Java中的IO流详解(20-字节流,21-字符流,22-IO流示例)
一.概述
IO流是用来处理设备间的数据传输。(上传文件和下载文件)
所谓流,就是一组有顺序的,有起点和终点的字节集合,是对数据传输的总称或抽象,相当于数据传输的通道。
IO流特性:先进先出、顺序存取、只读或者只写
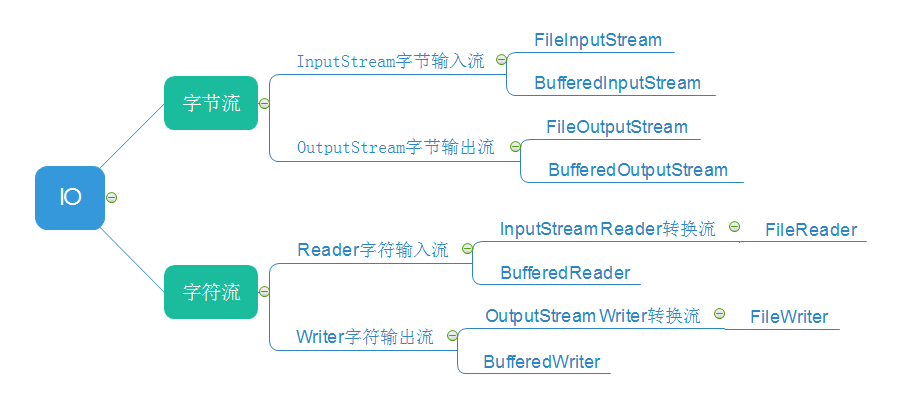
IO流分类:
按流向:
1.输入流:把数据从其他设备上读取到内存中的流。(比如将硬盘的数据读取到内存中->input)
2.输出流:把数据从内存中写出到其他设备上的流。(比如将内存中的数据写到硬盘的文件上->output)
注意:怎样记忆入和出?我们要以程式所在电脑的内存为参照标准,从外接设备读取数据称作“入”;从内存将数据写出到其他设备(如显示器),称作“出”。
按传输的数据类型:
建议在使用IO流前,先明确分析如下四点:
(1).明确要操作的数据是数据源还是数据目的(要读还是要写)
源:InputStream、Reader
目的:OutputStream、Writer (创建文件output,此时是一个空文件,再使用write往空文件中写数据)
(2).明确要操作的设备上的数据是字节还是字符(文本)
源:
字节:InputStream
字符:Reader
目的:
字节:OutputStream
字符:Writer
(3).明确数据所在的具体设备
源设备:
硬盘:File开头
内存:数组,字符串
键盘:System.in
网络:Socket
目的设备:
硬盘:File开头
内存:数组,字符串
屏幕:System.out
网络:Socket
(4).明确是否需要额外功能
无额外功能:普通流---FileInputStream、FileOutputStream、FileReader、FileWriter
需要转换:转换流---InputStreamReader、OutputStreamWriter
需要高效:缓冲流---BufferedInputStream、BufferedOutputStream、BufferedReader、BufferedWriter
区别:
普通流:每次读写都会访问硬盘,当读写频率高的时候,性能表现不佳。
缓冲流:读的时候,会一次读取较多的数据并存到缓存中,以后每次读取都是在缓存中访问,直到缓存中的数据读取完毕,再到硬盘中读取。
写的时候,先把数据写入到缓存中,直到缓存区达到一定的量,才把这些数据一起写到硬盘中去。
二.字节流
我们都知道,设备上的数据无论是图片还是视频、文字,他们都是以二进制存储的。
二进制最终都是以一个8位为数据单元进行体现,所以计算机中的最小数据单元就是字节。
这也意味着字节流可以处理设备上的所有数据,包括字符流能处理的数据。
* 但为了更加高效的传输,凡是用记事本打开后能读懂的数据,我们都用字符流来处理,其它的则用字节流。
字节流基类
InputStream:是所有的字节输入流的父类,是一个抽象类。
常用方法:
read():从该输入流读取下一个字节的数据。(返回的是该字节的int类型,比如字节a返回的是97,如需转换成字符型,则加上强制转换(char))
read(byte[] b):从该输入流读取最多b.length个字节的数据为字节数组,并存储在数组b中。(返回的是该字节数组的长度)
read(byte[] b,int off,int len):读取起始点为off,最大长度为len的字节数组。(返回的是指定长度的字节数组)
OutputStream:是所有的字节输出流的父类,是一个抽象类。
常用方法:
write(int b):将指定的字节写入此文件
write(byte[] b):将b.length个字节从指定的byte数组写入此文件
write(byte[] b,int off,int len):写入偏移量为off,最大长度为len的字节数组
注意:如何判断怎么才算是读取,怎样才算是写入,首先要选择好参照物--内存。
我们是编程人员,所以要站在程序的角度来思考问题。因此,Input和Output都应该是相对于程序而言。
Input:是输入的意思,就是从其他数据源(设备,比如硬盘)上读取数据,然后再输入到程序的控制台上。---先读取,再输入
使用的方法是read(),即读取的意思。(即:通过程序将硬盘上原本存在的文件显示出来)
Output:是输出的意思,就是将数据从内存输出,再将其写入到硬盘上。--先输出,再写入
使用的方法是write(),即写入的意思。(即:调用程序后会自动在硬盘上创建一个文件,并把内存中指定内容写入到该文件中)
字节文件操作流
FileInputStream:从文件系统的某个文件中获得输入字节,用于读取诸如图像数据的原始字节流。(数据文件必须提前创建好)
构造方法:
FileInputStream(File file):通过打开一个实际文件的连接来创建一个文件输入流,该文件通过File对象file指定。
FileInputStream(String name):通过打开一个实际文件的连接来创建一个文件输入流,该文件通过name指定。
常用方法:
覆盖和重写父类的方法。
FileOutputStream:用于将数据写入到file,诸如图像数据的原始字节流
构造方法:
FileOutputStream(File file):创建一个向指定File对象表示的文件中写入数据的文件输出流
FileOutputStream(File file,boolean append):创建一个向指定File对象表示的文件中追加数据的文件输出流(后面的布尔参数为true时即追加写入)。
FileOutputStream(String name):创建一个向具有指定名称的文件中写入数据的文件输出流
FileOutputStream(String name,boolean append):创建一个向具有指定名称的文件中写入数据的文件输出流
常用方法:
覆盖和重写父类的方法。
举例:
