JavaSE学习总结(十七)—— IO流
一、IO流概要
1.1、概念
开发中经常要进行输入输出操作,掌握Java中的IO流显得非常必要。
流(stream)的概念源于UNIX中管道(pipe)的概念。在UNIX中,管道是一条不间断的字节流,用来实现程序或进程间的通信,或读写外围设备、外部文件等。
一个流,必有源端和目的端,它们可以是计算机内存的某些区域,也可以是磁盘文件,甚至可以是Internet上的某个URL。
流的方向是重要的,根据流的方向,流可分为两类:输入流和输出流。用户可以从输入流中读取信息,但不能写它。相反,对输出流,只能往输入流写,而不能读它。
实际上,流的源端和目的端可简单地看成是字节的生产者和消费者,对输入流,可不必关心它的源端是什么,只要简单地从流中读数据,而对输出流,也可不知道它的目的端,只是简单地往流中写数据。
形象的比喻——水流 ,文件======程序,文件和程序之间连接一个管道,水流就在之间形成了,自然也就出现了方向:可以流进,也可以流出。便于理解,这么定义流: 流就是一个管道里面有流水,这个管道连接了文件和程序。
Java流操作有关的类或接口:
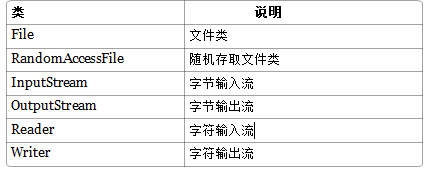
Java IO流的结构图:
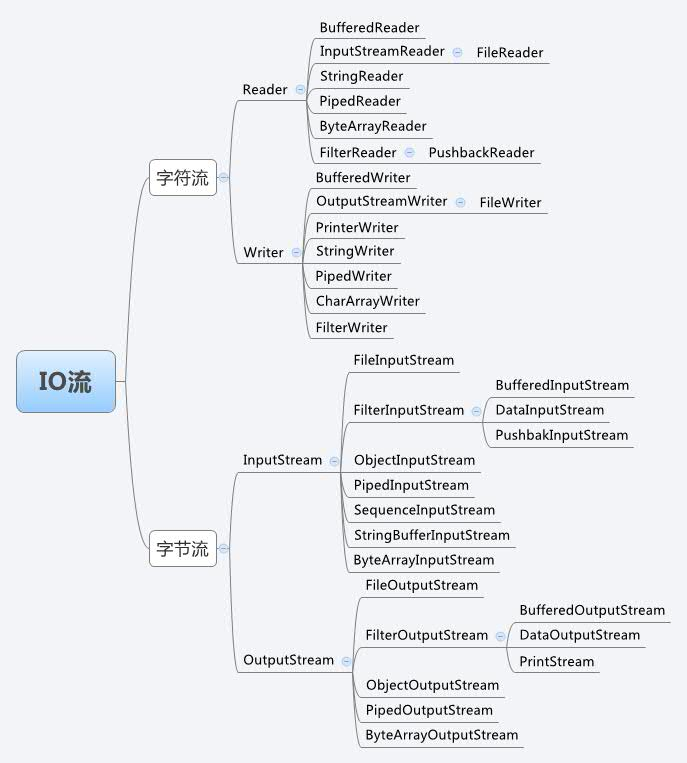
流是一组有顺序的,有起点和终点的字节集合,是对数据传输的总称或抽象。即数据在两设备间的传输称为流,流的本质是数据传输,根据数据传输特性将流抽象为各种类,方便更直观的进行数据操作。
1.2、IO流的分类
根据处理数据类型的不同分为:字符流和字节流
根据数据流向不同分为:输入流和输出流
1.2.1、字符流和字节流
字符流的由来: 因为数据编码的不同,而有了对字符进行高效操作的流对象。本质其实就是基于字节流读取时,去查了指定的码表。 字节流和字符流的区别:
读写单位不同:字节流以字节(8bit)为单位,字符流以字符为单位,根据码表映射字符,一次可能读多个字节。
处理对象不同:字节流能处理所有类型的数据(如图片、avi等),而字符流只能处理字符类型的数据。
结论:只要是处理纯文本数据,就优先考虑使用字符流。 除此之外都使用字节流。
1.2.2、输入流和输出流
对输入流只能进行读操作,对输出流只能进行写操作,程序中需要根据待传输数据的不同特性而使用不同的流。

二、File类
2.1、简介
File类是io包中唯一代表磁盘文件本身的对象。File类定义了一些与平台无关的方法来操作文件,可以通过调用File类中的方法,实现创建、删除、重命名文件等。File类的对象主要用来获取文件本身的一些信息,如文件所在目录、文件的长度、文件读写权限等。数据流可以将数据写入到文件中,而文件也是数据流最常用的数据媒体。
提供定位本地文件系统、描述文件和目录的功能
是 java.io 包中引用实际磁盘文件的唯一对象
File类对象描述文件路径、名字、长度、可否读写等属性,可用来命名文件、查询文件属性和处理目录,但不读写文件。
解决程序与文件系统的沟通
各种文件系统提供的基本服务一样,但实现细节互不兼容

构造函数
File(String pathname);
File(String dir, String subpath);
File(File dir, String subpath);
File(String path) 文件(相对路径),移植性较好: File f1 = new File(“mydir\\myfile.txt”); 目录(绝对路径): File f2 = new File(“d:\\mydir\\dir1”); File(String parent, String child ) 文件路径以及文件名: File f3 = new File(“d:\\d1” , “a.java”) File(File dir, String name) 文件对象与文件名:File f4 = new File(f2 , “myfile.txt”);
常用方法
canRead()、canWrite()、delete()、equals(object)、exists() getAbsolutePath() 和 length()
| 方法 | 描述 |
| String getName() | 获取文件的名称 |
| boolean canRead() | 判断文件是否是可读的 |
| boolean canWrite() | 品判断文件是否可被写入 |
| boolean exits() | 判断文件长度是否存在 |
| int length() | 获取文件的长度(以字节为单位) |
| String getAbsolutePath() | 获取文件的绝对路径 |
| String getParent() | 获取文件的父路径 |
| boolean isFile() | 判断此抽象路径名表示的文件是否为普通文件 |
| boolean isDirectory() | 判断此抽象路径名表示的是否是一个目录 |
| boolean isHidden | 判断文件是否是隐藏文件 |
| long lastModified() | 获取文件最后修改时间 |
| Boolean canExecute() |
测试应用程序是否可以执行此抽象路径名表示的文件。
|
| boolean createNewFile() | 当且仅当具有该名称的文件尚不存在时,原子地创建一个由该抽象路径名命名的新的空文件。 |
| boolean delete() | 删除由此抽象路径名表示的文件或目录。 |
| File[] listFiles() | 返回一个抽象路径名数组,表示由该抽象路径名表示的目录中的文件。 |
| String[] list() | 返回一个字符串数组,命名由此抽象路径名表示的目录中的文件和目录。 |
| boolean mkdirs() | 创建由此抽象路径名命名的目录,包括任何必需但不存在的父目录。可创建多层文件包 |
| boolean mkdir() | 创建由此抽象路径名命名的目录。只能创建一层文件包 |
| boolean reNameTo(File dest) | 重命名由此抽象路径名表示的文件。 |
| boolean setReadOnly() |
标记由此抽象路径名命名的文件或目录,以便只允许读取操作。
|
| boolean setWritable(boolean writable) |
一种方便的方法来设置所有者对此抽象路径名的写入权限。
|
2.2、文件操作示例
创建与删除文件:
package com.io; import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; public class IODemo1 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { File file=new File("d:"+File.separator, "file1.txt"); if(file.exists()){ file.delete(); System.out.println("删除成功!"); }else{ file.createNewFile(); System.out.println("创建成功!"); } } }
常见文件操作:

package com.file; import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.util.Date; public class IODemo1 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //创建方法 /* @SuppressWarnings("unused") File file = new File("F:\\a.txt"); //System.out.println("创建成功了吗?"+file.createNewFile()); //System.out.println("单级文件夹创建成功了吗?"+file.mkdir()); //System.out.println("多级文件夹创建成功了吗?"+file.mkdirs()); //File dest = new File("F:\\电影\\c.txt"); //System.out.println("重命名成功了吗?"+file.renameTo(dest)); */ /* //删除方法 File file = new File("F:\\电影"); System.out.println("删除成功了吗?"+file.delete()); file.deleteOnExit(); */ //判断方法 /* File file = new File("F:\\a.txt"); System.out.println("文件或者文件夹存在吗?"+file.exists()); System.out.println("是一个文件吗?"+file.isFile()); System.out.println("是一个文件夹吗?"+file.isDirectory()); System.out.println("是隐藏文件吗?"+file.isHidden()); System.out.println("此路径是绝对路径名?"+file.isAbsolute()); */ //获取方法 /* File file = new File("f:\\a.txt"); System.out.println("文件或者文件夹得名称是:"+file.getName()); System.out.println("绝对路径是:"+file.getPath()); System.out.println("绝对路径是:"+file.getAbsolutePath()); System.out.println("文件大小是(以字节为单位):"+file.length()); System.out.println("父路径是"+file.getParent()); //使用日期类与日期格式化类进行获取规定的时间 long lastmodified= file.lastModified(); Date data = new Date(lastmodified); SimpleDateFormat simpledataformat = new SimpleDateFormat("YY年MM月DD日 HH:mm:ss"); System.out.println("最后一次修改的时间是:"+simpledataformat.format(data)); */ //文件或者文件夹的方法 File[] file = File.listRoots(); System.out.println("所有的盘符是:"); for(File item : file){ System.out.println("\t"+item); } File filename =new File("F:\\Java workspace\\Java"); String[] name = filename.list(); System.out.println("指定文件夹下的文件或者文件夹有:"); for(String item : name){ System.out.println("\t"+item); } File[] f = filename.listFiles(); System.out.println("获得该路径下的文件或文件夹是:"); for(File item : f){ System.out.println("\t"+item.getName()); } } }
递归获得所有文件与文件夹:
package com.zhangguo.demo1; import java.io.File; public class FileDemo02 { public static void main(String[] args) { File file01 = new File("e:" + File.separator + "NF"+File.separator+"WebAPI"); ListFile(file01); } public static void ListFile(File file01) { if (file01.isDirectory()) { // 获得当前文件下所有的文件 File[] files = file01.listFiles(); for (File file : files) { System.out.println(file.getName()); ListFile(file); } } } }
结果:
2.3、Swing介绍
Swing是一个用于开发Java应用程序用户界面的开发工具包。
以抽象窗口工具包(AWT)为基础使跨平台应用程序可以使用任何可插拔的外观风格。Swing开发人员只用很少的代码就可以利用Swing丰富、灵活的功能和模块化组件来创建优雅的用户界面。 工具包中所有的包都是以swing作为名称,例如javax.swing,javax.swing.event。
