JDBC
快速入门
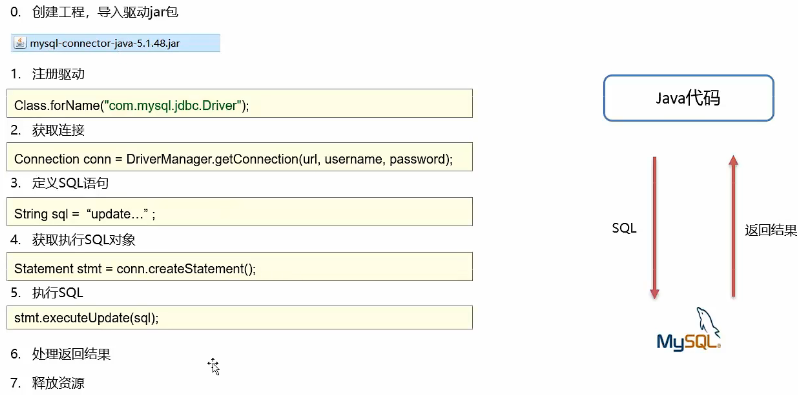
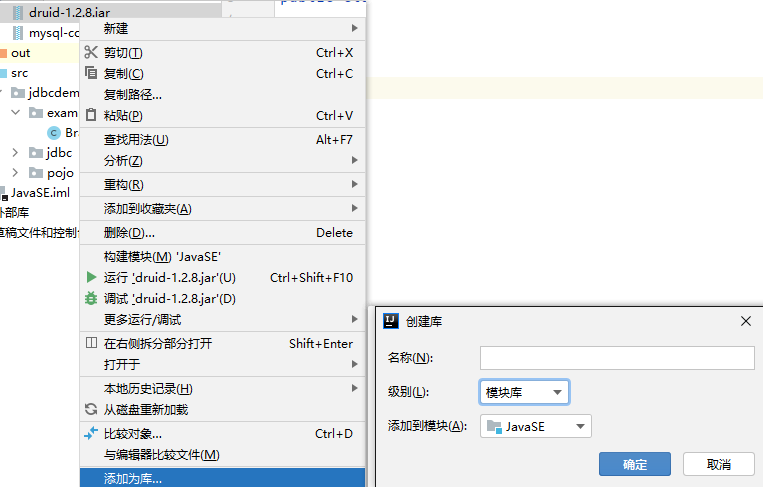
在模块下新建lib文件夹,将mysql的jar包粘贴进去并右键选择添加为库,范围选择模块库
package jdbc;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class JDBCDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1.注册驱动(反射)
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");//mysql5之后的jar可以不写这一行
//2.获取连接
String url = "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test";//固定写法 3306后面是要连接的数据库名
//jdbc:mysql:///test //如果数据库地址和端口是127.0.0.1:3306可以省略
String username = "root";
String password = "123456";
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
//3.定义sql
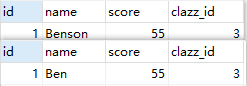
String sql = "update student set name = \"Ben\" where id = 1";
//4.获取执行sql语句的对象
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
//5.执行sql
int i = statement.executeUpdate(sql);//返回受影响的行数
//executeUpdate能执行DML和DDL语句
System.out.println(i);
//ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);能执行DQL语言
//6.释放资源
statement.close();
connection.close();
}
}

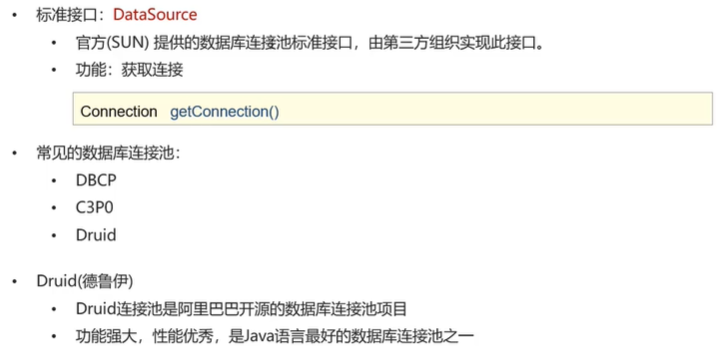
数据库连接池

如果不使用数据库连接池,如左图,有很多用户要同时访问数据库的情况下,先给用户1开一个连接对象conn,用完后关掉conn,再到下一个用户。开启数据库连接是一个非常耗时的工作,需要耗费一些资源,关闭连接也需要耗费资源。这种情况就是来一个用户就开一个连接,用完就关。又来一个用户又开一个连接,用完又关,很浪费时间和资源。
而连接池如右图,就是提前申请多个数据库连接放进连接池这个容器中,有用户来就给用户分配连接,用完后不会释放掉,而会回到连接池中,提高了资源复用和系统响应速度。
当用户特别多,第5个用户申请连接时连接池里的连接已经用完了,此时连接池会看前4个用户是否在有效利用连接。如果发现有用户没有利用连接池(如长时间无操作(挂机))就会强制中断该用户的连接,然后把那个连接分配给第5个用户。从而实现避免数据库连接遗漏。
连接池实现
Druid
先导入jar包
在src下编写配置文件
druid.properties
driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test
username=root
password=123456
# 初始化连接数量
initialSize=5
# 最大连接数
maxActive=10
# 最大等待时间
maxWait=3000
druidDemo.java
package jdbcdemo.druid;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSourceFactory;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.util.Properties;
public class druidDemo {
public static void main(String[]args) throws Exception{