1 /* 2 * 需求: 3 * 1.创立一个空的文档; 4 * 2.连续往文档中写入内容; 5 * 3.创立另一个空的文档; 6 * 4.将第一个文档的内容复制到第二个文档中。 7 */ 8 public class BenonDemo { 9 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 10 //使用输出流创建benon.txt文件 11 FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("benon.txt"); 12 13 //使用输入流读取刚创建的benon.txt文件 14 FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("benon.txt"); 15 16 //往benon.txt文件中连续写入内容并加上换行 17 fos.write("Hello benon".getBytes()); 18 fos.write("\n".getBytes()); 19 fos.write("Hello YY".getBytes()); 20 21 //使用输出流创建yy.txt文件,并将benon.txt的内容复制到yy.txt中 22 FileOutputStream fos2=new FileOutputStream("yy.txt"); 23 int by=0; 24 while((by=fis.read())!=-1) { 25 fos2.write(by); 26 } 27 28 //释放资源 29 fos.close(); 30 fos2.close(); 31 fis.close(); 32 } 33 }
字节缓冲流(高效流)
BufferedInputStream:字节缓冲输入流,提高了读取效率
需要以FileInputStream为参数,因为缓冲区流仅仅提供了缓冲区,为高效而设计,但真正的读操作还得靠基本的流对象实现。
BufferedOutputStream:字节缓冲输出流,提高了写出效率
需要以FileOutputStream为参数,因为缓冲区流仅仅提供了缓冲区,为高效而设计,但真正的写操作还得靠基本的流对象实现。
三.字符流
由于字节流操作中文不是特别方便,比如使用一次读取一个字节的方式时,就无法正确读取中文,因为一个中文占两个字节。
所以,Java就提供了字符流(也叫转换流):字符流=字节流+编码表
编码表:由字符及基对应的数值组成的一张表(常见的编码表有:ASCII/Unicode,BIG5,UTF-8,GB2312/GBK/GB18030)
字符流基类
Reader:读取字符流的抽象类---同字节流读取数据完全一样
常用方法:
int read():读取单个字符
int read(char[] cbuf):将字符读入数组
int read(char[] cbuf,int off,int len):将字符读入数组的某一部分
注意:括号内的参数一定要使用(char)将其强制转换成字符型,因为我们习惯性在初始化的时候会将其定义成int型。
前面使用字节流一次输入一个字节时,也是使用同样的方法,所以这点两者是一样的。
Writer:写入字符流的抽象类
常用方法:
void write(char[] cbuf):写入字符数组
void write(char[] cbuf,int off,int len):写入字符数组的某一部分
void write(int c):写入单个字符
void write(String str):写入字符串
void write(String str,int off,int len):写入字符串的某一部分
注意:由上面的5种方法可以看出字符流写数据时不用作转换,不论是字符数组,还是字符或字符串,都是直接写入。
而前面的字节流write()方法,不但只能写入字节,而且还要先调用getBytes()进行转换才能写入。
字符转换流
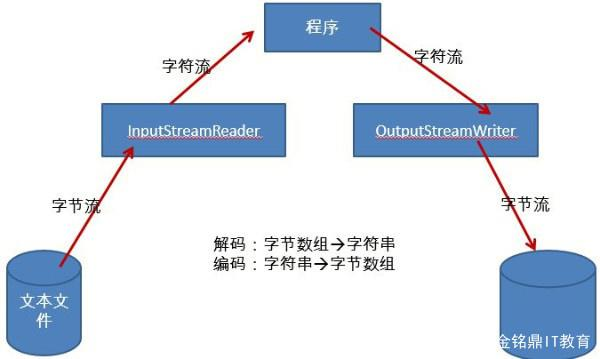
InputStreamReader:字节流转字符流的桥,读取字节并使用指定的charset将其解码为字符。
子类:FileReader -- 为了简化代码,我们一般会使用该子类。
构造方法:
InputStreamReader(InputStream in):创建一个使用默认字符集的InputStreamReader。
InputStreamReader(InputStream in,Charset cs):创建一个使用给定字符集的InputStreamReader。
InputStreamReader(InputStream in,CharsetDecorde dec ):创建一个使用给定字符集解码器的InputStreamReader。
InputStreamReader(InputStream in,String charsetName ):创建一个使用使用命名字符集的InputStreamReader。
OutputStreamWriter:字符流转字节流的桥,将向其写入的字符 编码成使用指定的字节charset。(它使用的字符集可以由名称指定,也可以被明确指定,或者接受默认字符集)
子类:FileWriter -- 为了简化代码,我们一般会使用该子类。
构造方法:
OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream Out):创建一个使用默认字符集的OutputStreamWriter。
OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream Out,Charset cs):创建一个使用给定字符集的OutputStreamWriter。
OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream Out,CharsetEncorde dec ):创建一个使用给定字符集解码器的OutputStreamWriter。
OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream Out,String charsetName ):创建一个使用使用命名字符集的OutputStreamWriter。