Swing 是一个为Java设计的GUI工具包。
Swing包括了图形用户界面(GUI)器件如:文本框,按钮,分隔窗格和表。
Swing提供许多比AWT更好的屏幕显示元素。它们用纯Java写成,所以同Java本身一样可以跨平台运行,这一点不像AWT。它们是JFC的一部分。它们支持可更换的面板和主题(各种操作系统默认的特有主题),然而不是真的使用原生平台提供的设备,而是仅仅在表面上模仿它们。这意味着你可以在任意平台上使用JAVA支持的任意面板。轻量级组件的缺点则是执行速度较慢,优点就是可以在所有平台上采用统一的行为。
示例一:
package com.zhangguo.demo1; import javax.swing.*; public class HelloWorldSwing { /** * 创建并显示GUI。出于线程安全的考虑, 这个方法在事件调用线程中调用。 */ private static void createAndShowGUI() { // 确保一个漂亮的外观风格 JFrame.setDefaultLookAndFeelDecorated(true); // 创建及设置窗口 JFrame frame = new JFrame("HelloWorldSwing"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); // 添加 "Hello World" 标签 JLabel label = new JLabel("Hello World"); frame.getContentPane().add(label); // 显示窗口 frame.pack(); frame.setVisible(true); } public static void main(String[] args) { // 显示应用 GUI javax.swing.SwingUtilities.invokeLater(new Runnable() { public void run() { createAndShowGUI(); } }); } }
运行结果:

示例二:
package com.zhangguo.demo1; import javax.swing.JButton; import javax.swing.JFrame; import javax.swing.JLabel; import javax.swing.JPanel; import javax.swing.JPasswordField; import javax.swing.JTextField; public class SwingLoginExample { public static void main(String[] args) { // 创建 JFrame 实例 JFrame frame = new JFrame("Login Example"); // Setting the width and height of frame frame.setSize(350, 200); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); /* 创建面板,这个类似于 HTML 的 div 标签 * 我们可以创建多个面板并在 JFrame 中指定位置 * 面板中我们可以添加文本字段,按钮及其他组件。 */ JPanel panel = new JPanel(); // 添加面板 frame.add(panel); /* * 调用用户定义的方法并添加组件到面板 */ placeComponents(panel); // 设置界面可见 frame.setVisible(true); } private static void placeComponents(JPanel panel) { /* 布局部分我们这边不多做介绍 * 这边设置布局为 null */ panel.setLayout(null); // 创建 JLabel JLabel userLabel = new JLabel("User:"); /* 这个方法定义了组件的位置。 * setBounds(x, y, width, height) * x 和 y 指定左上角的新位置,由 width 和 height 指定新的大小。 */ userLabel.setBounds(10,20,80,25); panel.add(userLabel); /* * 创建文本域用于用户输入 */ JTextField userText = new JTextField(20); userText.setBounds(100,20,165,25); panel.add(userText); // 输入密码的文本域 JLabel passwordLabel = new JLabel("Password:"); passwordLabel.setBounds(10,50,80,25); panel.add(passwordLabel); /* *这个类似用于输入的文本域 * 但是输入的信息会以点号代替,用于包含密码的安全性 */ JPasswordField passwordText = new JPasswordField(20); passwordText.setBounds(100,50,165,25); panel.add(passwordText); // 创建登录按钮 JButton loginButton = new JButton("login"); loginButton.setBounds(10, 80, 80, 25); panel.add(loginButton); } }
运行结果:
三、字节流操作
字节流和字符流的区别:
- 读写单位不同:字节流以字节(8bit)为单位,字符流以字符为单位,根据码表映射字符,一次可能读多个字节。
- 处理对象不同:字节流能处理所有类型的数据(如图片、avi等),而字符流只能处理字符类型的数据。
结论:只要是处理纯文本数据,就优先考虑使用字符流。 除此之外都使用字节流。
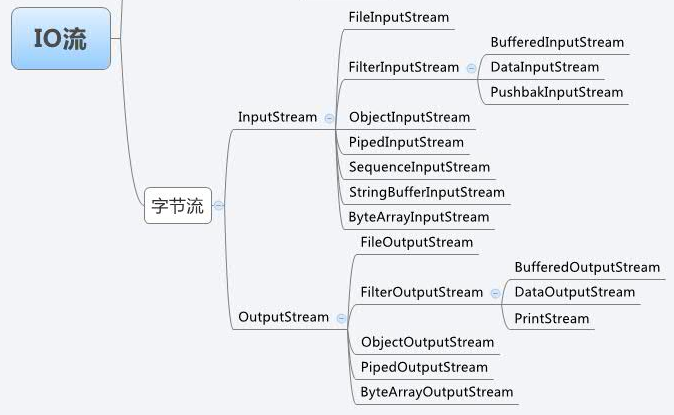
3.1、字节输出流
1.输出字节流OutputStream
IO 中输出字节流的继承图可见上图,可以看出:
OutputStream 是所有的输出字节流的父类,它是一个抽象类。
ByteArrayOutputStream、FileOutputStream 是两种基本的介质流,它们分别向Byte 数组、和本地文件中写入数据。PipedOutputStream 是向与其它线程共用的管道中写入数据,ObjectOutputStream 和所有FilterOutputStream 的子类都是装饰流。
字节输出流的常用方法:
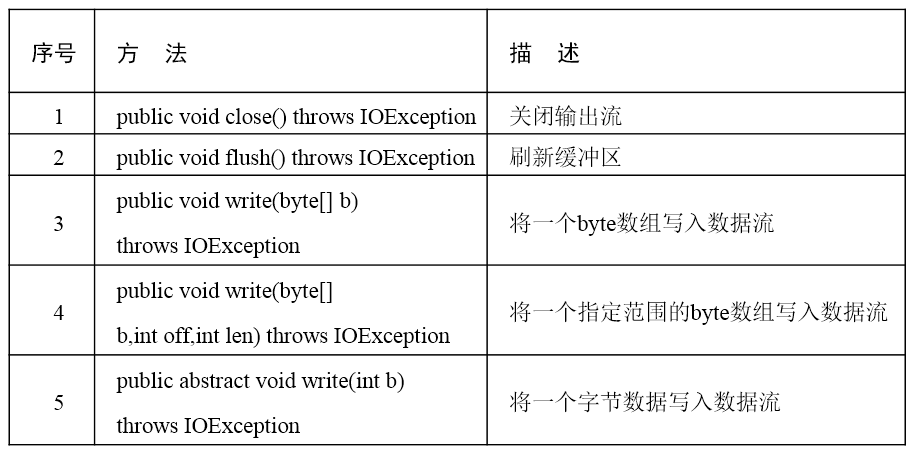
示例1:
import java.io.File; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.OutputStream; public class OutputStreamDemo01 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {//异常抛出不处理 // 第1步:使用File类找到一个文件 File f = new File("d:"+File.separator+"test.txt");//声明File对象 // 第2步:通过子类实例化父类对象 OutputStream out = null; // 准备好一个输出的对象 out = new FileOutputStream(f); // 通过对象多态性,进行实例化 // 第3步:进行写操作 String str = "Hello World!!!"; // 准备一个字符串 byte b[] = str.getBytes();// 只能输出byte数组,所以将字符串变为byte数组 out.write(b); //将内容输出,保存文件 // 第4步:关闭输出流 out.close(); // 关闭输出流 } }
追加文件内容
示例:
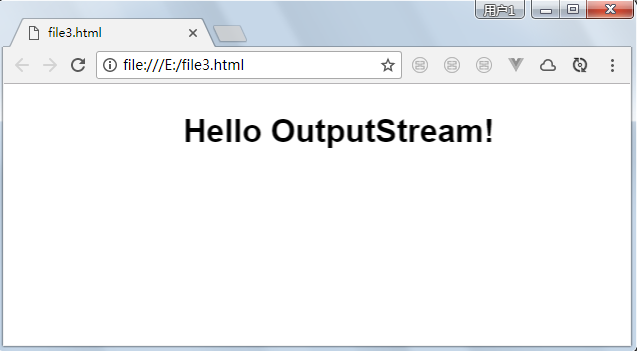
package com.zhangguo.demo1; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.OutputStream; public class FileDemo03 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { File file03 = new File("e:" + File.separator + "file3.html"); OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(file03); byte[] content = "<marquee><h1>Hello OutputStream!</h1></marquee>".getBytes(); os.write(content); os.close(); } }
结果:
3.2、字节输入流
输入字节流InputStreamIO 中输入字节流的继承图可见上图,可以看出:
InputStream 是所有的输入字节流的父类,它是一个抽象类。
ByteArrayInputStream、StringBufferInputStream、FileInputStream 是三种基本的介质流,它们分别从Byte 数组、StringBuffer、和本地文件中读取数据。PipedInputStream 是从与其它线程共用的管道中读取数据,与Piped 相关的知识后续单独介绍。
ObjectInputStream 和所有FilterInputStream 的子类都是装饰流(装饰器模式的主角)。
字节输入流的常用方法:
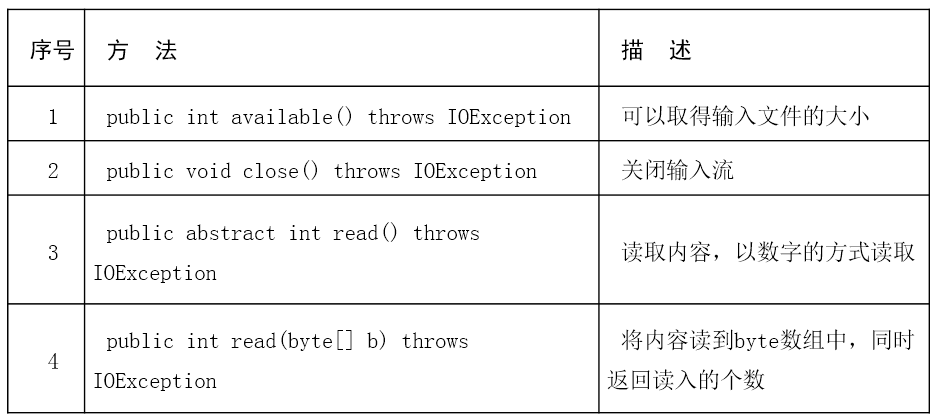
示例:
import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.InputStream; public class InputStramDemo01 { public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception {//异常抛出不处理 // 第1步:使用File类找到一个文件 File f = new File("d:"+File.separator+"test.txt"); // 声明File对象 // 第2步:通过子类实例化父类对象 InputStream input = null; // 准备好一个输入的对象 input = new FileInputStream(f); // 通过对象多态性进行实例化 // 第3步:进行读操作 byte b[] = new byte[1024]; // 所有的内容读到此数组中 input.read(b); // 把内容取出,内容读到byte数组中 // 第4步:关闭输入流 input.close(); // 关闭输入流 System.out.println("内容为:"+new String(b));//把byte数组变为字符串输出 } }
示例:
package com.zhangguo.demo1; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.InputStream; public class FileDemo04 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //模板文件 File file04 = new File("e:" + File.separator + "news.template"); InputStream is = new FileInputStream(file04); byte[] content =new byte[(int)file04.length()]; is.read(content); is.close(); String template=new String(content); System.out.println("模板的内容为:"+template); } }
结果:

3.2.1、简单的动态页面静态化
基本过程是:读模板文件->取内容->替换->生成静态页。