//加载配置文件
Properties prop = new Properties();
prop.load(new FileInputStream("src/druid.properties"));
//获取连接池对象
DataSource dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(prop);
//获取数据库连接
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection);//com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl@34b7ac2f
//如果prop.load报错,说明地址不对,可以用下面的方法查看当前工作目录
System.out.println(System.getProperty("user.dir"));//D:\Programme\code\JavaSE
}
}
管理事务

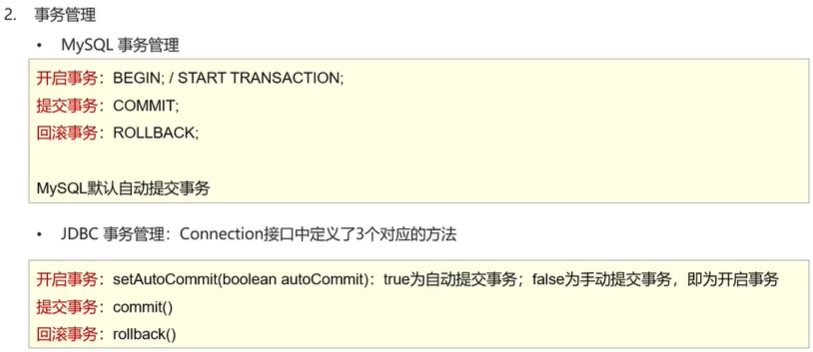
setAutoCommit(false)就是开启事务的代码
代码实现
5、6就是事务
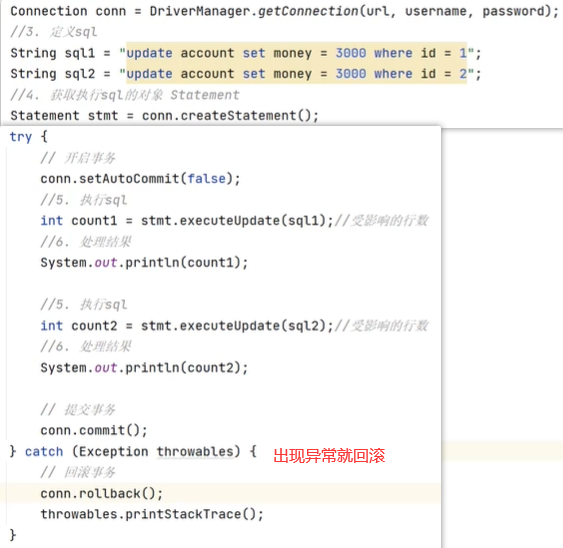
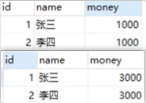
1000都变成了3000
现在人为制造异常
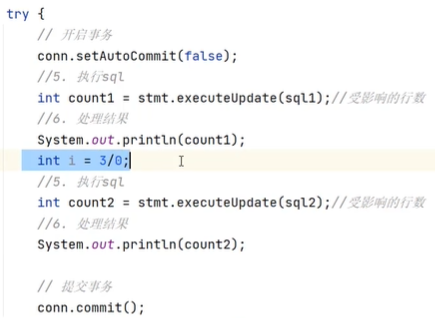
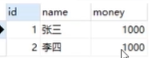
结果还是1000,说明回滚了
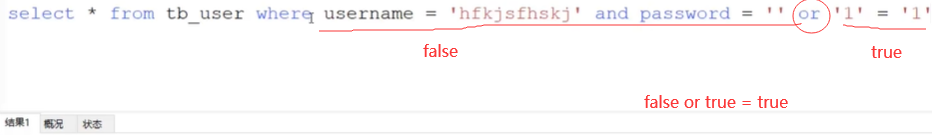
sql注入
sql注入的应用:在密码处输入
' or '1' = '1
发现账号乱写的也能登录成功
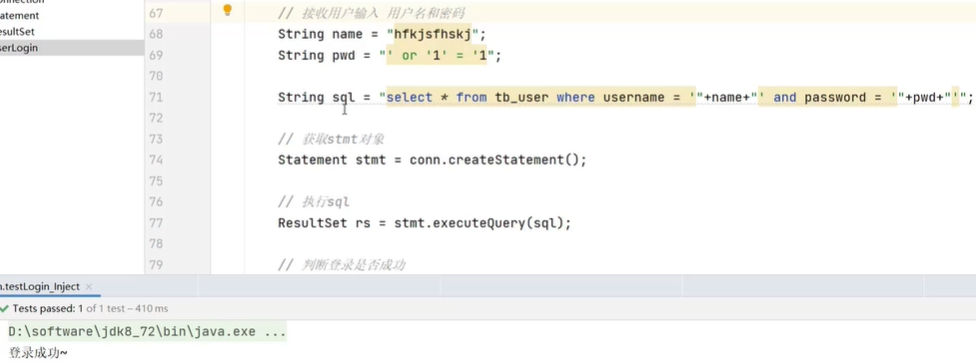
因为密码的字符串放到sql中使得sql语句的意思发生了变化
- 通过PrepareStatement来防止sql注入
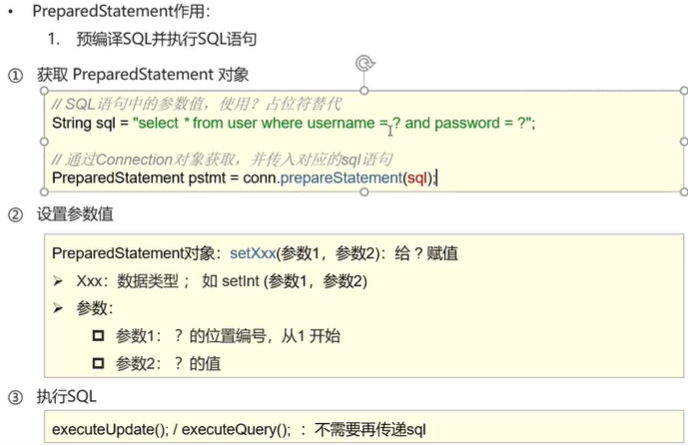
第2个作用就是防止sql注入
原理是把传递的值包含的关键字或者敏感字符都进行了转义处理
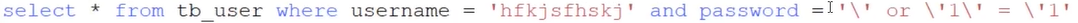
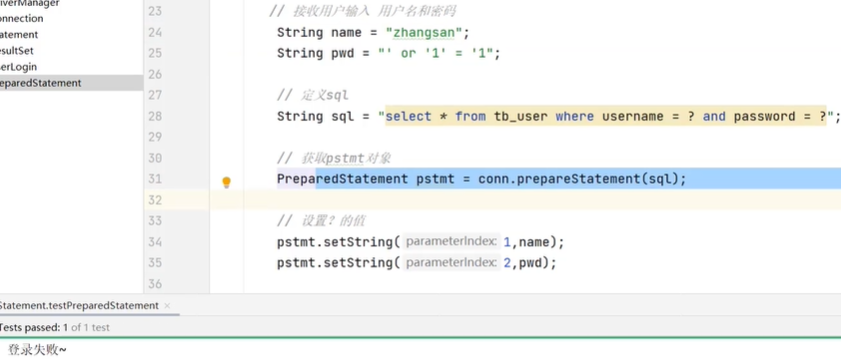
代码实现

现在sql注入就失败了
使用JDBC实现增删改查
项目结构
Brand.java
package jdbcdemo.pojo;
public class Brand {
private Integer id;
private String brandName;
private String companyName;
private Integer ordered;
private String description;
private Integer status;//0:禁用 1:启用
/*基本类型建议换成包装类,因为基本类型的默认值可能不适应需求
比如int的默认值是0,对于ordered和status而言不适合
而Integer的默认值是null,相比之下更合适些
*/
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getBrandName() {
return brandName;
}
public void setBrandName(String brandName) {
this.brandName = brandName;
}
public String getCompanyName() {
return companyName;
}
public void setCompanyName(String companyName) {
this.companyName = companyName;
}
public Integer getOrdered() {
return ordered;
}
public void setOrdered(Integer ordered) {