字符缓冲流
BufferedReader:从字符输入流读取文本,缓冲字符,以提供字符、数组和行的高效读取。
可以指定缓冲区大小,或者可以使用默认大小。一般来说,默认值足够大,可用于大多数用途。
需要以转换流的子类FileReader为参数。
构造方法:
BufferedReader(Reader in):创建使用默认大小的输入缓冲区的缓冲字符输入流。
BufferedReader(Reader in,int sz):创建使用指定大小的输入缓冲区的缓冲字符输入流。
常用方法:
String readLine():读一行文字,直到遇到换行符终止。返回值是读到的字符串,如果读到结尾的换行符刚返回null。
BufferedWriter:将文本写入字符输出流,缓冲字符,以提供单个字符、数组和字符串的高效写入。
需要以转换流的子类FileWriter为参数。
构造方法:
BufferedWriter(Writer out):创建使用默认大小的输出缓冲区的缓冲字符输出流。
BufferedWriter(Writer out,int sz):创建使用默认大小的输出缓冲区的缓冲字符输出流。
常用方法:
void newLine():写一行行分隔符。
四.IO流应用:
下面先举例说明一个我们比较常用到的IO流:复制文本文件
示例说明:复制文本(数据源:a.txt,目的地:b.txt)
步骤分析:
1.从数据源a.txt读取数据,使用read()方法;
2.上面的步骤会将数据输入到内存中存放,故使用InputStream输入流;
3.将数据写入到b.txt中,使用write()方法;
4.上面的步骤会从内存中输出数据,故使用OutputStream输出流;
前面有提到过,用windows自带的记事本打开后能读懂的数据,我们一般采用字符流,其余都用字节流。(当然,用字节流也是可以的,但是没有这么高效)
复制文件:
字节流复制数据:4种方式 -----(图片、视频等用字节流处理)
基本字节流:先一次读取一个字节:FileInputStream调用int read()
再一次写一个字节:FileOutputStream调用void write(int by)
基本字节流:先一次读取一个字节数组:FileInputStream调用int read(byte[] bys)
再一次写一个字节数组的一部分:FileOutStream调用void write(byte[] bys,int i,int len)
高效字节流:先一次读取一个字节:BufferedInputStream调用int read()
再一次写一个字节:BufferedOutputStream调用void write(int by)
高效字节流:先一次读取一个字节数组:BufferedInputStream调用int read(byte[] bys)
再一次写一个字节数组的一部分:BufferedOutStream调用void write(byte[] bys,int i,int len)
字符流复制数据:5种方式 ------(能用记事本读懂的数据用字符流处理)
基本字符流:先一次读取一个字符:FileReader调用int read()
再一次写一个字符:FileWriter调用void write(int ch)
基本字符流:先一次读取一个字符数组:FileReader调用int read(char[] chs)
再一次写一个字符数组:FileWriter调用void write(char[] chs,int i,int len)
高效字符流:先一次读取一个字符:BufferedReader调用int read()
再一次写一个字符:BufferedWriter调用void write(int ch)
高效字符流:先一次读取一个字符数组:BufferedReader调用int read(char[] chs)
再一次写一个字符数组:BufferedWriter调用void write(char[] chs,int i,int len)
高效字符流:先一次读一行数据:BufferedReader调用String readline()
再一次写一行数据:BufferedWriter调用void write(String s)
同时使用void newline()换行,flush()刷新
以下是代码举例:
1.字节流复制的4种方式:
1 package cn.itcast_02; 2 3 import java.io.BufferedInputStream; 4 import java.io.BufferedOutputStream; 5 import java.io.File; 6 import java.io.FileInputStream; 7 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 8 import java.io.IOException; 9 10 /* 11 * 复制图片:使用4种方式 12 */ 13 public class CopyImageDemo { 14 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 15 // 方式一:使用字符串作为路径 16 // String srcString = "d:\\a.jpg"; 17 // String destString = "d:\\Java\\b.jpg"; 18 19 // 方式二:使用File对象做为参数 20 File srcFile = new File("d:\\a.jpg"); 21 File destFile = new File("d:\\Java\\b.jpg"); 22 23 method1(srcFile, destFile); 24 method2(srcFile, destFile); 25 method3(srcFile, destFile); 26 method4(srcFile, destFile); 27 } 28 29 // 基本字节流:一次读取一个字节 30 private static void method1(File