package com.zhangguo.demo1; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.OutputStream; import java.util.UUID; public class FileDemo04 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //模板文件 File file04 = new File("e:" + File.separator + "news.template"); InputStream is = new FileInputStream(file04); byte[] content =new byte[(int)file04.length()]; is.read(content); is.close(); String template=new String(content); System.out.println("模板的内容为:"+template); //生成新闻页 File file05 = new File("e:" + File.separator + "index.html"); OutputStream os=new FileOutputStream(file05); StringBuffer strb=new StringBuffer(); strb.append("<ul>"); for (int i = 0; i <10; i++) { strb.append("<li>"); strb.append("<a href='news0"+i+".html' >"+UUID.randomUUID()+"</a>"); strb.append("</li>"); } strb.append("</ul>"); String news=template.replace("<!--%content%-->", strb.toString()); os.write(news.getBytes()); os.close(); } }
结果:
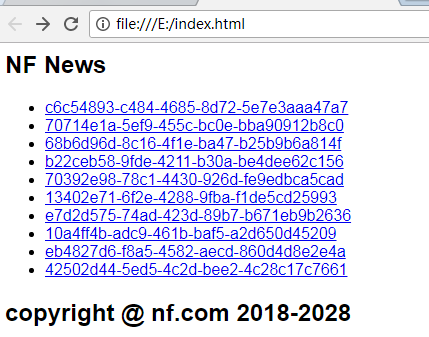
四、字符流操作
字符流的由来: 因为数据编码的不同,而有了对字符进行高效操作的流对象。本质其实就是基于字节流读取时,去查了指定的码表。
程序中的输入输出都是以流的形式保存的,流中保存的实际上全都是字节文件。
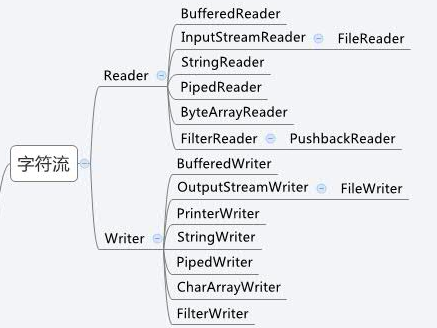
4.1、字符流输出
在Java中IO操作也是有相应步骤的,以文件操作为例,主要的操作流程如下:
1 使用File类打开一个文件
2 通过字节流或字符流的子类,指定输出的位置
3 进行读/写操作
4 关闭输入/输出
IO操作属于资源操作,一定要记得关闭
输出流: OutputStream 写出 就是将数据从程序写入到外部文件。对应 Writer;
import java.io.File; import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.Writer; public class WriterDemo1 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { File f = new File("d:"+File.pathSeparator+"test.txt"); Writer out; out = new FileWriter(f); String str = "Hello,World"; out.write(str); out.flush(); out.close(); } }
示例:
package com.zhangguo.demo1; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.Writer; public class FileDemo05 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { File file05 = new File("e:" + File.separator + "file05.txt"); //追加 Writer writer = new FileWriter(file05,true); writer.write("\r\nHello FileWriter!"); writer.flush(); writer.close(); } }
结果:
Hello FileWriter!
Hello FileWriter!
4.2、字符流输入
输入流:InputStream 读入 就是从外部文件中读取数据到程序。对应 Reader;
import java.io.*; public class ReaderDemo2 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { File f = new File("d:"+ File.pathSeparator+"test.txt"); Reader reader = new FileReader(f); int len = 0; char[] c = new char[1024]; int temp = 0; while((temp = reader.read()) != -1){ c[len] = (char)temp; len++; } reader.close(); System.out.println("内容为:"+ new String(c,0,len)); } }
示例一:
package com.zhangguo.demo1; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.Reader; public class FileDemo06 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { File file06 = new File("e:" + File.separator + "file05.txt"); //追加 Reader reader=new FileReader(file06); char[] content=new char[(int) file06.length()]; reader.read(content); reader.close(); System.out.println("内容:"+new String(content)); } }
结果一:
内容:Hello FileWriter!
Hello FileWriter!
示例二:
package com.zhangguo.demo1; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.Reader; public class FileDemo06 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { File file06 = new File("e:" + File.separator + "file05.txt"); Reader reader = new FileReader(file06); char[] content = new char[(int) file06.length()]; int temp; int i = 0; while ((temp = reader.read()) != -1) { content[i++] = (char) temp; } System.out.println("内容:" + new String(content)); } }
结果二:
内容:Hello FileWriter!
Hello FileWriter!
五、文件操作工具类与封装
5.1、文件工具类fileUtil(文件增删改,文件拷贝等)

package com.zhangguo.demo1; import java.io.*; import java.net.MalformedURLException; import java.net.URL; /** * 文件工具类 */ public class FileUtil { /** * 读取文件内容 * * @param is * @return */ public static String readFile(InputStream is) { BufferedReader br = null; StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); try { br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is, "UTF-8")); String readLine = null; while ((readLine = br.readLine()) != null) { sb.append(readLine+"\r\n"); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { br.close(); is.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } return sb.toString(); } public static String readFile(String path){ File file07 = new File(path); InputStream is=null; try { is = new FileInputStream(file07); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return readFile(is); } /** * 判断指定的文件是否存在。 * * @param fileName * @return */ public static boolean isFileExist(String fileName) { return new File(fileName).isFile(); } /** * 创建指定的目录。 如果指定的目录的父目录不存在则创建其目录书上所有需要的父目录。 * 注意:可能会在返回false的时候创建部分父目录。 * * @param file * @return */ public static boolean makeDirectory(File file) { File parent = file.getParentFile(); if (parent != null) { return parent.mkdirs(); } return false; } /** * 返回文件的URL地址。 * * @param file * @return * @throws MalformedURLException */ public static URL getURL(File file) throws MalformedURLException { String fileURL = "file:/" + file.getAbsolutePath(); URL url = new URL(fileURL); return url; } /** * 从文件路径得到文件名。 * * @param filePath * @return */ public static String getFileName(String filePath) { File file = new File(filePath); return file.getName(); } /** * 从文件名得到文件绝对路径。 * * @param fileName * @return */ public static String getFilePath(String fileName) { File file = new File(fileName); return file.getAbsolutePath(); } /** * 将DOS/Windows格式的路径转换为UNIX/Linux格式的路径。 * * @param filePath * @return */ public static String toUNIXpath(String filePath) { return filePath.replace("", "/"); } /** * 从文件名得到UNIX风格的文件绝对路径。 * * @param fileName * @return */ public static String getUNIXfilePath(String fileName) { File file = new File(fileName); return toUNIXpath(file.getAbsolutePath()); } /** * 得到文件后缀名 * * @param fileName * @return */ public static String getFileExt(String fileName) { int point = fileName.lastIndexOf('.'); int length = fileName.length(); if (point == -1 || point == length - 1) { return ""; } else { return fileName.substring(point + 1, length); } } /** * 得到文件的名字部分。 实际上就是路径中的最后一个路径分隔符后的部分。 * * @param fileName * @return */ public static String getNamePart(String fileName) { int point = getPathLastIndex(fileName); int length = fileName.length(); if (point == -1) { return fileName; } else if (point == length - 1) { int secondPoint = getPathLastIndex(fileName, point - 1); if (secondPoint == -1) { if (length == 1) { return fileName; } else { return fileName.substring(0, point); } } else { return fileName.substring(secondPoint + 1, point); } } else { return fileName.substring(point + 1); } } /** * 得到文件名中的父路径部分。 对两种路径分隔符都有效。 不存在时返回""。 * 如果文件名是以路径分隔符结尾的则不考虑该分隔符,例如"/path/"返回""。 * * @param fileName * @return */ public static String getPathPart(String fileName) { int point = getPathLastIndex(fileName); int length = fileName.length(); if (point == -1) { return ""; } else if (point == length - 1) { int secondPoint = getPathLastIndex(fileName, point - 1); if (secondPoint == -1) { return ""; } else { return fileName.substring(0, secondPoint); } } else { return fileName.substring(0, point); } } /** * 得到路径分隔符在文件路径中最后出现的位置。 对于DOS或者UNIX风格的分隔符都可以。 * * @param fileName * @return */ public static int getPathLastIndex(String fileName) { int point = fileName.lastIndexOf("/"); if (point == -1) { point = fileName.lastIndexOf(""); } return point; } /** * 得到路径分隔符在文件路径中指定位置前最后出现的位置。 对于DOS或者UNIX风格的分隔符都可以。 * * @param fileName * @param fromIndex * @return */ public static int getPathLastIndex(String fileName, int fromIndex) { int point = fileName.lastIndexOf("/", fromIndex); if (point == -1) { point = fileName.lastIndexOf("", fromIndex); } return point; } /** * 得到路径分隔符在文件路径中首次出现的位置。 对于DOS或者UNIX风格的分隔符都可以。 * * @param fileName * @return */ public static int getPathIndex(String fileName) { int point = fileName.indexOf("/"); if (point == -1) { point = fileName.indexOf(""); } return point; } /** * 得到路径分隔符在文件路径中指定位置后首次出现的位置。 对于DOS或者UNIX风格的分隔符都可以。 * * @param fileName * @param fromIndex * @return */ public static int getPathIndex(String fileName, int fromIndex) { int point = fileName.indexOf("/", fromIndex); if (point == -1) { point = fileName.indexOf("", fromIndex); } return point; } /** * 将文件名中的类型部分去掉。 * * @param filename * @return */ public static String removeFileExt(String filename) { int index = filename.lastIndexOf("."); if (index != -1) { return filename.substring(0, index); } else { return filename; } } /** * 得到相对路径。 文件名不是目录名的子节点时返回文件名。 * * @param pathName * @param fileName * @return */ public static String getSubpath(String pathName, String fileName) { int index = fileName.indexOf(pathName); if (index != -1) { return fileName.substring(index + pathName.length() + 1); } else { return fileName; } } /** * 删除一个文件。 * * @param filename * @throws IOException */ public static void deleteFile(String filename) throws IOException { File file = new File(filename); if (file.isDirectory()) { throw new IOException("IOException -> BadInputException: not a file."); } if (!file.exists()) { throw new IOException("IOException -> BadInputException: file is not exist."); } if (!file.delete()) { throw new IOException("Cannot delete file. filename = " + filename); } } /** * 删除文件夹及其下面的子文件夹 * * @param dir * @throws IOException */ public static void deleteDir(File dir) throws IOException { if (dir.isFile()) throw new IOException("IOException -> BadInputException: not a directory."); File[] files = dir.listFiles(); if (files != null) { for (int i = 0; i < files.length; i++) { File file = files[i]; if (file.isFile()) { file.delete(); } else { deleteDir(file); } } } dir.delete(); } /** * 复制文件 * * @param src * @param dst * @throws Exception */ public static void copy(File src, File dst) throws Exception { int BUFFER_SIZE = 4096; InputStream in = null; OutputStream out = null; try { in = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(src), BUFFER_SIZE); out = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(dst), BUFFER_SIZE); byte[] buffer = new byte[BUFFER_SIZE]; int len = 0; while ((len = in.read(buffer)) > 0) { out.write(buffer, 0, len); } } catch (Exception e) { throw e; } finally { if (null != in) { try { in.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } in = null; } if (null != out) { try { out.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } out = null; } } } /** * @复制文件,支持把源文件内容追加到目标文件末尾 * @param src * @param dst * @param append * @throws Exception */ public static void copy(File src, File dst, boolean append) throws Exception { int BUFFER_SIZE = 4096; InputStream in = null; OutputStream out = null; try { in = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(src), BUFFER_SIZE); out = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(dst, append), BUFFER_SIZE); byte[] buffer = new byte[BUFFER_SIZE]; int len = 0; while ((len = in.read(buffer)) > 0) { out.write(buffer, 0, len); } } catch (Exception e) { throw e; } finally { if (null != in) { try { in.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } in = null; } if (null != out) { try { out.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } out = null; } } } }
运行结果:
Hello FileWriter!
Hello FileWriter!
5.2、文件操作工具类