this.ordered = ordered;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public void setDescription(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
public Integer getStatus() {
return status;
}
public void setStatus(Integer status) {
this.status = status;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Brand{" +
"id=" + id +
", brandName='" + brandName + '\'' +
", companyName='" + companyName + '\'' +
", ordered=" + ordered +
", description='" + description + '\'' +
", status=" + status +
'}';
}
}
BrandTest.java
package jdbcdemo.example;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSourceFactory;
import jdbcdemo.pojo.Brand;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Properties;
public class BrandTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BrandTest bt = new BrandTest();
bt.selectAll();
bt.add();
bt.selectAll();
bt.updateTest();
bt.selectAll();
bt.deleteTest();
bt.selectAll();
}
public void selectAll() throws Exception {
//1.获取connection
Properties prop = new Properties();
prop.load(new FileInputStream("src/druid.properties"));
//获取连接池对象
DataSource dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(prop);
//获取数据库连接
Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection();
//2.定义sql
String sql = "select * from tb_brand;";
//3.获取prepareStatement对象
PreparedStatement pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
/*用PreparedStatement是因为它比Statement效率更高*/
//4.执行sql
ResultSet rs = pstmt.executeQuery();//执行DQL语句
//5.处理结果
//获取数据
/*ResultSet的对象rs像一个游标在mysql表格中,默认在表头(字段那一行)
获取数据时会往下一行移动,先判断此行的数据是否有效(是否全都是null)
有效才会在此行逐列读取数据
*/
Brand brand = null;
/*把Brand brand提取出来,brand每次循环指向新new出的对象,节约栈内存
不提取出来,循环几次,栈中就会有几个同名的brand。提取出来就能复用brand
*/
List<Brand> brands = new ArrayList<>();
while (rs.next()) {//rs.next就是往下一行判断该行数据是否有效的方法,返回布尔值
int id = rs.getInt("id");
/*rs.getXxx就是rs获取数据的方法如getInt,获取int类型的数据
getXxx(第几列)如,getInt(1) 表示获取该行第1列的数据,从1开始算