srcFile, File destFile) throws IOException { 31 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(srcFile);//读取源文件 32 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile);//创建目的文件 33 34 int by = 0; 35 while ((by = fis.read()) != -1) { 36 fos.write(by); 37 } 38 39 fos.close(); 40 fis.close(); 41 } 42 43 // 基本字节流:一次读取一个字节数组 44 private static void method2(File srcFile, File destFile) throws IOException { 45 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(srcFile); 46 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile); 47 48 byte[] bys = new byte[1024];//因为byte和Kb、Mb之间的进制是1024 49 int len = 0; 50 while ((len = fis.read(bys)) != -1) { 51 fos.write(bys, 0, len); 52 } 53 54 fos.close(); 55 fis.close(); 56 } 57 //缓冲字节流:一次读取一个字节 58 private static void method3(File srcFile, File destFile) throws IOException{ 59 BufferedInputStream bis=new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(srcFile)); 60 BufferedOutputStream bos=new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(destFile)); 61 62 int by=0; 63 while((by=bis.read())!=-1) { 64 bos.write(by); 65 } 66 67 bos.close(); 68 bis.close(); 69 } 70 //缓冲字节流:一次读取一个字节数组 71 private static void method4(File srcFile, File destFile) throws IOException{ 72 BufferedInputStream bis=new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(srcFile)); 73 BufferedOutputStream bos=new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(destFile)); 74 75 byte[] bys=new byte[1024]; 76 int len=0; 77 while((len=bis.read(bys))!=-1) { 78 bos.write(bys,0,len); 79 } 80 81 bos.close(); 82 bis.close(); 83 } 84 }
2.字符流复制的5种方式:
1 package cn.itcast_01; 2 3 import java.io.BufferedReader; 4 import java.io.BufferedWriter; 5 import java.io.FileReader; 6 import java.io.FileWriter; 7 import java.io.IOException; 8 9 /* 10 * 复制文本文件:分别使用5种方式复制D盘中的文本文件a.txt 11 */ 12 public class CpoyFileDemo { 13 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 14 String srcString = "D:\\a.txt";// 数据源 15 String destString = "D:\\Java\\b.txt";// 目的地 16 17 method1(srcString, destString); 18 method2(srcString, destString); 19 method3(srcString, destString); 20 method4(srcString, destString); 21 method5(srcString, destString); 22 } 23 //字符缓冲流:一次读写一行字符串----这是最高效的方式 24 private static void method5(String srcString, String destString) throws IOException { 25 BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new FileReader(srcString)); 26 BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(destString)); 27 28 String line=null; 29 while((line=br.readLine())!