添加键/值对
public int compareTo(Object b) {
StudentKey st = (StudentKey) b;
if ((this.d - st.d) == 0)
return -1;
else
return (int) ((this.d - st.d) * 1000);
}
String str[] = {"赵一", "钱二", "孙三", "李四"};
double math[] = {89, 45, 78, 76};
double english[] = {67, 66, 90, 56};
Student student[] = new Student[4];
Example15_10
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>(); //创建链表
list.add(i); //自动装箱,实际添加到list中的是new Integer(i)。
int m = list.get(k); //自动拆箱,获取Integer对象中的int型数据