也可以根据字段来获取,getInt("id"),获取该行名为id的字段,必须跟表中的字段名一致
*/
String brandName = rs.getString("brand_name");
String companyName = rs.getString("company_name");
int ordered = rs.getInt("ordered");
String description = rs.getString("description");
int status = rs.getInt("status");
//将每一行的数据都封装进一个Brand对象中
brand = new Brand();
brand.setId(id);
brand.setBrandName(brandName);
brand.setCompanyName(companyName);
brand.setOrdered(ordered);
brand.setDescription(description);
brand.setStatus(status);
//把对象放到集合中
brands.add(brand);
}
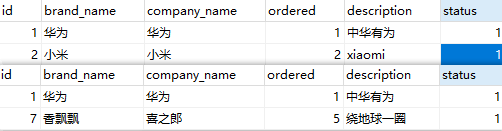
System.out.println(brands);
//6.释放资源
rs.close();
pstmt.close();
conn.close();
}
public void add() throws Exception {
//模拟前端传来的数据
String brandName = "香飘飘";
String companyName = "喜之郎";
int ordered = 5;
String description = "绕地球一圈";
int status = 1;
//1.获取connection
Properties prop = new Properties();
prop.load(new FileInputStream("src/druid.properties"));
//获取连接池对象
DataSource dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(prop);
//获取数据库连接
Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection();
//2.定义sql
String sql = "insert into tb_brand(brand_name,company_name,ordered,description,status) values(?,?,?,?,?);";
//id自增,不需要写
//3.获取prepareStatement对象
PreparedStatement pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
/*用PreparedStatement是因为它比Statement效率更高*/
//4.设置参数
pstmt.setString(1, brandName);
pstmt.setString(2, companyName);
pstmt.setInt(3, ordered);
pstmt.setString(4, description);
pstmt.setInt(5, status);
//5.执行sql
int count = pstmt.executeUpdate();//受影响的行数
//6.处理结果
if (count > 0) {
System.out.println("添加成功");
} else {
System.out.println("添加失败");
}
//7.释放资源
pstmt.close();
conn.close();
}
public void updateTest() throws Exception {
//模拟前端传来的数据
String brandName = "红米";
String companyName = "小米子公司红米";
int ordered = 4;
String description = "redmi";
int status = 1;
int id = 2;
//1.获取connection