=null) { 30 bw.write(line); 31 bw.newLine(); 32 bw.flush(); 33 } 34 35 bw.close(); 36 br.close(); 37 } 38 //字符缓冲流:一次读写一个字符数组 39 private static void method4(String srcString, String destString) throws IOException { 40 BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new FileReader(srcString)); 41 BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(destString)); 42 43 char[] chs=new char[1024]; 44 int len=0; 45 while((len=br.read(chs))!=-1) { 46 bw.write(chs,0,len); 47 } 48 49 bw.close(); 50 br.close(); 51 } 52 53 // 字符缓冲流:一次读写一个字符 54 private static void method3(String srcString, String destString) throws IOException { 55 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(srcString)); 56 BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(destString)); 57 58 int ch=0; 59 while((ch=br.read())!=-1) { 60 bw.write(ch); 61 } 62 63 bw.close(); 64 br.close(); 65 } 66 67 // 基本字符流:一次读写一个字符数组 68 private static void method2(String srcString, String destString) throws IOException { 69 FileReader fr = new FileReader(srcString); 70 FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(destString); 71 72 char[] chs = new char[1024]; 73 int len = 0; 74 while ((len = fr.read(chs)) != -1) { 75 fw.write(chs, 0, len); 76 } 77 78 fw.close(); 79 fr.close(); 80 } 81 82 // 基本字符流:一次读写一个字符 83 private static void method1(String srcString, String destString) throws IOException { 84 FileReader fr = new FileReader(srcString); 85 FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(destString); 86 87 int ch = 0; 88 while ((ch = fr.read()) != -1) { 89 fw.write(ch); 90 } 91 92 fw.close(); 93 fr.close(); 94 } 95 }
示例:将ArrayList集合中的数据存储到文本文件中
1 public class ArrayListToFileDemo { 2 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 3 // 创建集合对象 4 ArrayList<String> array = new ArrayList<String>(); 5 array.add("hello"); 6 array.add("world"); 7 array.add("java"); 8 9 // 封装目的地 10 BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("a.txt")); 11 12 // 遍历集合 13 for (String s : array) { 14 bw.write(s); 15 bw.newLine(); 16 bw.flush(); 17 } 18 19 bw.close(); 20 } 21 }
示例:从文本文件中随机获取一个人的名字
1 /* 2 * 需求:一个文本文件中存储了几个名称,现要随机获取一个人的名字 3 * 分析:1.将文本文件的数据放到集合中; 4 * 2.随机产生一个索引; 5 * 3.根据这个索引获取一个值 6 */ 7 public class GetName { 8 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 9 //封装数据源,读取数据 10 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("b.txt")); 11 //封装目的地,创建集合对象 12 ArrayList<String> array = new ArrayList<String>(); 13 //读取数据并将其存储到集合中 14 String line = null; 15 while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { 16 array.add(line); 17 } 18 br.close(); 19 //产生一个随机数给索引 20 Random r = new Random(); 21 int index = r.nextInt(array.size()); 22 23 String name = array.get(index); 24 System.out.println("获奖者是:" + name); 25 } 26 }



