2022-1-18图day5
题1:
有 n 个网络节点,标记为 1 到 n。
给你一个列表 times,表示信号经过 有向 边的传递时间。 times[i] = (ui, vi, wi),其中 ui 是源节点,vi 是目标节点, wi 是一个信号从源节点传递到目标节点的时间。
现在,从某个节点 K 发出一个信号。需要多久才能使所有节点都收到信号?如果不能使所有节点收到信号,返回 -1 。
示例 1:

输入:times = [[2,1,1],[2,3,1],[3,4,1]], n = 4, k = 2 输出:2
示例 2:
输入:times = [[1,2,1]], n = 2, k = 1 输出:1
示例 3:
输入:times = [[1,2,1]], n = 2, k = 2 输出:-1
提示:
1 <= k <= n <= 1001 <= times.length <= 6000times[i].length == 31 <= ui, vi <= nui != vi0 <= wi <= 100- 所有
(ui, vi)对都 互不相同(即,不含重复边)
1 class Solution { 2 public int networkDelayTime(int[][] times, int n, int k) { 3 int inf=Integer.MAX_VALUE/2; 4 int[][] weight=new int[n][n]; 5 for (int i=0;i<n;i++) Arrays.fill(weight[i],inf); 6 for (int[] x:times){ 7 weight[x[0]-1][x[1]-1]=x[2]; 8 } 9 int[] dist=new int[n]; 10 Arrays.fill(dist,inf); 11 dist[k-1]=0; 12 boolean[] used=new boolean[n]; 13 for (int i=0;i<n;i++){ 14 int node=-1; 15 for (int j=0;j<n;j++) { 16 if (!used[j]&&(node==-1||dist[j]<dist[node])){ 17 node=j; 18 } 19 } 20 used[node]=true; 21 for (int j=0;j<n;j++){ 22 dist[j]=Math.min(dist[j],dist[node]+weight[node][j]); 23 } 24 } 25 int ans=-1; 26 for (int i=0;i<n;i++){ 27 ans=Math.max(ans,dist[i]); 28 } 29 return ans==inf?-1:ans; 30 } 31 }
思路:dijkstra算法。计算起点到目标点最短距离。将点分为确定顶点和非确定顶点,每次挑选离目标点最近的非确定点(或者枚举),利用这个点松弛到目标点的距离,再把这个点加入确定顶点,直到所有点都确定。
题2:
你准备参加一场远足活动。给你一个二维 rows x columns 的地图 heights ,其中 heights[row][col] 表示格子 (row, col) 的高度。一开始你在最左上角的格子 (0, 0) ,且你希望去最右下角的格子 (rows-1, columns-1) (注意下标从 0 开始编号)。你每次可以往 上,下,左,右 四个方向之一移动,你想要找到耗费 体力 最小的一条路径。
一条路径耗费的 体力值 是路径上相邻格子之间 高度差绝对值 的 最大值 决定的。
请你返回从左上角走到右下角的最小 体力消耗值 。
示例 1:
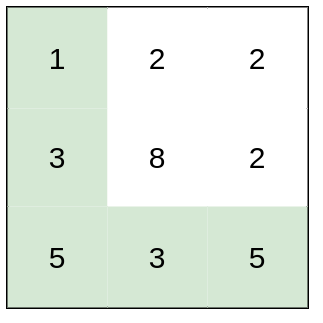
输入:heights = [[1,2,2],[3,8,2],[5,3,5]] 输出:2 解释:路径 [1,3,5,3,5] 连续格子的差值绝对值最大为 2 。 这条路径比路径 [1,2,2,2,5] 更优,因为另一条路径差值最大值为 3 。
示例 2:
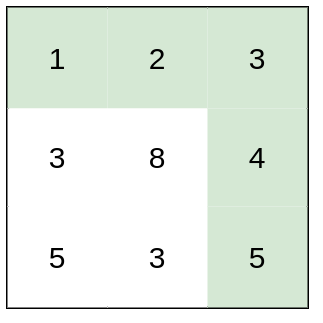
输入:heights = [[1,2,3],[3,8,4],[5,3,5]] 输出:1 解释:路径 [1,2,3,4,5] 的相邻格子差值绝对值最大为 1 ,比路径 [1,3,5,3,5] 更优。
示例 3:
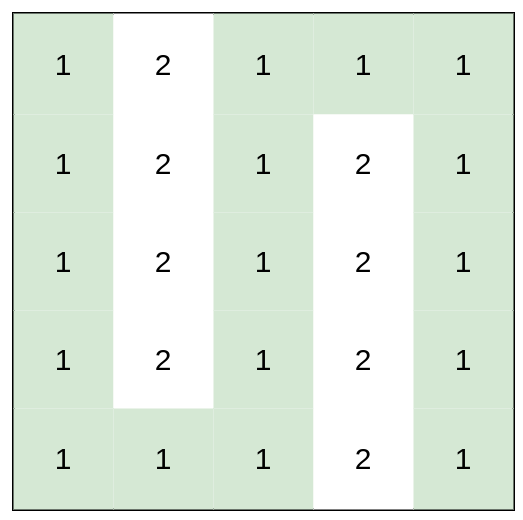
输入:heights = [[1,2,1,1,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,1,1,2,1]] 输出:0 解释:上图所示路径不需要消耗任何体力。
提示:
rows == heights.lengthcolumns == heights[i].length1 <= rows, columns <= 1001 <= heights[i][j] <= 106
1 class Solution { 2 //方向数组 3 int[][] dirs = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}}; 4 public int minimumEffortPath(int[][] heights) { 5 int m = heights.length; 6 int n = heights[0].length; 7 //队列里记录坐标x, y ,以及起点到这个点的距离 8 //并且按照距离从小到大排序 9 PriorityQueue<int[]> pq = new PriorityQueue<int[]>((a,b)->(a[2]-b[2])); 10 pq.offer(new int[]{0, 0, 0}); 11 int[] dist = new int[m * n]; 12 Arrays.fill(dist, Integer.MAX_VALUE); 13 dist[0] = 0; 14 boolean[] seen = new boolean[m * n]; 15 16 while (!pq.isEmpty()) { 17 int[] edge = pq.poll(); 18 int x = edge[0], y = edge[1], d = edge[2]; 19 int id = x * n + y; 20 //确定的点 21 if (seen[id]) { 22 continue; 23 } 24 //到终点了 25 if (x == m - 1 && y == n - 1) { 26 break; 27 } 28 seen[id] = true; 29 //标记为确定点 30 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { 31 int nx = x + dirs[i][0]; 32 int ny = y + dirs[i][1]; 33 //移动点合法且经过当前点到移动点的距离更小,更新距离并进队列 34 if (nx >= 0 && nx < m && ny >= 0 && ny < n && Math.max(d, Math.abs(heights[x][y] - heights[nx][ny])) < dist[nx * n + ny]) { 35 dist[nx * n + ny] = Math.max(d, Math.abs(heights[x][y] - heights[nx][ny])); 36 pq.offer(new int[]{nx, ny, dist[nx * n + ny]}); 37 } 38 } 39 } 40 41 return dist[m * n - 1]; 42 } 43 }
思路:见注释、
题3:
给你一个由 n 个节点(下标从 0 开始)组成的无向加权图,该图由一个描述边的列表组成,其中 edges[i] = [a, b] 表示连接节点 a 和 b 的一条无向边,且该边遍历成功的概率为 succProb[i] 。
指定两个节点分别作为起点 start 和终点 end ,请你找出从起点到终点成功概率最大的路径,并返回其成功概率。
如果不存在从 start 到 end 的路径,请 返回 0 。只要答案与标准答案的误差不超过 1e-5 ,就会被视作正确答案。
示例 1:
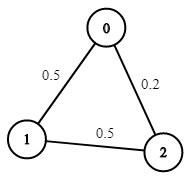
输入:n = 3, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[0,2]], succProb = [0.5,0.5,0.2], start = 0, end = 2 输出:0.25000 解释:从起点到终点有两条路径,其中一条的成功概率为 0.2 ,而另一条为 0.5 * 0.5 = 0.25
示例 2:
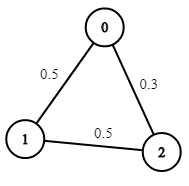
输入:n = 3, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[0,2]], succProb = [0.5,0.5,0.3], start = 0, end = 2 输出:0.30000
示例 3:
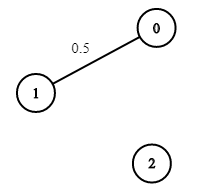
输入:n = 3, edges = [[0,1]], succProb = [0.5], start = 0, end = 2 输出:0.00000 解释:节点 0 和 节点 2 之间不存在路径
提示:
2 <= n <= 10^40 <= start, end < nstart != end0 <= a, b < na != b0 <= succProb.length == edges.length <= 2*10^40 <= succProb[i] <= 1- 每两个节点之间最多有一条边
1 class Solution { 2 3 class Eage{ 4 int node; 5 double weight; 6 Eage(int x,double y){ 7 this.node=x; 8 this.weight=y; 9 } 10 11 } 12 13 public double maxProbability(int n, int[][] edges, double[] succProb, int start, int end) { 14 List<List<Eage>> graph=new ArrayList<>(); 15 for (int i=0;i<n;i++){ 16 graph.add(new ArrayList<>()); 17 } 18 PriorityQueue<Eage> queue=new PriorityQueue<>( 19 (a,b)->(a.weight-b.weight>0?-1:1) 20 ); 21 double[] dist=new double[n]; 22 dist[start]=1; 23 for (int i=0;i<succProb.length;i++) { 24 graph.get(edges[i][0]).add(new Eage(edges[i][1],succProb[i])); 25 graph.get(edges[i][1]).add(new Eage(edges[i][0],succProb[i])); 26 } 27 queue.offer(new Eage(start,1)); 28 //boolean[] used=new boolean[n]; 29 while (!queue.isEmpty()){ 30 Eage temp=queue.poll(); 31 if (temp.weight<dist[temp.node]) continue; 32 for (Eage x:graph.get(temp.node)){ 33 if (dist[x.node]<dist[temp.node]*x.weight){ 34 dist[x.node]=dist[temp.node]*x.weight; 35 queue.offer(new Eage(x.node,dist[x.node])); 36 } 37 } 38 } 39 return dist[end]; 40 } 41 }
思路:同样的算法,利用优先队列优化遍历算法。要注意优先队列的定义。具体见https://www.cnblogs.com/benbicao/p/15818002.html





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· DeepSeek 开源周回顾「GitHub 热点速览」
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 物流快递公司核心技术能力-地址解析分单基础技术分享
· .NET 10首个预览版发布:重大改进与新特性概览!
· .NET10 - 预览版1新功能体验(一)