Properties prop = new Properties();
prop.load(new FileInputStream("src/druid.properties"));
//获取连接池对象
DataSource dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(prop);
//获取数据库连接
Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection();
//2.定义sql
String sql = "update tb_brand set\n" +
"brand_name = ?,\n" +
"company_name = ?,\n" +
"ordered = ?," +
"description = ?,\n" +
"status = ?\n" +
"where id = ?";
//3.获取prepareStatement对象
PreparedStatement pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
/*用PreparedStatement是因为它比Statement效率更高*/
//4.设置参数
pstmt.setString(1, brandName);
pstmt.setString(2, companyName);
pstmt.setInt(3, ordered);
pstmt.setString(4, description);
pstmt.setInt(5, status);
pstmt.setInt(6, id);
//5.执行sql
int count = pstmt.executeUpdate();//受影响的行数
//6.处理结果
if (count > 0) {
System.out.println("修改成功");
} else {
System.out.println("修改失败");
}
//7.释放资源
pstmt.close();
conn.close();
}
public void deleteTest() throws Exception {
//1.获取connection
Properties prop = new Properties();
prop.load(new FileInputStream("src/druid.properties"));
//获取连接池对象
DataSource dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(prop);
//获取数据库连接
Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection();
//2.定义sql
String sql = "delete from tb_brand where id = ?";
//3.获取prepareStatement对象
PreparedStatement pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
/*用PreparedStatement是因为它比Statement效率更高*/
//4.设置参数
int id = 2;//模拟前端传来的数据
pstmt.setInt(1, id);
//5.执行sql
int count = pstmt.executeUpdate();//受影响的行数
//6.处理结果
if (count > 0) {
System.out.println("删除成功");
} else {//DDL语句成功删除后count可能为0,这种判断不严谨。一般不报异常就算成功了
System.out.println("删除失败");
}
//7.释放资源
pstmt.close();
conn.close();
}
}





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 使用C#创建一个MCP客户端
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列1:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 按钮权限的设计及实现