2019.09.16 课堂总结
一、动手动脑1
1、问题:仔细阅读示例: EnumTest.java,运行它,分析运行结果?你能得到什么结论?你掌握了枚举类型的基本用法了吗?
2、 代码如下:
1 public class EnumTest { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 Size s = Size.SMALL; 5 Size t = Size.LARGE; 6 // s和t引用同一个对象? 7 System.out.println(s == t); // 8 // 是原始数据类型吗? 9 System.out.println(s.getClass().isPrimitive()); 10 // 从字符串中转换 11 Size u = Size.valueOf("SMALL"); 12 System.out.println(s == u); // true 13 // 列出它的所有值 14 for (Size value : Size.values()) { 15 System.out.println(value); 16 } 17 } 18 19 } 20 21 enum Size { 22 SMALL, MEDIUM, LARGE 23 };
3、运行结果截图

4、结论
①枚举变量中实例化的对象的不同元素的地址不同
②从字符串中转换的枚举变量中实例化的对象的的元素赋给新的变量和原变量的地址相同
二、动手动脑2
1、问题:
以下代码的输出结果是什么? 为什么会有这样的输出结果?
1 public class Test { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 int X=100; 4 int Y=200; 5 System.out.println("X+Y="+X+Y); 6 System.out.println(X+Y+"=X+Y"); 7 } 8 }
2、运行结果截图
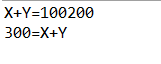
3、结论
在System.out.println()输出语句中“+”可用来连接字符串,例如第一行的输出"X+Y="+X+Y在等号右边的加号即为连接X和Y字符串的符号,所以输出结果为100200;
加号也可用来进行代数运算,但要将进行运算的数字之间用括号括起来。
三、课堂测试1、2
课堂测试1:像二柱子那样,花二十分钟写一个能自动生成30道小学四则运算题目的 “软件”
课堂测试2: (1)题目避免重复;
(2)可定制(数量/打印方式);
代码如下:
1 import java.util.Random; 2 import java.util.Scanner; 3 4 public class ceishi { 5 static Scanner sc = null; 6 static String a3 = new String(" "); 7 public static int s1 = new Random().nextInt(100); 8 public static int s2 = new Random().nextInt(100); 9 public static int s3 = new Random().nextInt(100); 10 public static int a[][] = new int[100000][2]; 11 public static int s[] = new int[100000]; 12 13 public static void main(String[] args) { 14 sc = new Scanner(System.in); 15 System.out.println("请输入题目数:"); 16 int n = sc.nextInt(); 17 System.out.println("请输入每行的题数:"); 18 int m = sc.nextInt(); 19 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { 20 if ((i) % m == 0) 21 System.out.print("\n"); 22 System.out.print((i + 1) + ":"); 23 s1 = new Random().nextInt(100); 24 System.out.print(s1); 25 s2 = new Random().nextInt(100); 26 s3 = new Random().nextInt(100); 27 // 重复 28 a[i][0] = s1; 29 a[i][1] = s3; 30 s[i] = s2; 31 for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) { 32 if (a[j][0] == s1 && a[j][1] == s3 && s[j] == s2) { 33 s3 = new Random().nextInt(100); 34 while (s3 == a[i][1]) { 35 s3 = new Random().nextInt(100); 36 } 37 s3 = new Random().nextInt(100); 38 while (s3 == a[i][1]) { 39 } 40 } 41 } 42 if (s2 % 4 == 0) 43 System.out.print("+"); 44 if (s2 % 4 == 1) { 45 System.out.print("-"); 46 while (s1 < s3) { 47 s3 = new Random().nextInt(100); 48 } 49 } 50 if (s2 % 4 == 2) { 51 System.out.print("*"); 52 while (s1 * s3 >= 100) { 53 s3 = new Random().nextInt(100); 54 } 55 } 56 if (s2 % 4 == 3) { 57 System.out.print("/"); 58 while (s3 != 0 && s1 / s3 != 0) { 59 s3 = new Random().nextInt(100); 60 } 61 } 62 System.out.print(s3); 63 System.out.print("="); 64 System.out.print(a3); 65 } 66 } 67 }