package com.zhangguo.demo1; import java.io.*; import java.util.StringTokenizer; public class FileUtil2 { private static String message; /** * 读取文本文件内容 * * @param filePathAndName * 带有完整绝对路径的文件名 * @param encoding * 文本文件打开的编码方式 * @return 返回文本文件的内容 */ public static String readTxt(String filePathAndName, String encoding) throws IOException { encoding = encoding.trim(); StringBuffer str = new StringBuffer(""); String st = ""; try { FileInputStream fs = new FileInputStream(filePathAndName); InputStreamReader isr; if (encoding.equals("")) { isr = new InputStreamReader(fs); } else { isr = new InputStreamReader(fs, encoding); } BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr); try { String data = ""; while ((data = br.readLine()) != null) { str.append(data + " "); } } catch (Exception e) { str.append(e.toString()); } st = str.toString(); } catch (IOException es) { st = ""; } return st; } /** * @description 写文件 * @param args * @throws UnsupportedEncodingException * @throws IOException */ public static boolean writeTxtFile(String content, File fileName, String encoding) { FileOutputStream o = null; boolean result=false; try { o = new FileOutputStream(fileName); o.write(content.getBytes(encoding)); result=true; } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (o != null) { try { o.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } return result; } /** * * @param content * @param fileName * @return */ public static boolean writeTxtFile(String content,String fileName) { return writeTxtFile(content,new File(fileName),"UTF-8"); } /** * 新建目录 * * @param folderPath * 目录 * @return 返回目录创建后的路径 */ public static String createFolder(String folderPath) { String txt = folderPath; try { java.io.File myFilePath = new java.io.File(txt); txt = folderPath; if (!myFilePath.exists()) { myFilePath.mkdir(); } } catch (Exception e) { message = "创建目录操作出错"; } return txt; } /** * 多级目录创建 * * @param folderPath * 准备要在本级目录下创建新目录的目录路径 例如 c:myf * @param paths * 无限级目录参数,各级目录以单数线区分 例如 a|b|c * @return 返回创建文件后的路径 例如 c:myfac */ public static String createFolders(String folderPath, String paths) { String txts = folderPath; try { String txt; txts = folderPath; StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(paths, "|"); for (int i = 0; st.hasMoreTokens(); i++) { txt = st.nextToken().trim(); if (txts.lastIndexOf("/") != -1) { txts = createFolder(txts + txt); } else { txts = createFolder(txts + txt + "/"); } } } catch (Exception e) { message = "创建目录操作出错!"; } return txts; } /** * 新建文件 * * @param filePathAndName * 文本文件完整绝对路径及文件名 * @param fileContent * 文本文件内容 * @return */ public static void createFile(String filePathAndName, String fileContent) { try { String filePath = filePathAndName; filePath = filePath.toString(); File myFilePath = new File(filePath); if (!myFilePath.exists()) { myFilePath.createNewFile(); } FileWriter resultFile = new FileWriter(myFilePath); PrintWriter myFile = new PrintWriter(resultFile); String strContent = fileContent; myFile.println(strContent); myFile.close(); resultFile.close(); } catch (Exception e) { message = "创建文件操作出错"; } } /** * 有编码方式的文件创建 * * @param filePathAndName * 文本文件完整绝对路径及文件名 * @param fileContent * 文本文件内容 * @param encoding * 编码方式 例如 GBK 或者 UTF-8 * @return */ public static void createFile(String filePathAndName, String fileContent, String encoding) { try { String filePath = filePathAndName; filePath = filePath.toString(); File myFilePath = new File(filePath); if (!myFilePath.exists()) { myFilePath.createNewFile(); } PrintWriter myFile = new PrintWriter(myFilePath, encoding); String strContent = fileContent; myFile.println(strContent); myFile.close(); } catch (Exception e) { message = "创建文件操作出错"; } } /** * 删除文件 * * @param filePathAndName * 文本文件完整绝对路径及文件名 * @return Boolean 成功删除返回true遭遇异常返回false */ public static boolean delFile(String filePathAndName) { boolean bea = false; try { String filePath = filePathAndName; File myDelFile = new File(filePath); if (myDelFile.exists()) { myDelFile.delete(); bea = true; } else { bea = false; message = (filePathAndName + "删除文件操作出错"); } } catch (Exception e) { message = e.toString(); } return bea; } /** * 删除文件夹 * * @param folderPath * 文件夹完整绝对路径 * @return */ public static void delFolder(String folderPath) { try { delAllFile(folderPath); // 删除完里面所有内容 String filePath = folderPath; filePath = filePath.toString(); java.io.File myFilePath = new java.io.File(filePath); myFilePath.delete(); // 删除空文件夹 } catch (Exception e) { message = ("删除文件夹操作出错"); } } /** * 删除指定文件夹下所有文件 * * @param path * 文件夹完整绝对路径 * @return * @return */ public static boolean delAllFile(String path) { boolean bea = false; File file = new File(path); if (!file.exists()) { return bea; } if (!file.isDirectory()) { return bea; } String[] tempList = file.list(); File temp = null; for (int i = 0; i < tempList.length; i++) { if (path.endsWith(File.separator)) { temp = new File(path + tempList[i]); } else { temp = new File(path + File.separator + tempList[i]); } if (temp.isFile()) { temp.delete(); } if (temp.isDirectory()) { delAllFile(path + "/" + tempList[i]);// 先删除文件夹里面的文件 delFolder(path + "/" + tempList[i]);// 再删除空文件夹 bea = true; } } return bea; } /** * 复制单个文件 * * @param oldPathFile * 准备复制的文件源 * @param newPathFile * 拷贝到新绝对路径带文件名 * @return */ public static void copyFile(String oldPathFile, String newPathFile) { try { int bytesum = 0; int byteread = 0; File oldfile = new File(oldPathFile); if (oldfile.exists()) { // 文件存在时 InputStream inStream = new FileInputStream(oldPathFile); // 读入原文件 FileOutputStream fs = new FileOutputStream(newPathFile); byte[] buffer = new byte[1444]; while ((byteread = inStream.read(buffer)) != -1) { bytesum += byteread; // 字节数 文件大小 System.out.println(bytesum); fs.write(buffer, 0, byteread); } inStream.close(); } } catch (Exception e) { message = ("复制单个文件操作出错"); } } /** * 复制整个文件夹的内容 * * @param oldPath * 准备拷贝的目录 * @param newPath * 指定绝对路径的新目录 * @return */ public static void copyFolder(String oldPath, String newPath) { try { new File(newPath).mkdirs(); // 如果文件夹不存在 则建立新文件夹 File a = new File(oldPath); String[] file = a.list(); File temp = null; for (int i = 0; i < file.length; i++) { if (oldPath.endsWith(File.separator)) { temp = new File(oldPath + file[i]); } else { temp = new File(oldPath + File.separator + file[i]); } if (temp.isFile()) { FileInputStream input = new FileInputStream(temp); FileOutputStream output = new FileOutputStream(newPath + "/" + (temp.getName()).toString()); byte[] b = new byte[1024 * 5]; int len; while ((len = input.read(b)) != -1) { output.write(b, 0, len); } output.flush(); output.close(); input.close(); } if (temp.isDirectory()) {// 如果是子文件夹 copyFolder(oldPath + "/" + file[i], newPath + "/" + file[i]); } } } catch (Exception e) { message = "复制整个文件夹内容操作出错"; } } /** * 移动文件 * * @param oldPath * @param newPath * @return */ public static void moveFile(String oldPath, String newPath) { copyFile(oldPath, newPath); delFile(oldPath); } /** * 移动目录 * * @param oldPath * @param newPath * @return */ public static void moveFolder(String oldPath, String newPath) { copyFolder(oldPath, newPath); delFolder(oldPath); } /** * 得到错误信息 */ public static String getMessage() { return message; } }
