spring缓存笔记 半注解版
注解的方式使用缓存:
第一步:导入jar包
(1)spring-context-support-4.2.4.RELEASE.jar包
提供了平台缓存管理器相关class。
引入:
(2)导入spring-framework-3.0.2.RELEASE-dependencies\net.sourceforge.ehcache\com.springsource.net.sf.ehcache\1.6.2\com.springsource.net.sf.ehcache-1.6.2.jar
第二步:引入ehcache.xml文件:
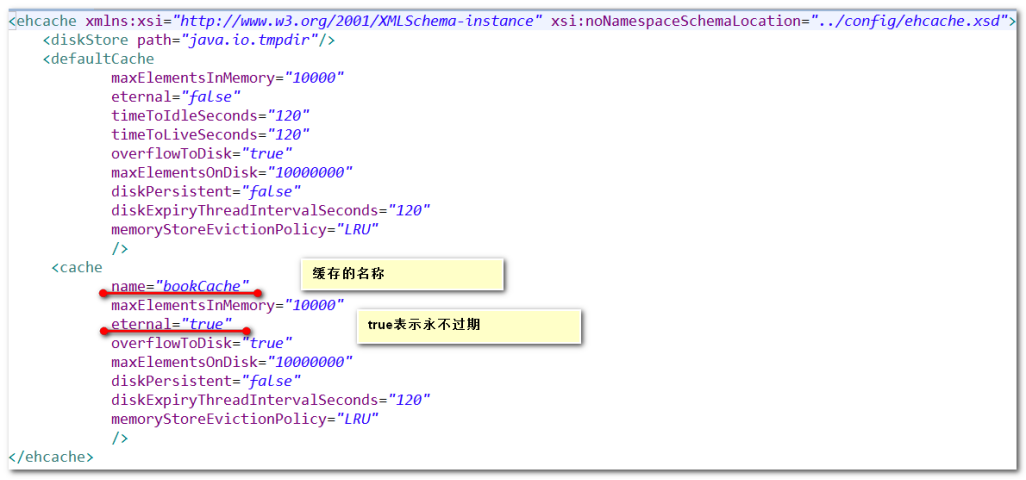
第三步:引入头信息(和上面一样)
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:cache="http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache/spring-cache.xsd">
第四步:编写applicationContext.xml,使用注解方式:
<!-- 使用注解的方式配置缓存 --> <!-- 第一步:定义ehcache的对象EhCacheManager:spring提供了工厂,专业来new对象 --> <bean id="ehCacheManager" class="org.springframework.cache.ehcache.EhCacheManagerFactoryBean"> <!-- 注入ehcache的核心配置文件 通过源代码发现,这里即使不配置,默认就到classpath中寻找ehcache.xml --> <property name="configLocation" value="classpath:ehcache.xml"/> </bean> <!-- 第二步:具体平台缓存管理器:整合ehcache的实现,需要导入jar --> <bean id="cacheManager" class="org.springframework.cache.ehcache.EhCacheCacheManager"> <!-- 注入ehcache的缓存对象 --> <property name="cacheManager" ref="ehCacheManager"/> </bean> <!-- 第三步:配置缓存注解驱动 --> <cache:annotation-driven cache-manager="cacheManager"/>
第五步:使用缓存的bean的类型的方法上,加两个注解:
在cn.itcast.ssh.service包中的类BookServiceImpl.java中添加缓存的注解
//图书业务层 @Service("bookService") @Transactional(readOnly=true)//事务(类级别的事务,一般定义成只读,方法级别的事务定义成可写) public class BookServiceImpl implements IBookService{ //注入dao层 @Autowired private IBookDao bookDao; //保存图书 @Transactional(readOnly=false)//事务(方法级别的事务,覆盖类级别的事务) @CacheEvict(value="bookCache",allEntries=true) public void saveBook(Book book){ //调用dao层 bookDao.save(book); } //查询:复杂条件查询,根据书名模糊查询 @Cacheable(value="bookCache")//value:echache缓存区域的名字 public List<Book> findBookListByNameLike(String name){ //1.qbn return bookDao.findByNamedQuery("Book.findBookListByNameLike", "%"+name+"%"); //2.qbc // DetachedCriteria criteria =DetachedCriteria.forClass(Book.class);//root对象类型 // criteria.add(Restrictions.like("name", "%"+name+"%")); // return bookDao.findByCriteria(criteria); } }
第六步:测试代码:在cn.itcast.ssh.test包中创建BookServiceTest进行测试
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration(locations="classpath:applicationContext.xml") public class BookServiceTest { //注入service @Autowired private IBookService bookService; @Test public void testSaveBook() { Book book = new Book(); book.setName("葵花宝典233"); book.setPrice(998d); bookService.saveBook(book); } @Test public void testFindBookListByNameLike() { List<Book> list = bookService.findBookListByNameLike("星"); System.out.println(list); List<Book> list2 = bookService.findBookListByNameLike("星"); System.out.println(list2); Book book = new Book(); book.setName("葵花宝典2"); book.setPrice(998d); bookService.saveBook(book); List<Book> list3 = bookService.findBookListByNameLike("星"); System.out.println(list3); List<Book> list4 = bookService.findBookListByNameLike("星"); System.out.println(list4); } }
查看测试结果,控制台中输出:
第一次查询数据库,第二次从缓存中查询!
小结:推荐是用注解,简单,xml配置麻烦。