测试:
package com.zhangguo.demo1; import java.io.File; import java.util.Date; public class FileDemo07 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { String path = "e:" + File.separator + "file07.txt"; if (FileUtil2.writeTxtFile("当前时间:"+new Date().toString(), path)) { System.out.println(FileUtil.readFile(path)); System.out.println(FileUtil2.readTxt(path, "UTF-8")); } } }
结果:
当前时间:Fri Jul 20 10:37:07 CST 2018
当前时间:Fri Jul 20 10:37:07 CST 2018
更多封装:

import java.io.BufferedInputStream; import java.io.BufferedOutputStream; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.io.OutputStream; import java.io.PrintWriter; import java.net.URLEncoder; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Calendar; import java.util.Date; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.List; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; /** * <p>文件操作工具类<p> * @version 1.0 * @author li_hao * @date 2017年1月18日 */ @SuppressWarnings({"resource","unused"}) public class FileUtils { /** * 获取windows/linux的项目根目录 * @return */ public static String getConTextPath(){ String fileUrl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().getResource("").getPath(); if("usr".equals(fileUrl.substring(1,4))){ fileUrl = (fileUrl.substring(0,fileUrl.length()-16));//linux }else{ fileUrl = (fileUrl.substring(1,fileUrl.length()-16));//windows } return fileUrl; } /** * 字符串转数组 * @param str 字符串 * @param splitStr 分隔符 * @return */ public static String[] StringToArray(String str,String splitStr){ String[] arrayStr = null; if(!"".equals(str) && str != null){ if(str.indexOf(splitStr)!=-1){ arrayStr = str.split(splitStr); }else{ arrayStr = new String[1]; arrayStr[0] = str; } } return arrayStr; } /** * 读取文件 * * @param Path * @return */ public static String ReadFile(String Path) { BufferedReader reader = null; String laststr = ""; try { FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(Path); InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(fileInputStream, "UTF-8"); reader = new BufferedReader(inputStreamReader); String tempString = null; while ((tempString = reader.readLine()) != null) { laststr += tempString; } reader.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (reader != null) { try { reader.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } return laststr; } /** * 获取文件夹下所有文件的名称 + 模糊查询(当不需要模糊查询时,queryStr传空或null即可) * 1.当路径不存在时,map返回retType值为1 * 2.当路径为文件路径时,map返回retType值为2,文件名fileName值为文件名 * 3.当路径下有文件夹时,map返回retType值为3,文件名列表fileNameList,文件夹名列表folderNameList * @param folderPath 路径 * @param queryStr 模糊查询字符串 * @return */ public static HashMap<String, Object> getFilesName(String folderPath , String queryStr) { HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); List<String> fileNameList = new ArrayList<>();//文件名列表 List<String> folderNameList = new ArrayList<>();//文件夹名列表 File f = new File(folderPath); if (!f.exists()) { //路径不存在 map.put("retType", "1"); }else{ boolean flag = f.isDirectory(); if(flag==false){ //路径为文件 map.put("retType", "2"); map.put("fileName", f.getName()); }else{ //路径为文件夹 map.put("retType", "3"); File fa[] = f.listFiles(); queryStr = queryStr==null ? "" : queryStr;//若queryStr传入为null,则替换为空(indexOf匹配值不能为null) for (int i = 0; i < fa.length; i++) { File fs = fa[i]; if(fs.getName().indexOf(queryStr)!=-1){ if (fs.isDirectory()) { folderNameList.add(fs.getName()); } else { fileNameList.add(fs.getName()); } } } map.put("fileNameList", fileNameList); map.put("folderNameList", folderNameList); } } return map; } /** * 以行为单位读取文件,读取到最后一行 * @param filePath * @return */ public static List<String> readFileContent(String filePath) { BufferedReader reader = null; List<String> listContent = new ArrayList<>(); try { reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filePath)); String tempString = null; int line = 1; // 一次读入一行,直到读入null为文件结束 while ((tempString = reader.readLine()) != null) { listContent.add(tempString); line++; } reader.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (reader != null) { try { reader.close(); } catch (IOException e1) { } } } return listContent; } /** * 读取指定行数据 ,注意:0为开始行 * @param filePath * @param lineNumber * @return */ public static String readLineContent(String filePath,int lineNumber){ BufferedReader reader = null; String lineContent=""; try { reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filePath)); int line=0; while(line<=lineNumber){ lineContent=reader.readLine(); line++; } reader.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (reader != null) { try { reader.close(); } catch (IOException e1) { } } } return lineContent; } /** * 读取从beginLine到endLine数据(包含beginLine和endLine),注意:0为开始行 * @param filePath * @param beginLineNumber 开始行 * @param endLineNumber 结束行 * @return */ public static List<String> readLinesContent(String filePath,int beginLineNumber,int endLineNumber){ List<String> listContent = new ArrayList<>(); try{ int count = 0; BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filePath)); String content = reader.readLine(); while(content !=null){ if(count >= beginLineNumber && count <=endLineNumber){ listContent.add(content); } content = reader.readLine(); count++; } } catch(Exception e){ } return listContent; } /** * 读取若干文件中所有数据 * @param listFilePath * @return */ public static List<String> readFileContent_list(List<String> listFilePath) { List<String> listContent = new ArrayList<>(); for(String filePath : listFilePath){ File file = new File(filePath); BufferedReader reader = null; try { reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file)); String tempString = null; int line = 1; // 一次读入一行,直到读入null为文件结束 while ((tempString = reader.readLine()) != null) { listContent.add(tempString); line++; } reader.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (reader != null) { try { reader.close(); } catch (IOException e1) { } } } } return listContent; } /** * 文件数据写入(如果文件夹和文件不存在,则先创建,再写入) * @param filePath * @param content * @param flag true:如果文件存在且存在内容,则内容换行追加;false:如果文件存在且存在内容,则内容替换 */ public static String fileLinesWrite(String filePath,String content,boolean flag){ String filedo = "write"; FileWriter fw = null; try { File file=new File(filePath); //如果文件夹不存在,则创建文件夹 if (!file.getParentFile().exists()){ file.getParentFile().mkdirs(); } if(!file.exists()){//如果文件不存在,则创建文件,写入第一行内容 file.createNewFile(); fw = new FileWriter(file); filedo = "create"; }else{//如果文件存在,则追加或替换内容 fw = new FileWriter(file, flag); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(fw); pw.println(content); pw.flush(); try { fw.flush(); pw.close(); fw.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return filedo; } /** * 写文件 * @param ins * @param out */ public static void writeIntoOut(InputStream ins, OutputStream out) { byte[] bb = new byte[10 * 1024]; try { int cnt = ins.read(bb); while (cnt > 0) { out.write(bb, 0, cnt); cnt = ins.read(bb); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { out.flush(); ins.close(); out.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } /** * 判断list中元素是否完全相同(完全相同返回true,否则返回false) * @param list * @return */ private static boolean hasSame(List<? extends Object> list){ if(null == list) return false; return 1 == new HashSet<Object>(list).size(); } /** * 判断list中是否有重复元素(无重复返回true,否则返回false) * @param list * @return */ private static boolean hasSame2(List<? extends Object> list){ if(null == list) return false; return list.size() == new HashSet<Object>(list).size(); } /** * 增加/减少天数 * @param date * @param num * @return */ public static Date DateAddOrSub(Date date, int num) { Calendar startDT = Calendar.getInstance(); startDT.setTime(date); startDT.add(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH, num); return startDT.getTime(); } }
5.2、commons-io
commons-io是一款处理io流的工具,封装了很多处理io流和文件的方法,可以大大简化我们处理io流和操作文件的代码。从common-io的官方使用文档可以看出,它主要分为工具类、尾端类、行迭代器、文件过滤器、文件比较器和扩展流。
官网:http://commons.apache.org/proper/commons-io/
下载 :http://commons.apache.org/proper/commons-io/download_io.cgi
5.2.1、工具类
工具类包括FileUtils、IOUtils、FilenameUtils和FileSystemUtils,前三者的方法并没有多大的区别,只是操作的对象不同,故名思议:FileUtils主要操作File类,IOUtils主要操作IO流,FilenameUtils则是操作文件名,FileSystemUtils包含了一些JDK没有提供的用于访问文件系统的实用方法。当前,只有一个用于读取硬盘空余空间的方法可用。实例如下
FileUtils的使用:
import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.List; import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils; import org.junit.After; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.Test; public class FileUtilsTest { private String basePath = null; @Before public void setUp() { basePath = System.getProperty("user.dir") + "\\file\\"; } @After public void tearDown() throws Exception { } /** * 拷贝文件 * @throws IOException */ @Test public void testCopy() throws IOException { File srcFile = new File(basePath + "a.txt"); File destFile = new File(basePath + "b.txt"); FileUtils.copyFile(srcFile, destFile); } /** * 删除文件 * @throws IOException */ @Test public void testDelete() throws IOException{ File delFile = new File(basePath + "b.txt"); FileUtils.forceDelete(delFile); //FileUtils.forceMkdir(delFile); } /** * 比较文件内容 * @throws IOException */ @Test public void testCompareFile() throws IOException{ File srcFile = new File(basePath + "a.txt"); File destFile = new File(basePath + "b.txt"); boolean result = FileUtils.contentEquals(srcFile, destFile); System.out.println(result); } /** * 移动文件 * @throws IOException */ @Test public void testMoveFile() throws IOException{ File srcFile = new File(basePath + "b.txt"); File destDir = new File(basePath + "move"); FileUtils.moveToDirectory(srcFile, destDir, true); } /** * 读取文件内容 * @throws IOException */ @Test public void testRead() throws IOException{ File srcFile = new File(basePath + "a.txt"); String content = FileUtils.readFileToString(srcFile); List<String> contents = FileUtils.readLines(srcFile); System.out.println(content); System.out.println("******************"); for (String string : contents) { System.out.println(string); } } /** * 写入文件内容 * @throws IOException */ @Test public void testWrite() throws IOException{ File srcFile = new File(basePath + "a.txt"); FileUtils.writeStringToFile(srcFile, "\nyes文件", true); } }
测试:
package com.zhangguo.demo1; import java.io.File; import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils; public class FileDemo07 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { String path = "e:" + File.separator + "file08.txt"; FileUtils.write(new File(path), "org.apache.commons.io\r\n","utf-8", true); String result=FileUtils.readFileToString(new File(path), "utf-8"); System.out.println(result); } }
结果:
org.apache.commons.io
org.apache.commons.io
org.apache.commons.io
六、IO流应用
6.1、下载文件
1. 下载就是向客户端响应字节数据!
原来我们响应的都是html的字符数据!
把一个文件变成字节数组,使用response.getOutputStream()来各应给浏览器。
2. 下载的要求
* 两个头一个流!
> Content-Type:你传递给客户端的文件是什么MIME类型,例如:image/pjpeg
通过文件名称调用ServletContext的getMimeType()方法,得到MIME类型!
> Content-Disposition:它的默认值为inline,表示在浏览器窗口中打开!attachment;filename=xxx
在filename=后面跟随的是显示在下载框中的文件名称!
> 流:要下载的文件数据!
自己new一个输入流即可!
示例一:
Servlet:
package com.zhangguo.controller; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.net.URLEncoder; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; /** * 下载 */ @WebServlet("/Download") public class Download extends HttpServlet { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { String filename = request.getParameter("filename"); request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); //获得要下载的文件路径 String path=getServletContext().getRealPath(filename); System.out.println(path); //获得文件名 //H:\workspace\.metadata\.plugins\org.eclipse.wst.server.core\tmp0\wtpwebapps\AjaxResult\images\12.jpg String name=path.substring(path.lastIndexOf("\\")+1); //转码 name=URLEncoder.encode(name,"utf-8"); //修改http头部,设置输出为附件 response.setHeader("Content-Disposition", "attachment;filename="+name); //输入流,获得文件的字节流 InputStream is=new FileInputStream(path); byte[] bytes=new byte[is.available()]; is.read(bytes); //将字节流写入response中 response.getOutputStream().write(bytes); is.close(); response.flushBuffer(); response.getOutputStream().flush(); } }
HTML:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <p> <a href="Download?filename=images/猴哥.jpg">下载猴哥0</a><br /> <a href="Download?filename=images/12.jpg">下载图片1</a><br /> <a href="Download?filename=images/11.jpg">下载图片2</a><br /> <a href="Download?filename=images/10.jpg">下载图片3</a> </p> <p> <a href="Download?filename=LICENSE.txt">下载文本</a> </p> <P> <a href="DownloadXLS">导出xls</a> </P> </body> </html>
结果:

示例二:
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { //处理请求 //读取要下载的文件 File f = new File("E:/好久不见.mp3"); if(f.exists()){ FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(f); String filename=URLEncoder.encode(f.getName(),"utf-8"); //解决中文文件名下载后乱码的问题 byte[] b = new byte[fis.available()]; fis.read(b); response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); response.setHeader("Content-Disposition","attachment; filename="+filename+""); //获取响应报文输出流对象 ServletOutputStream out =response.getOutputStream(); //输出 out.write(b); out.flush(); out.close(); } }
示例三:
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { //通过路径得到一个输入流 String path = this.getServletContext().getRealPath("/WEB-INF/classes/1.jpg"); FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(path); //创建字节输出流 ServletOutputStream sos = response.getOutputStream(); //得到要下载的图片文件名 String filename = path.substring(path.lastIndexOf("\\"+1)); //告诉客户端需要下载图片(通过响应消息头) response.setHeader("content-disposition", "attachment;filename="+filename); //告诉客户端下载文件的类型 response.setHeader("content-type", "image/jpeg"); //执行输出操作 int len = 1; byte[] b = new byte[1024]; while((len=fis.read(b)) != -1){ sos.write(b,0,len); } sos.close(); fis.close(); }
示例四:
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { // 给下载文件命名 SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("YYYYMMddHHmmss"); String s = simpleDateFormat.format(new Date()); String fileName = s+".zip"; // 下载必须设置头 response.setHeader("content-disposition", "attachment;filename="+fileName); // 获得文件 InputStream is = this.getServletContext().getResourceAsStream("/config/new.zip"); // 输出流 OutputStream os = response.getOutputStream(); byte[] buffer = new byte[1024]; int len = -1; while ((len=is.read(buffer))!=-1) { os.write(buffer, 0, len); } os.close(); is.close(); }
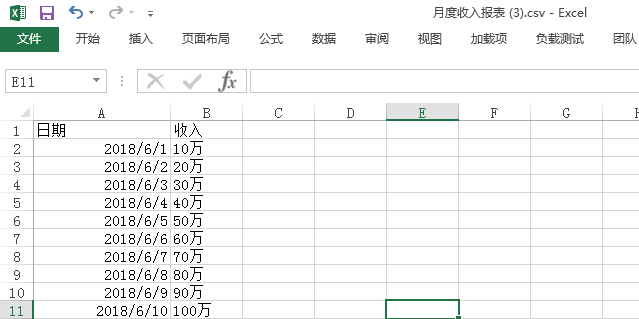
6.2、导出Excel文件
这里特别需要注意乱码的问题
示例:
Servlet:
package com.zhangguo.controller; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.URLEncoder; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; /** * 下载 */ @WebServlet("/DownloadXLS") public class DownloadXLS extends HttpServlet { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { String filename = request.getParameter("filename"); request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); // 写入bom头 byte[] uft8bom={(byte)0xef,(byte)0xbb,(byte)0xbf}; String name=URLEncoder.encode("月度收入报表.csv","utf-8"); //修改http头部,设置输出为附件 response.setHeader("Content-Disposition", "attachment;filename="+name); String result="日期,收入\r\n"; for (int i = 1; i <=10; i++) { result+="2018-06-"+i+","+(i*10)+"万\r\n"; } result=new String(result.getBytes(),"utf-8"); //将字节流写入response中 response.getOutputStream().write(uft8bom); //写入头部解决乱码问题 response.getOutputStream().write(result.getBytes()); response.flushBuffer(); response.getOutputStream().flush(); } }
HTML
<a href="DownloadXLS">导出xls</a>
结果:
七、视频
https://www.bilibili.com/video/av9219224/
八、作业
8.1、在c:\log目录下创建一个文件hello.html,存在就重命名为当前年月日.html,不存在就创建。
8.2、递归显示目录结构下的所有信息,如下图所示

8.3、请完成一个简单的新闻发布系统,实现动态页面的静态化,要求前端全部使用后台生成,如新闻列表,新闻详细,数据要求存放到数据库,至少有10条以上的新闻,每篇至少500字以上。
新闻列表:

新闻详细:

8.4、在8.3的每一条新闻列表后增加一个下载图标链接,点击时将html文件下载到本地。
8.5、将项目中的任意一个表的数据显示在界面上,点击搜索后可以实现导出功能,导出时要根据搜索条件过滤出要导出的数据,不应该全部导出。
参考:
https://www.cnblogs.com/rollenholt/archive/2011/09/11/2173787.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/oubo/archive/2012/01/06/2394638.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/pepcod/archive/2013/01/20/2913435.html



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号